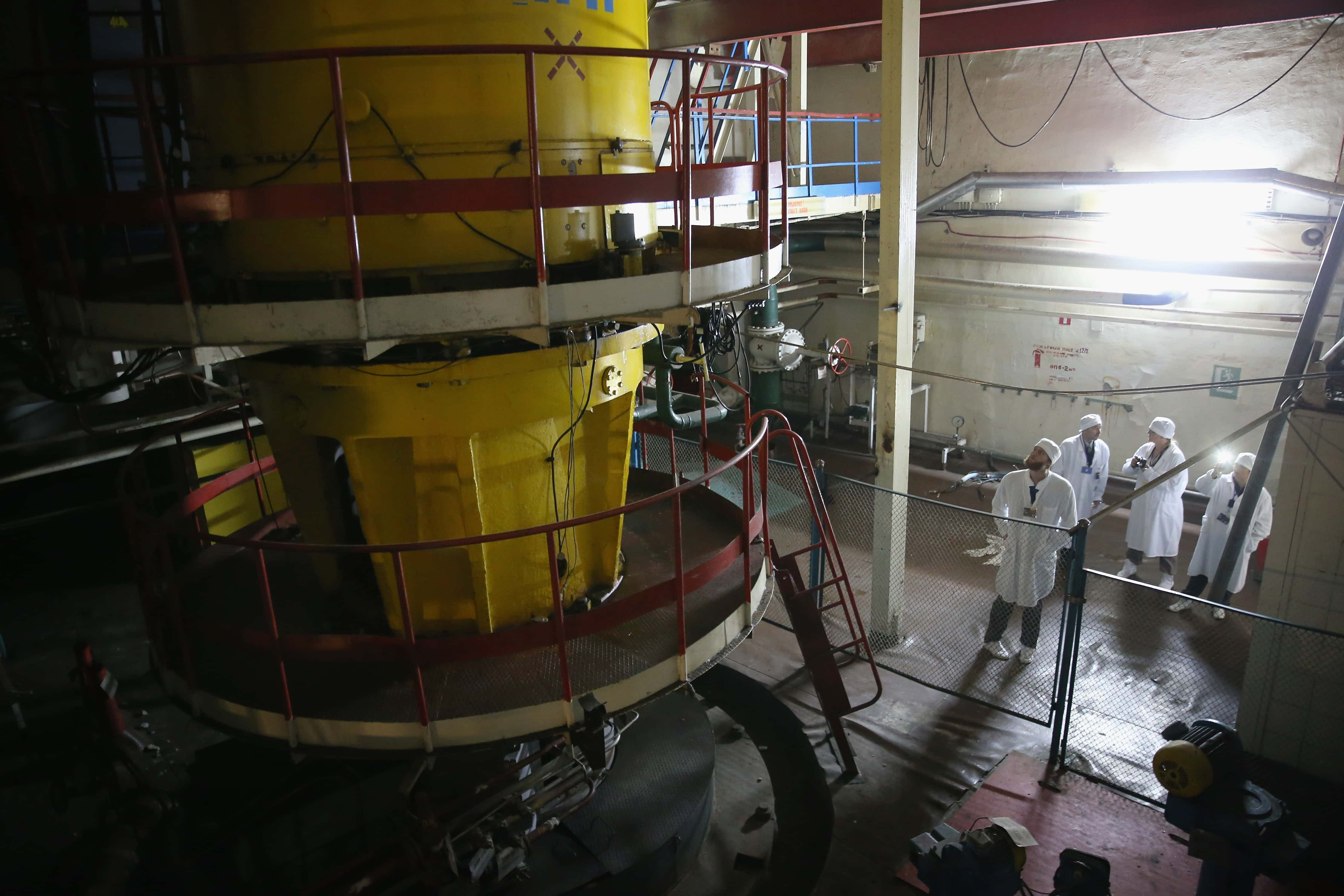
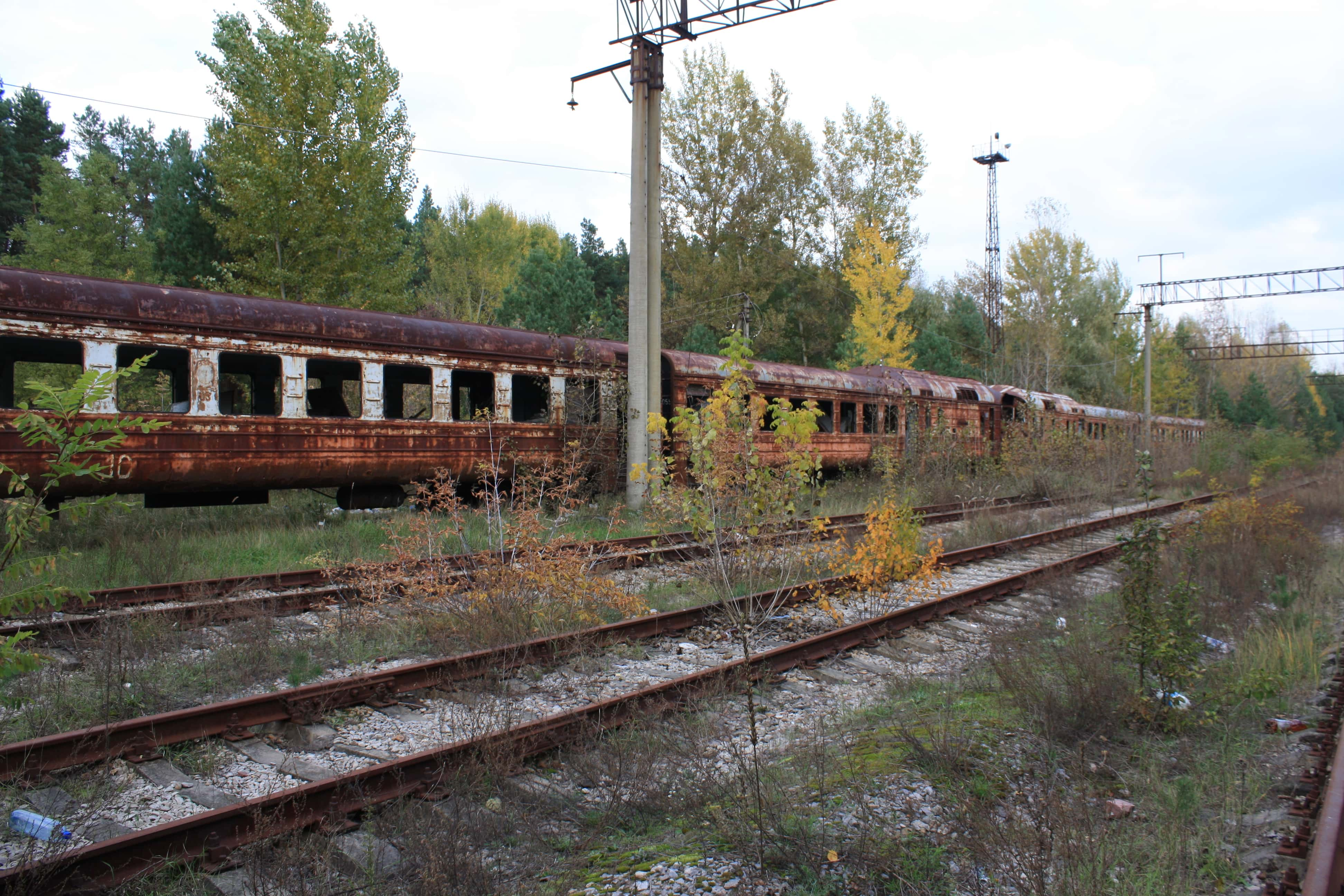
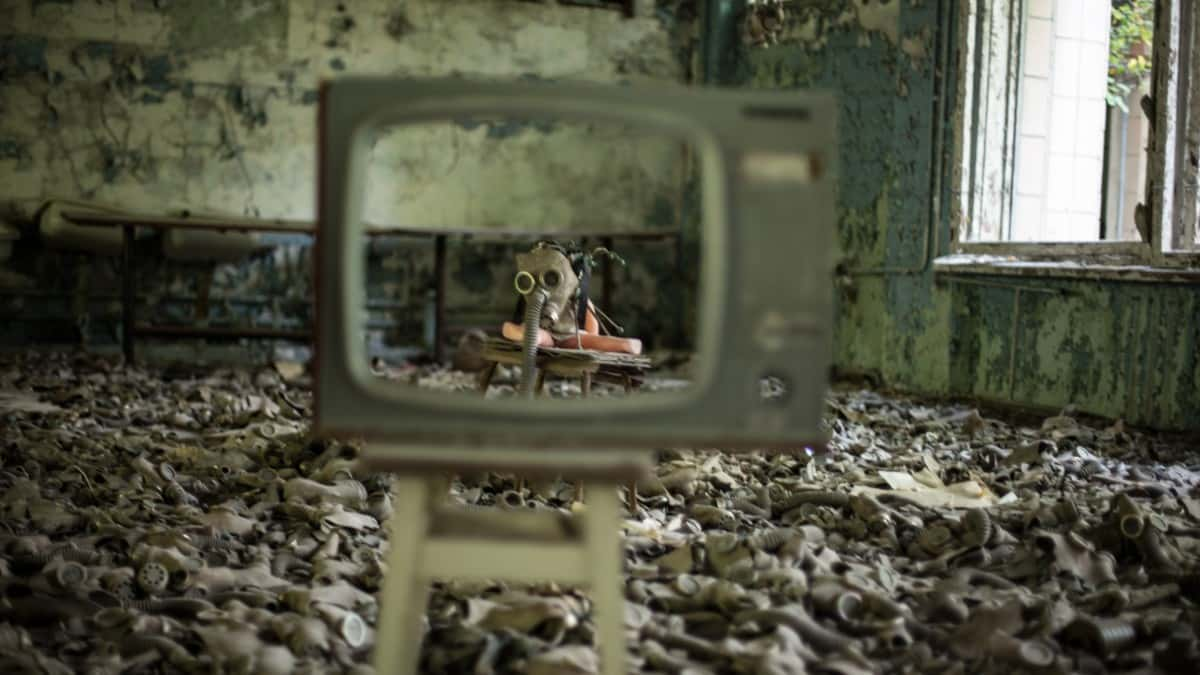
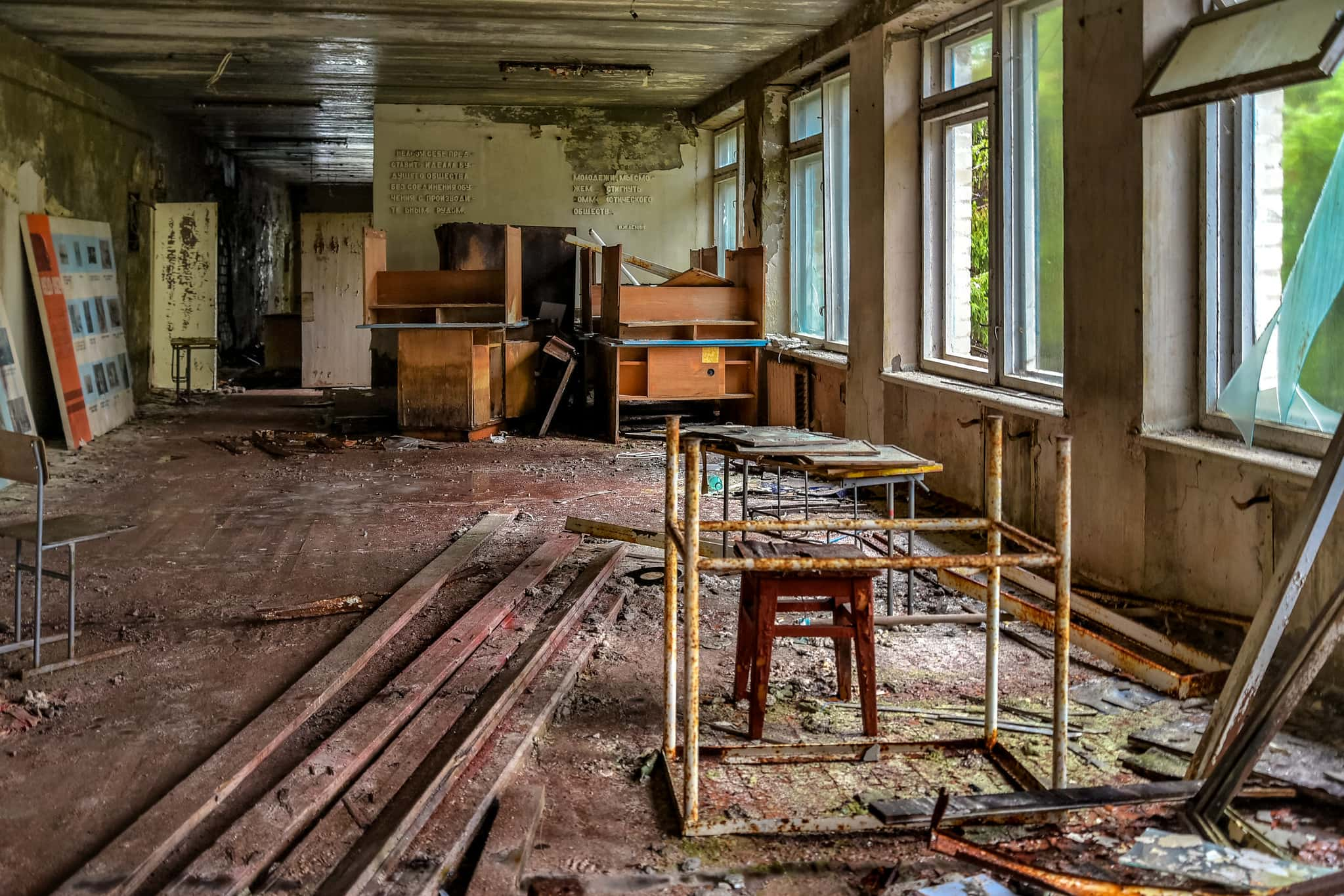
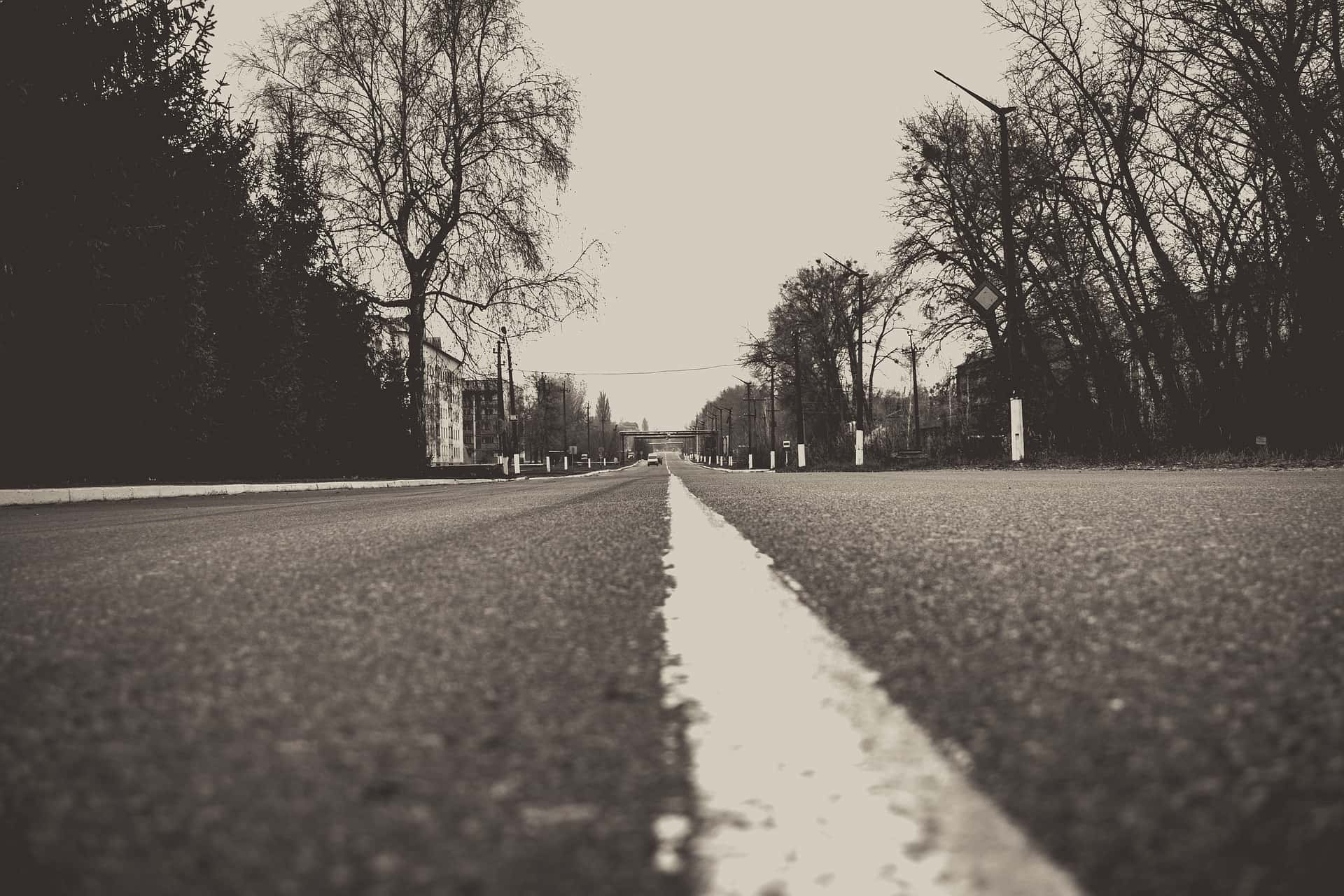
“Mankind has never experienced a misfortune of this magnitude with consequences so grave and so hard to eliminate". —Boris Yeltsin
The Chernobyl Disaster is one of the worst, if not the worst, nuclear accidents of all time, and laid claim to both immediate and future victims. At the time, misinformation about the disaster and distrust for the Soviet government abounded. What do we really know about the day that changed how we view nuclear power? Keep reading to discover more about this disastrous day and the effects that followed.
42. The Why and When
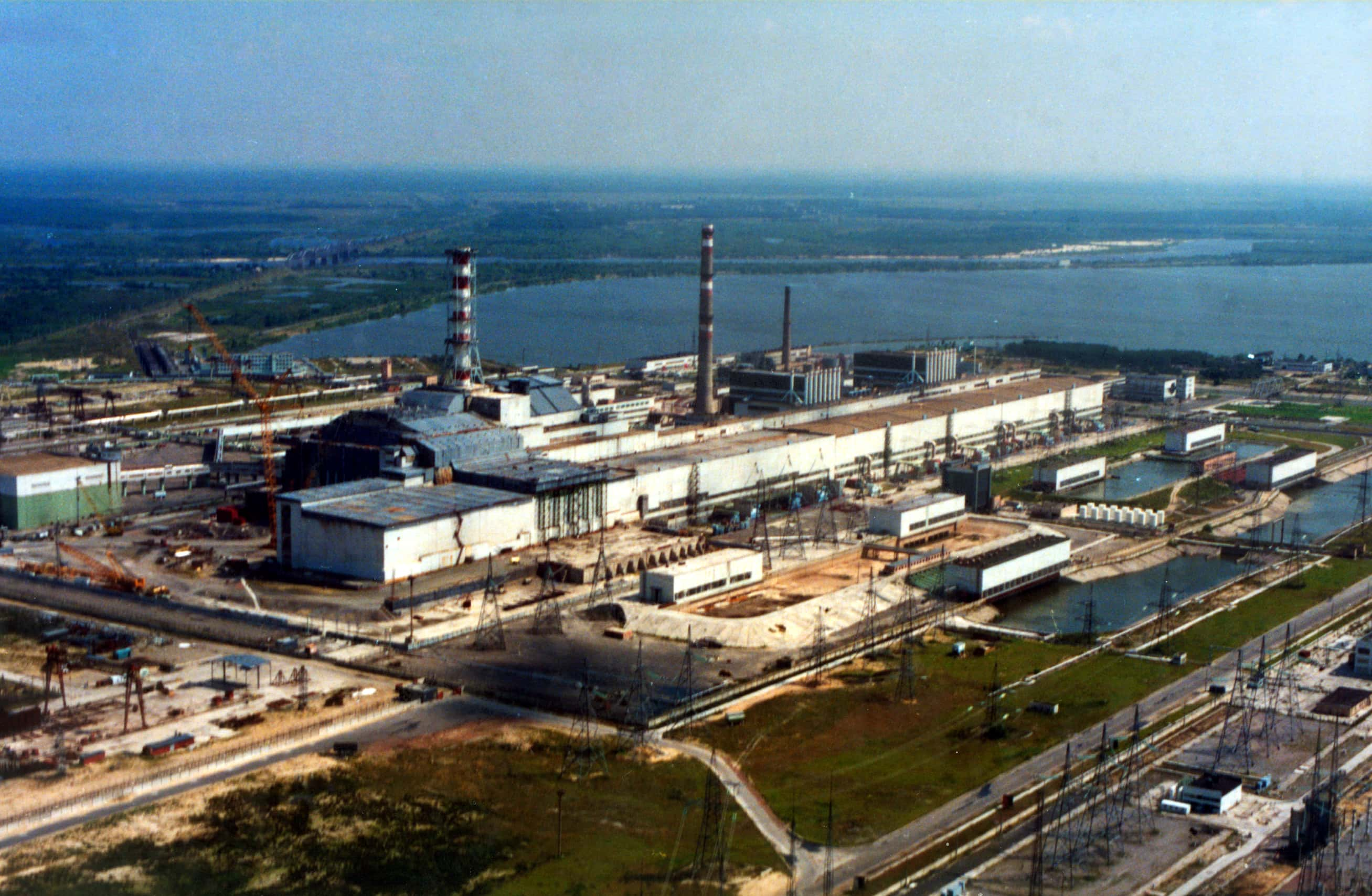
How and why did the disaster occur? Initially, the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant scheduled a systems test of Reactor Four in the early hours of April 26, 1986. The plant was located near Pripyat, roughly 104 km (64.6 mi) north of Kiev, Ukraine. At the time, the area was part of the USSR.

41. The Where
The plant's reactors were designed and built between the 1970s and 1980s, and the plant also had its own massive reservoir. The Pripyat river fed into the reservoir, with the water acting as the coolant for the plant.
40. The Who
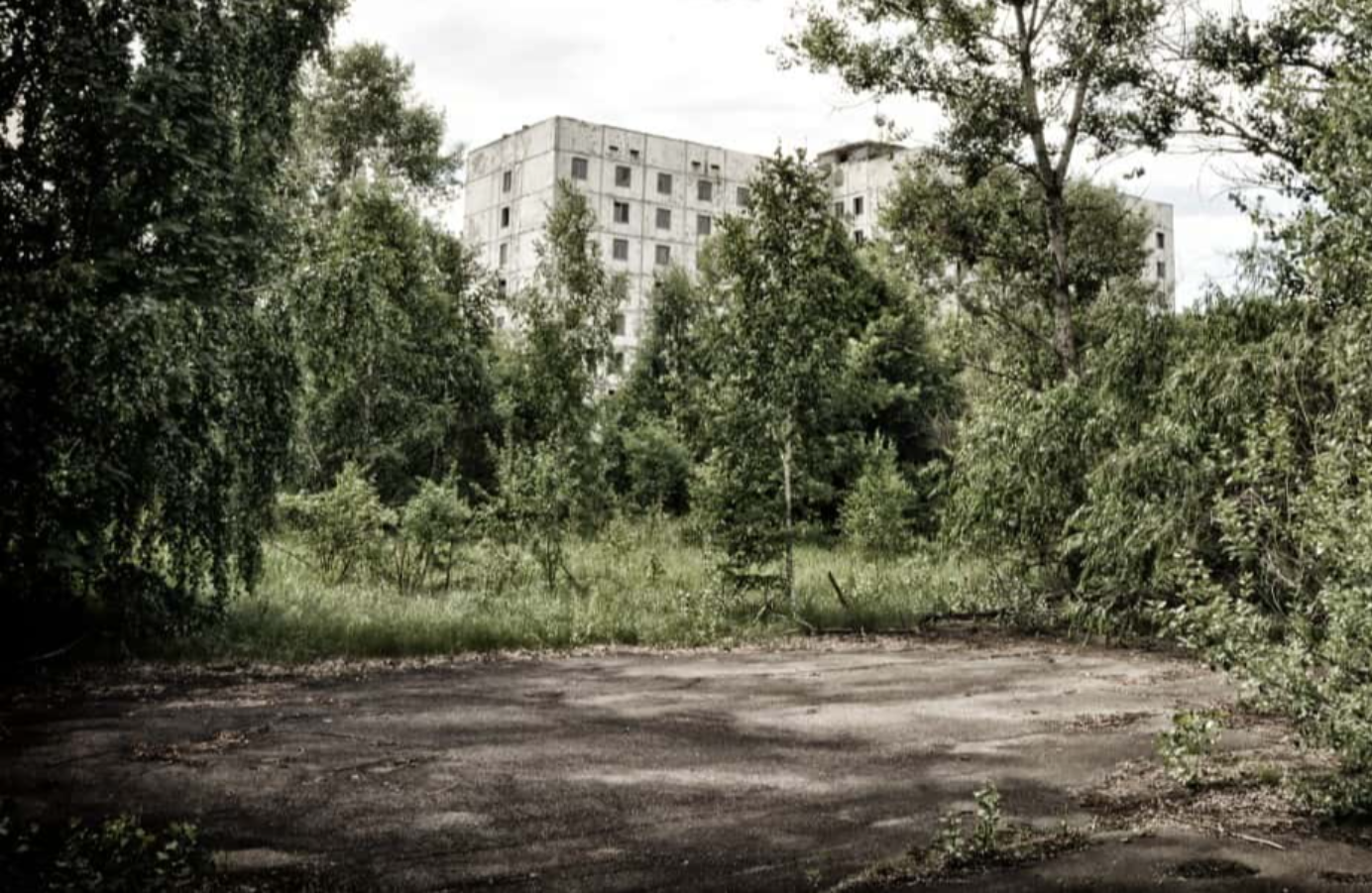
In 1986, some 50,000 residents lived in Pripyat. The other closest town? Chernobyl. It was tiny, housing only about 12,000 residents at the time.
39. The What
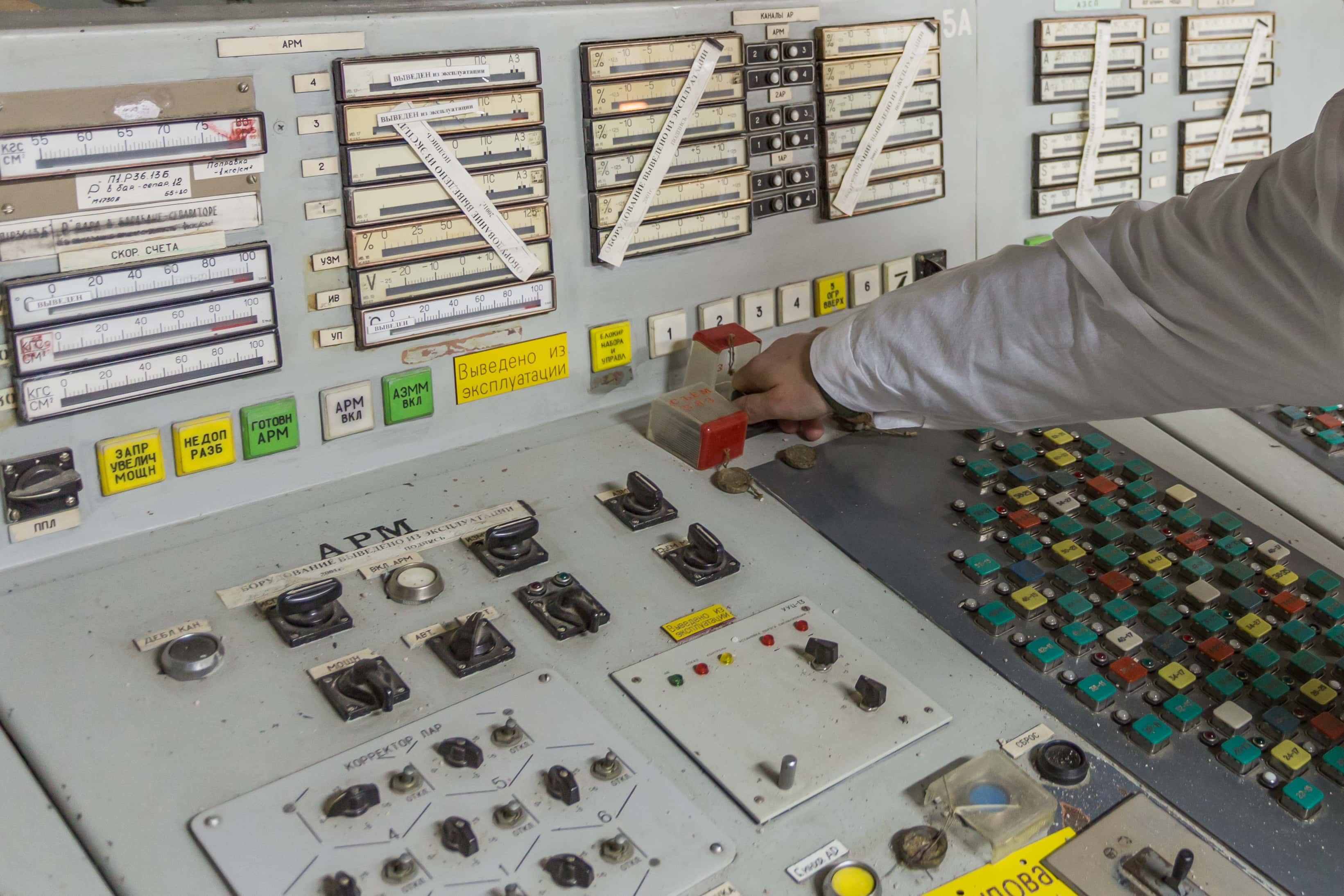
When the Chernobyl Plant was built, it used four Soviet-designed RBMK-1000 nuclear reactors. You wouldn’t often find this type of reactor today in modern plants–they’re got major flaws in their design and concept (more on that...basically throughout this whole article).
38. Electrifying
RBMK reactors heat water with U-235 uranium, creating steam that then powers turbines and produces electricity.
37. The Crack in the Foundation
Today, most modern reactors use water as cooling moderator to help mitigate core reactivity. RBMK reactors lack this main water moderator feature (though they can use water as a coolant); instead, they use a graphite moderator, which doesn't stabilize the core as well. In fact, by keeping a continuous nuclear reaction in the core, graphite actually makes the core more reactive.
36. Safety First
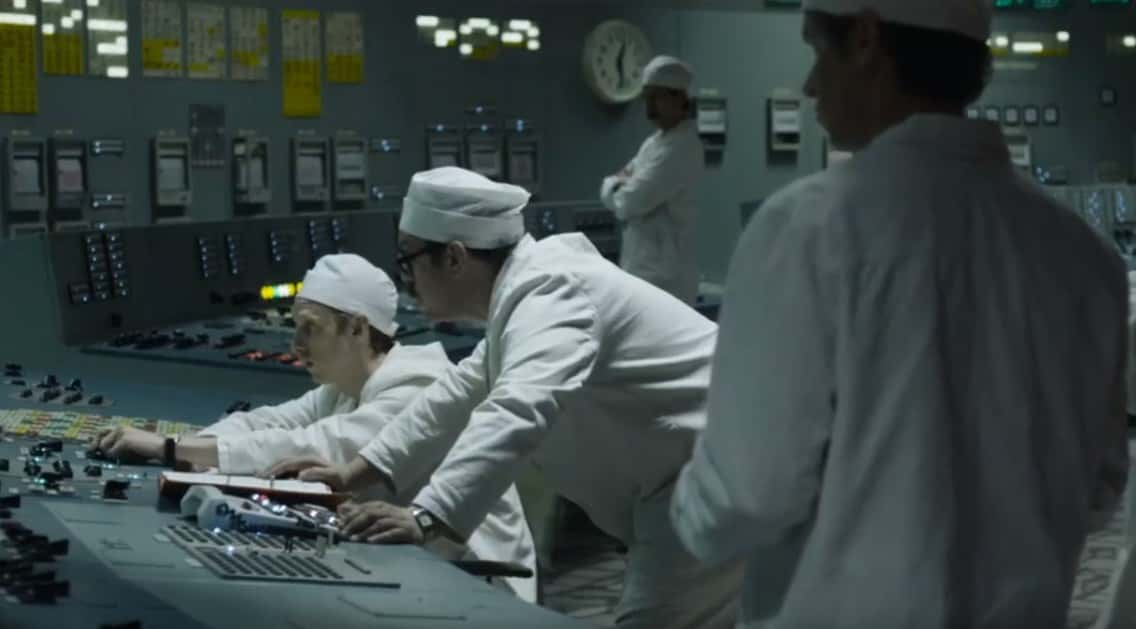
On the morning of April 26, just before the disaster, the plant performed a safety test that greatly contributed to the explosion. Ironic, right?
35. Time Is of the Essence
What exactly was this safety test for? Well, if it ever needed to cool down, the reactor needed a massive 28 metric tons of water coolant flow per hour—and the coolant pumps needed electricity, electricity which in turn took about 60-75 seconds to supply (from backup generators) in the worst-case-scenario event of a power failure. So basically, for the utmost safety, the plant needed to find a way to briefly generate electrical power from an alternative source (a steam turbine) in order to engage the cooling pumps and ride out this minute or so without generator power. The problem? The plant couldn't do it, and the higher-ups wanted to correct this safety issue. The test scheduled for the night of the accident was supposed to help fix this.
34. Four Times Too Many
The Chernobyl Plant had failed this provisional electrical power test no less than three times in previous years. They had tried, and failed, to generate alternative forms of power to make it through the 60-75 seconds in 1982, in 1984, and 1985. On April 26, 1986, they tried again—when Reactor Four was set to shut down for maintenance.
33. Safety Last
Neither the chief designer of the reactor nor the scientific manager were involved in this fourth attempt. The director of the plant was informed, but even his approval didn't follow proper procedures.
32. A Series of Unfortunate Events
Over the course of the day during April 25, in preparation for the test, the reactor was put into an increasingly fragile state. Many safety procedures were bypassed and other mistakes were made, so that by the evening, the reactor would not be able to automatically recuperate if something went wrong.
31. Surging Ahead
Then disaster struck. During the test, partly because of attempts to boost reactor's output a bit, the reactor experienced an unexpected power surge. And when I say power surge, I mean power surge: the reactor was supposed to be operating at about 700 MW for the test—it rocketed to 30,000 MW.  Cs szabo, CC BY 2.5, Wikimedia Commons
Cs szabo, CC BY 2.5, Wikimedia Commons
30. Domino Effect
The power surge caused a series of explosions in the core, which then put out radioactive isotopes into the atmosphere and started a fire. The fire only made things worse—it carried the isotopes further, since the reactor wasn't encased in a safety container.
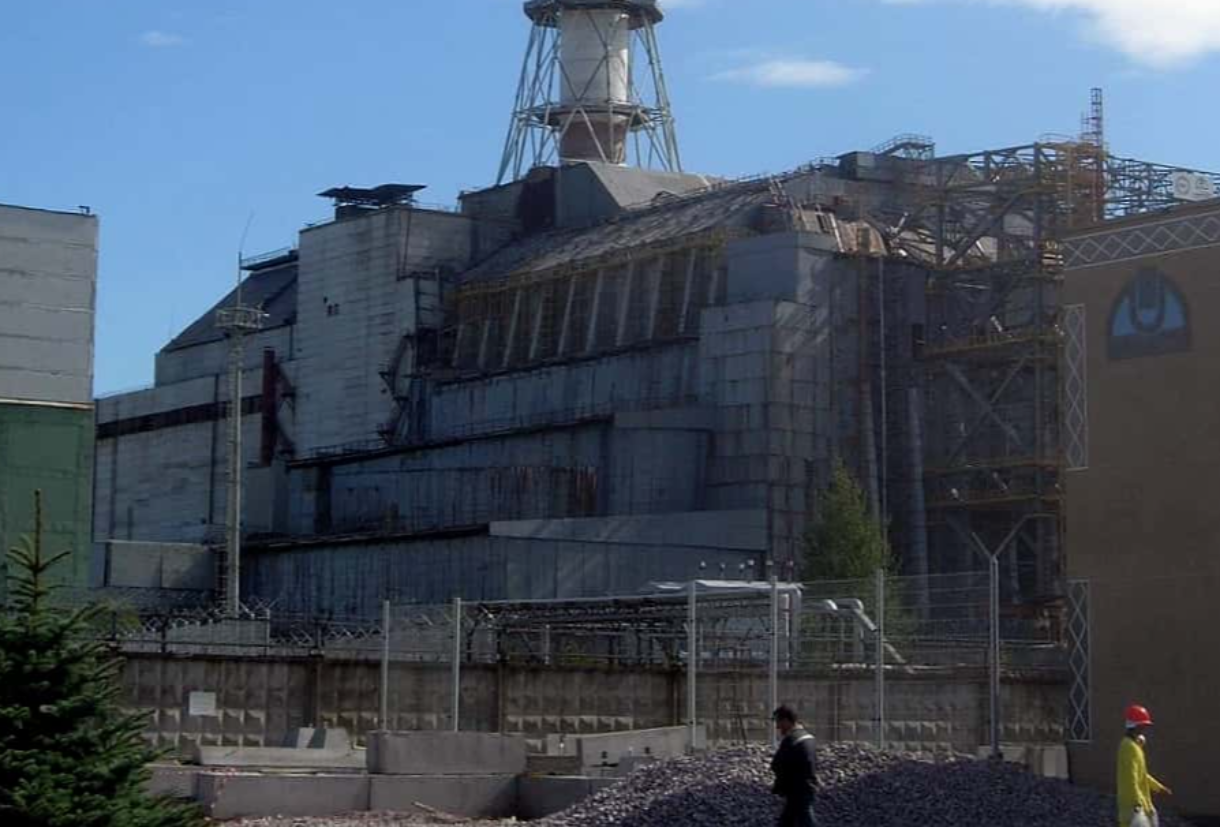
29. Blast the Roof Off the Place
When the explosion happened, the 1,000-ton plate that covered the reactor core was blown off. That’s how intense the reaction was. A second, even more powerful, explosion happened just moments after the first, and blew the building apart. Even Reactor Three saw damage.
28. The Fire Outside
The fire raged for a week, and high plumes of radioactive smoke billowed into the air over vast swaths of land, even going over large areas of the western Soviet Union and parts of Europe. 60% of the fallout settled over Belarus, which was close by.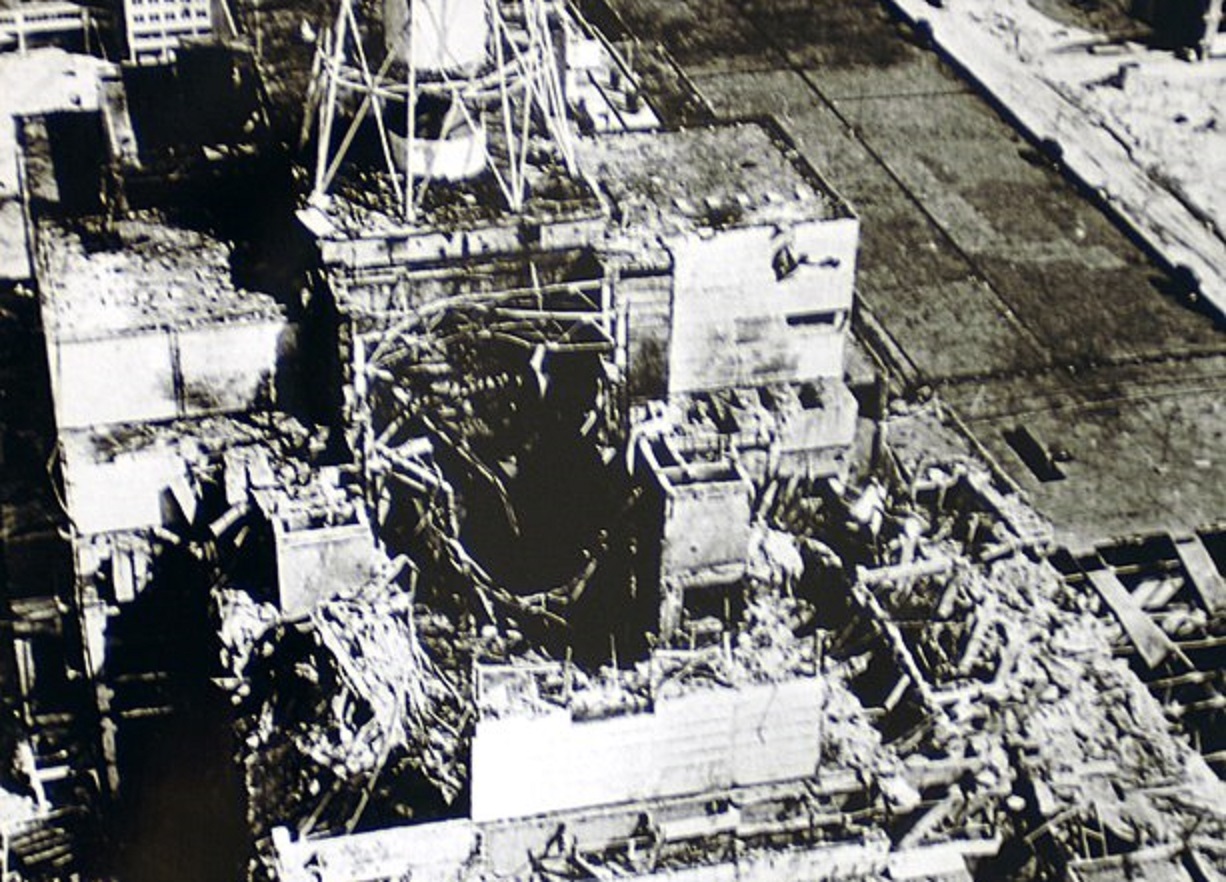  IAEA Imagebank, CC BY-SA 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
IAEA Imagebank, CC BY-SA 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
27. To Infinity and Beyond
The very, very few survivors who were on the scene that day reported seeing bluish-light in the reactor hall (this was caused by the ionization of the air) that looked like it "flood[ed] up to infinity".
26. No Quick-Thinking
There was no immediate evacuation of Pripyat, and would take 36 hours before Soviet officials evacuated anyone within a 10 km (6.2 mi) radius of the plant.
25. That's So Metal
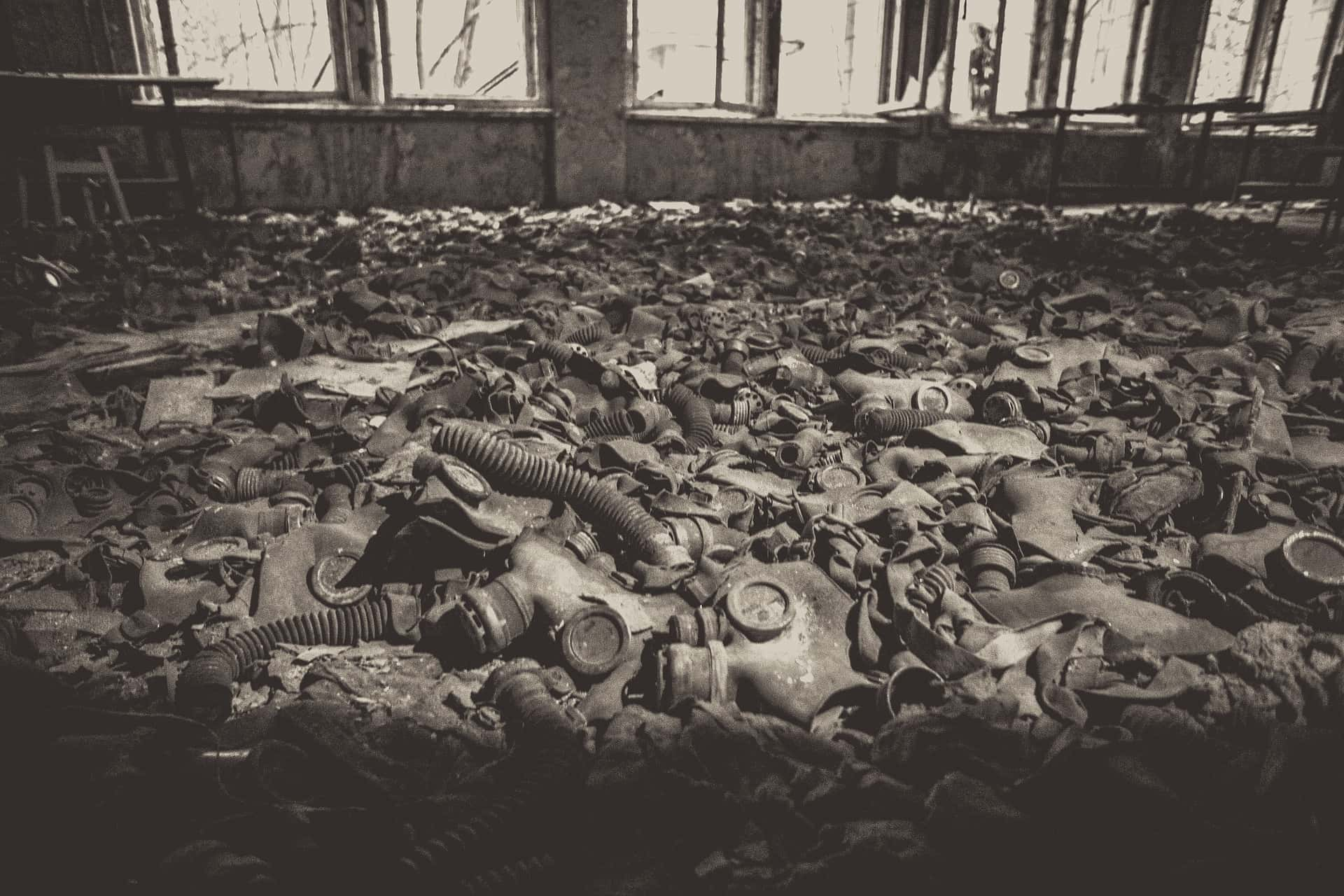
Those mere 36 hours took a staggering toll on the residents of Pripyat. They experienced headaches, vomiting, and a strange metallic taste in their mouths.
24. A Quick Trip
Officials told evacuees that they would be returning to their homes within days; many only took the most essential of their items with them.
23. Diaspora
In a week, officials expanded the evacuation radius from 10 km (6.2 mi) to 30 km (18.6 mi), resulting in another 68,000 evacuees. Residents of Chernobyl would be included in this second round of evacuations. Altogether that first year, more than 135,000 people were evacuated in the long-term. In the years to follow, about 350,000 people would have to be relocated.
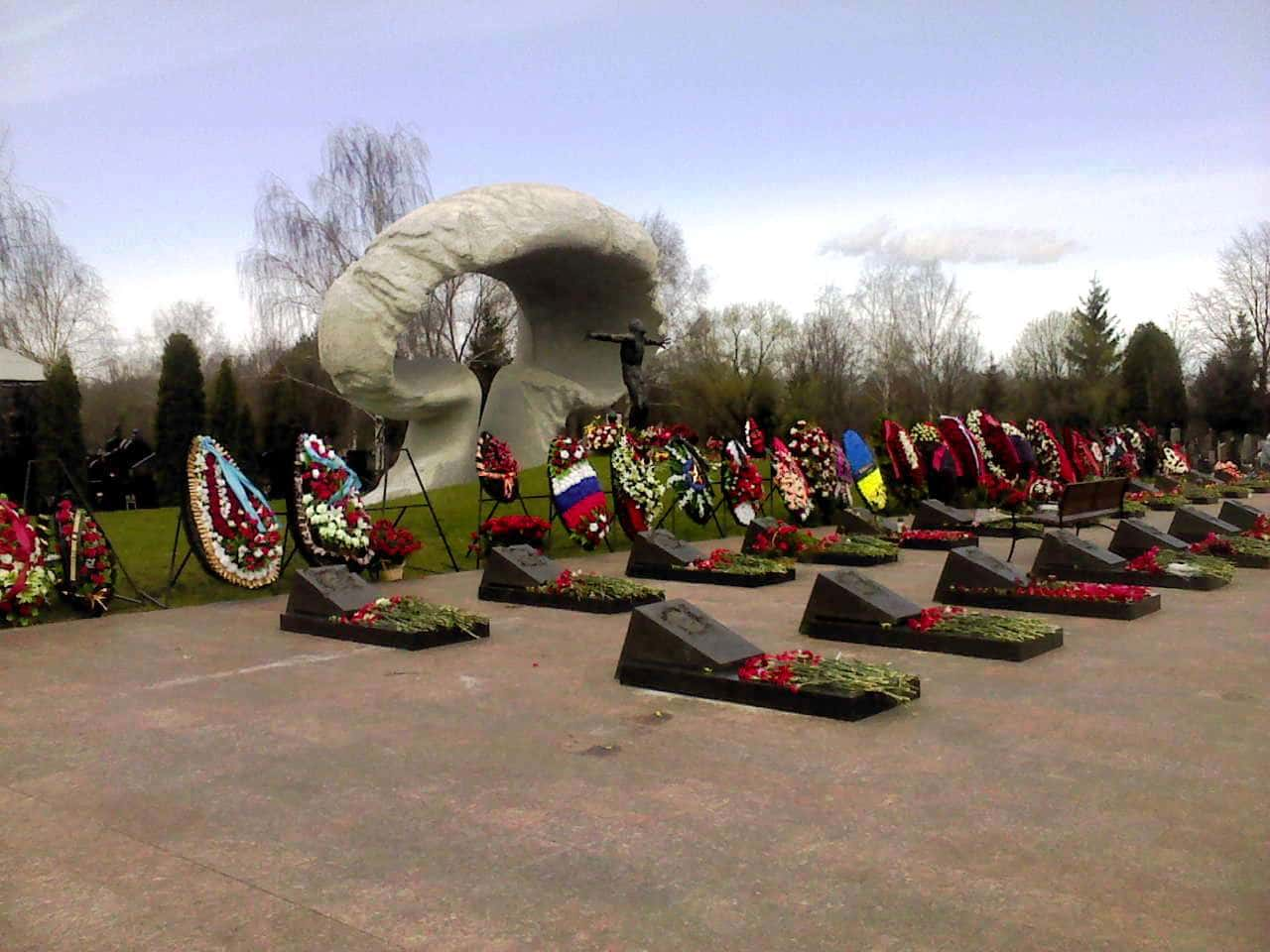
22. A Quick End
A number of plant workers passed within hours of the explosion, and as the days went on, more would succumb to the high levels of radiation. The fires raged, and the radiation continued to seep out, mostly from iodine-131, cesium-134 and cesium-137.
21. A Long End
Iodine-131 has a short half-life (eight days) and is quickly absorbed, often settling into the thyroid gland (hello, thyroid cancer!). The two cesium isotopes, however, have much longer half-lives. Cesium-137, for example, has a half-life of 30 years. As of the writing of this article, we’ve just passed that 30-year mark—which means that radiation is still very much around.
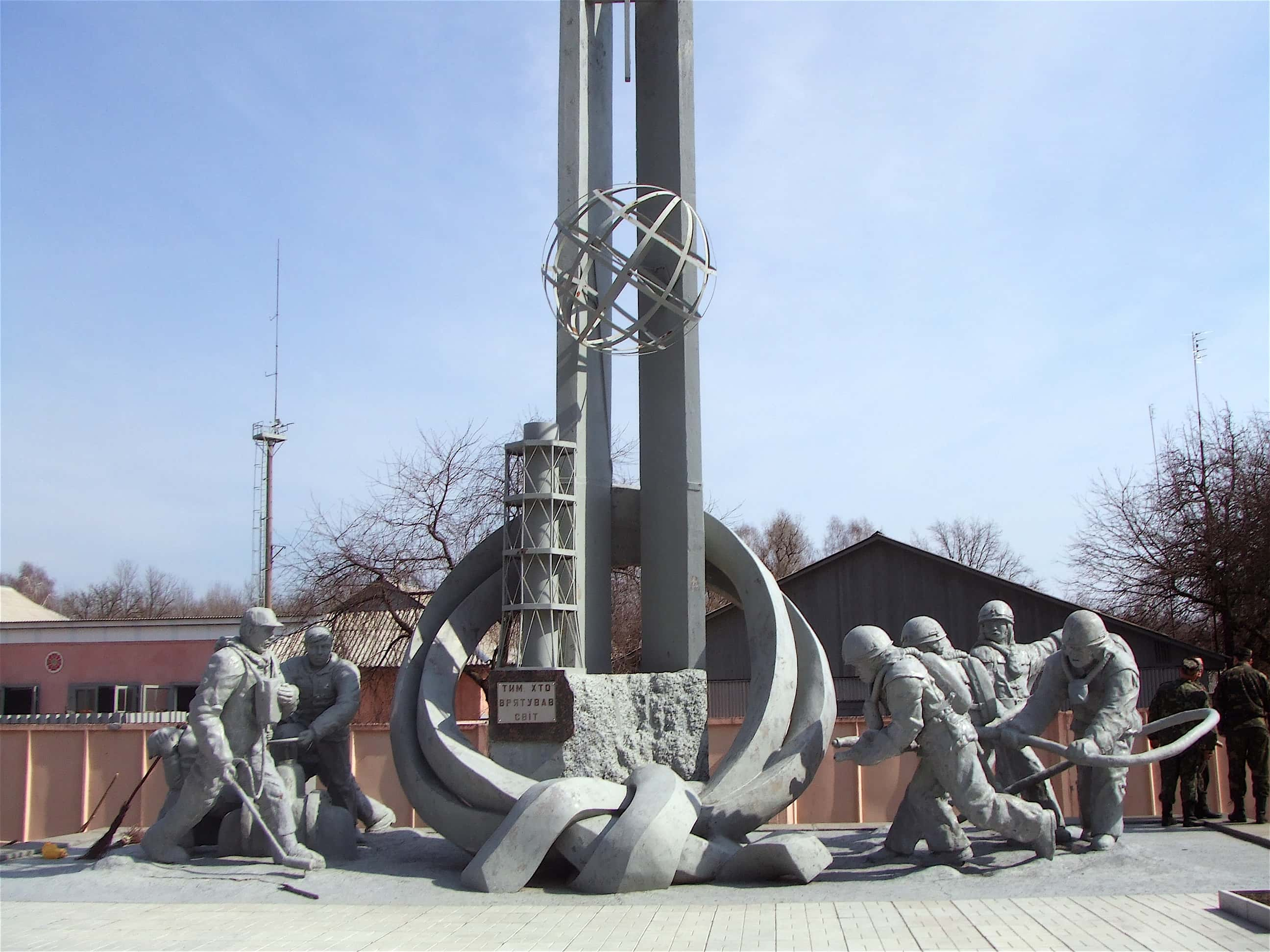
20. Heroic
The US Nuclear Regulatory Commission estimates that 28 Chernobyl workers passed from radiation exposure within four months of the disaster. Some of these workers knew full well what they were getting themselves into, but selflessly tried to help contain the radiation from leaking further.
19. Soviets Keeping Secrets
The Soviets dragged their feet on fully announcing the disaster or releasing any information about it. What made them actually admit proper information regarding the explosion? Nuclear alarms that were set off in Sweden. Sweden! That’s how far the radiation had traveled by way of the winds.
18. Thyroid Cancer
The exact amount of thyroid cancer cases (from iodine-131) in Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus linked to the Chernobyl accident will never be known, but estimates place it at around 6,000. During the aftermath, officials recommended that residents drink booze to stave off thyroid cancer.
17. Fear-Mongering
Fears about other health concerns, including leukemia and other cancers, were rampant. Doctors even suggested that women who were pregnant have abortions so their babies wouldn’t have any issues. This, however, was likely an unfortunate overreaction, as these women were often exposed to very little radiation.
16. The Red Forest
The environment also took a big hit: the trees in the surrounding area were gone and their leaves turned a bright ginger, like an eternal autumn. The area was known as "The Red Forest". In time, the trees were bulldozed and buried in trenches.
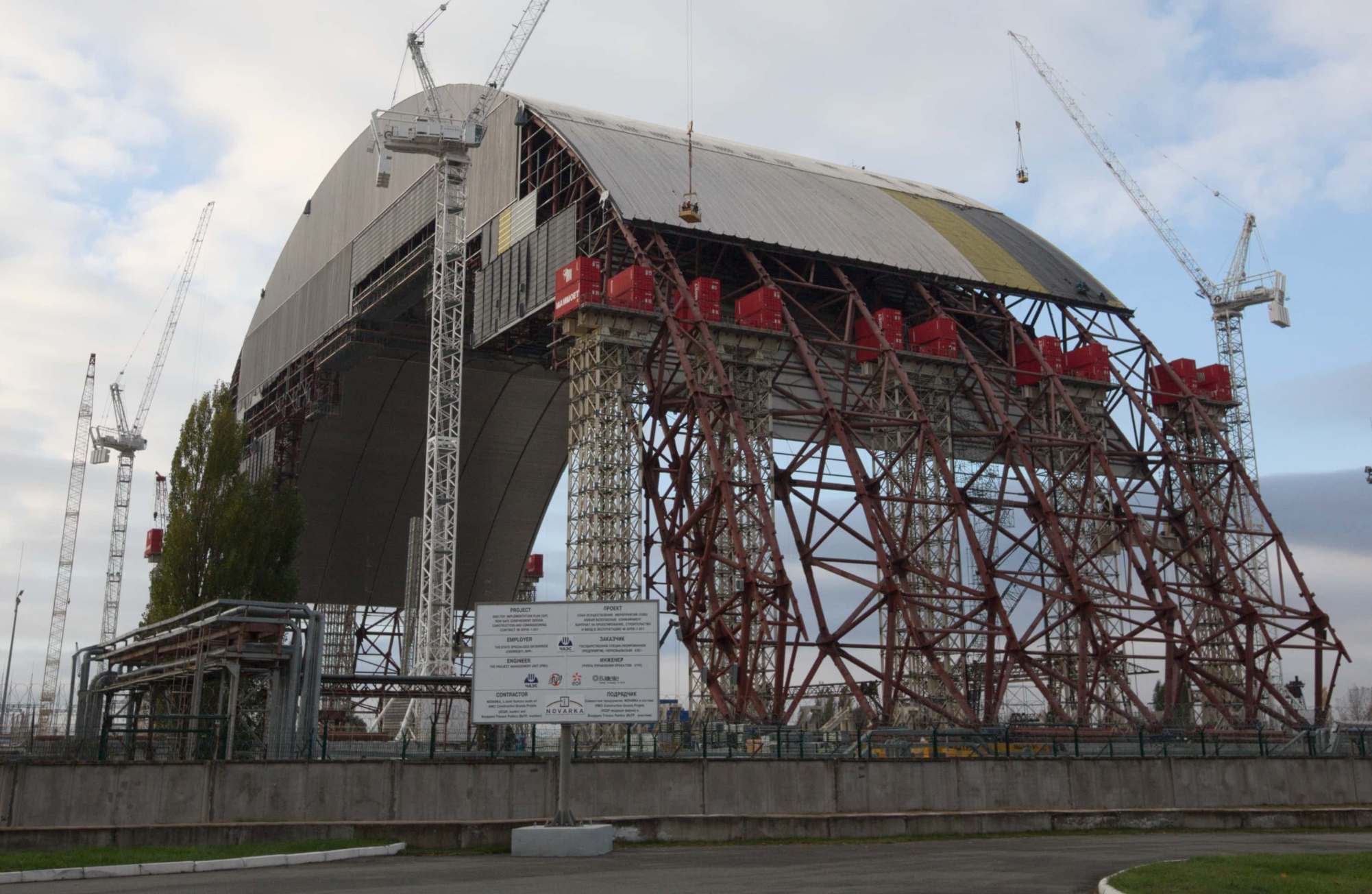
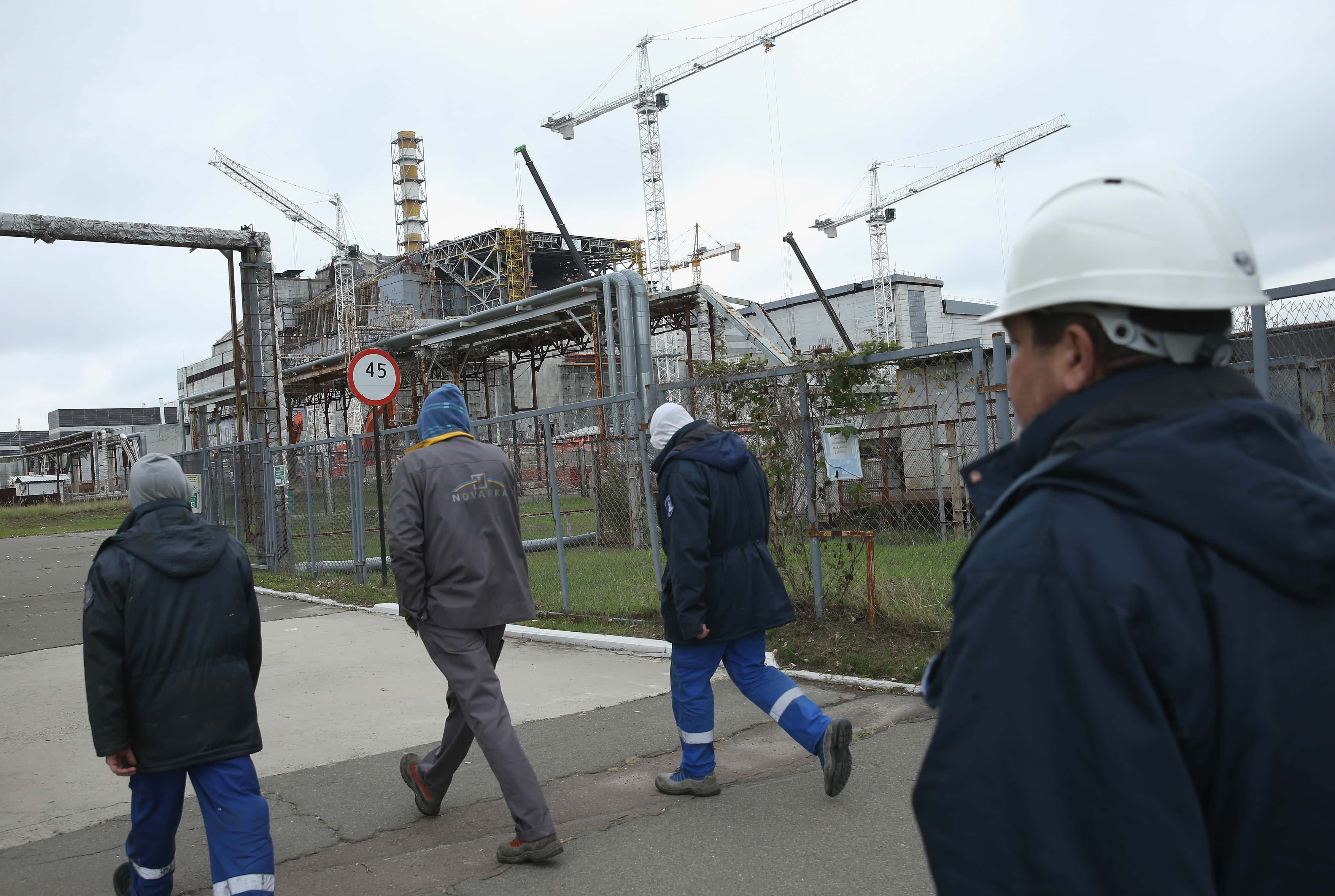
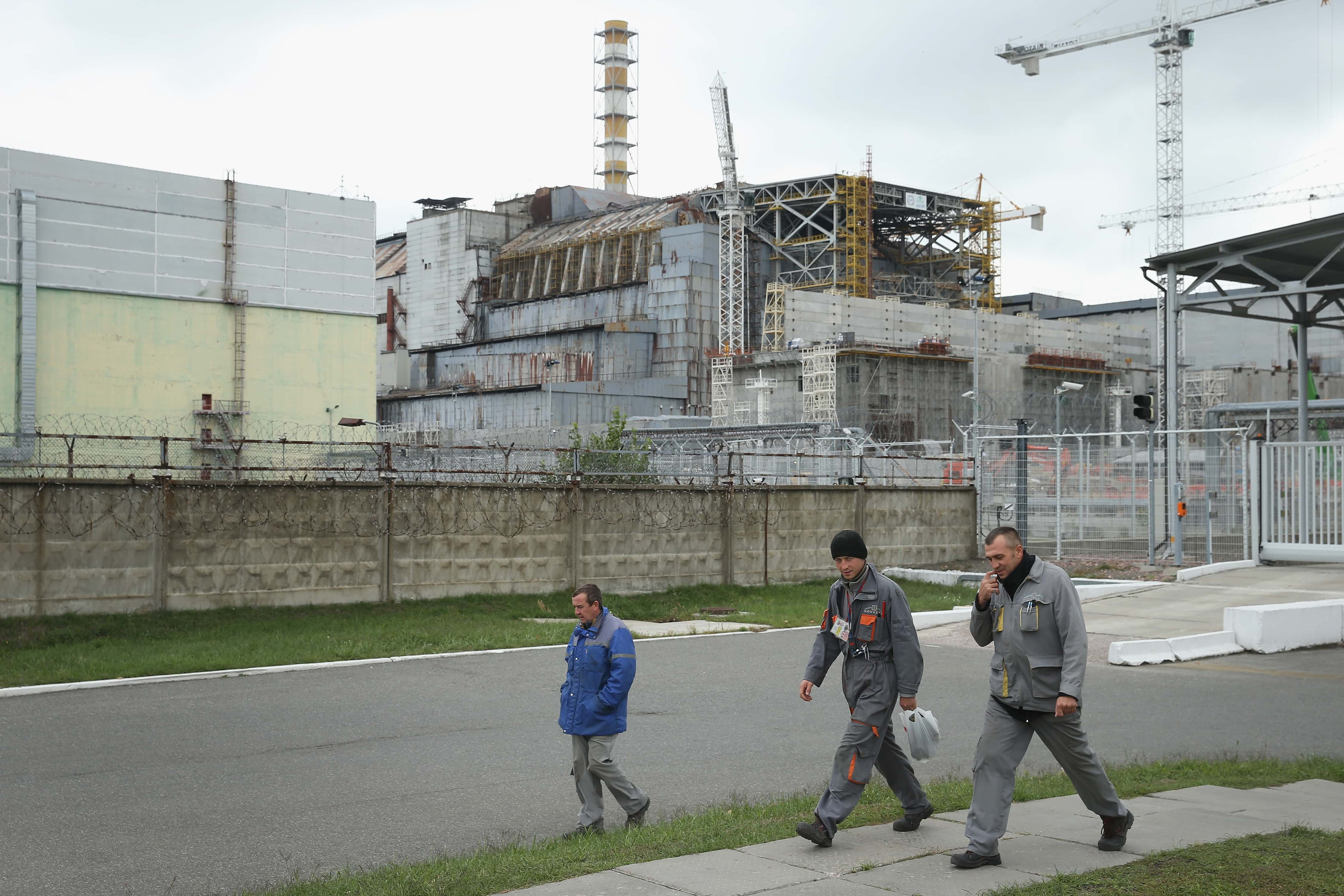
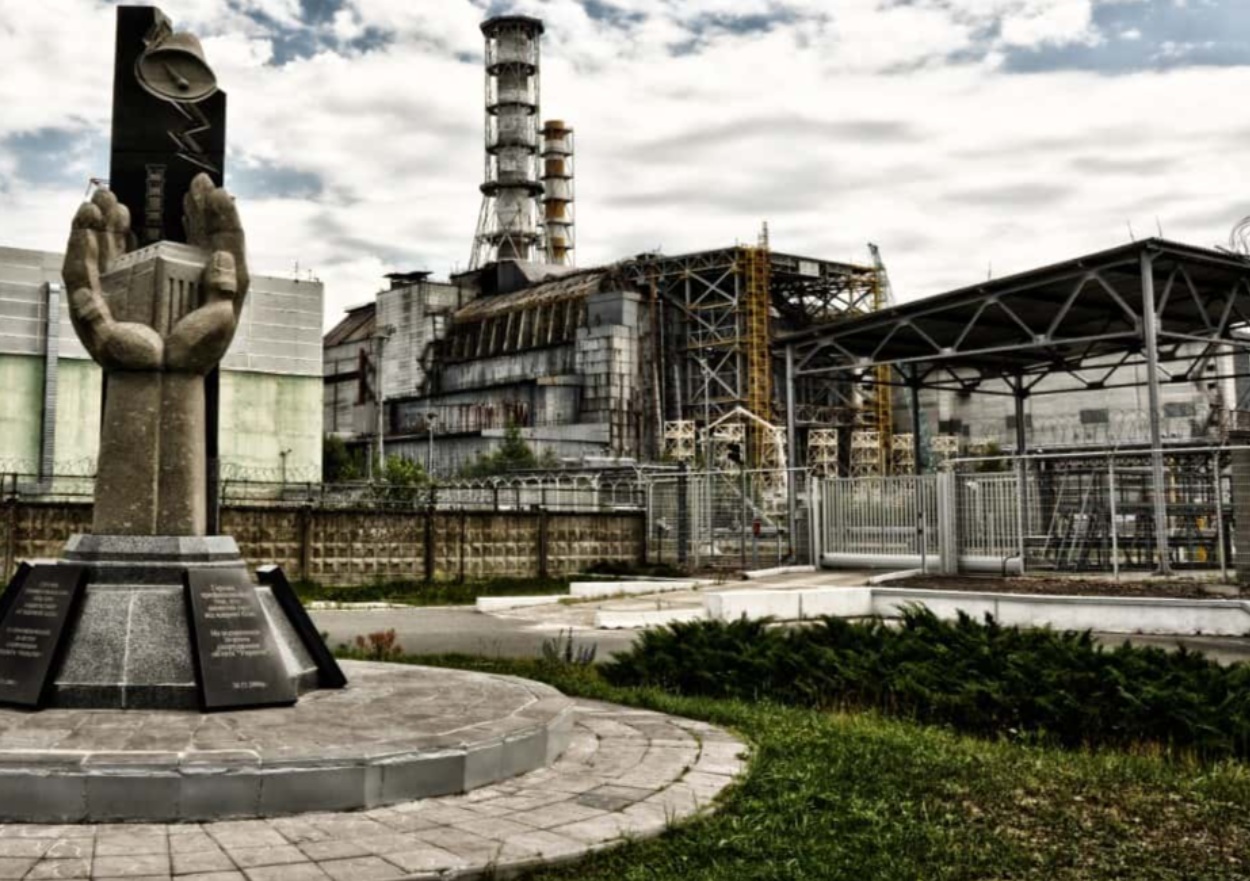
15. The Sarcophagus
A concrete encasement, known as the sarcophagus, was built over Reactor Four in an effort to contain any further radiation. The actual effectiveness of this covering was widely debated, and a New Safe Confinement was put on top of the reactor in 2016.
14. Short Days, Long Term Effects
Any workers on site are subject to strict labor laws because of the radiation exposure. They can only work for five hours a day for one month, and then they must take 15 days off.
13. Fourteen More Years
Surprisingly enough, the Chernobyl Plant was in operation until the year 2000, and still used the same RBMK reactors.
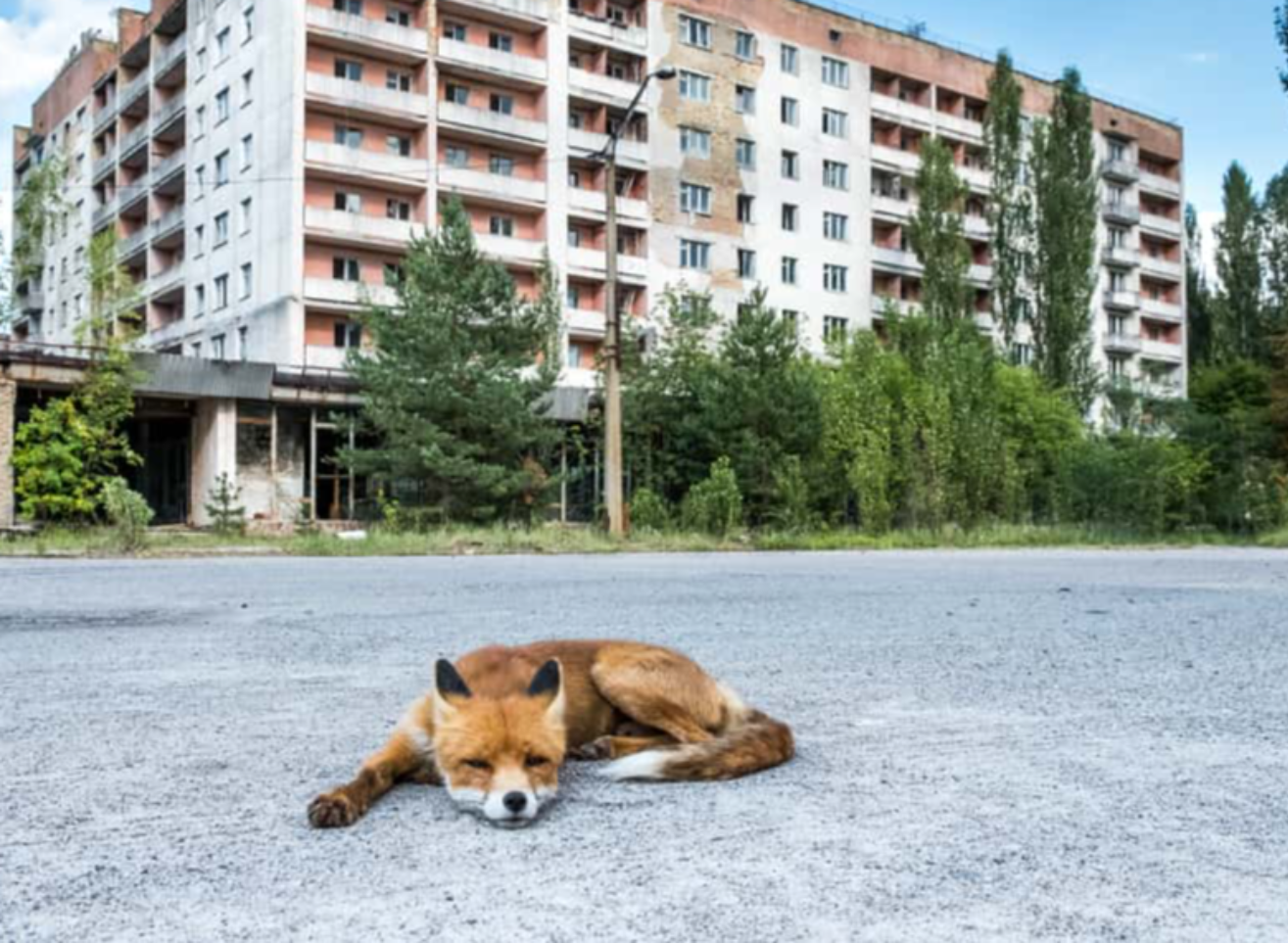
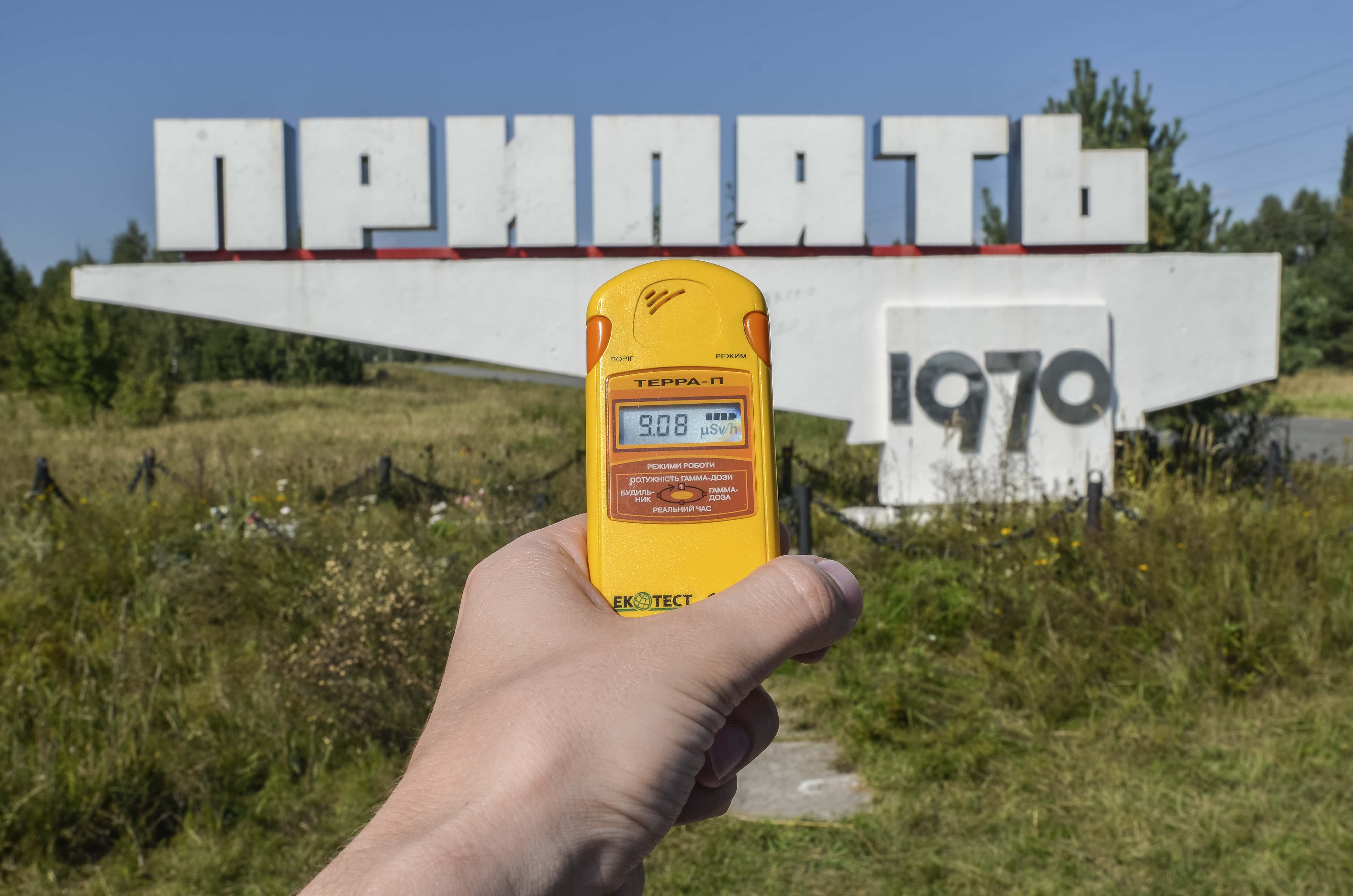
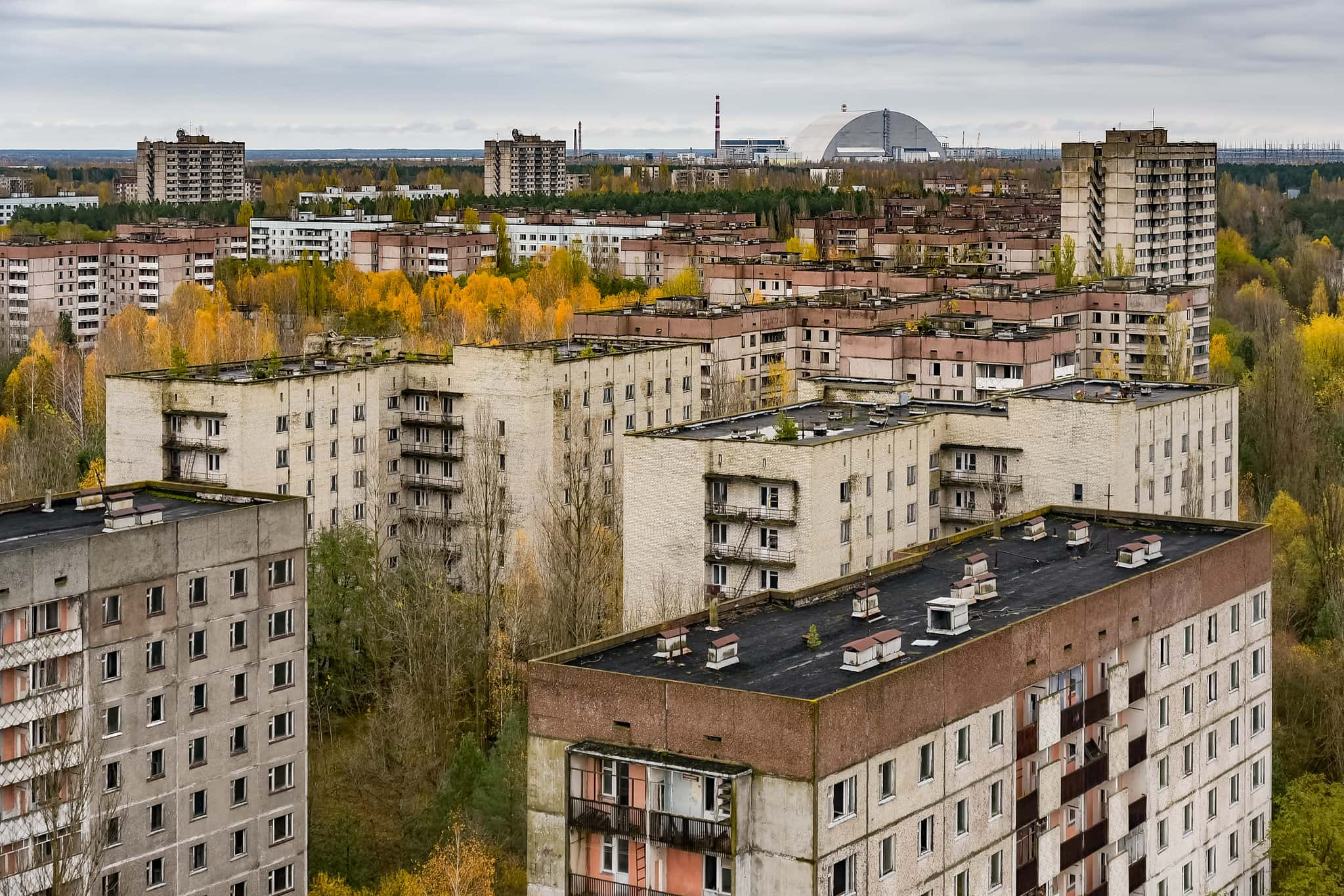
12. Just Wild
The 30 km (18.6 mi) area around Chernobyl is called the "zone of alienation". Undeterred by this name, however, 300 inhabitants refused to leave, and still live in the area.
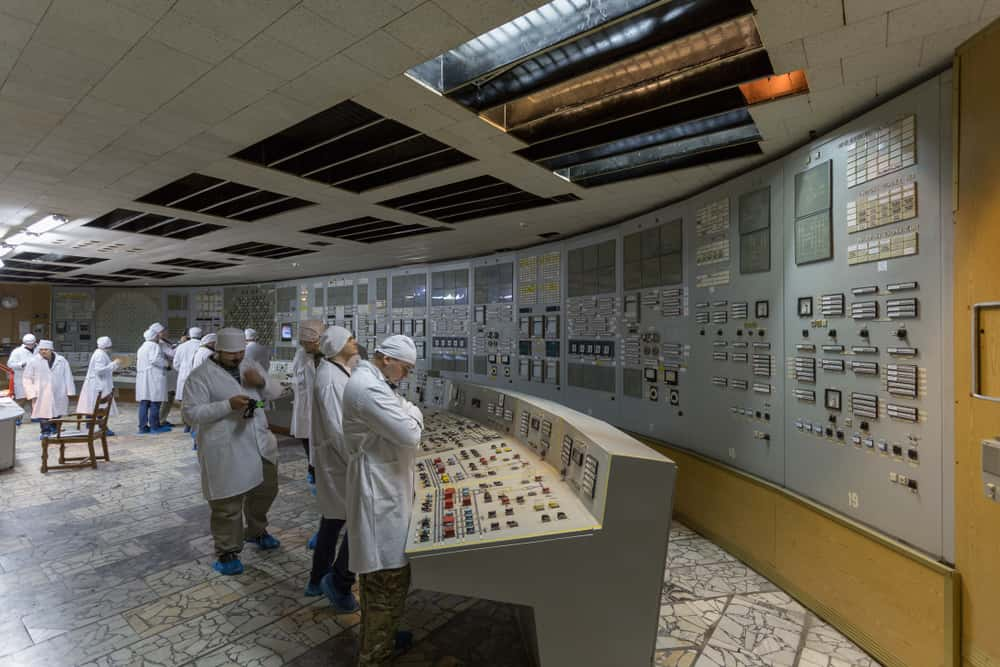
11. No Trespassing?
By 2016, 187 Ukrainians had moved back to the area as well. Starting in 2011, the Ukrainian government also began allowing tourists to come view the Chernobyl Plant.
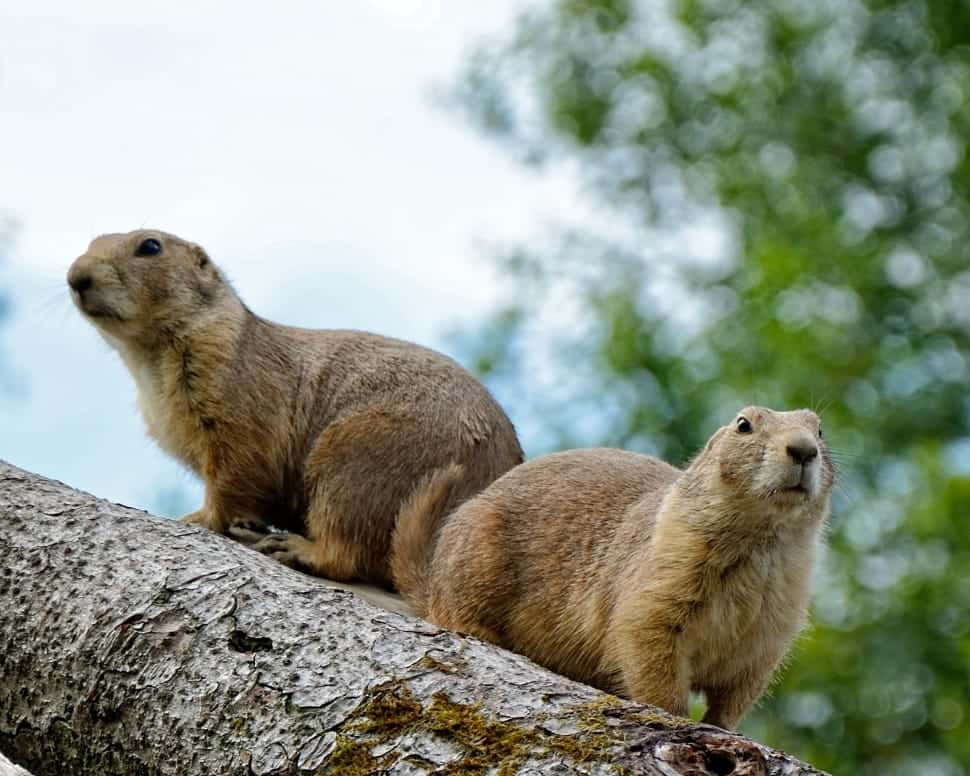
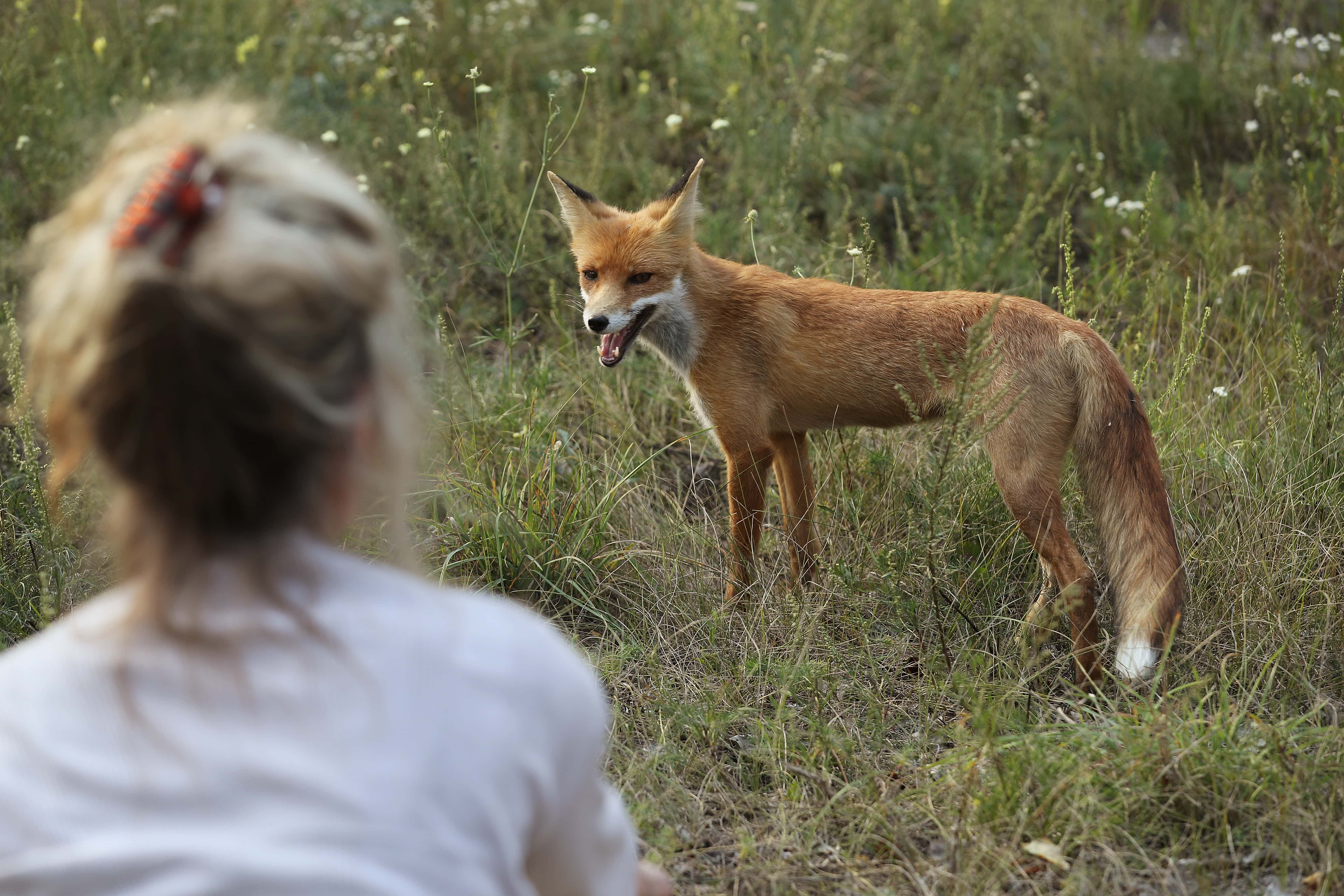
10. The Wild Lands
Because of the lack of competing human life in the area surrounding the plant, a wide variety of wildlife live in the remaining woodland. Wolves and deer, lynx and beavers, eagles, boars, elk, bears, and any number of other species call Chernobyl home. Some of the animals still show traces of cesium-137, and stunted trees try to grow.
9. Life Finds a Way
The National Academy of Sciences in Ukraine is one of the few groups allowed to keep track of the goings on of animals in the affected area. In 2016, they released a study that detailed observations over a five-week period. Camera footage showed them a bison, 21 boars, nine badgers, 26 gray wolves, 60 raccoon dogs, and 10 red foxes.
8. Pre-Collapse
Marina Shkvyria, a wolf expert from the National Academy of Sciences, believes the land can return to a pre-plant state—with help from beavers. If the beavers can bring down trees, the land can eventually become bog-rich. "It will become like it was a hundred years ago,” Shkvyria told National Geographic.
7. A Long, Long, Long Lasting Effect
Don’t be fooled by all of the wildlife living in the disaster area, though. Ukrainian officials estimate that the land around the Chernobyl Plant won't be habitable for humans for 20,000 years.
6. Good News
It's not all doom and gloom: The United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR) released an encouraging report in 2010. “There is a tendency" the report stated, "to attribute increases in the rates of all cancers over time to the Chernobyl accident, but it should be noted that increases were also observed before the accident in the affected areas". The report goes on to say that the radiation level the population experienced was “comparable to or a few times higher than the natural background levels, and future exposures continue to slowly diminish as the radionuclides decay".
5. Not Just a Soviet Issue
The disaster had lasting impacts on other countries and governments as well. In Italy, for example, a referendum in 1987 helped decide the fate of nuclear power plants—and the country began phasing nuclear power out a year later.
 Max Pixel
Max Pixel
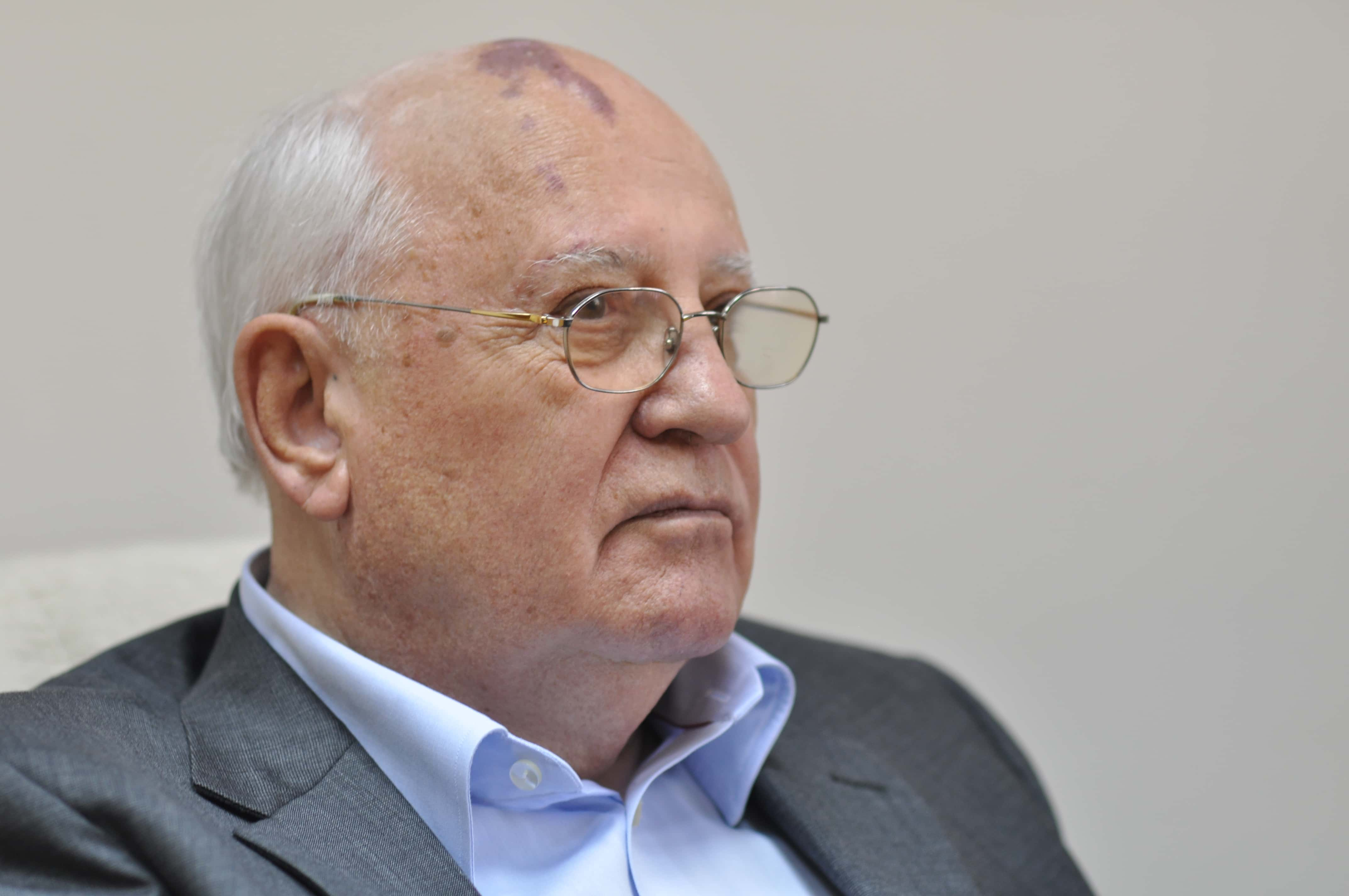
4. The Financial Cost
The economic fallout also shouldn’t be ignored. Mikhail Gorbachev estimated that the Soviet Union spent the equivalent of US $18 billion (not adjusted for inflation) to contain and decontaminate the disaster zone.
3. Cha-Ching
Costs keep coming, too: the Chernobyl Forum suggests that in Ukraine, 5-7% of government spending is still set aside for Chernobyl-related reasons.
2. Even More Fallout
Although the causes are of course complex, the financial, human, and moral costs of the Chernobyl Disaster were undoubtedly key contributors to the collapse and dissolution of the USSR in 1991. After becoming independent countries, both Ukraine and Belarus lowered the threshold for lawful amounts of radiation.
1. Contagion
There are still dangers to watch out for: if the woodland area near the Chernobyl Plant catches fire, it will still spread radioactive material through the winds.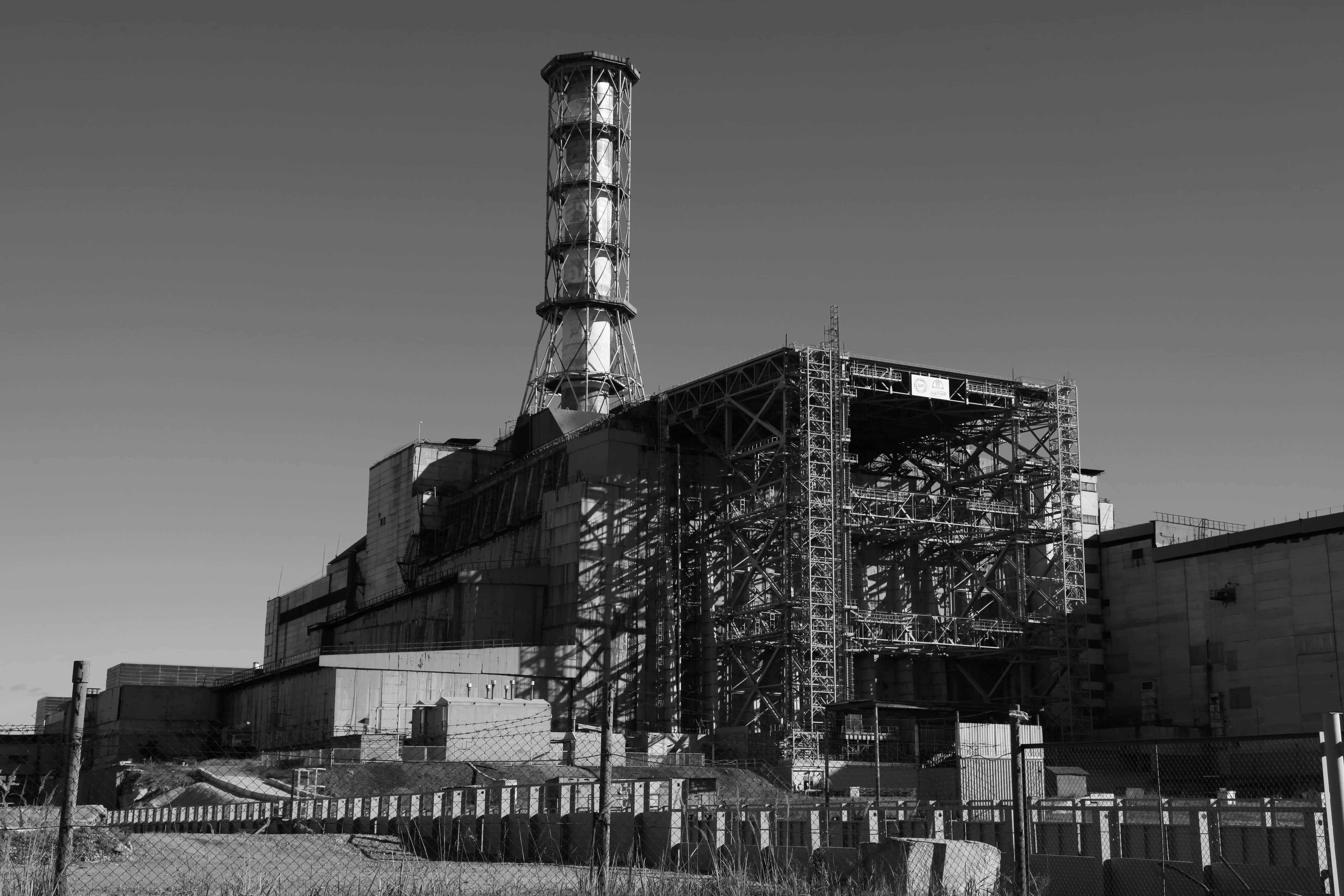 Flickr, Dana Sacchetti/IAEA
Flickr, Dana Sacchetti/IAEA