The Earliest Creative Impulse
Imagine discovering a painting so old it predates the earliest known European art traditions. Archaeologists just did, and the images are detailed and unsettling enough to force a rethink of when creativity began.
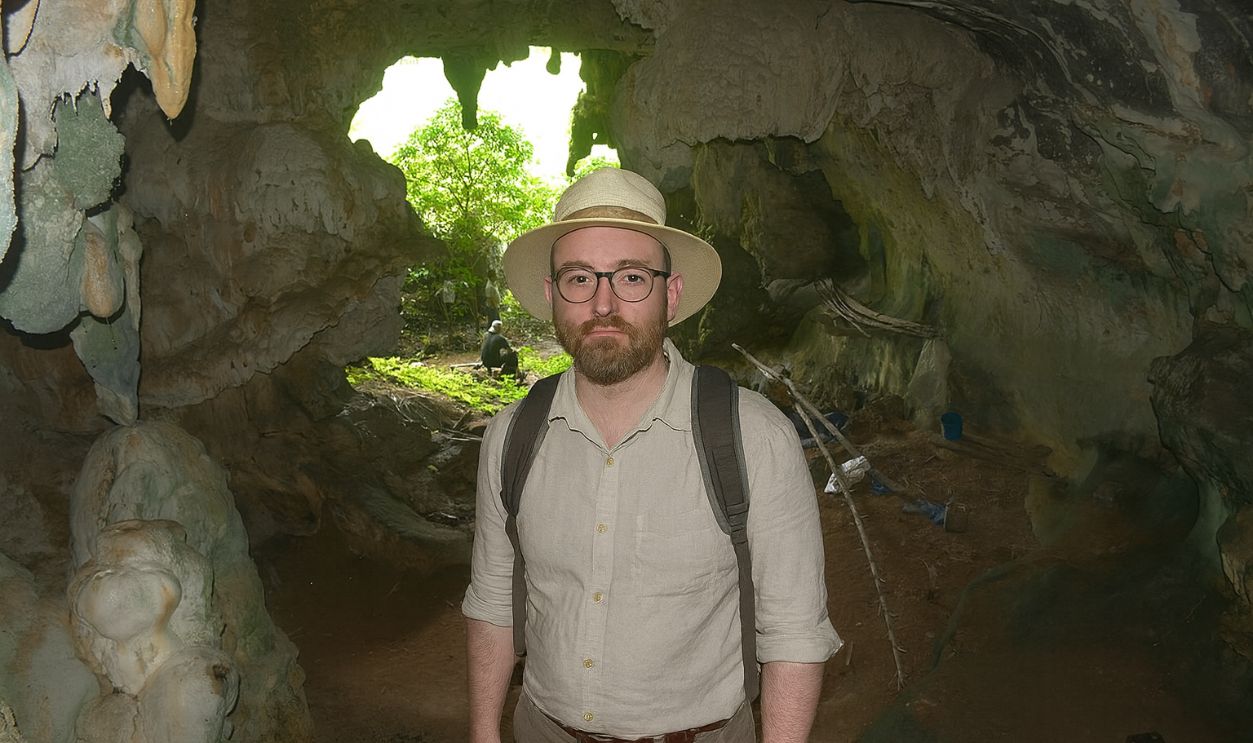

The Oldest Paintings Ever Found
Archaeologists weren’t looking for a turning point in human history. Then they stepped into an Indonesian cave and found images so old they predate everything we associate with civilization. These paintings quietly suggest creativity existed far earlier than we ever imagined.
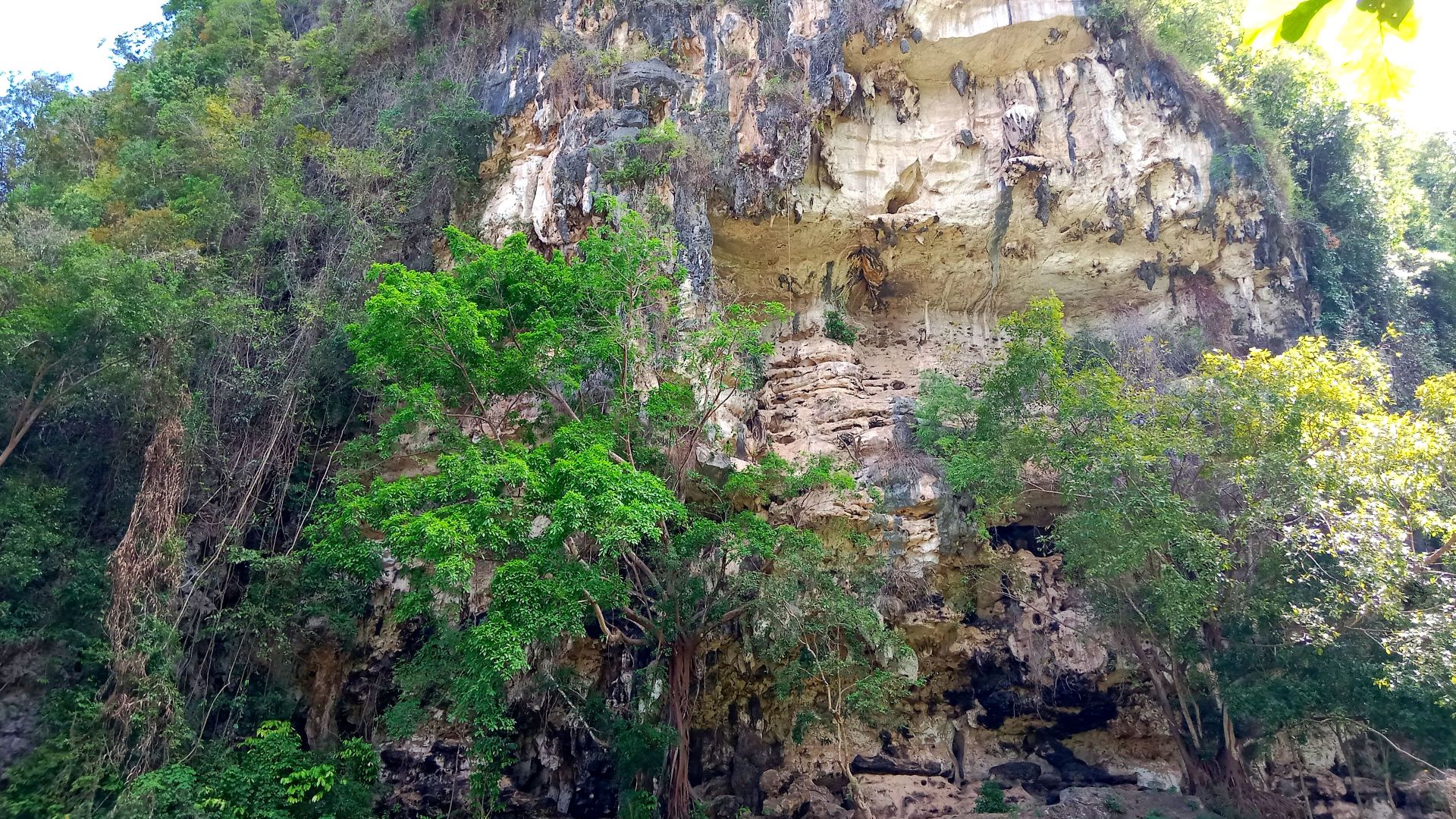 Anhar Karim, Wikimedia Commons
Anhar Karim, Wikimedia Commons
Earliest Creative Impulse
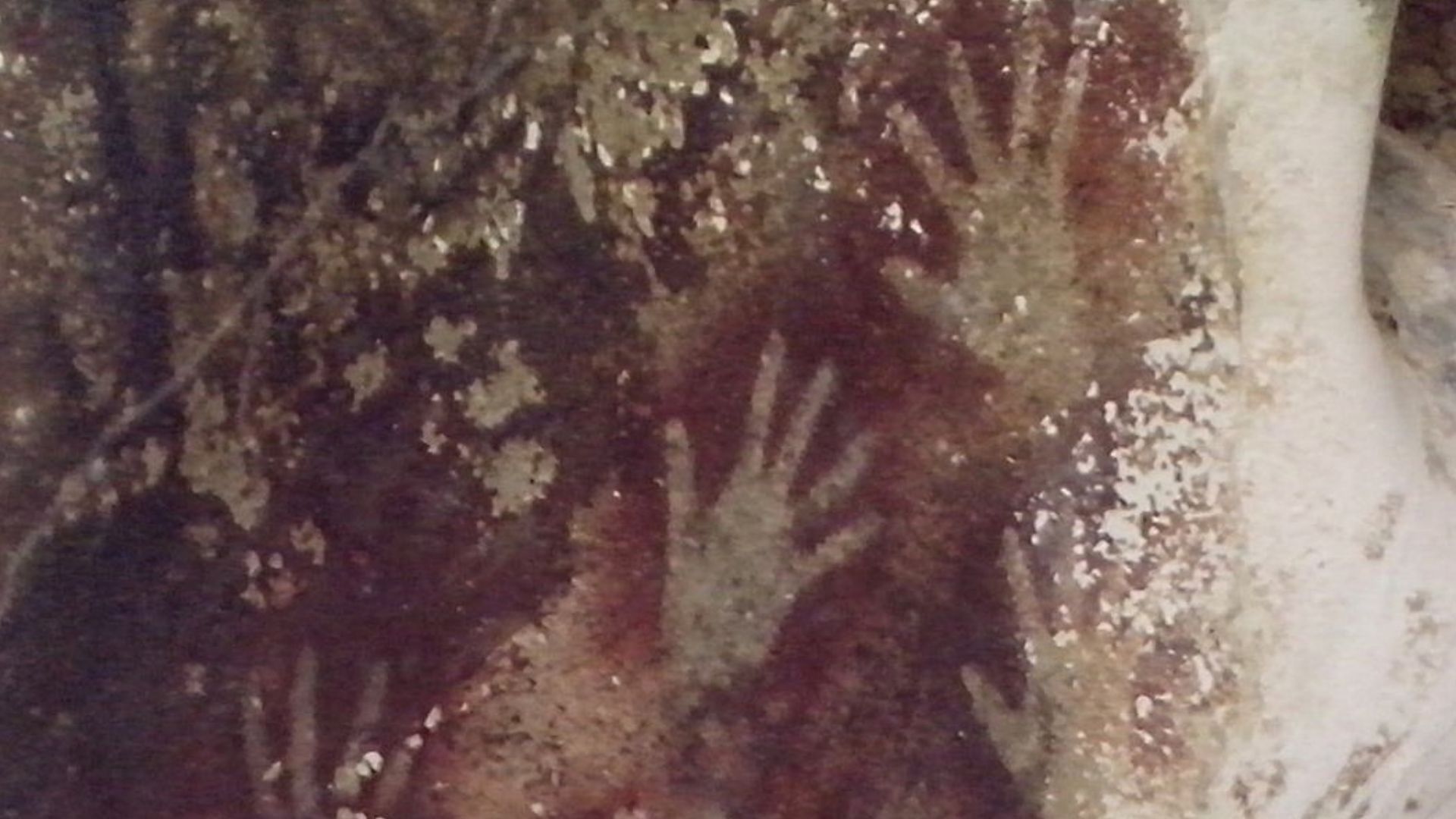
Creativity has long been treated as a defining human trait. This discovery challenges that comfort. The urge to create images and leave meaning behind appears to have emerged during the early migrations of modern humans, unlike the ways we thought we knew.
 Claude Valette, Wikimedia Commons
Claude Valette, Wikimedia Commons
Art Before Humans
For decades, people thought that symbolic art belonged exclusively to Homo sapiens and cave paintings were the proof of this cognitive leap. Now, images from early Homo sapiens migrations raise a startling idea: artistic expression emerged independently in multiple regions.
The Discovery In Sulawesi
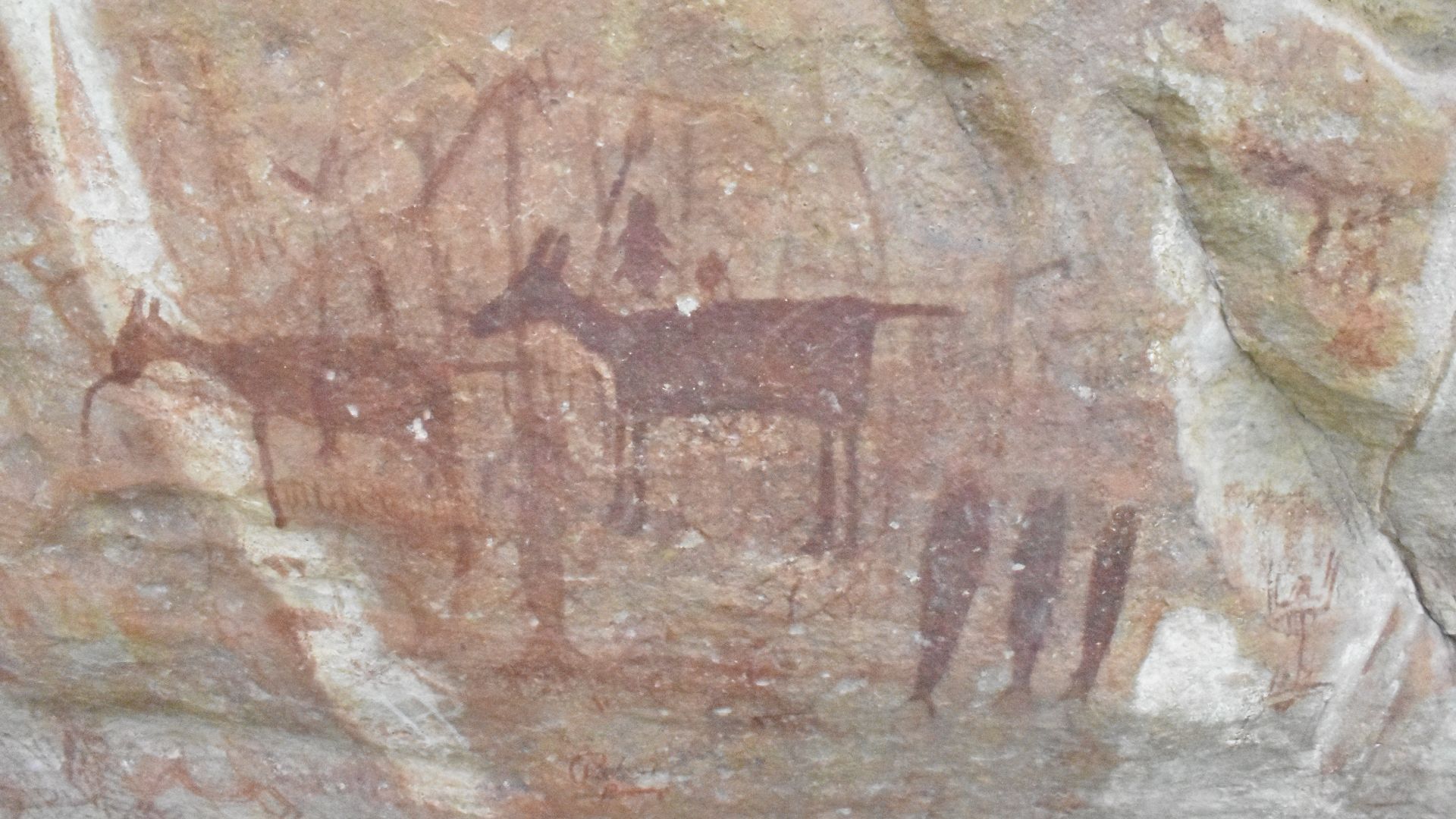
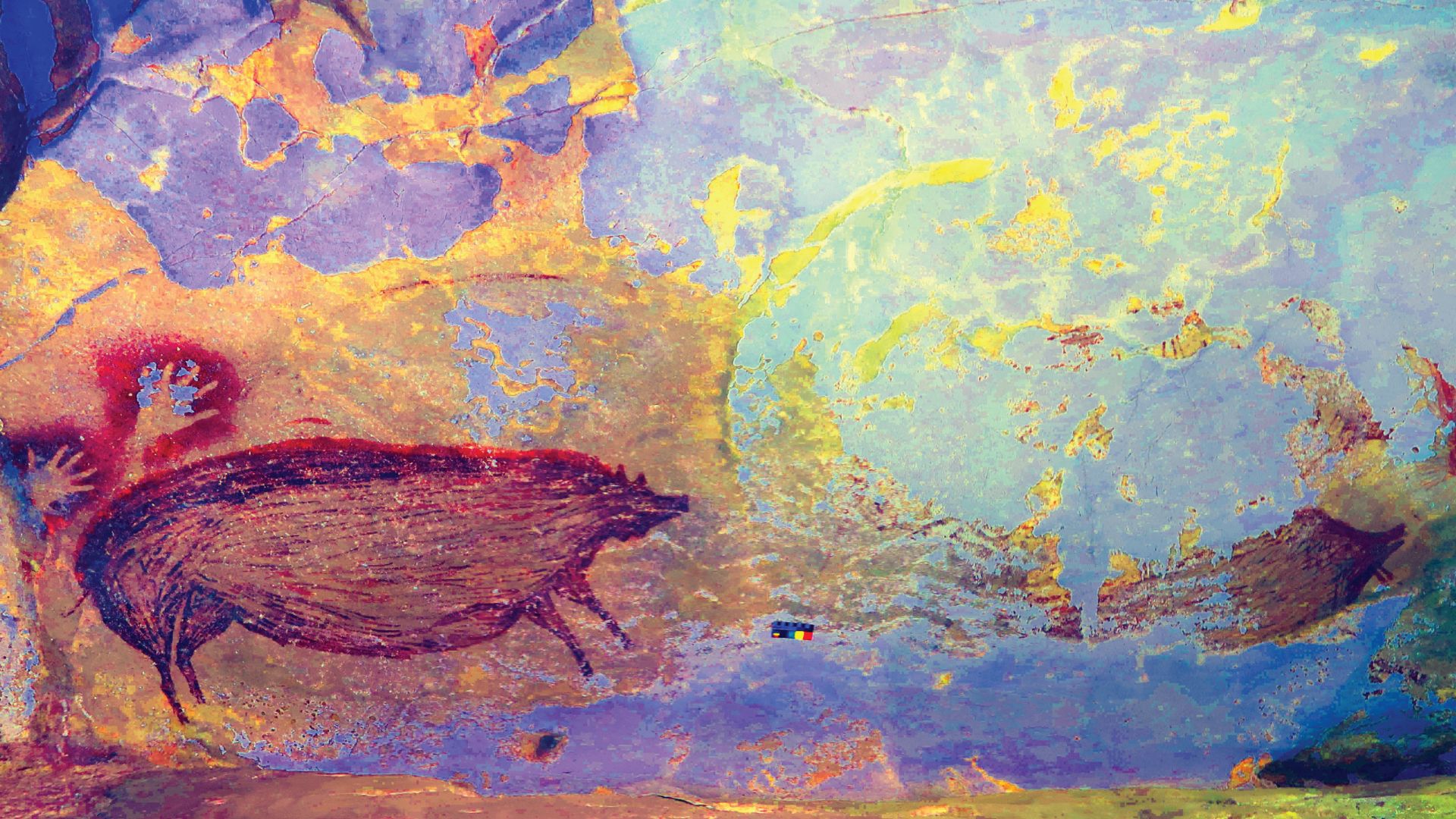
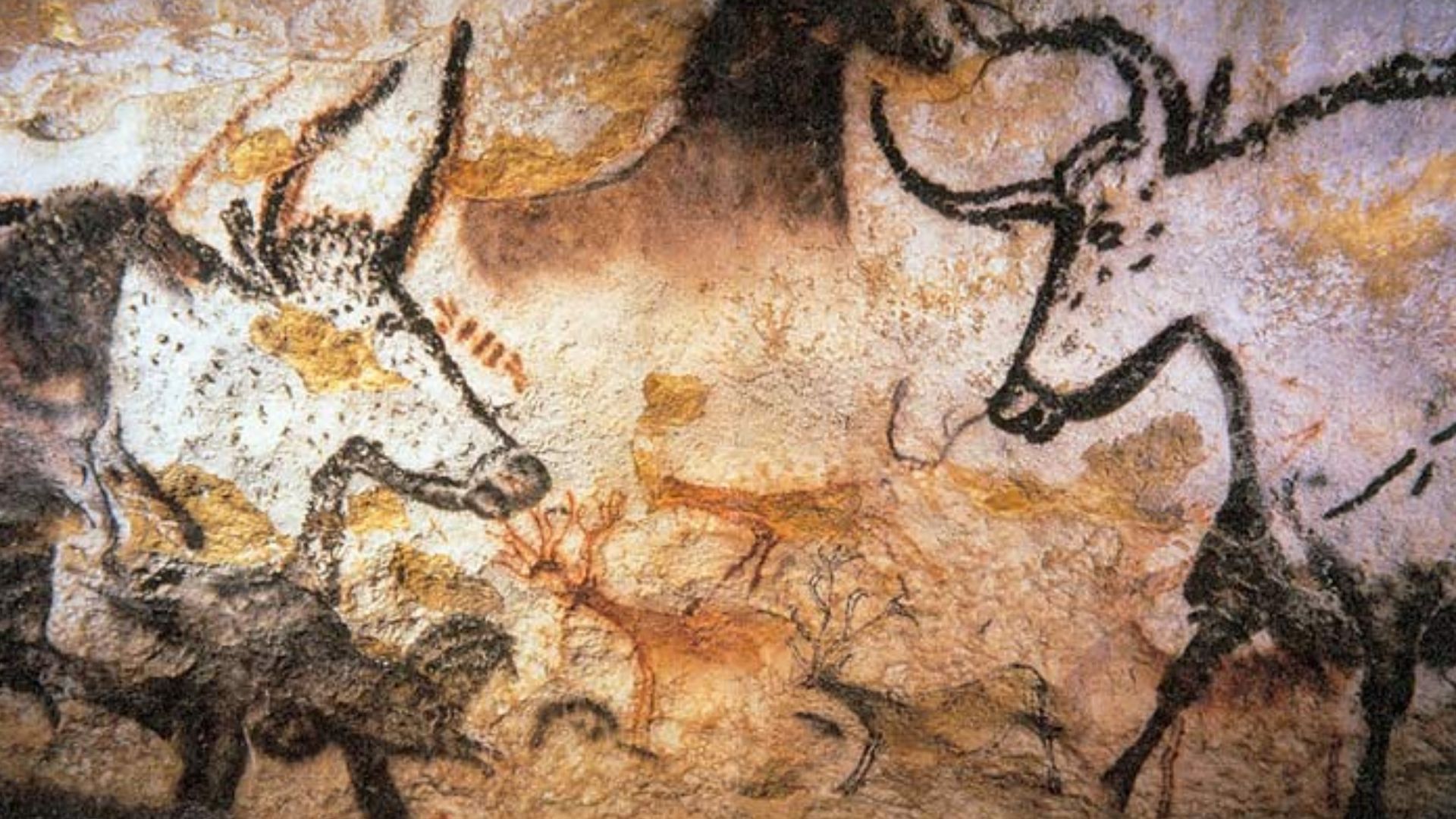
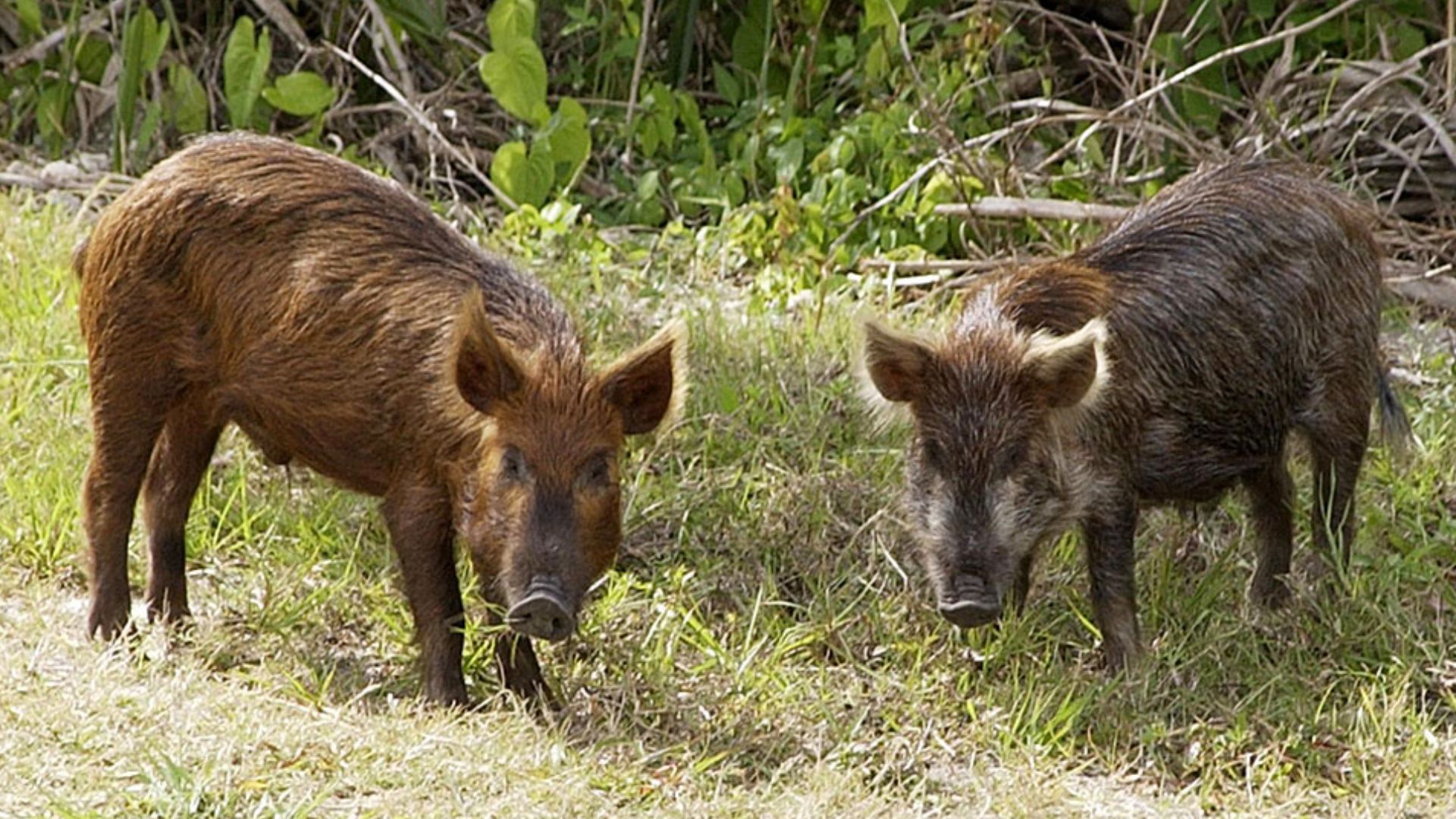
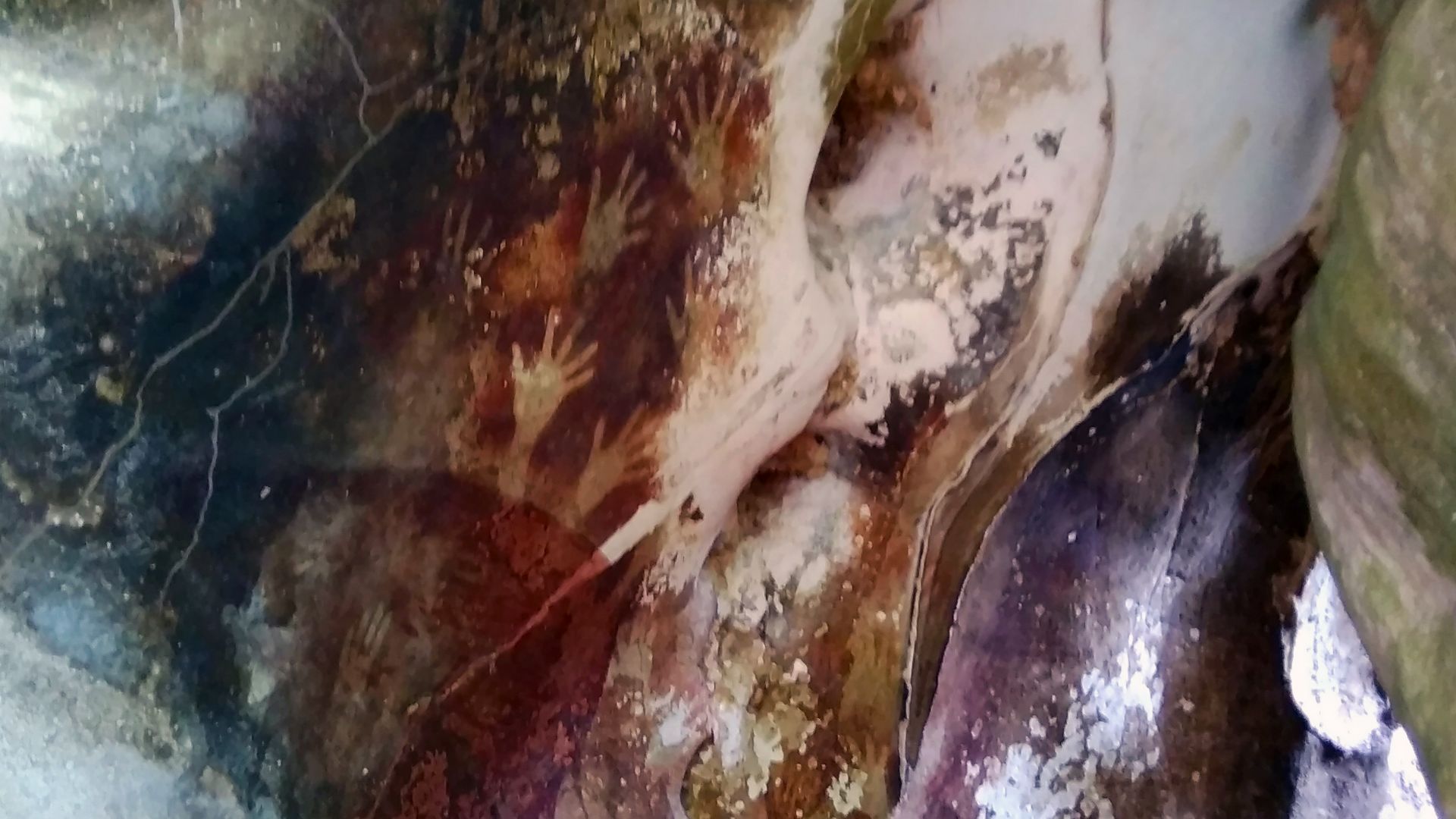
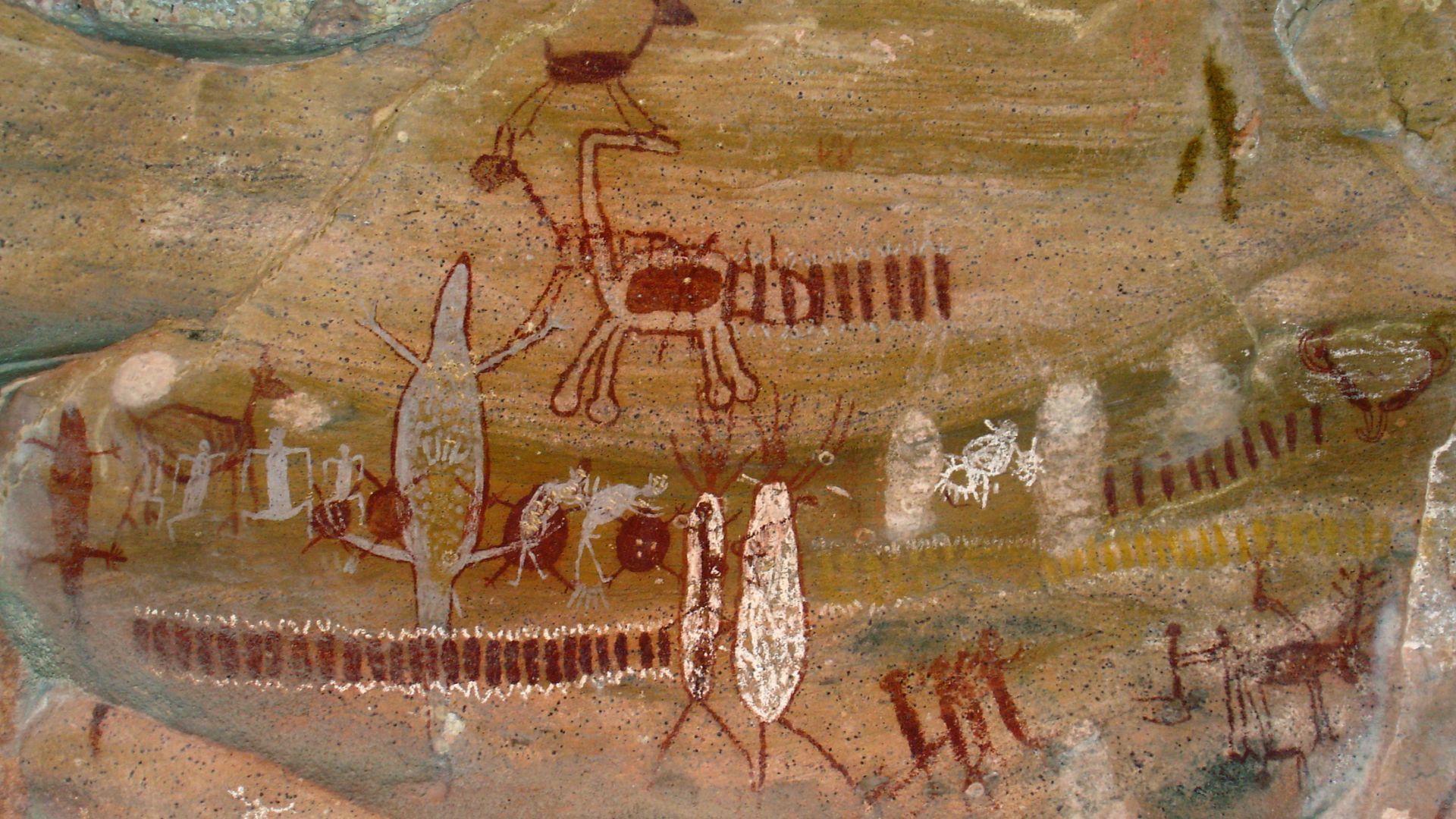
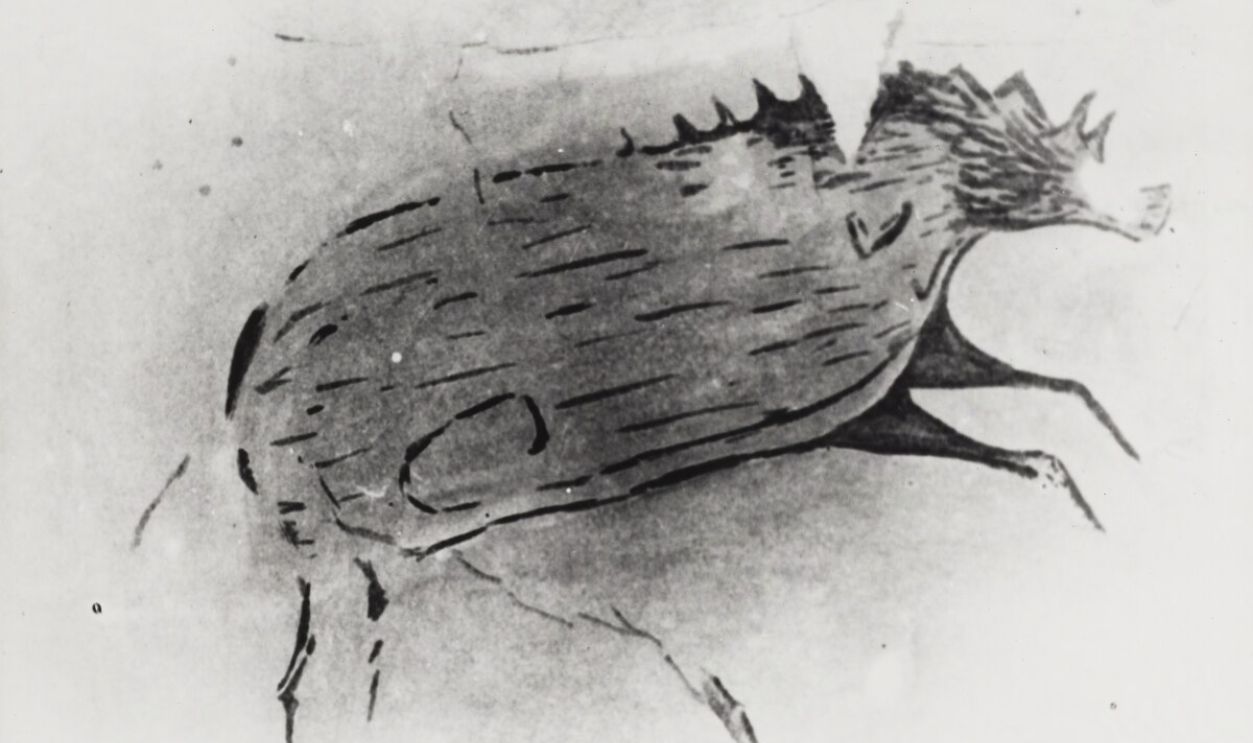
Inside a limestone cave on Indonesia’s Sulawesi island, archaeologists uncovered a life-sized painting of a warty pig. Rendered in red ochre, the figure shows deliberate proportions and distinctive features, which place Southeast Asia at the center of the earliest figurative imagery.
Dating The Paintings
To determine age, scientists analyzed mineral crusts formed naturally over the artwork. Using uranium-series dating, they measured radioactive decay inside calcium carbonate layers to establish when the crust developed and confirmed that the painting beneath belongs to a far earlier period globally.
What The Paintings Depict
The Sulawesi cave art depicts animals central to local life, especially wild pigs, shown with facial markings and body detail. Nearby sites include scenes of animals interacting. This is an observation of behavior and an interest in recording meaningful moments for communities.
 NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wikimedia Commons
NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wikimedia Commons
Symbolism In Pre-Human Art
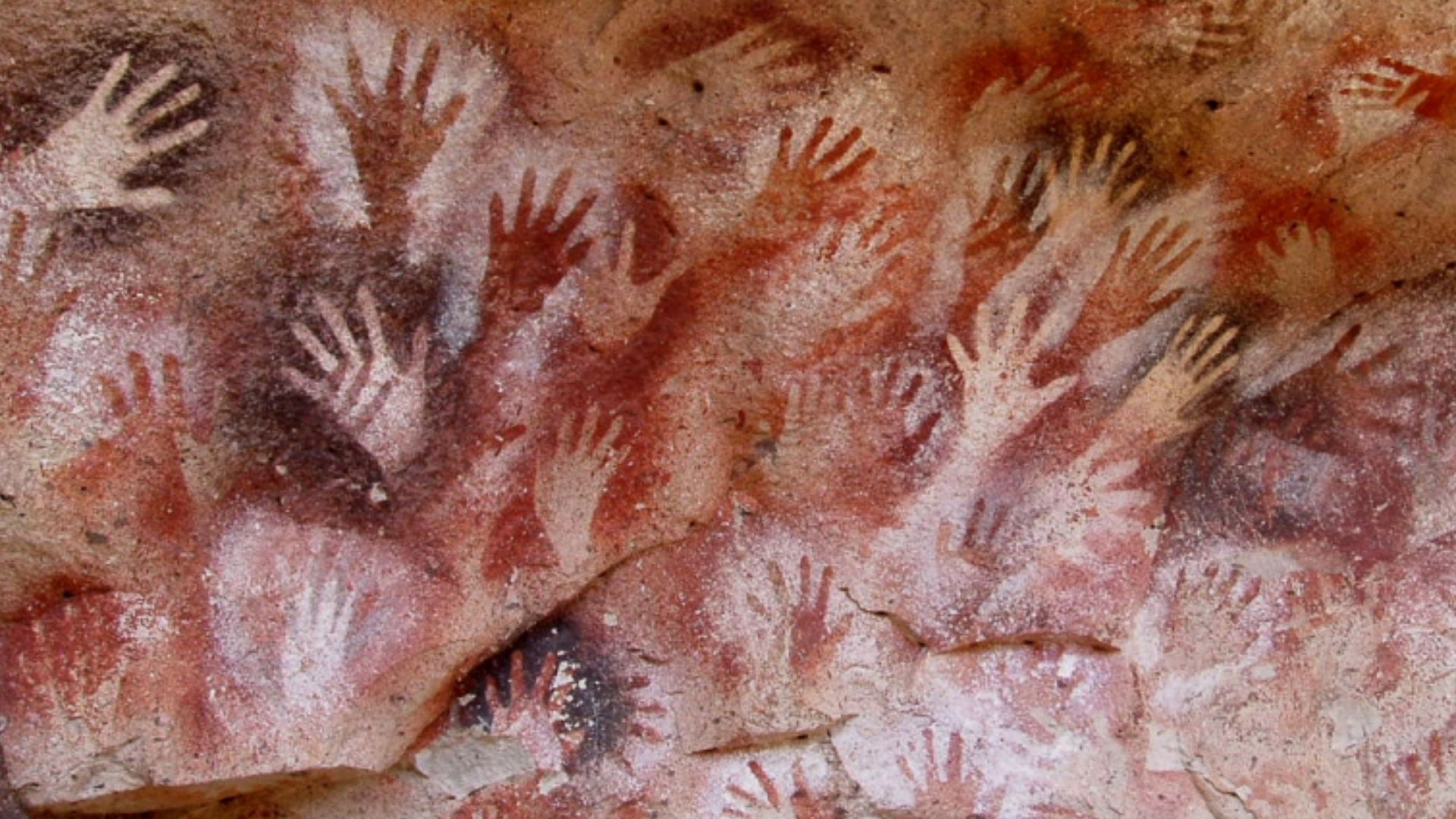
These images suggest symbolic thinking rooted in shared understanding. Repeated animal forms and consistent themes point toward storytelling traditions, in which pictures carried meanings understood collectively and were passed across generations through visual memory within early Homo sapiens social groups.
 Sabjan Badio, Wikimedia Commons
Sabjan Badio, Wikimedia Commons
Challenging Human-Centric Narratives
This finding invites a shift away from a strictly human-centered story of creativity. If complex images appear in regions outside Europe during early modern human migrations, artistic expression becomes a broader evolutionary trait within Homo sapiens rather than a single-regional achievement.
 Sabjan Badio, Wikimedia Commons
Sabjan Badio, Wikimedia Commons
Tools And Materials Used
The artists relied on naturally available materials such as red ochre, which provided a durable pigment. It is believed that people used natural resources like plant fibers or animal hair to apply different-hued pigments. This is how they created contrast.
 BHARATHESHA ALASANDEMAJALU, Wikimedia Commons
BHARATHESHA ALASANDEMAJALU, Wikimedia Commons
Advanced Techniques In Early Art
The thing about ancient artists is that they positioned figures to follow the natural ridges and curves of cave walls. These contours enhance the body shape and movement, and they create an intentional relationship between image and surface. Here, the rock itself contributed to the visual rhythm of the scenes.
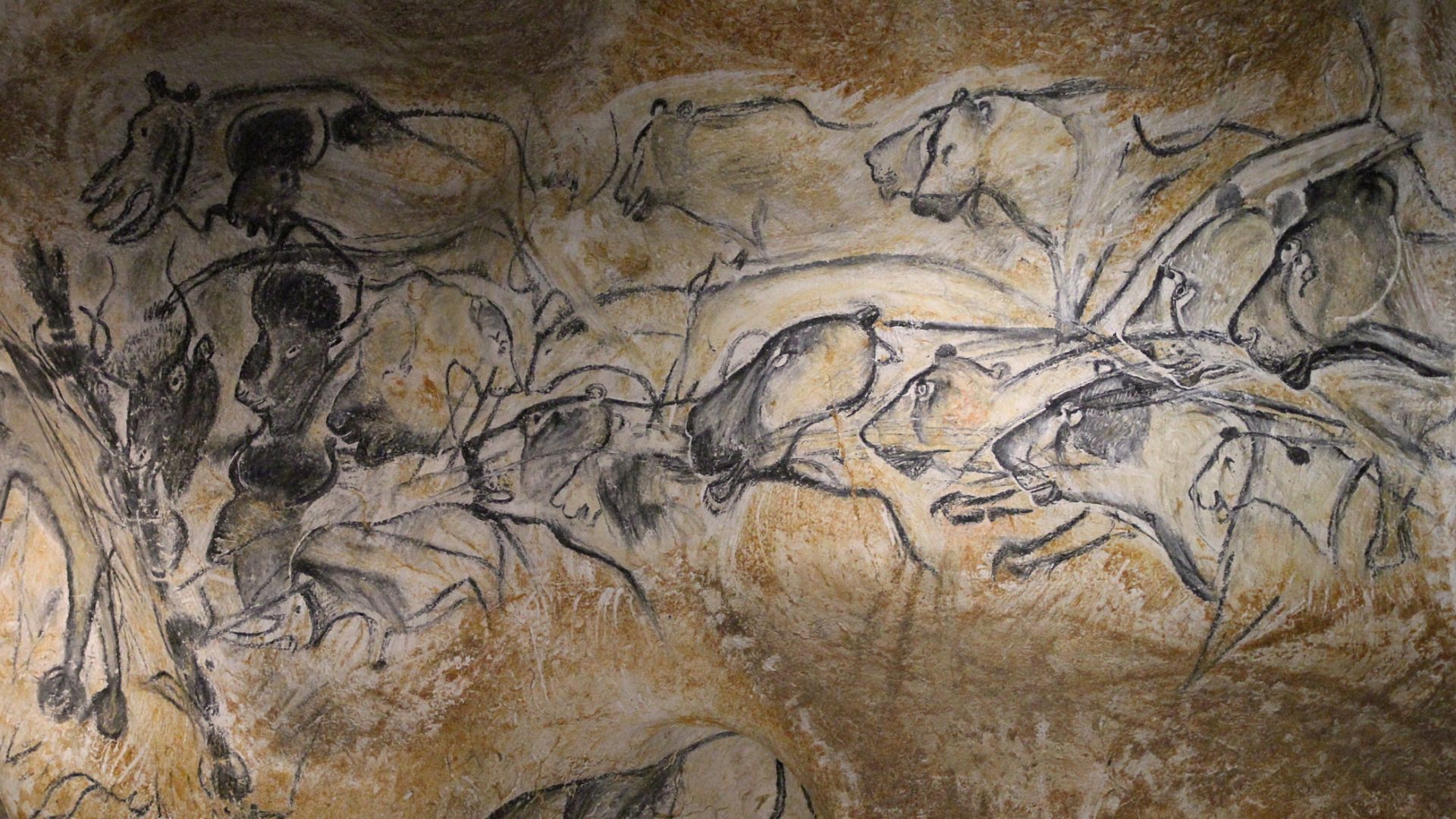
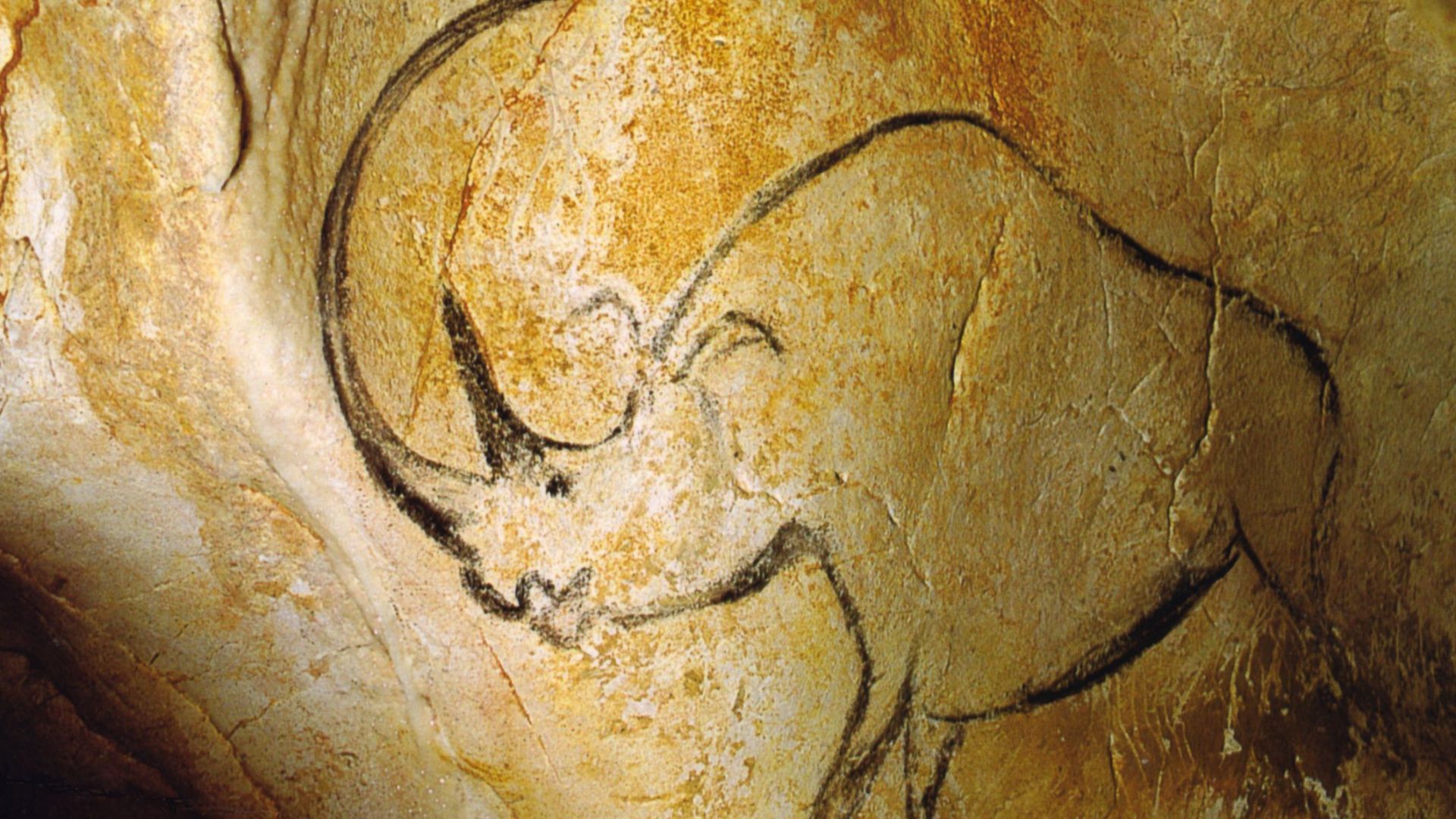
Comparison With European Cave Art
Caves like Chauvet and Lascaux in France feature paintings of animals from around 30,000 years ago. Sulawesi’s imagery predates them by millennia. It is a living proof that figurative art emerged earlier in Southeast Asia and developed independently alongside later European artistic traditions.
 Inocybe at French Wikipedia, Wikimedia Commons
Inocybe at French Wikipedia, Wikimedia Commons
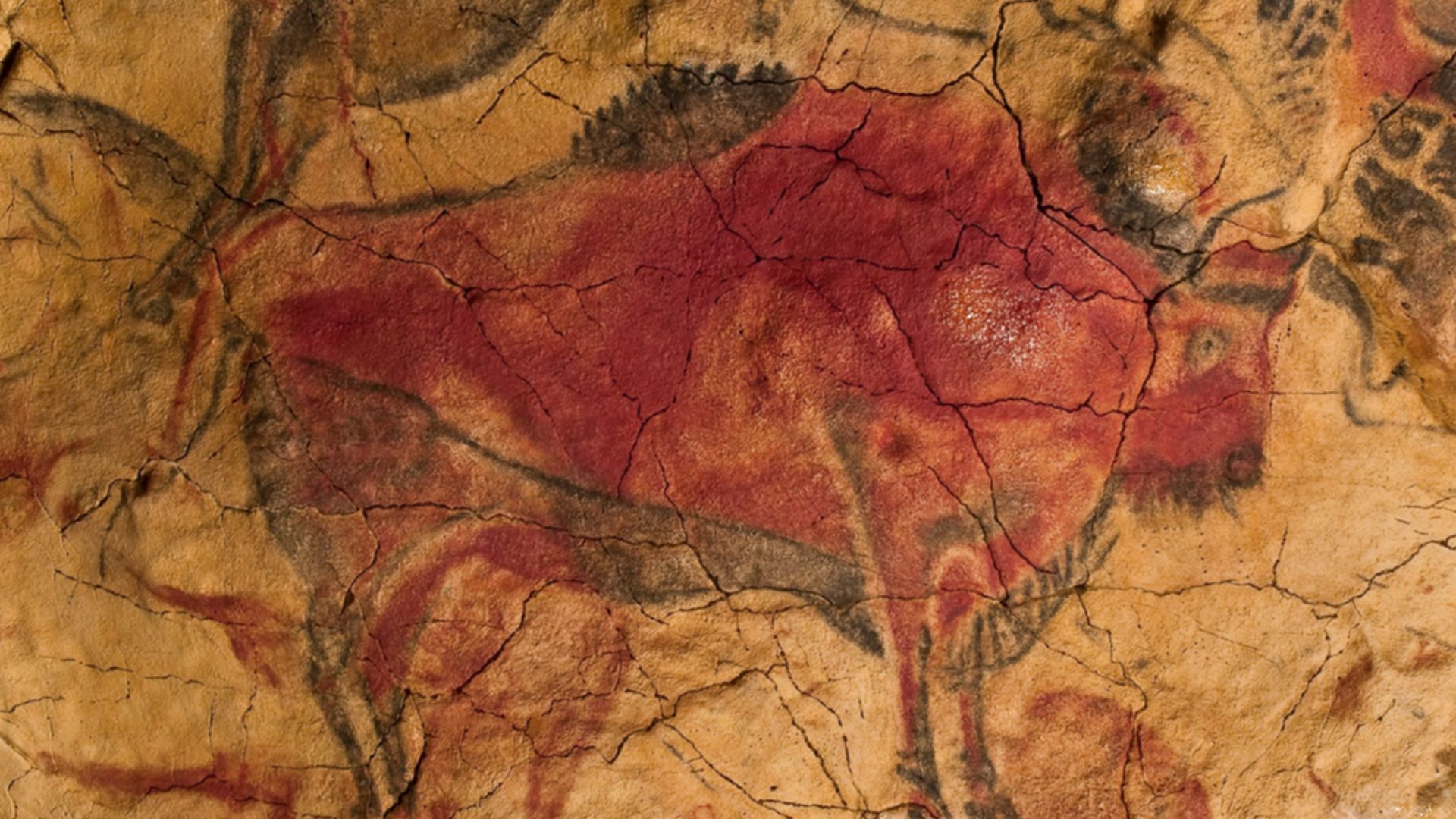
Global Spread Of Early Art
Engraved ochre in southern Africa, painted caves in Indonesia, and symbolic markings in Spain reveal early image-making across continents. It's evident that artistic expression arose in multiple regions to reflect a shared cognitive capacity rather than a single cultural origin.
 Museo de Altamira y D. Rodriguez, Wikimedia Commons
Museo de Altamira y D. Rodriguez, Wikimedia Commons
The Role Of Ritual And Belief
One detail stands out in these discoveries. Many paintings appear in secluded cave chambers reached through narrow passages. People likely chose these protected spaces to create images that recorded daily life and traditions, preserving their heritage so future generations could remember and pass it on.
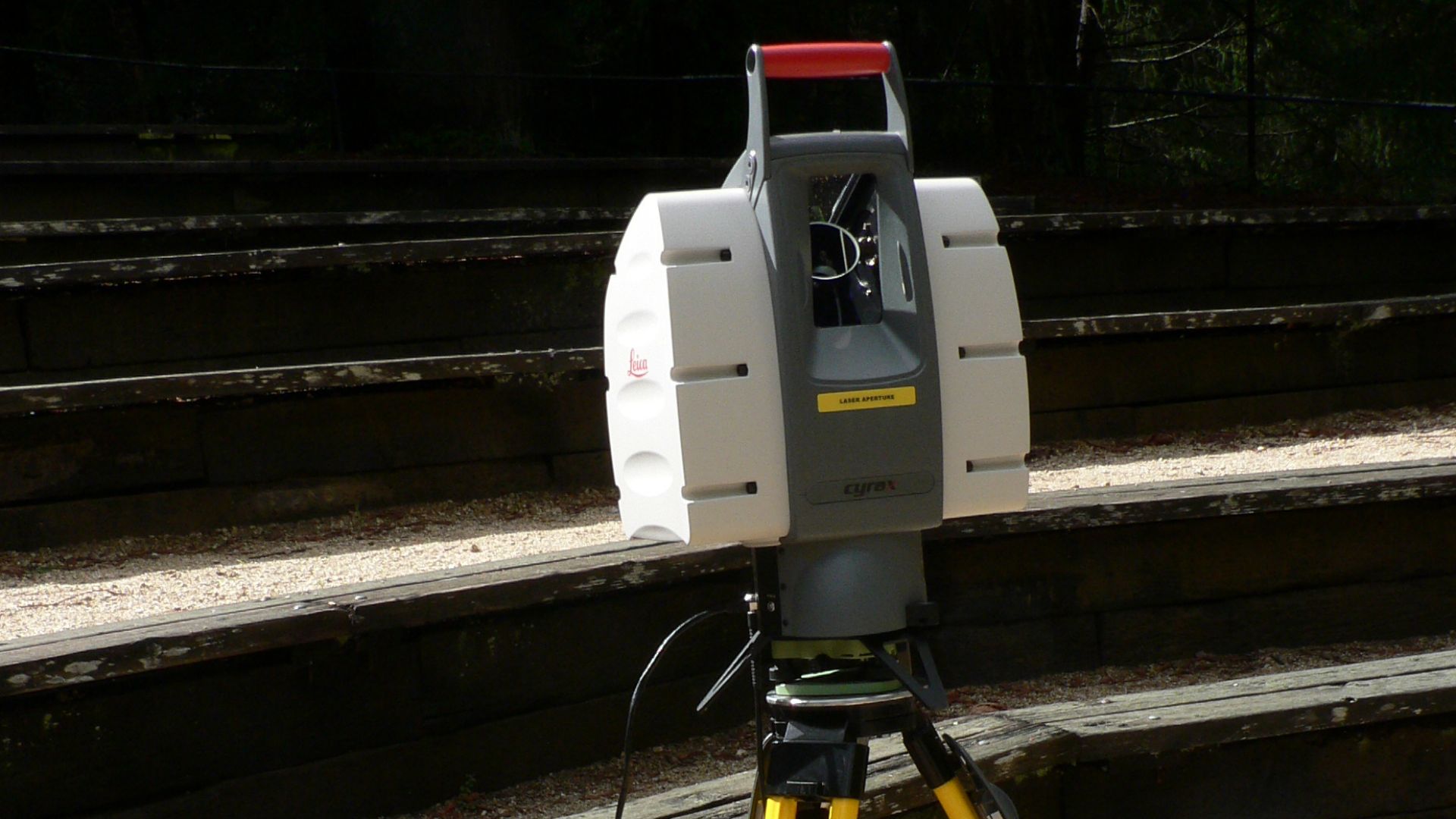
Archaeological Methods Of Discovery
Researchers document cave art using 3D scanning and high-resolution photography. The chemical sampling helped with exact preservation methods. They capture surface textures and mineral growth patterns, and this allows scientists to study the site while maintaining the integrity of fragile cave environments.
 David Monniaux, Wikimedia Commons
David Monniaux, Wikimedia Commons
Why This Discovery Is Revolutionary
The Sulawesi painting provides a securely dated reference that helps align early art discoveries worldwide. It allows archaeologists to compare imagery and development across regions using a shared chronological marker rooted in physical geological evidence.
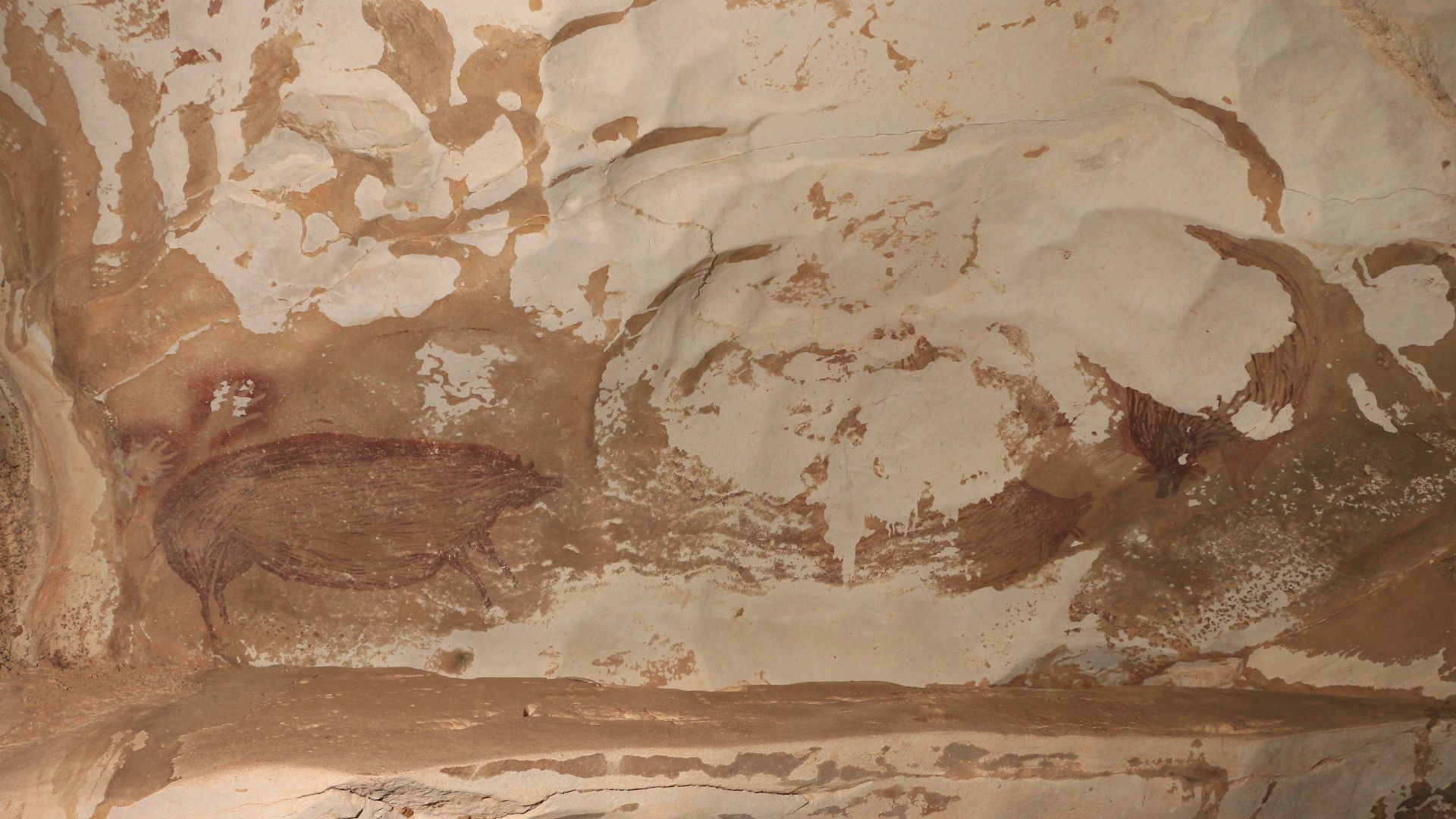 Basran Burhan, Wikimedia Commons
Basran Burhan, Wikimedia Commons
The Debate Among Scientists
Scholars examine migration timelines and genetic evidence to determine which hominin group created the paintings. The conversation centers on how creativity developed alongside movement across islands. It also talks about multiple pathways for symbolic expression in early populations.
 Rudolf Cronau, Wikimedia Commons
Rudolf Cronau, Wikimedia Commons
Implications For Human Evolution
Art has always been a form of knowledge sharing within various generations. The presence of figurative imagery suggests that early groups communicated complex ideas visually, supporting social learning and cohesion as populations expanded into diverse environments that required collaboration and adaptability for long-term success.
 James St. John, Wikimedia Commons
James St. John, Wikimedia Commons
Art As A Survival Tool
Images of animals likely reinforced hunting strategies and group traditions. Even seasonal awareness. Visual symbols helped preserve knowledge beyond individual lifespans to strengthen coordination. It also gave communities a shared understanding to work through challenging environments together.
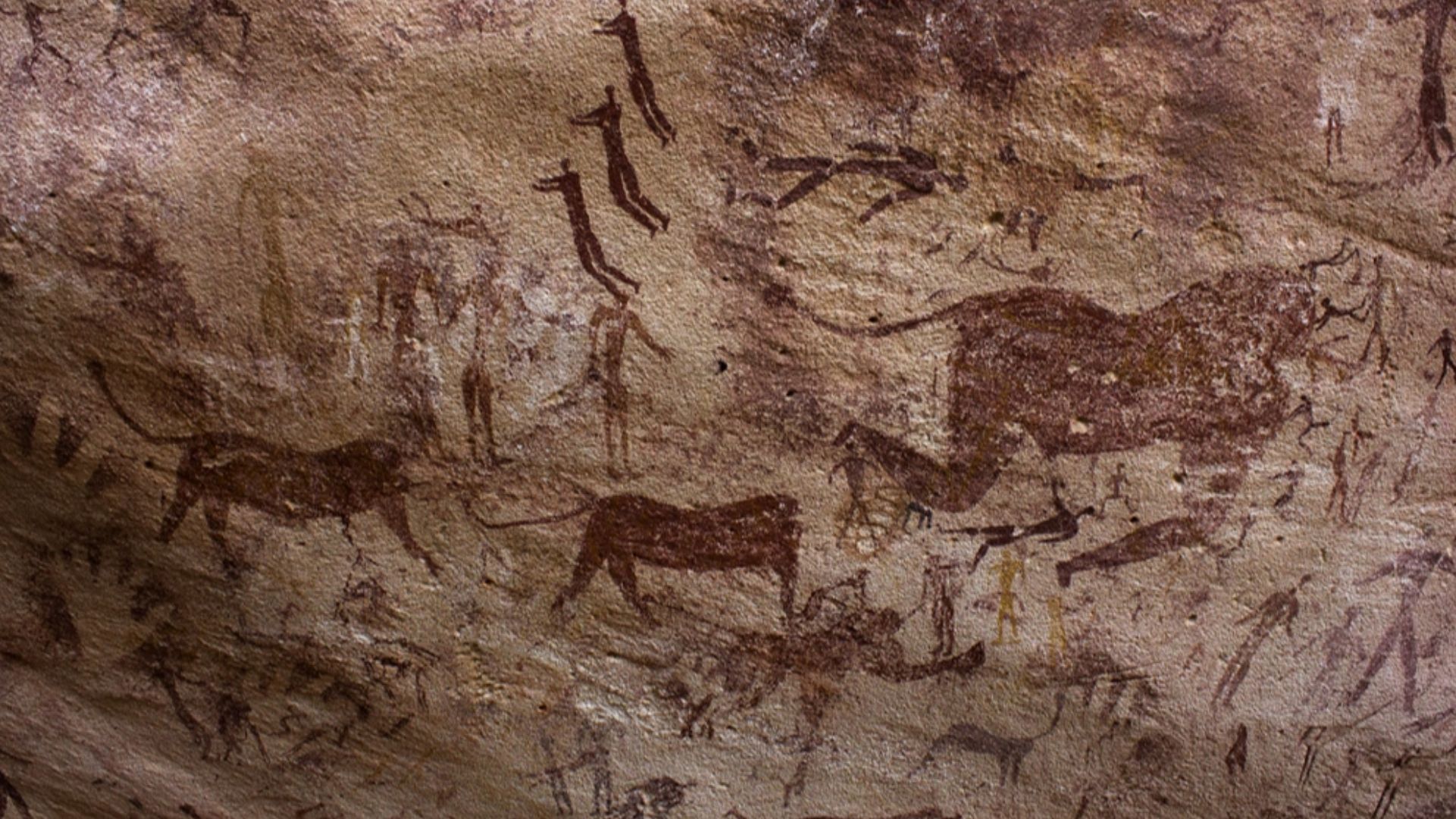 Clemens Schmillen, Wikimedia Commons
Clemens Schmillen, Wikimedia Commons
The Mystery Of The Artists
The creators remain unidentified, yet the paintings endure as evidence of meaningful expression. Even without physical remains, the artwork reveals observation and shared values. Here, creativity itself stands as the clearest trace of its makers.
 Unknown authorUnknown author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown authorUnknown author, Wikimedia Commons
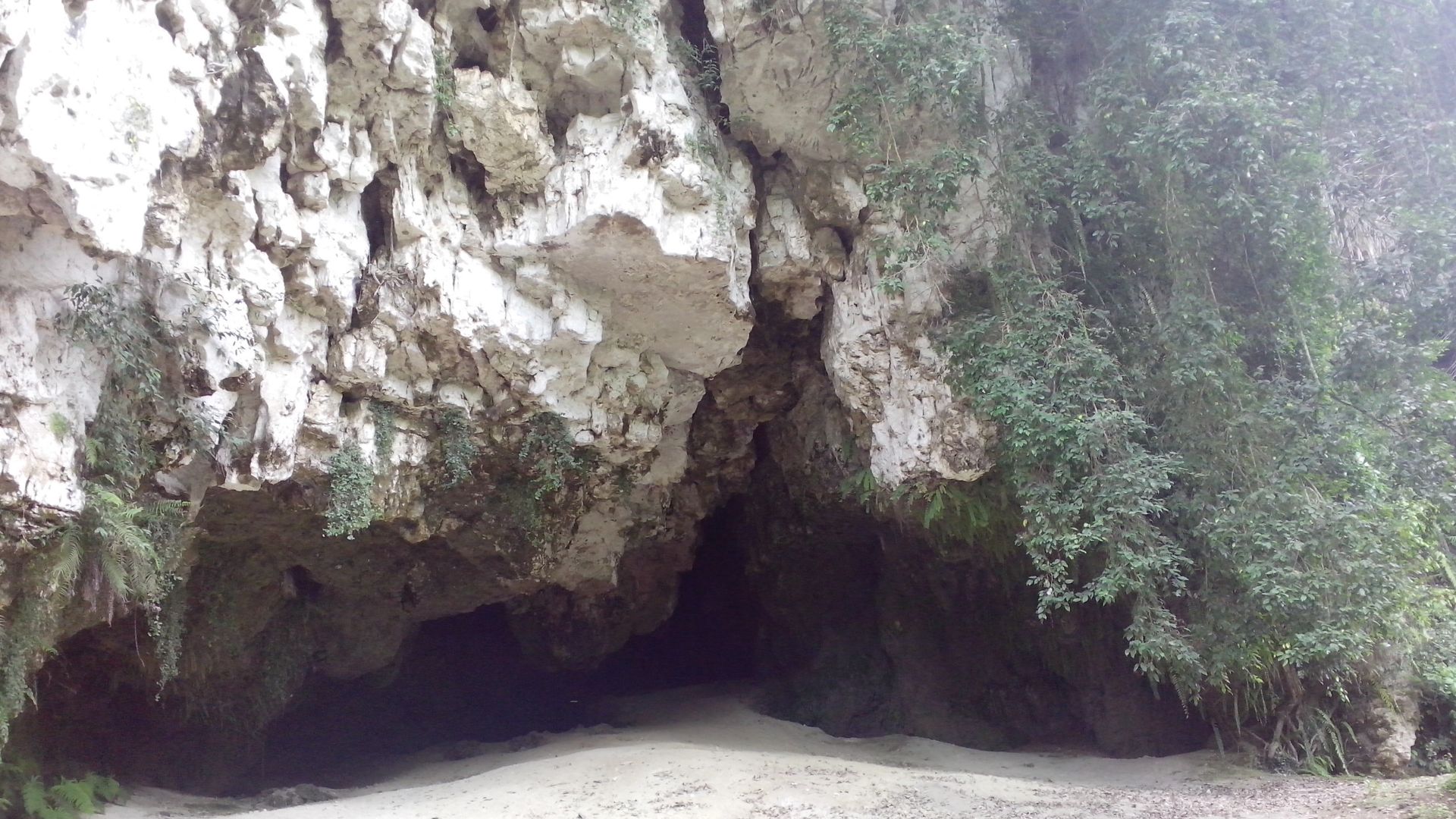
Preservation Challenges
Sulawesi’s cave paintings exist within delicate limestone environments. Humidity, temperature shifts, and salt crystal growth gradually affect rock surfaces. Scientists monitor these changes closely to prioritize documentation and controlled access to ensure the artwork remains stable for future study.
 Cahyo Ramadhani, Wikimedia Commons
Cahyo Ramadhani, Wikimedia Commons
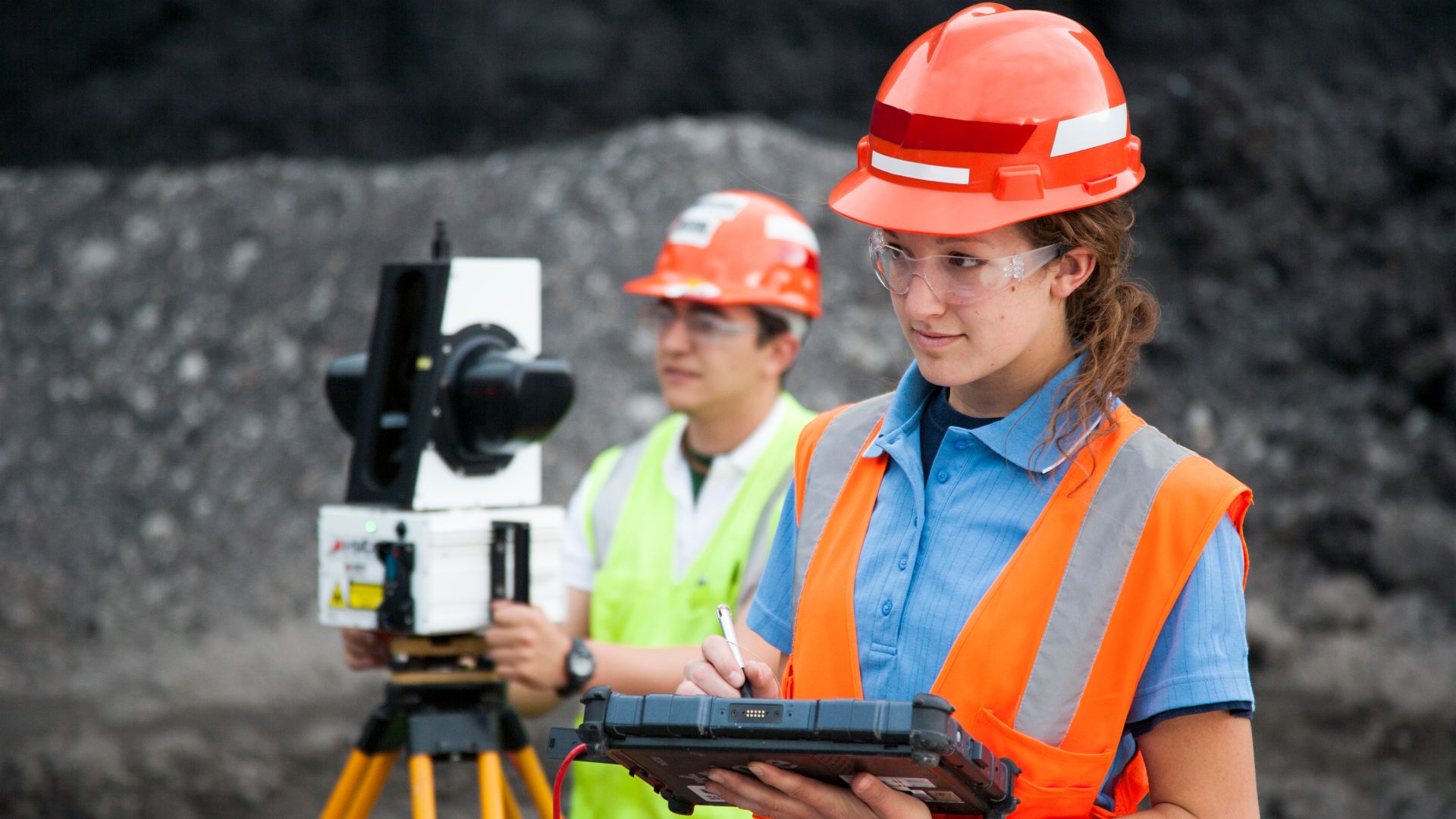
Technology Meets Archaeology
Modern tools now extend research beyond the cave. Laser scanning and digital reconstruction reveal faded details, track surface changes, and create precise models. Even AI-assisted imaging came to the rescue as scholars worldwide study ancient art without physical exposure or environmental disturbance.
 Peabody Energy, Inc., Wikimedia Commons
Peabody Energy, Inc., Wikimedia Commons
Public Fascination With Ancient Art
These discoveries resonate deeply because the images feel familiar and intentional. Seeing animals painted tens of thousands of years ago sparks emotional curiosity, connecting modern viewers to ancient minds and reminding us that creativity has long shaped how beings interpret their world.
Philosophical Questions Raised
If image-making emerged so early in modern human history, creativity may reflect a fundamental evolutionary trait. The paintings invite reflection on consciousness, meaning, and expression. This suggests that art emerges wherever minds seek to understand surroundings and share experiences beyond immediate survival.
Global Heritage
Sulawesi’s cave art stands as humanity’s shared legacy to reframe creativity as a collective inheritance. Rather than a regional phenomenon, these ancient paintings reveal art’s universal roots, which connect diverse cultures through timeless expression and redefine our understanding of early imagination.
 AnonymousUnknown author, CC BY 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
AnonymousUnknown author, CC BY 4.0, Wikimedia Commons














