The Past Is Still Present
We often think of the past as gone forever; after all, the past is the past. However, we are influenced by what comes before us every single day. Even civilizations gone for millennia still have subtle effects on modern life. Here are just a few ancient civilizations that still influence us today.

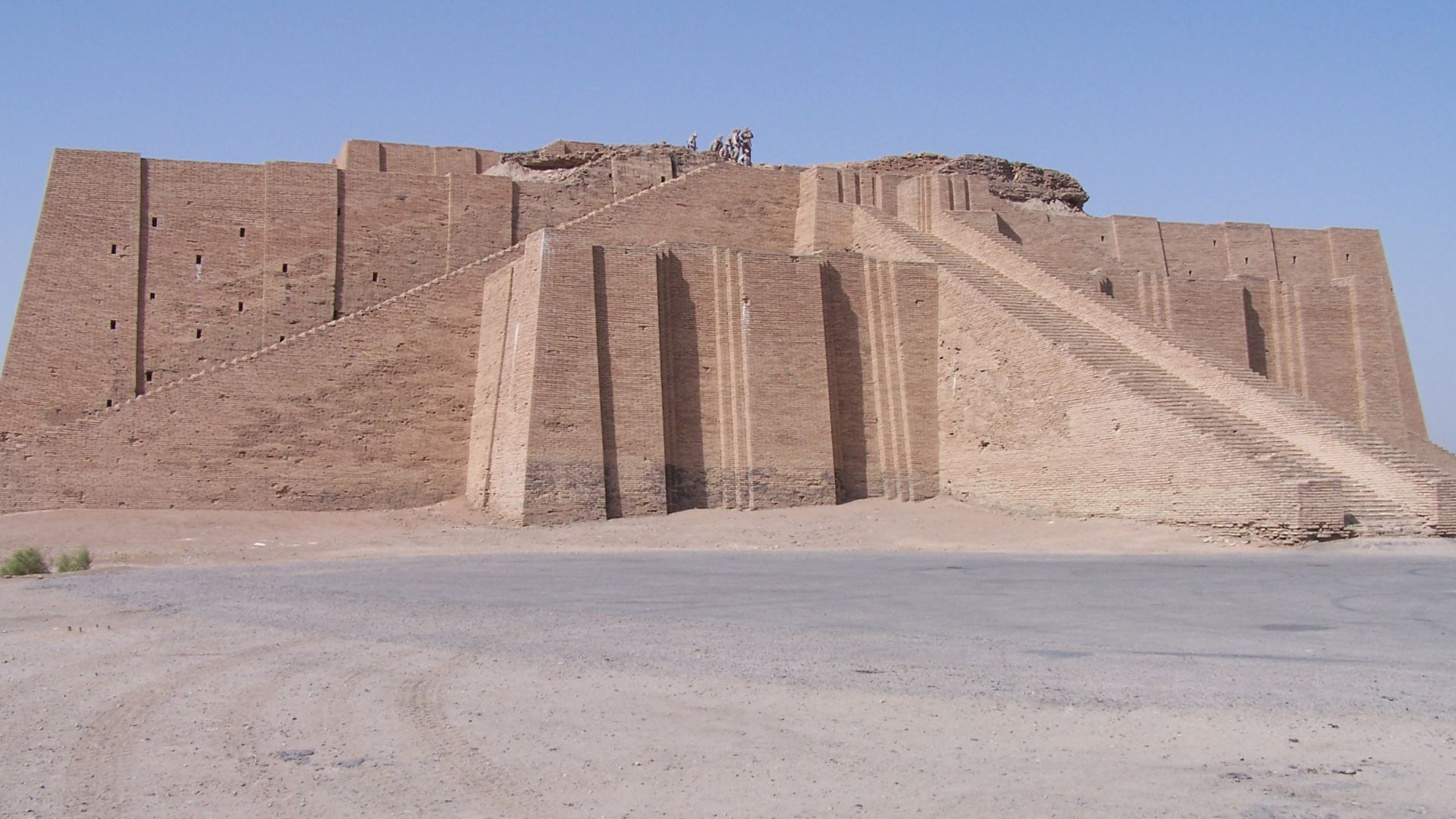
The Sumerians
If not for the Sumerian civilization, none of our current societies would exist today. The Sumerians and their homeland of ancient Mesopotamia are referred to as the “Cradle of Civilization”, with good reason.
The Sumerians
Civilizations began settling around the floodplains of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers (in modern-day West Asia) around 10,000 BC. This area was superb for planting and growing, leading to it being referred to as the “Fertile Cresent”. It also allowed these civilizations to prosper, growing large cities around 4500 BC.
The Sumerians
Three of the major Sumerian cities that have been identified by modern historians are Eridu, Uruk, and Ur. They could not have existed if the land was not so fertile. The ability to cultivate an excess of crops allowed the populations in this area to boom, creating cities without starving its members.
 en:User:Hardnfast, Wikimedia Commons
en:User:Hardnfast, Wikimedia Commons
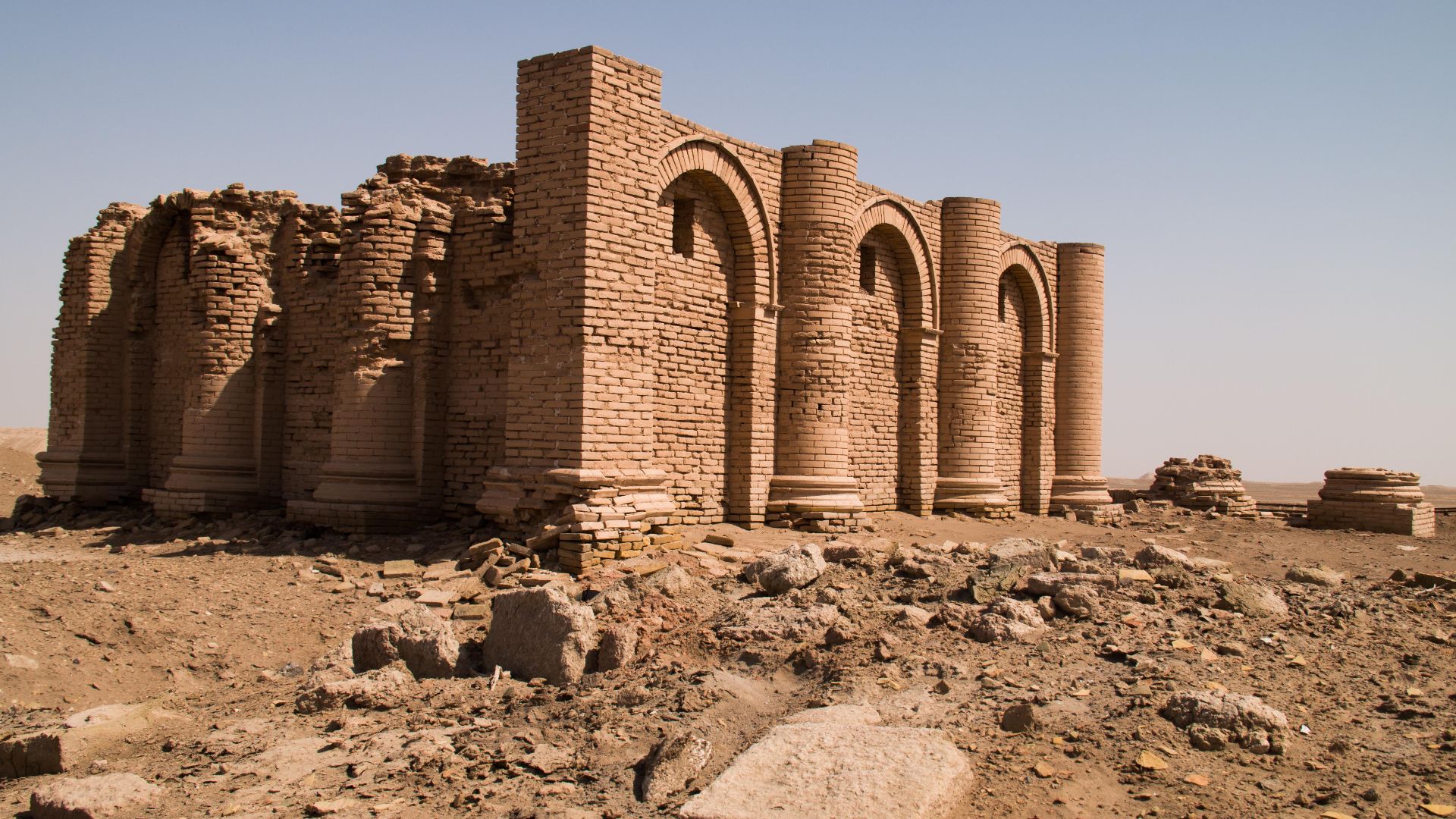
The Sumerians
It was in these cities, with their tall temple and palace complexes, that civilization as we know it today began to flourish. Well-fed and supported by their communities, the Sumerians had the freedom to begin to develop the nuances of society that we see today.
 Osama alqasab, Wikimedia Commons
Osama alqasab, Wikimedia Commons
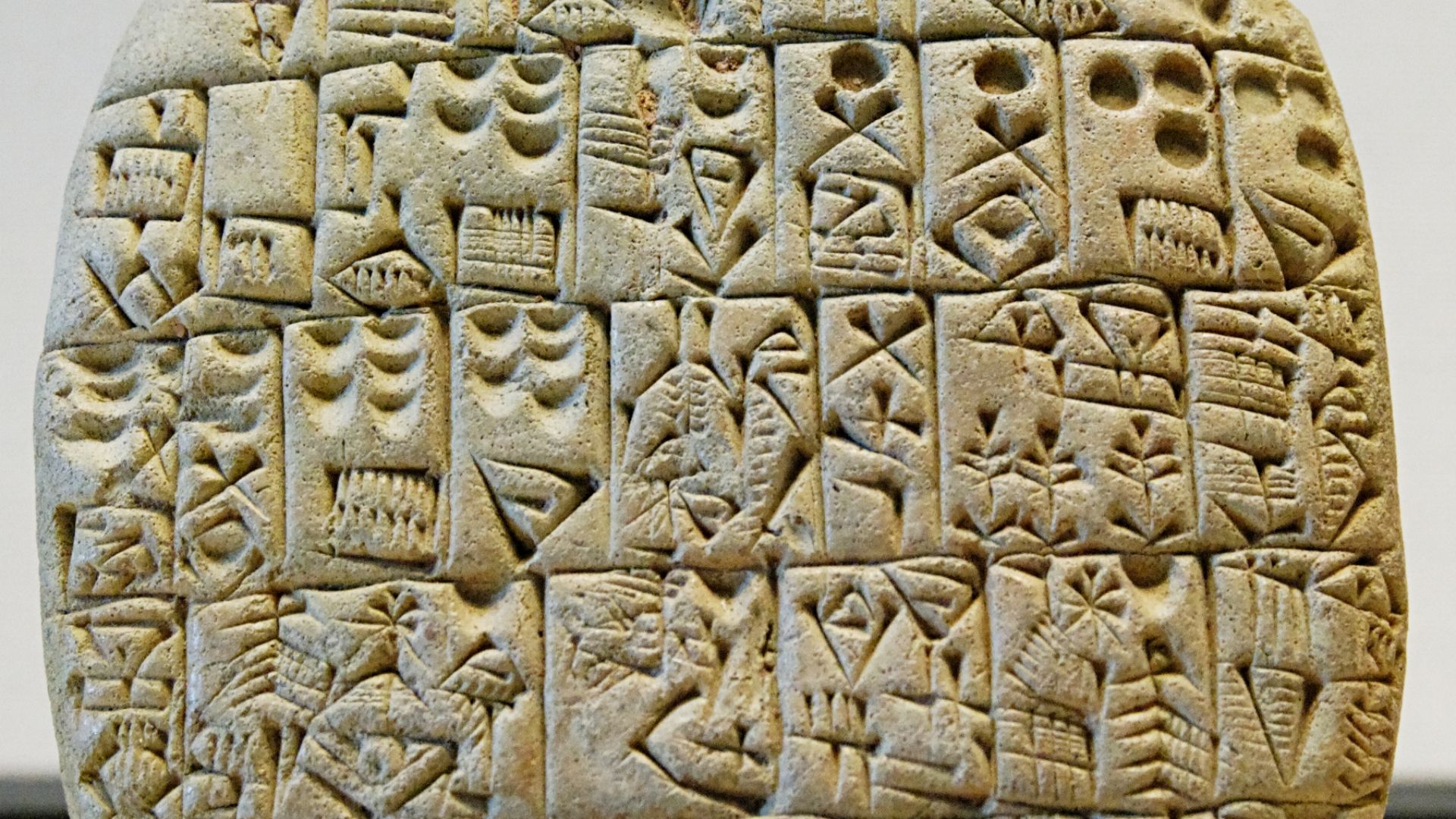
The Sumerians
The ancient Sumerians are credited with creating the first written word. Using clay tablets, they scratched out a writing system called “cuneiform”. This allowed them to track their grain, as well as share their culture—all happening as far back as 5,000 years ago.
 Unknown artistUnknown artist, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown artistUnknown artist, Wikimedia Commons
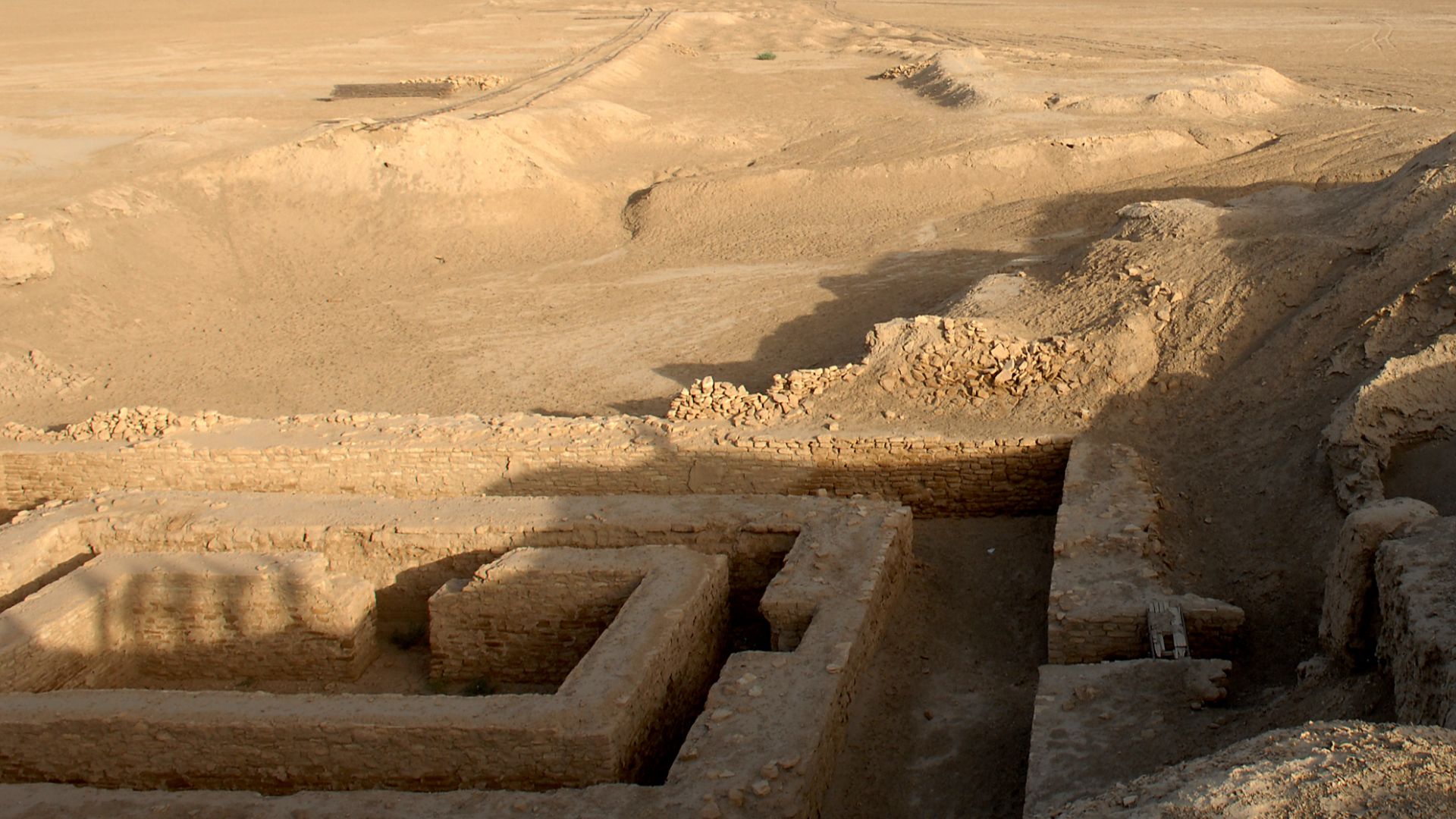
The Sumerians
Sumerians had some of the earliest examples of mathematics, astronomy, and astrology. They created schools, invented irrigation, and had early codified laws. Moreover, you owe time to the Sumerians. They created the concept of time as broken down into hours, minutes, and seconds, which we still use today.
 SAC Andy Holmes (RAF), Wikimedia Commons
SAC Andy Holmes (RAF), Wikimedia Commons
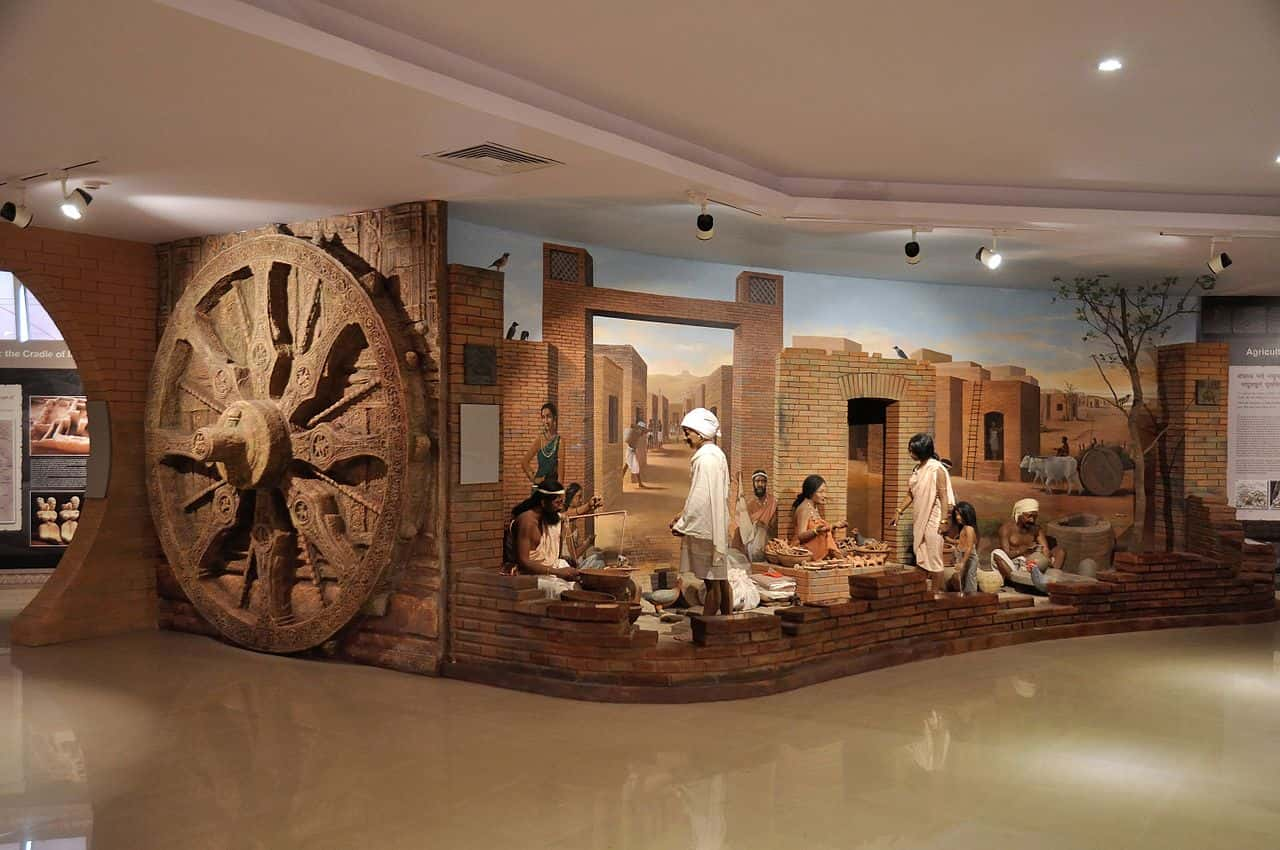
The Indus Valley
Not far from Mesopotamia’s fertile valley, another culture was beginning to blossom in the area known today as India and Pakistan. Only a few thousand years behind the Sumerians, cultures began to bloom along the Indus River Valley around 7000 BC.
The Indus Valley
The settlements of Harappa and Mohenjo-daro were a few centuries too late to be credited as the first cities. That honor still goes to the Sumerians. However, the civilizations of the Indus Valley improved upon the concept that the Sumerians started.
 Saqib Qayyum, Wikimedia Commons
Saqib Qayyum, Wikimedia Commons
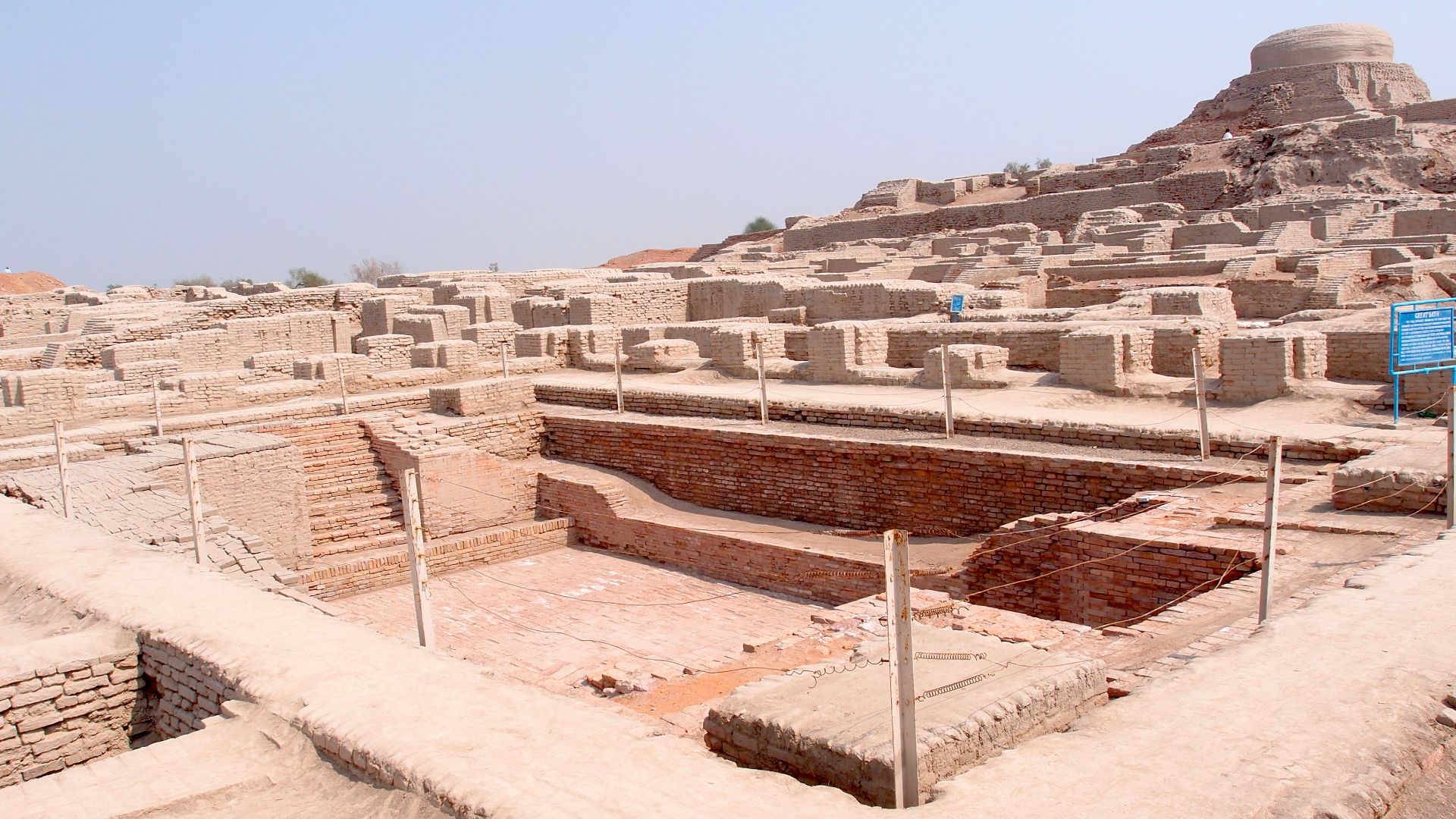
The Indus Valley
Today, in most modern cities, we walk down the streets without sparing a thought for where our water comes from, or where our “waste” goes. Sewers and water treatment are considered standard expectations. However, without the civilizations in the Indus Valley, we may never have had these.
 Saqib Qayyum, Wikimedia Commons
Saqib Qayyum, Wikimedia Commons
The Indus Valley
The cities of the Indus Valley were clean, spacious, and organized, despite housing anywhere from 40,000–50,000 individuals. They kept their cities clean through sewer and water supply systems that show a sophistication similar to modern times.
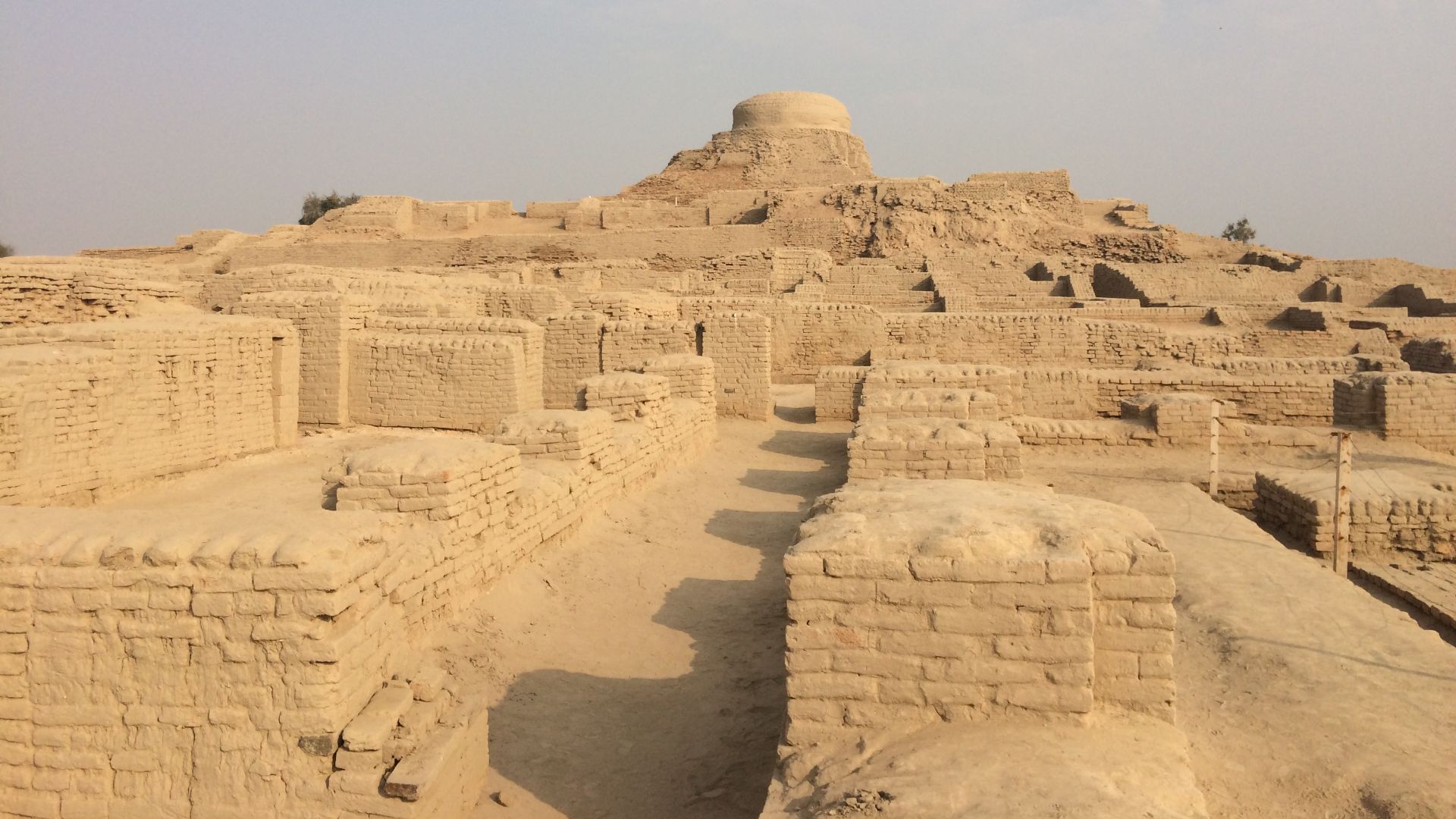 Wah1d Abbas, Wikimedia Commons
Wah1d Abbas, Wikimedia Commons
The Indus Valley
The evidence left behind in the Indus Valley shows a civilization that planned their cities carefully. Their streets formed neat grids, and their bricks all met a uniformity that suggest standardized weight and measuring systems.
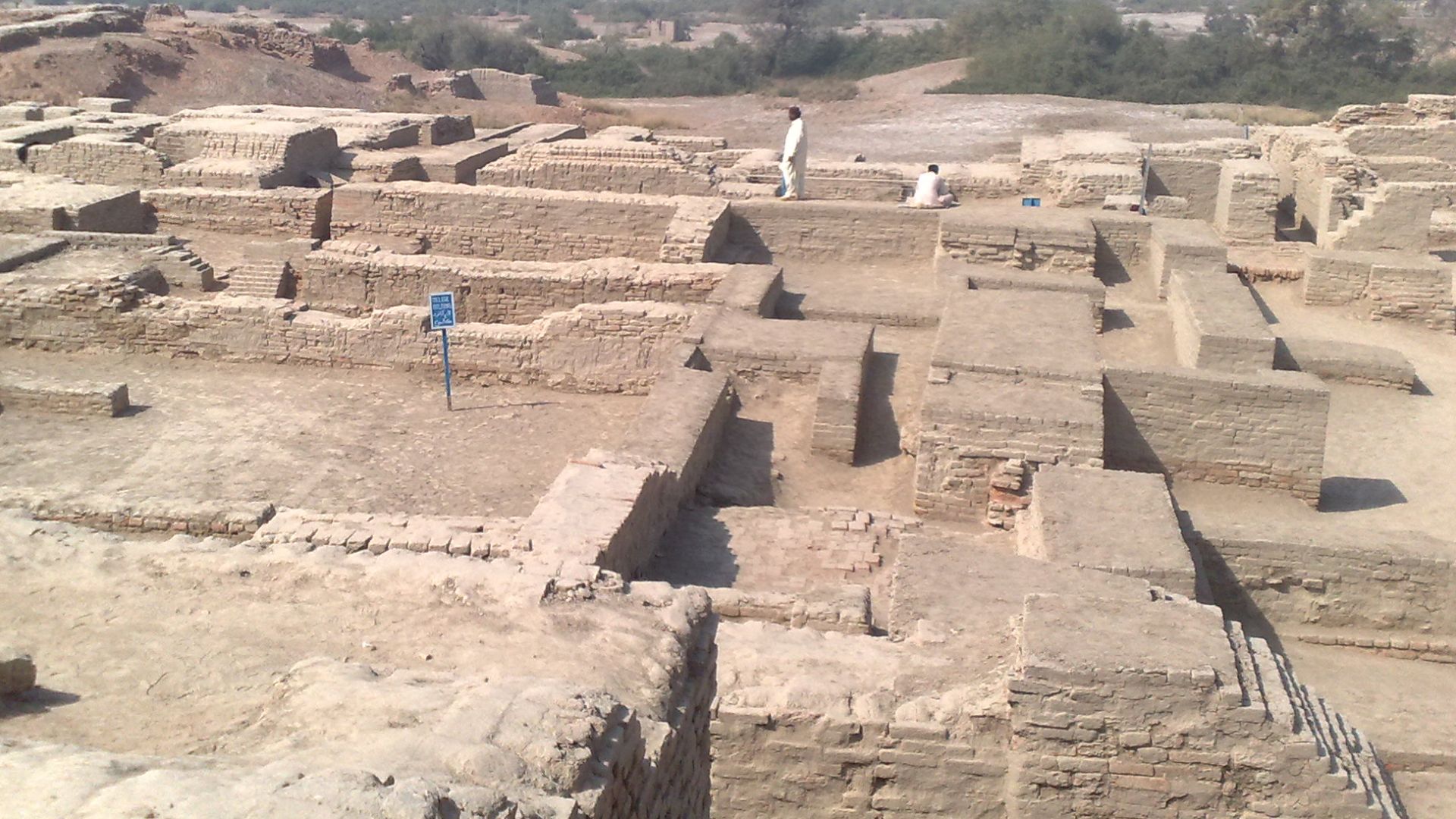 Nawabtanweer, Wikimedia Commons
Nawabtanweer, Wikimedia Commons
The Indus Valley
The Indus Valley still has its secrets. While they too had a writing system, no modern historian has yet been able to decipher it; some of their knowledge remains lost with them forever.
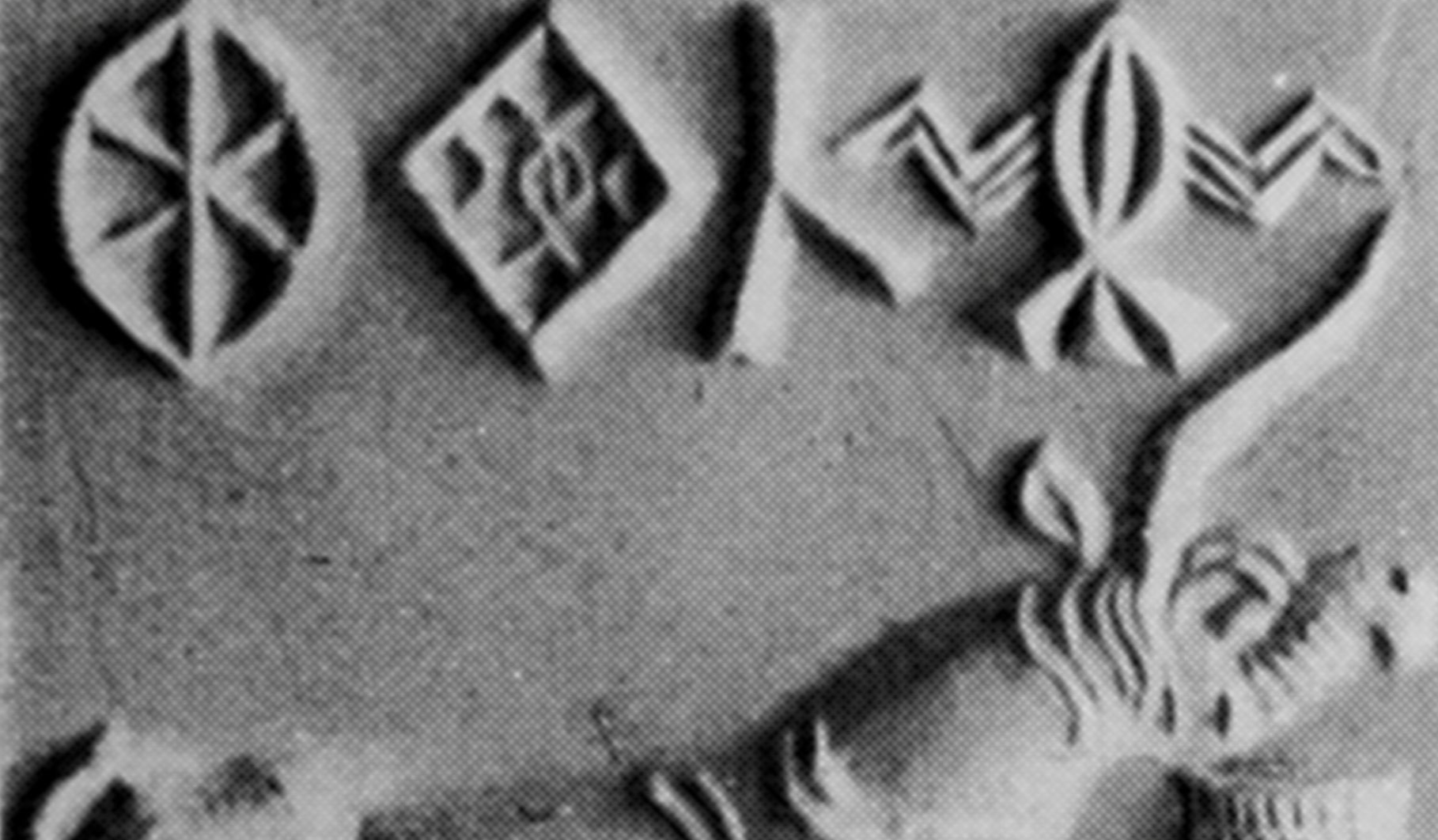 Ernest John Henry Mackay (5 July 1880 – 2 October 1943), Wikimedia Commons
Ernest John Henry Mackay (5 July 1880 – 2 October 1943), Wikimedia Commons
The Ancient Egyptians
Civilization appeared to be moving increasingly westward. The mesmerizing cities of ancient Egypt, which continue to capture the imagination even today, began somewhere around 6000 BC, with cities forming around 3,000 years later.
The Ancient Egyptians
The ancient Egyptians were able to build structures that still mark the earth today; many travel hundreds and thousands of miles to marvel at the pyramids or sphynx. A common conspiracy theory states that aliens helped the ancient Egyptians build these icons. However, the truth is far simpler—they were smart.
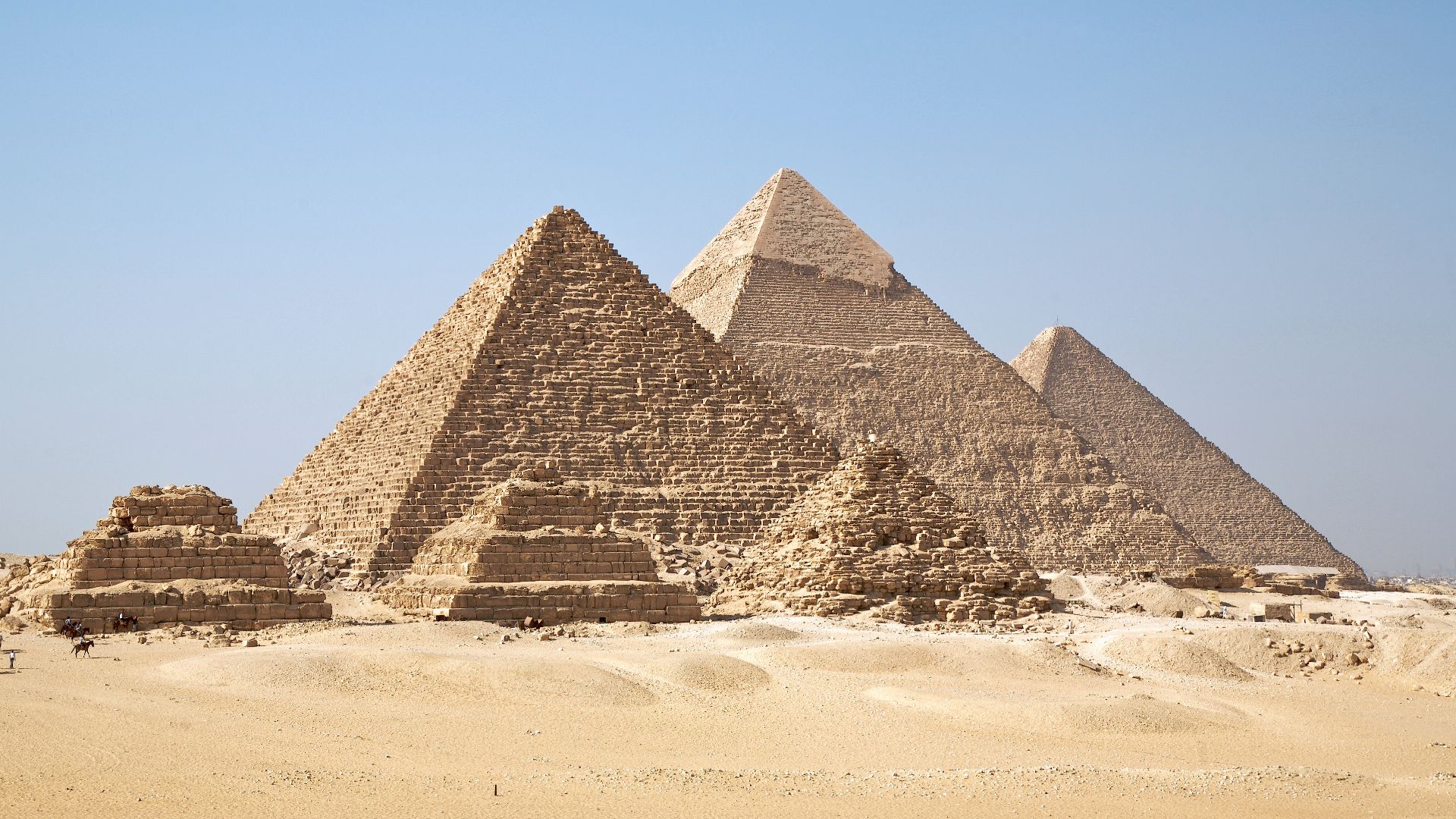 Ricardo Liberato, Wikimedia Commons
Ricardo Liberato, Wikimedia Commons
The Ancient Egyptians
The ancient Egyptian civilization bloomed and thrived for thousands of years; their longevity and power remain integral to the development of civilization as we know it today. Many things we do now would be far more difficult, if not impossible, without the Egyptians.
 Norman de Garis Davies, Wikimedia Commons
Norman de Garis Davies, Wikimedia Commons
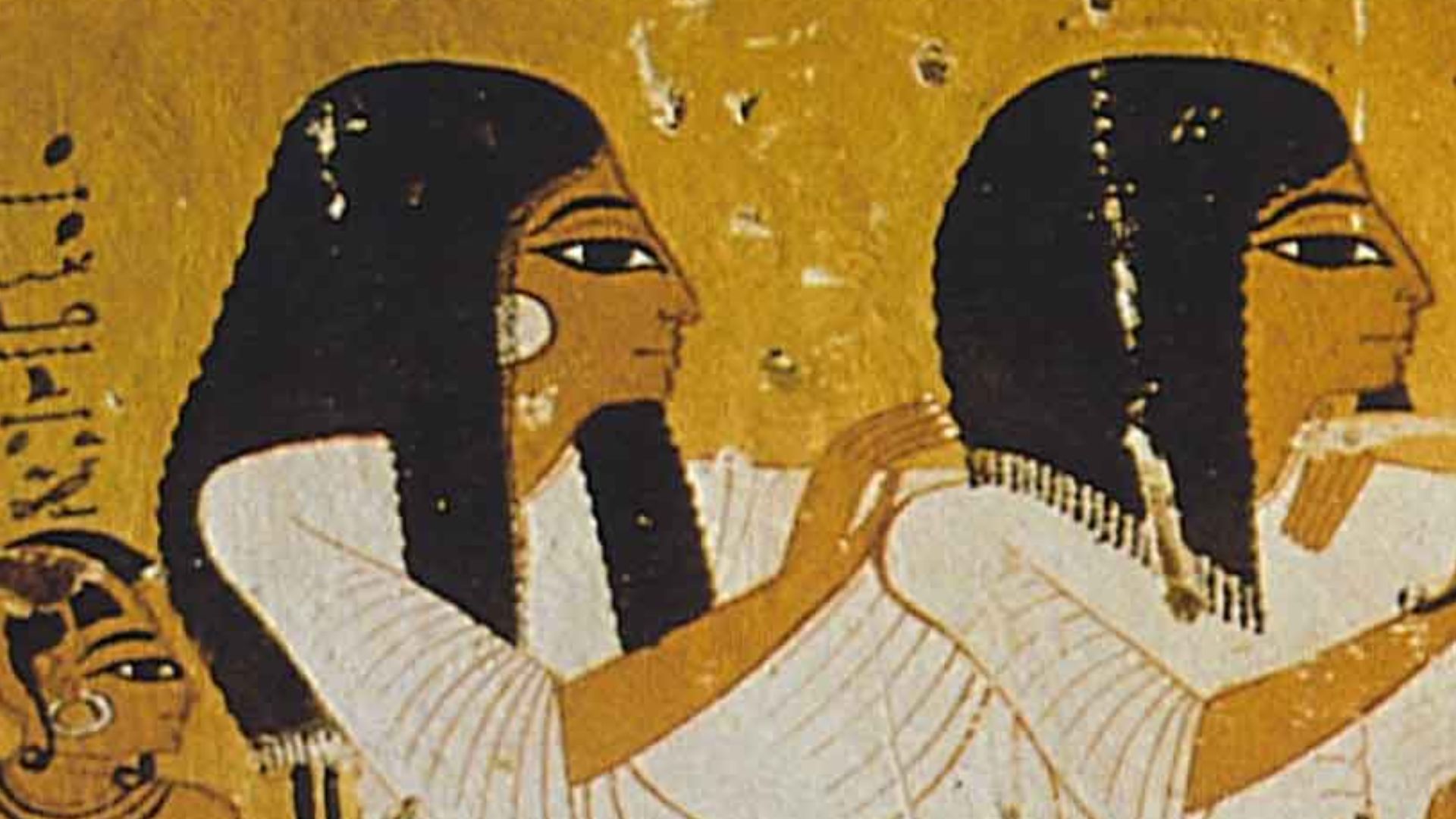
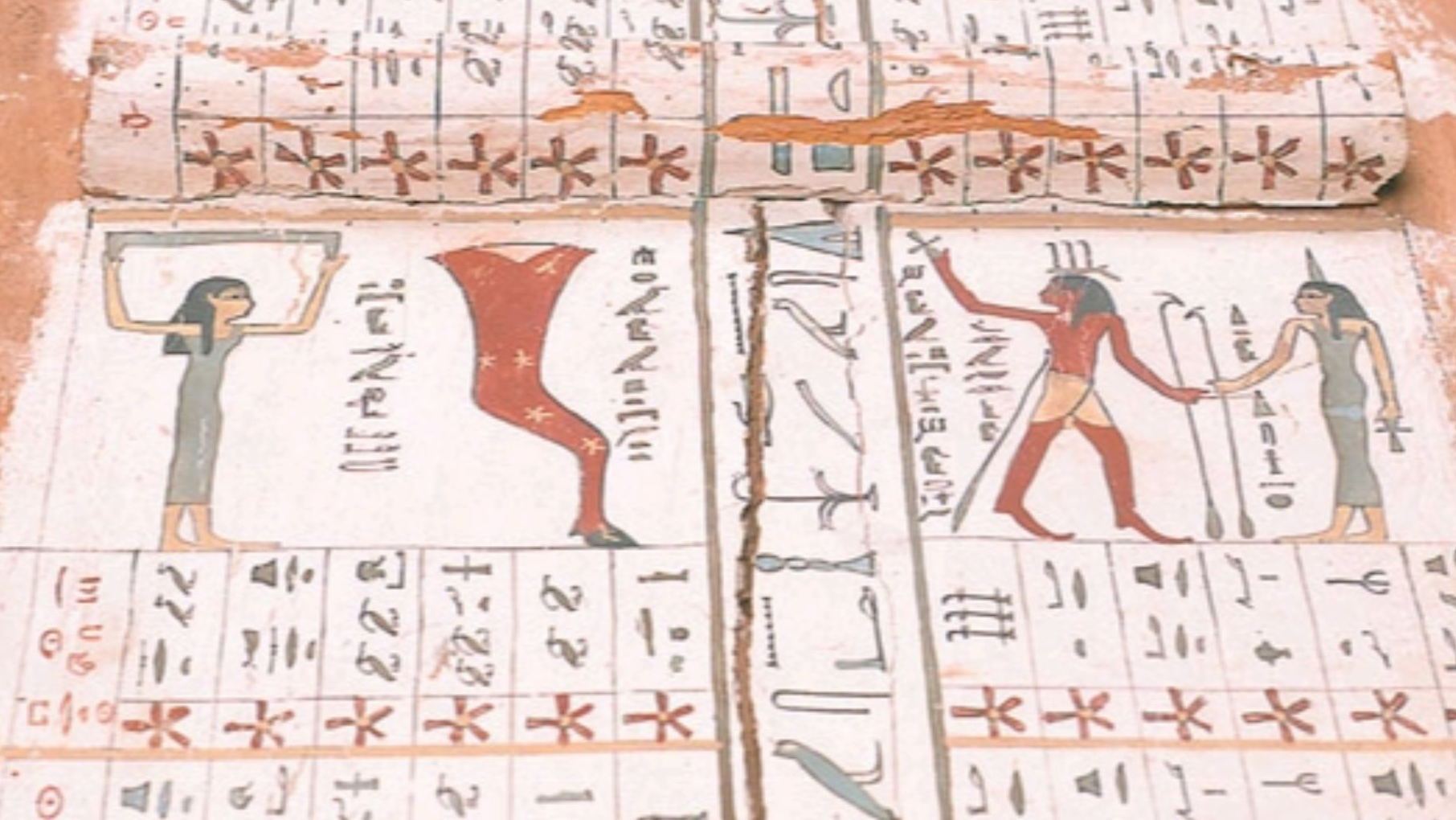
The Ancient Egyptians
History proves ancient Egypt to be a scientific culture. The ancient Egyptians’ awareness of arithmetic, astronomy, and especially anatomy rival modern times; we owe our ability to perform medical surgery to them.
The Ancient Egyptians
The ancient Egyptians had an advanced knowledge of medicine, among ancient peoples. They would stitch up wounds, and reset bones. Some theorize their unique process of preserving the recently departed (mummification) gave them a leg up on their medical advancements.
 Unknown authorUnknown author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown authorUnknown author, Wikimedia Commons
The Ancient Egyptians
While the Sumerians are still credited with the first form of the written word, the Egyptians perfected it. Their complex system of hieroglyphics, as well as variations found on papyrus, are one of the biggest literary wonders of the ancient world.
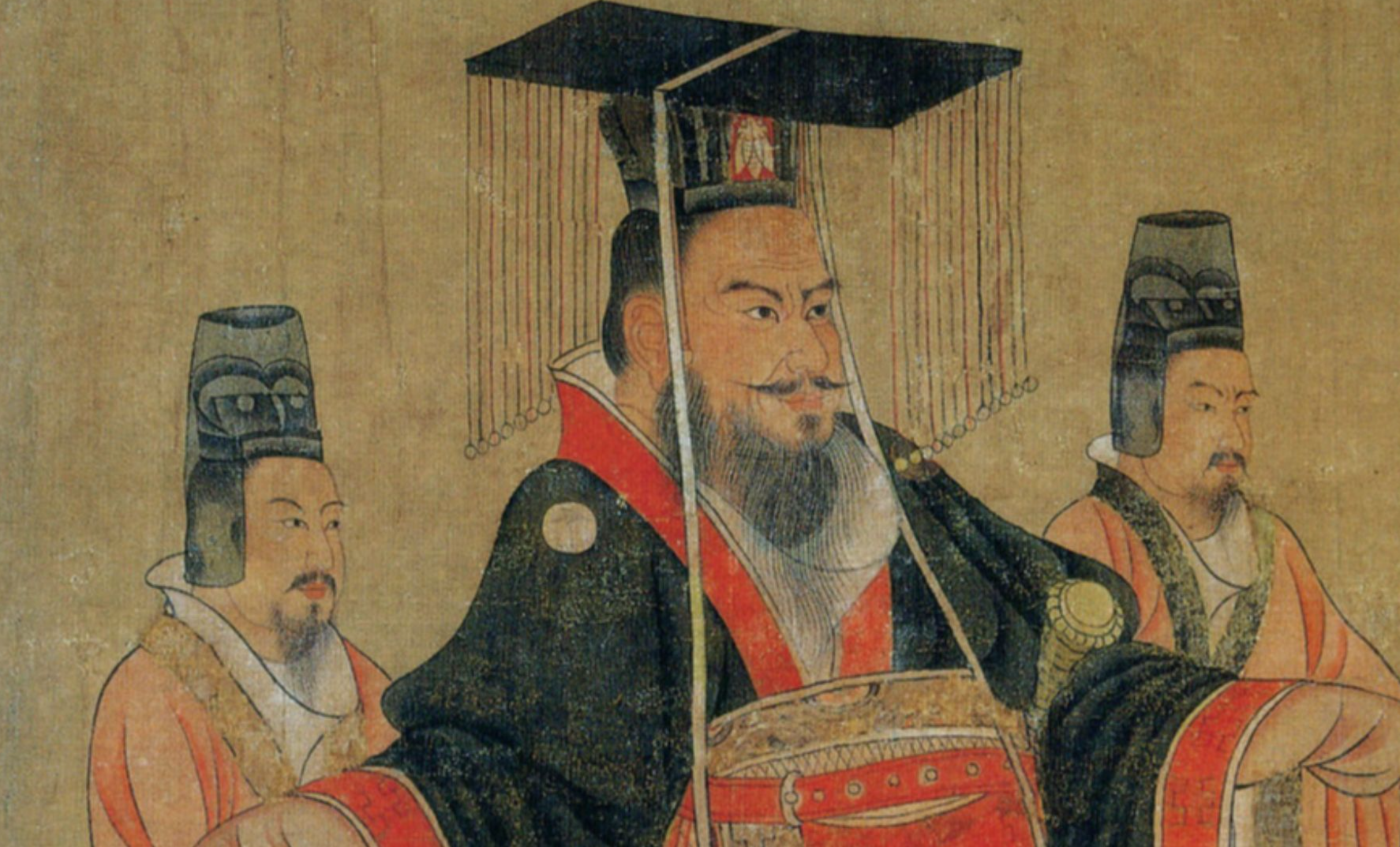
The Ancient & Imperial Chinese
The Western world may like to claim authority on many things. However, no one can deny that Chinese culture was developing and thriving long before many of our famous Western ones.
The Ancient & Imperial Chinese
Farming settlements first appeared in China around 5000 BC, and over the centuries, these communities developed into a strong centralized government; ancient and imperial China was ruled by dynasties as early as 2070 BC.
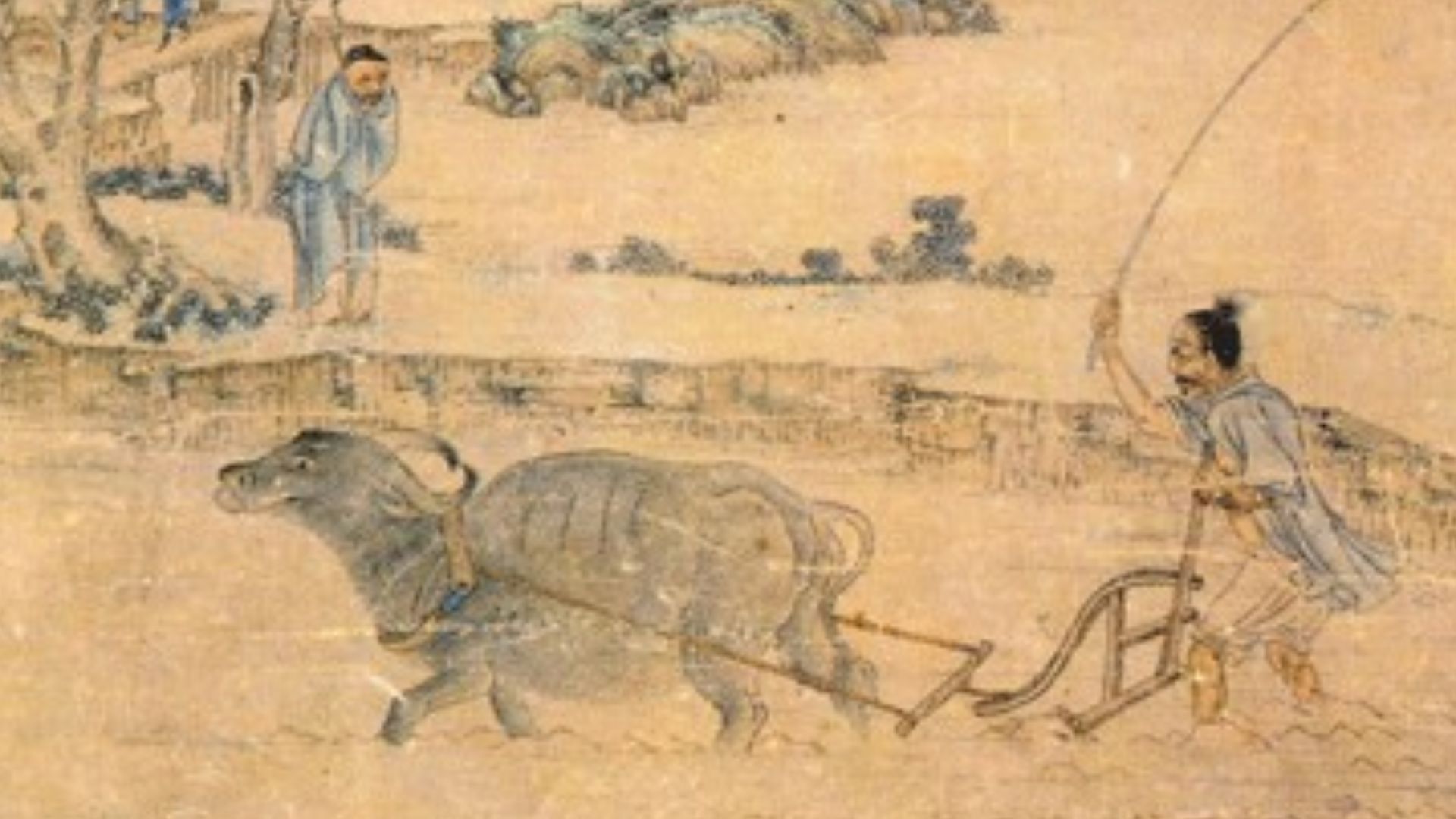 Unknown authorUnknown author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown authorUnknown author, Wikimedia Commons
The Ancient & Imperial Chinese
Like many of the kingdoms that would follow, the ancient and imperial Chinese dynasties believed in a divine decree that gifted them their right to rule; this, for China, developed into the “Mandate of Heaven”. Through this mandate, rulers were considered the stewards of their people. They were warned against bad behavior.
The Ancient & Imperial Chinese
The written language that China uses today can date back to the Shang Dynasty (1600—1046 BC); while not identical, the characters that were used during this time are similar to the characters that are still used today.
The Ancient & Imperial Chinese
Ancient Chinese philosophers developed belief systems that are still used today. Confucius remains a quoted figure throughout the world; his writings date back to 400 BC. However, even if you are not a philosopher, you still have things to thank ancient and imperial China for.
 Kevinsmithnyc, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Kevinsmithnyc, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
The Ancient & Imperial Chinese
It was ancient Chinese artists who created the first silk, as well as the first forms of paper. They created the first block printing process and maritime compasses. The traditional forms of Chinese medicine, including acupuncture and herbal medicine, are still used today as well.
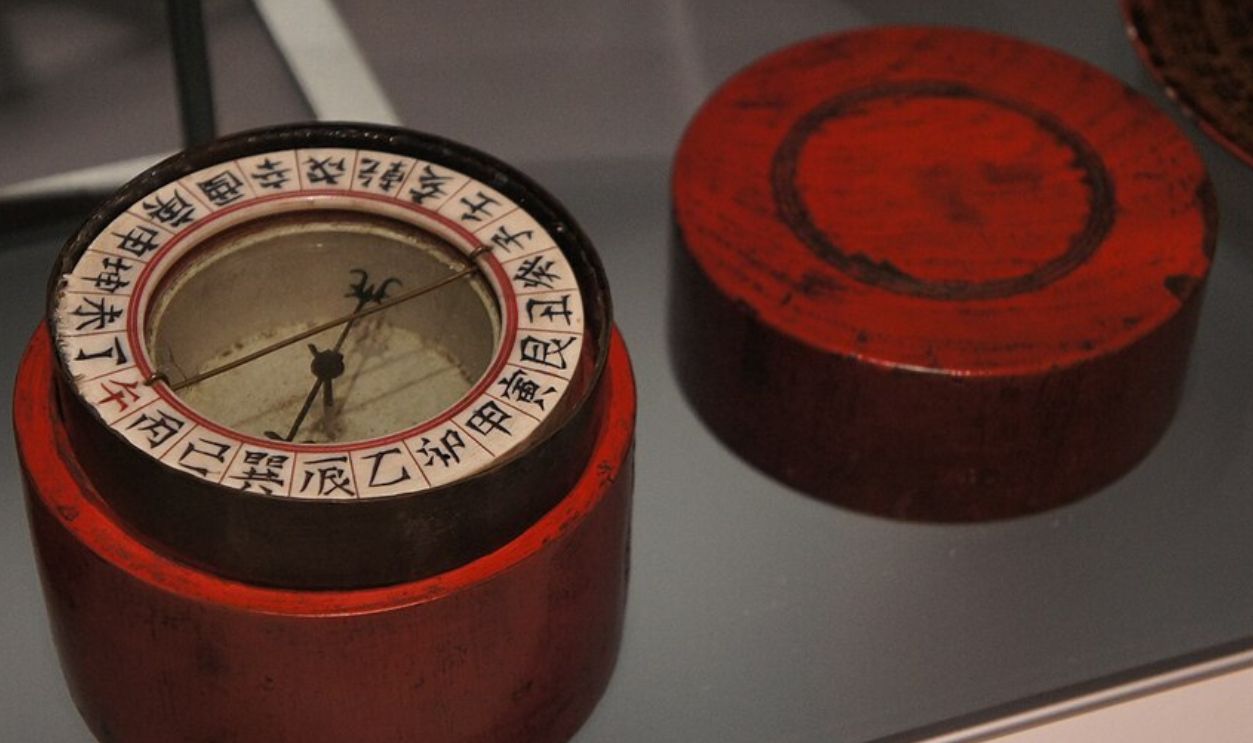 Victoria C, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Victoria C, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
The Maya
Around the same time that the civilizations of the Indus Valley were developing, so were the communities in Mesoamerica, which today spans southeastern Mexico, Guatemala, and Belize, as well as portions of El Salvador and Honduras.
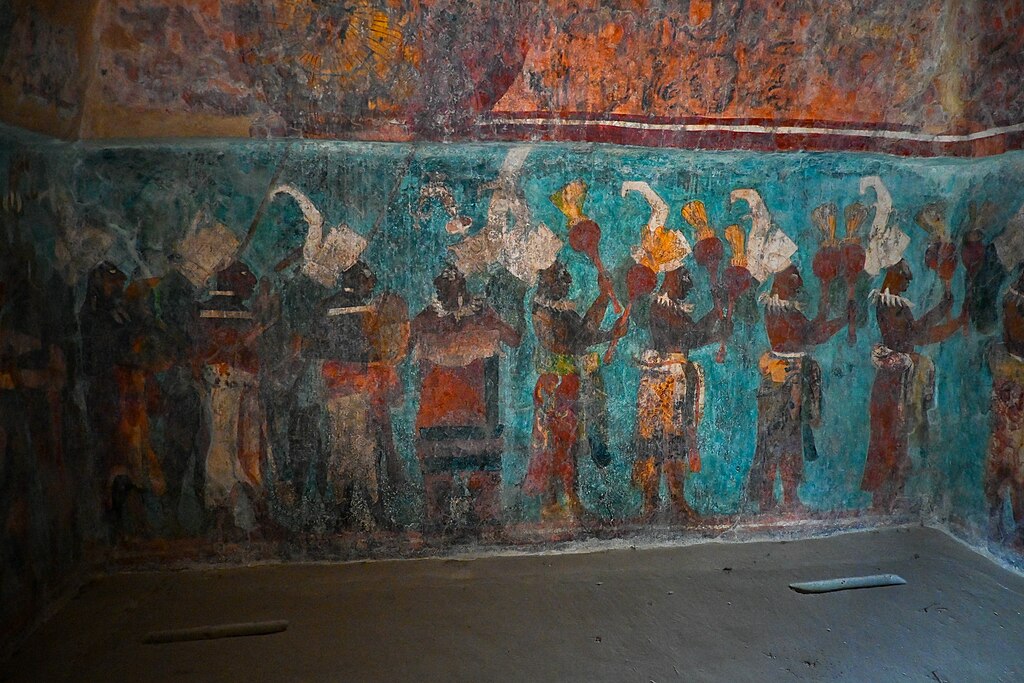 ProtoplasmaKid, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
ProtoplasmaKid, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
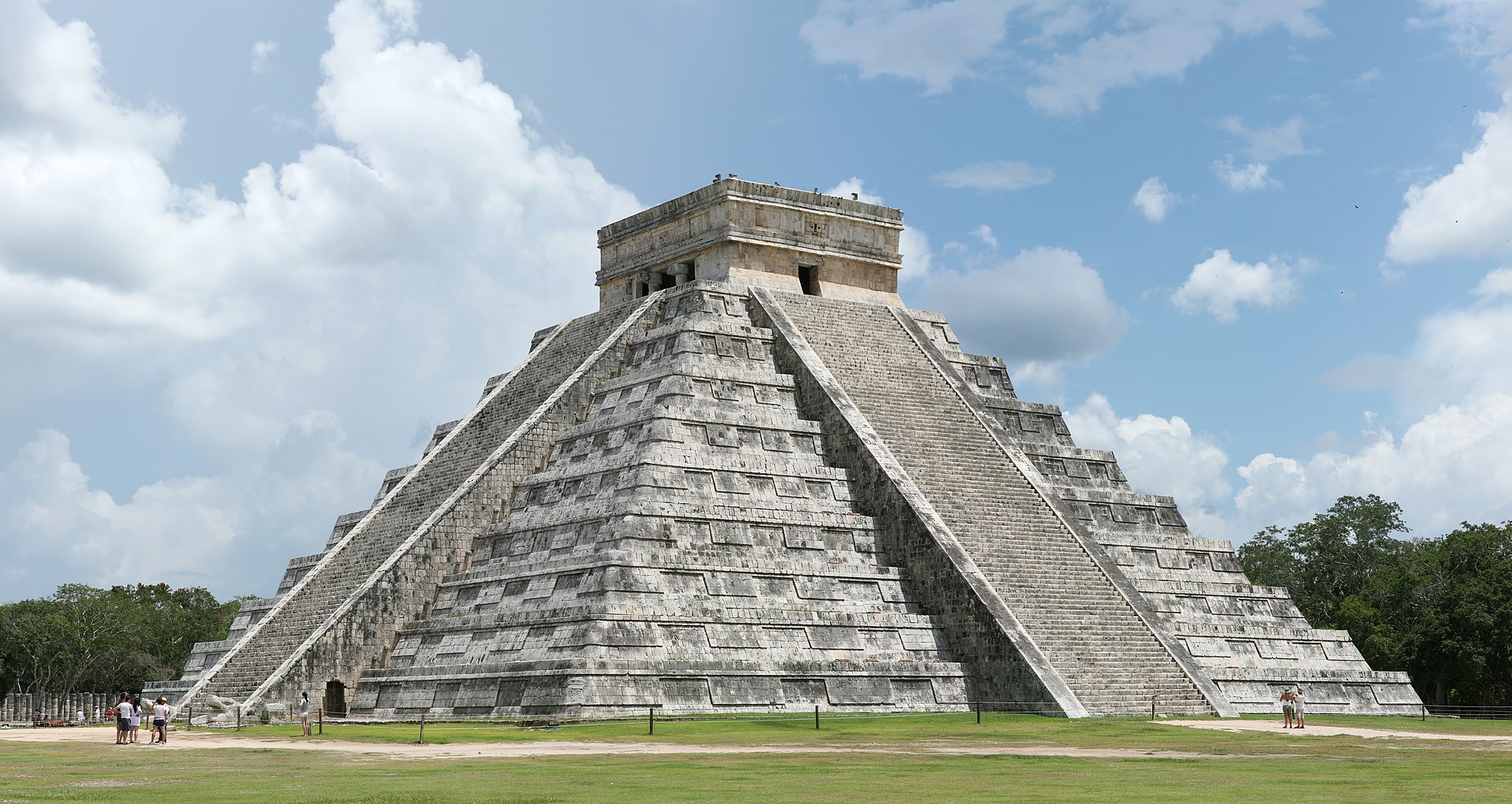
The Maya
These civilizations began to develop into cities and were replaced by a better-known culture: the Maya Civilization. Like the ancient Egyptians, the Maya built tall structures that continue to stand the test of time—though their reasoning for it was a little different.
 Daniel Schwen, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Daniel Schwen, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
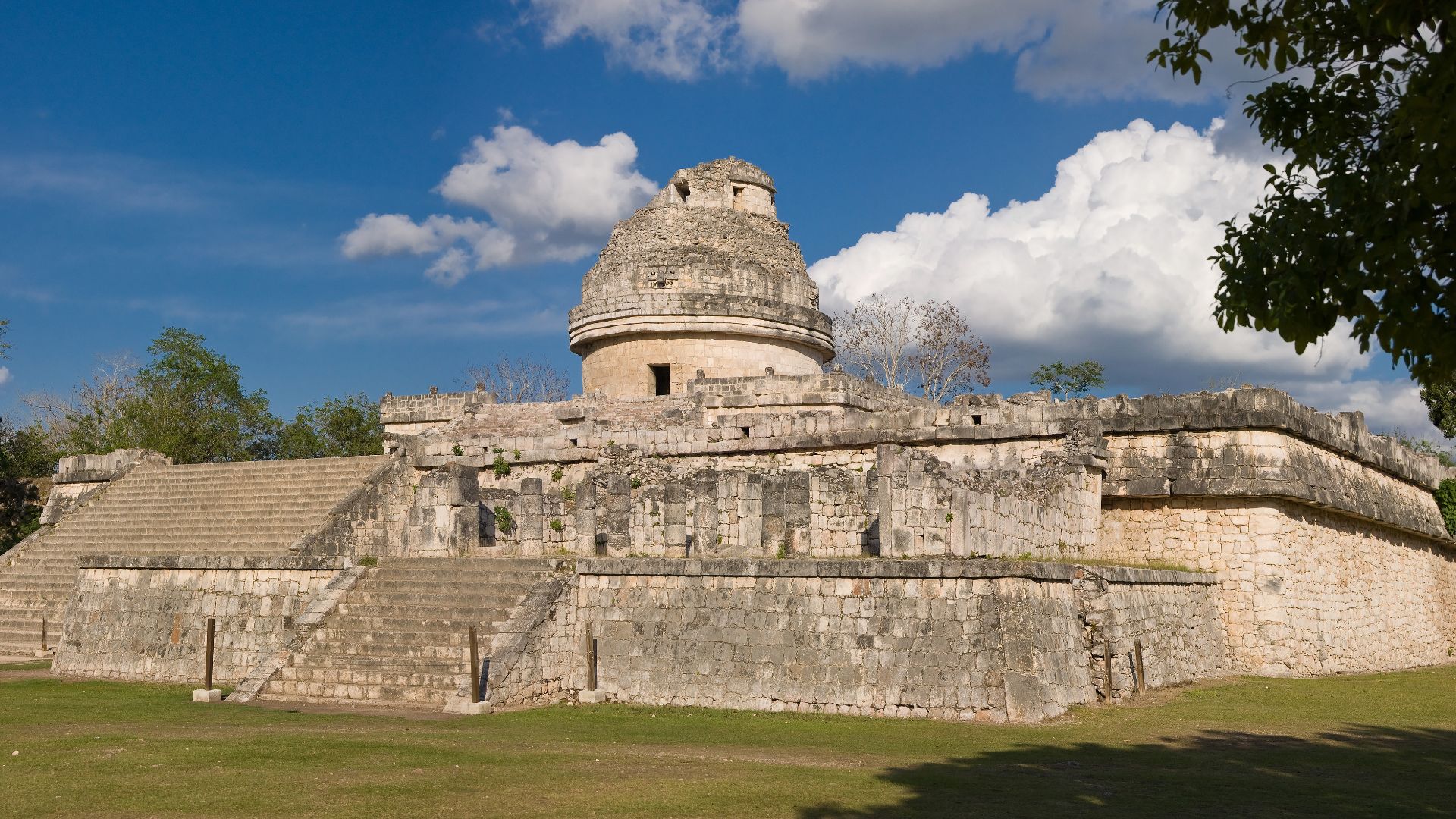
The Maya
The sky fascinated the Maya; their cities were built around massive complexes that appeared to reach out to the stars. Among those complexes were observatories, where the Maya would record their meticulous observations of the planets.
The Maya
The Maya’s understanding of astronomy was far from basic. Their records, which used a system combining pictorial and phonetic characters, showed a true understanding of the movements of their beloved celestial objects.
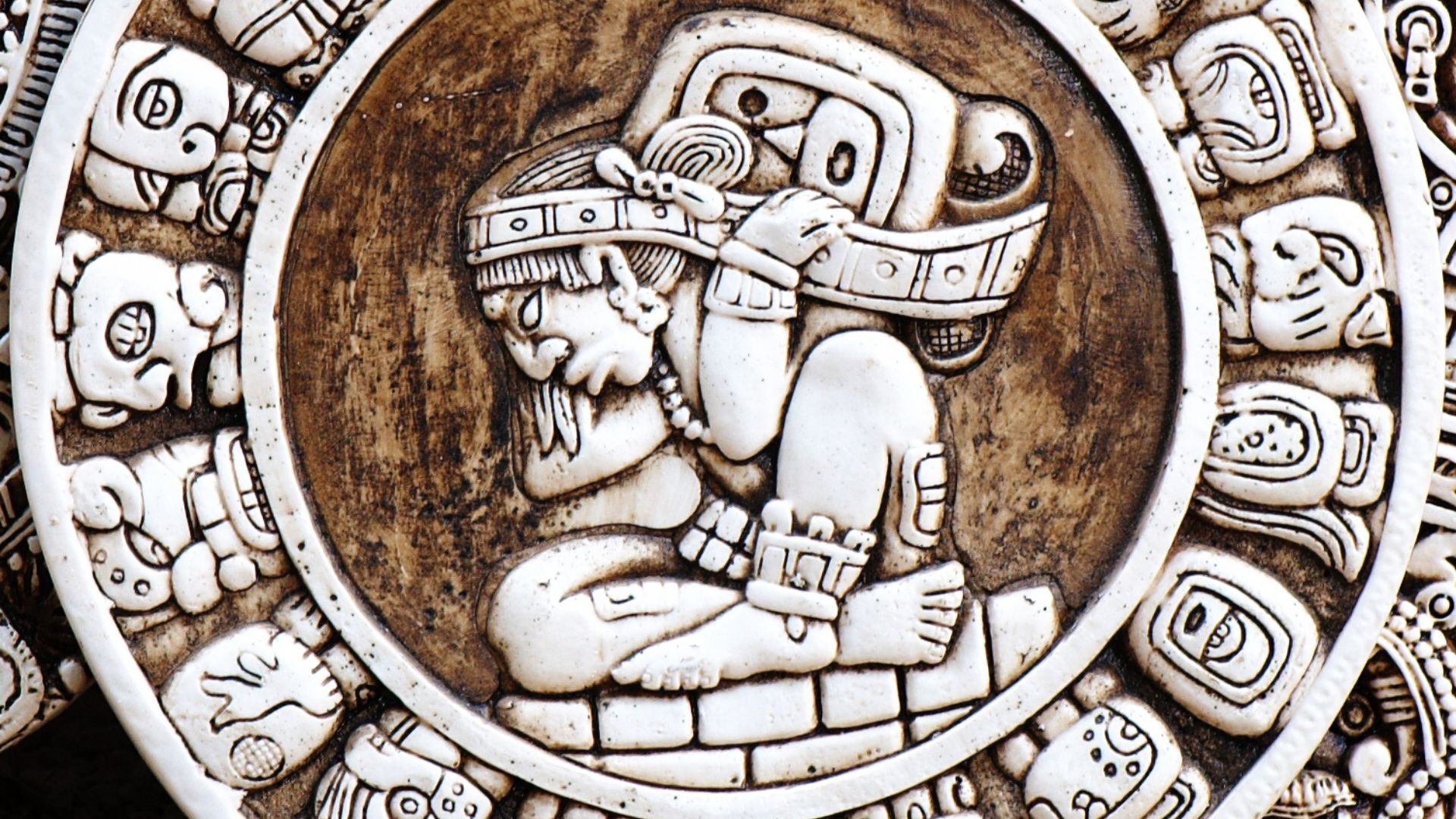
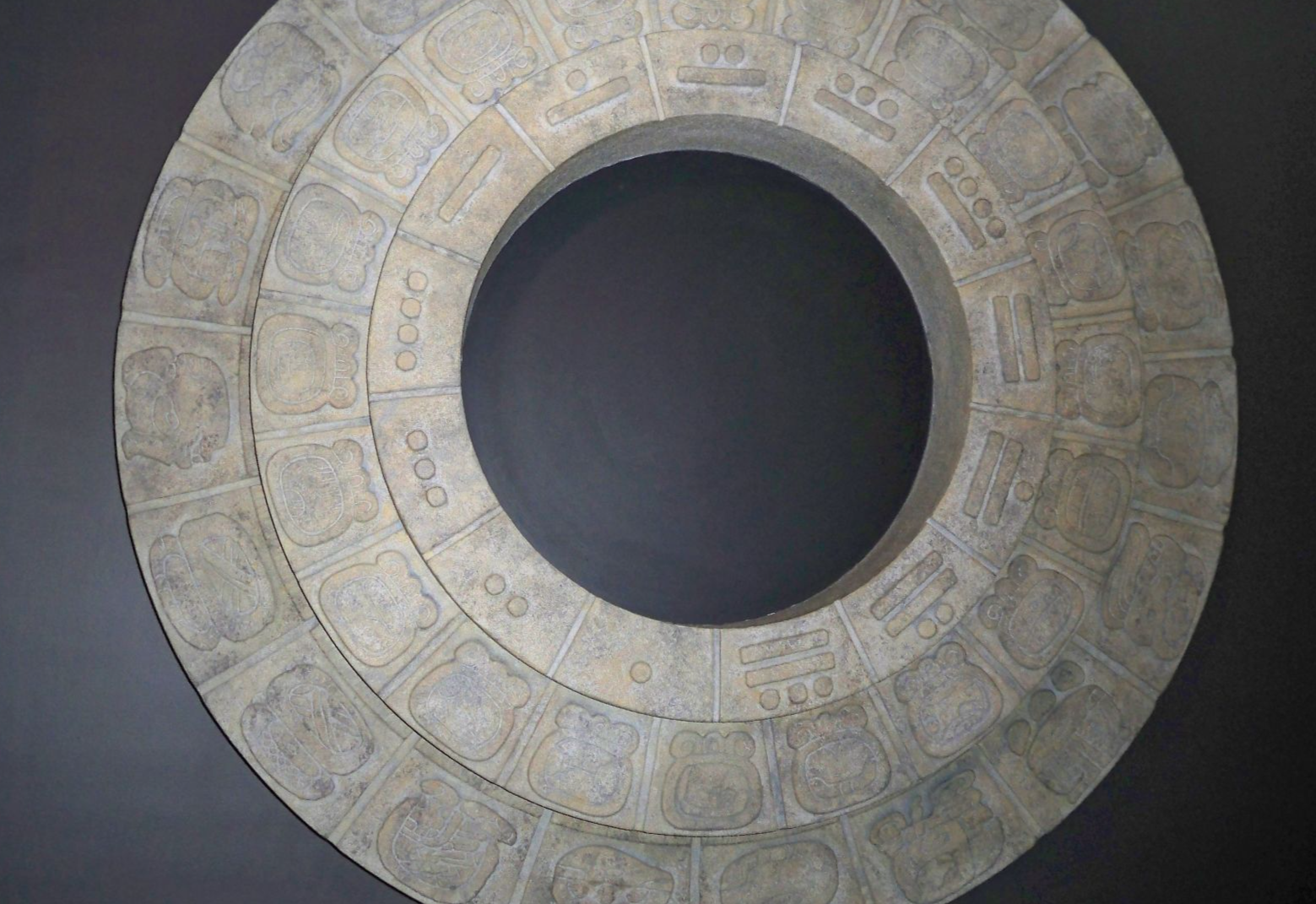
The Maya
The Maya made predictions on the position of various celestial objects that proved to be correct, long into the future. Moreover, they used Venus, Mars, and the Moon to keep track of time.
 wikipedia user Brian0918, Wikimedia Commons
wikipedia user Brian0918, Wikimedia Commons
The Maya
The Maya means of time management used a complex system of interlocking calendars, all of which scheduled both their agricultural activities and religious rituals to coincide with specific astronomical arrangements. To this day, 6 million modern Maya descendants still use this system.
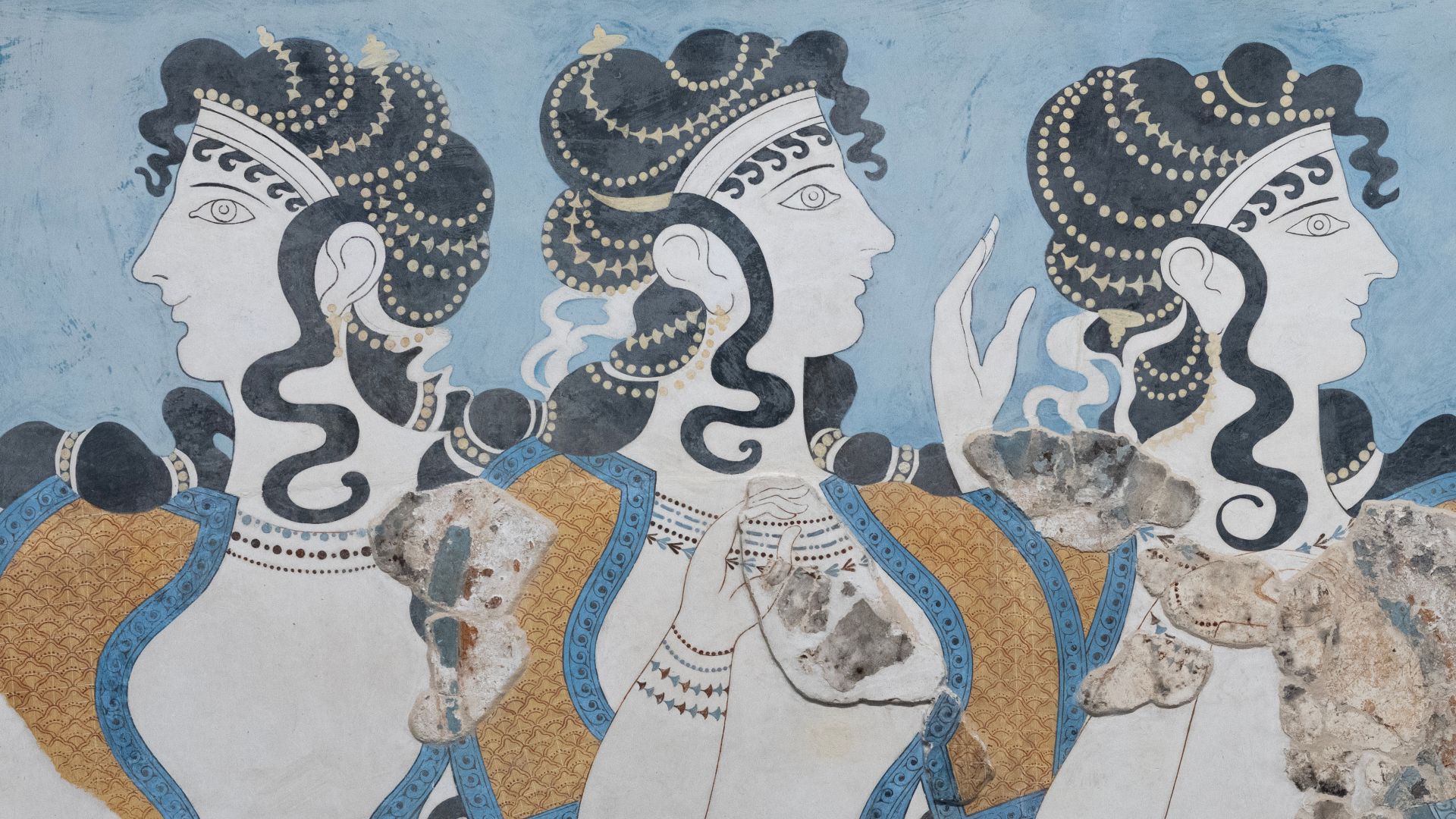
The Greeks
7000 BC appears to have been the prime time for civilizations to grow. It was around this time that the settlements that would become Greece’s famous Minoan and Mycenean societies began to form along the Aegean Sea.
 Gleb Simonov, Wikimedia Commons
Gleb Simonov, Wikimedia Commons
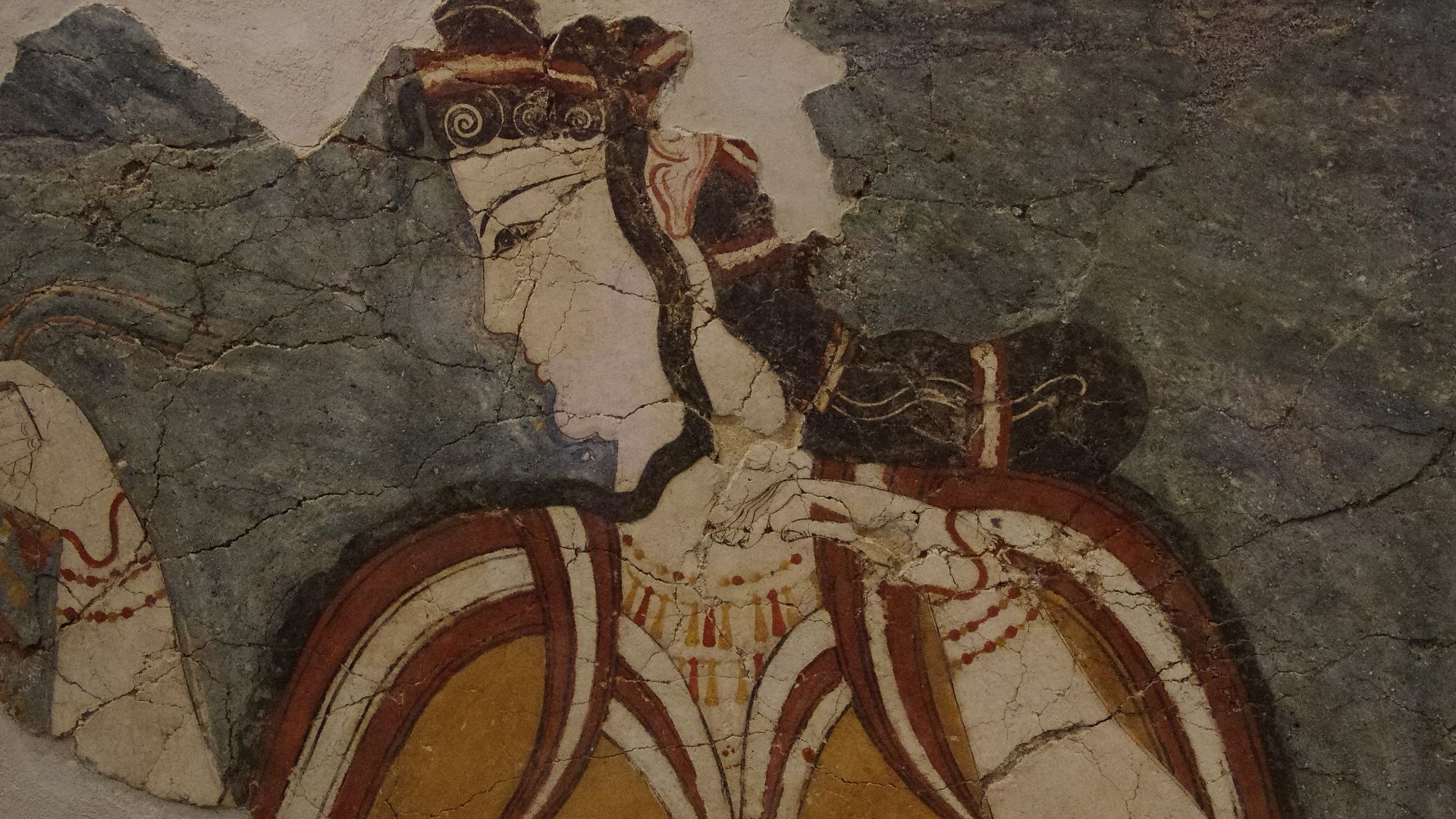
The Greeks
These two civilizations influenced much of what followed in ancient Greece. The Myceneans, in particular, dictated the development of the language and the early Greek deities. Even today, if you understand a reference to Achillies, Odysseus, or the Trojan War, then you are remembering the Myceneans, for Achillies and Odysseus were great Mycenean heroes.
 Paolo Villa, Wikimedia Commons
Paolo Villa, Wikimedia Commons
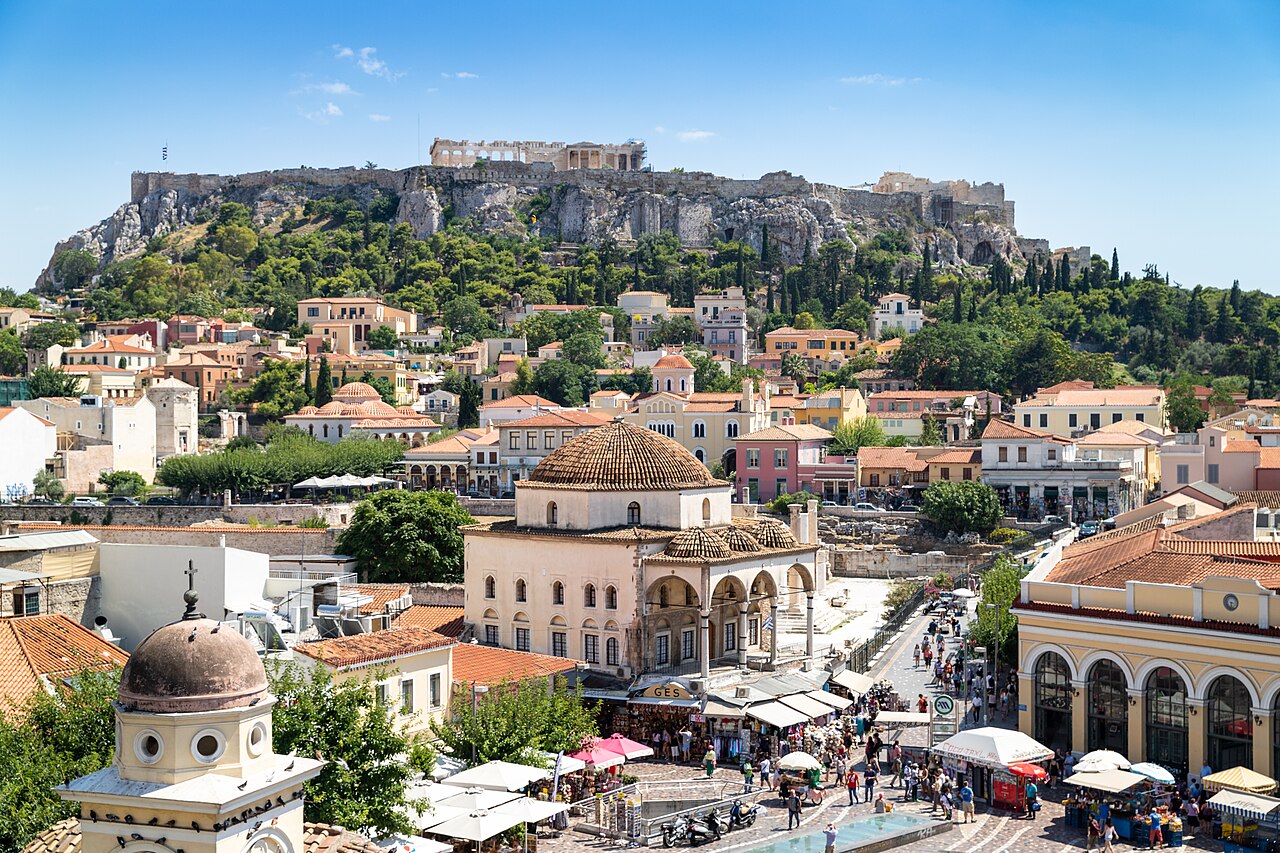
The Greeks
The fact that the Minoan and Mycenean cultures collapsed by 1100 BC is likely the root cause of them being remembered, by name, by only true classicists. The cities that replaced them, however—Athens, Sparta, and Thebes—live on in the memories of most in the Western world.
 dronepicr, CC BY 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
dronepicr, CC BY 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
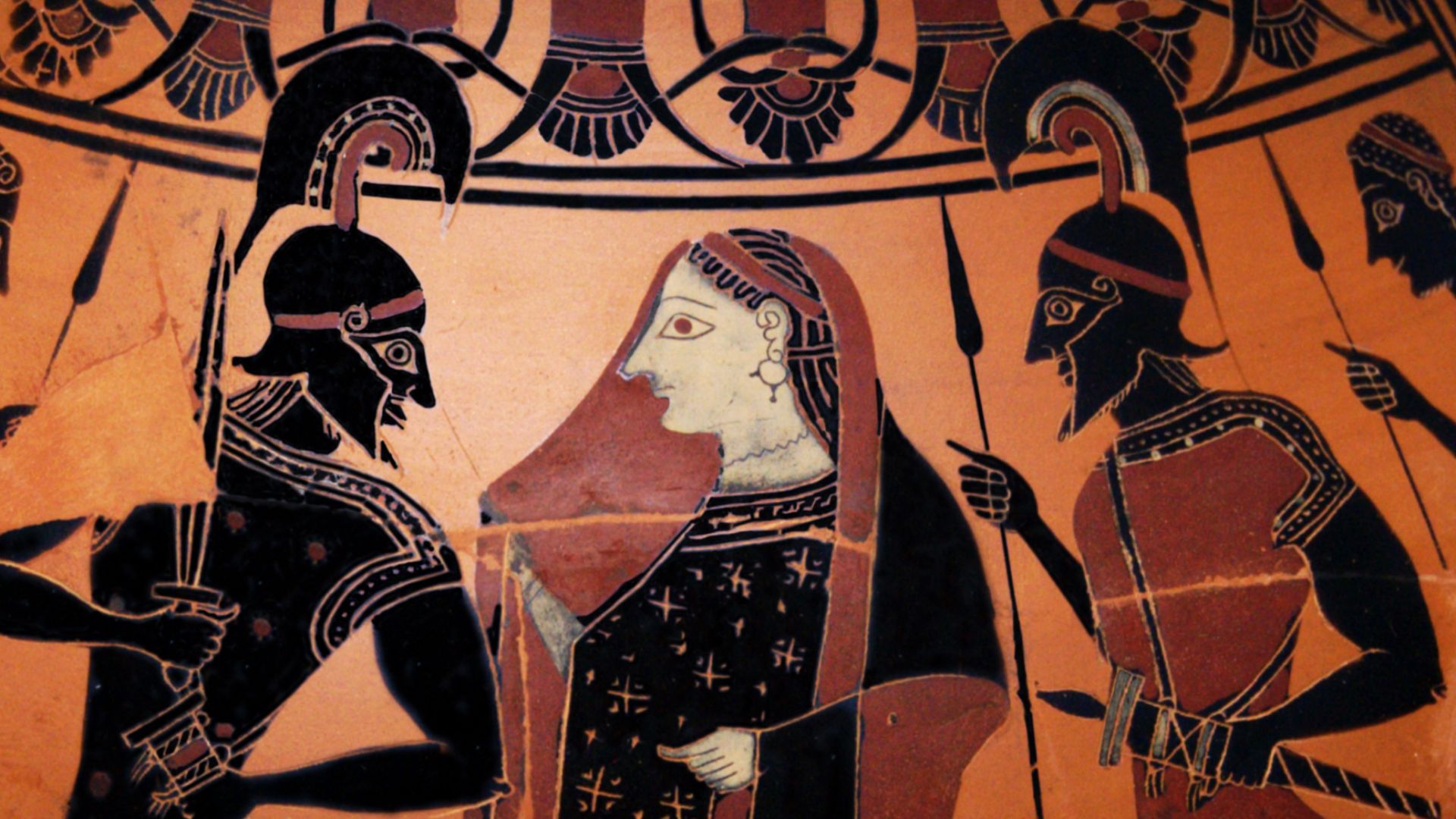
The Greeks
Greek culture was very divided. Each city-state had its ruler and its own culture. However, they shared a language, and their shared interest in innovation has led to ancient Greece still being an influential player in society today.
 Amasis Painter, Wikimedia Commons
Amasis Painter, Wikimedia Commons
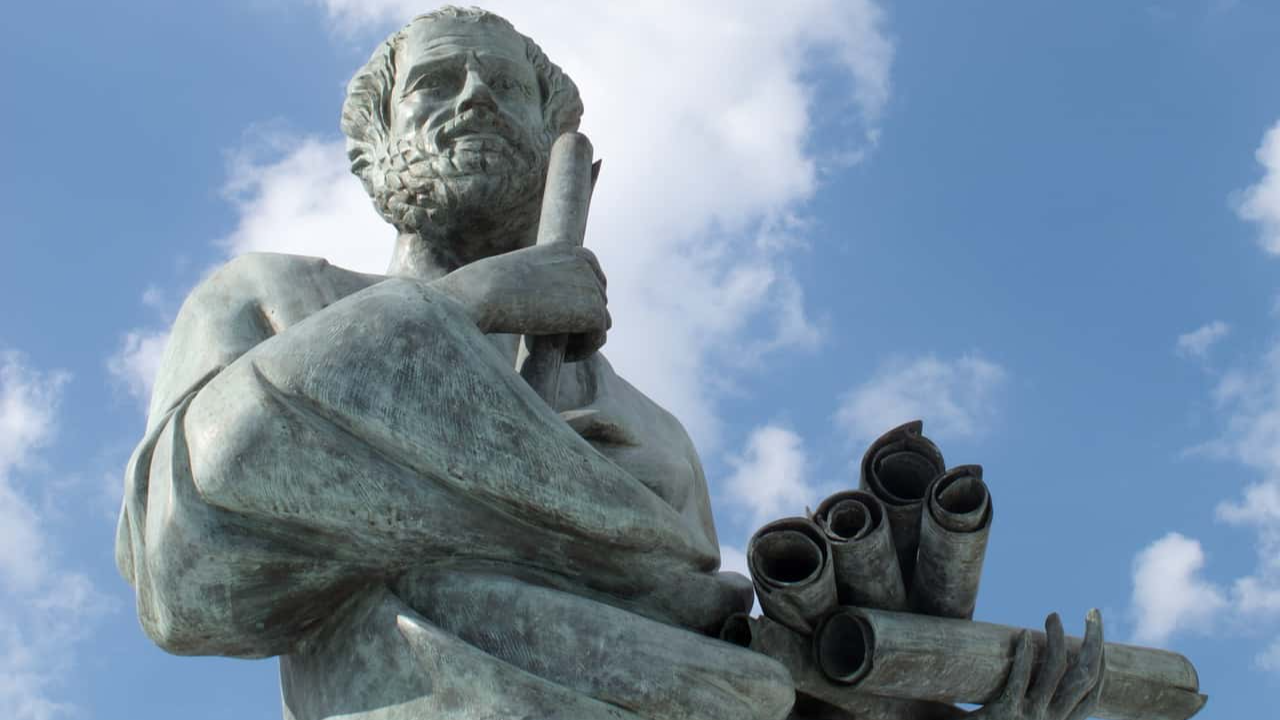
The Greeks
Much of Western literature owes its start to ancient poets, such as Homer and Hesiod (both of which are still studied today); Greek philosophers such as Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle continue to have influence on modern thinking, as well.
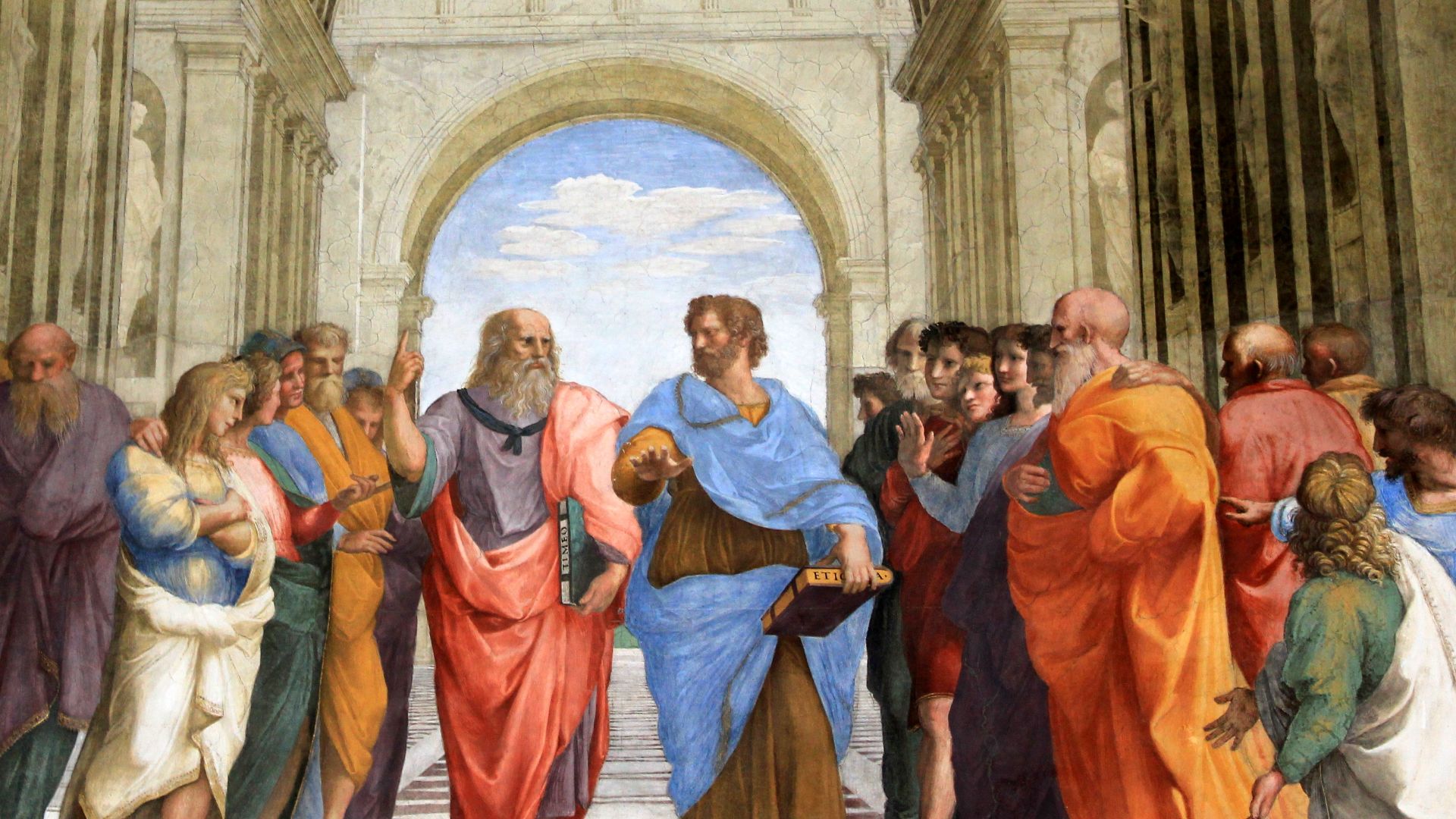
The Greeks
Modern medicine, mathematics, and science all owe their starts to the ancient thinkers of Greece. They paved the way for what followed; however, the biggest influence that Greece is credited for is democracy. Ancient Greece laid the foundation for modern democracies to be built.
 Jorge Valenzuela A, Wikimedia Commons
Jorge Valenzuela A, Wikimedia Commons
The Romans
As suits the theme of this article, ancient Rome owes much of its development to ancient Greece. They borrowed basic principles from the Greeks and elevated them. Therefore, modern civilization owes just as much to the Romans as the Romans owe to the Greeks.
The Romans
Of all our civilizations, Rome is the youngest, beginning as a small village along the Tiber around 750 BC. However, the Romans took that small village and turned it into an empire that is still relevant in Western culture today.
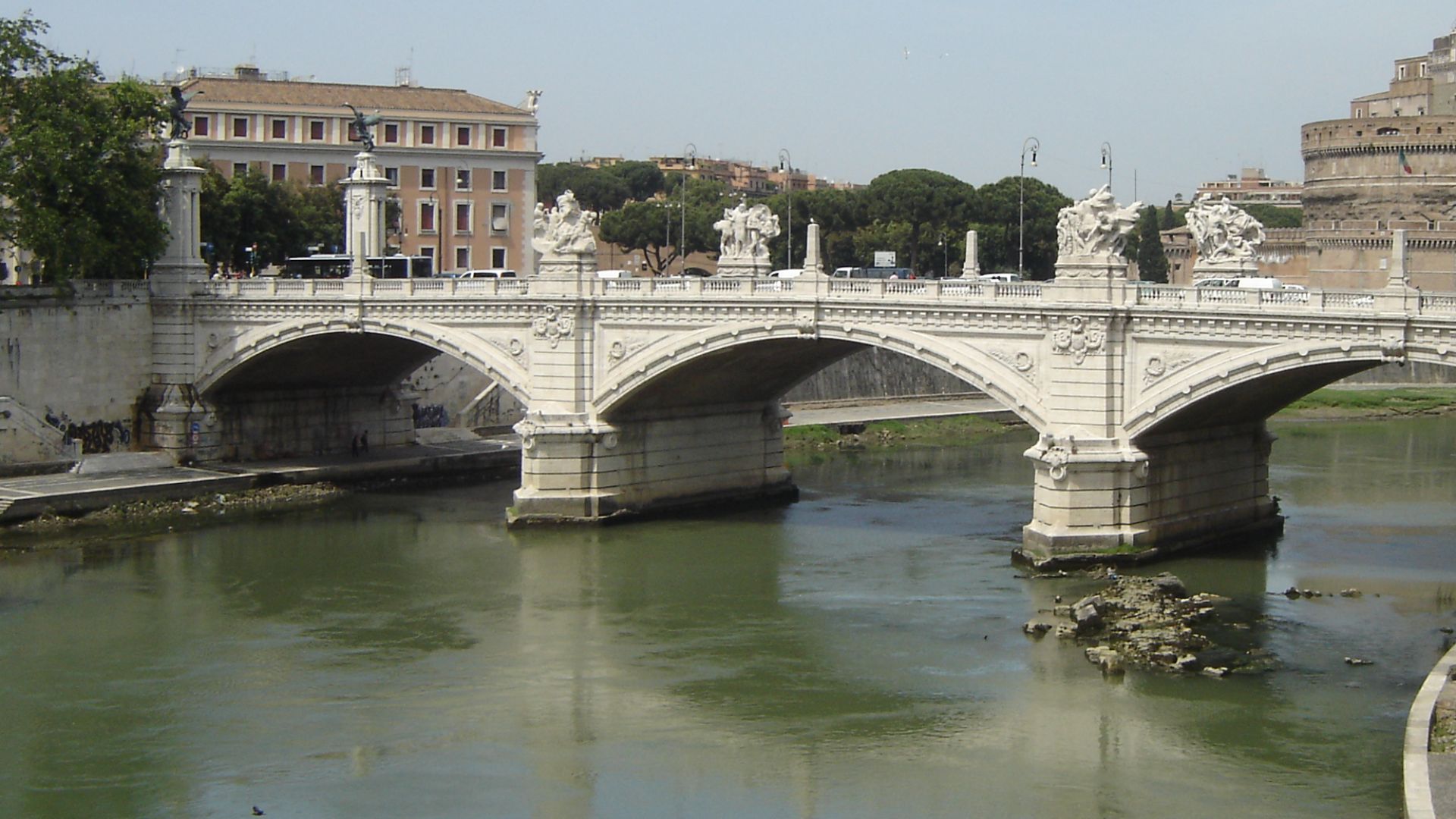 Kalajoki~commonswiki, Wikimedia Commons
Kalajoki~commonswiki, Wikimedia Commons
The Romans
As hinted at already, much of Roman culture was absorbed by others. Their deities were primarily the same as the Greeks, with some influence from the Egyptians as well. They also cataloged the information that they learned from other nations as well.
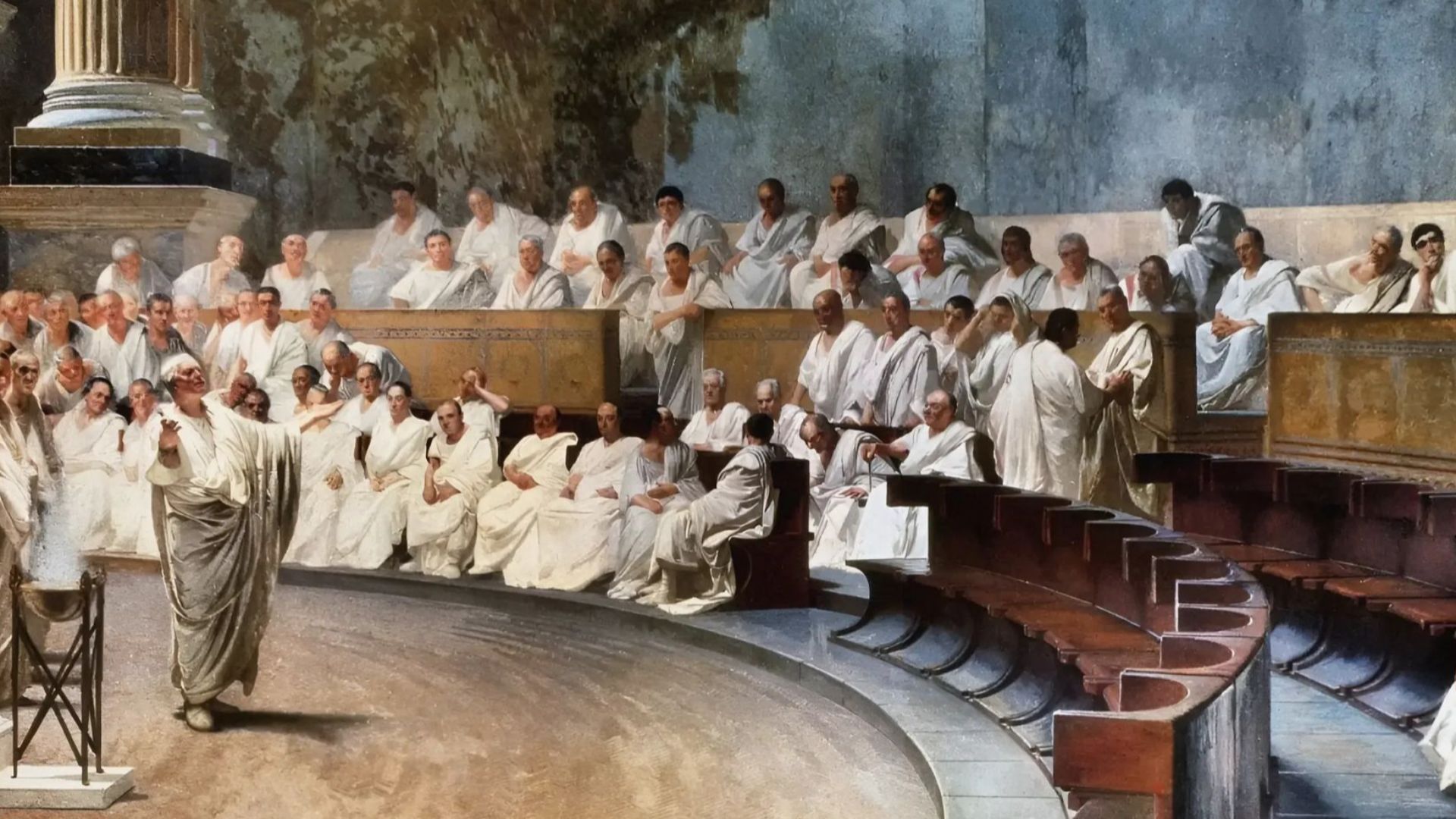 Cesare Maccari, Wikimedia Commons
Cesare Maccari, Wikimedia Commons
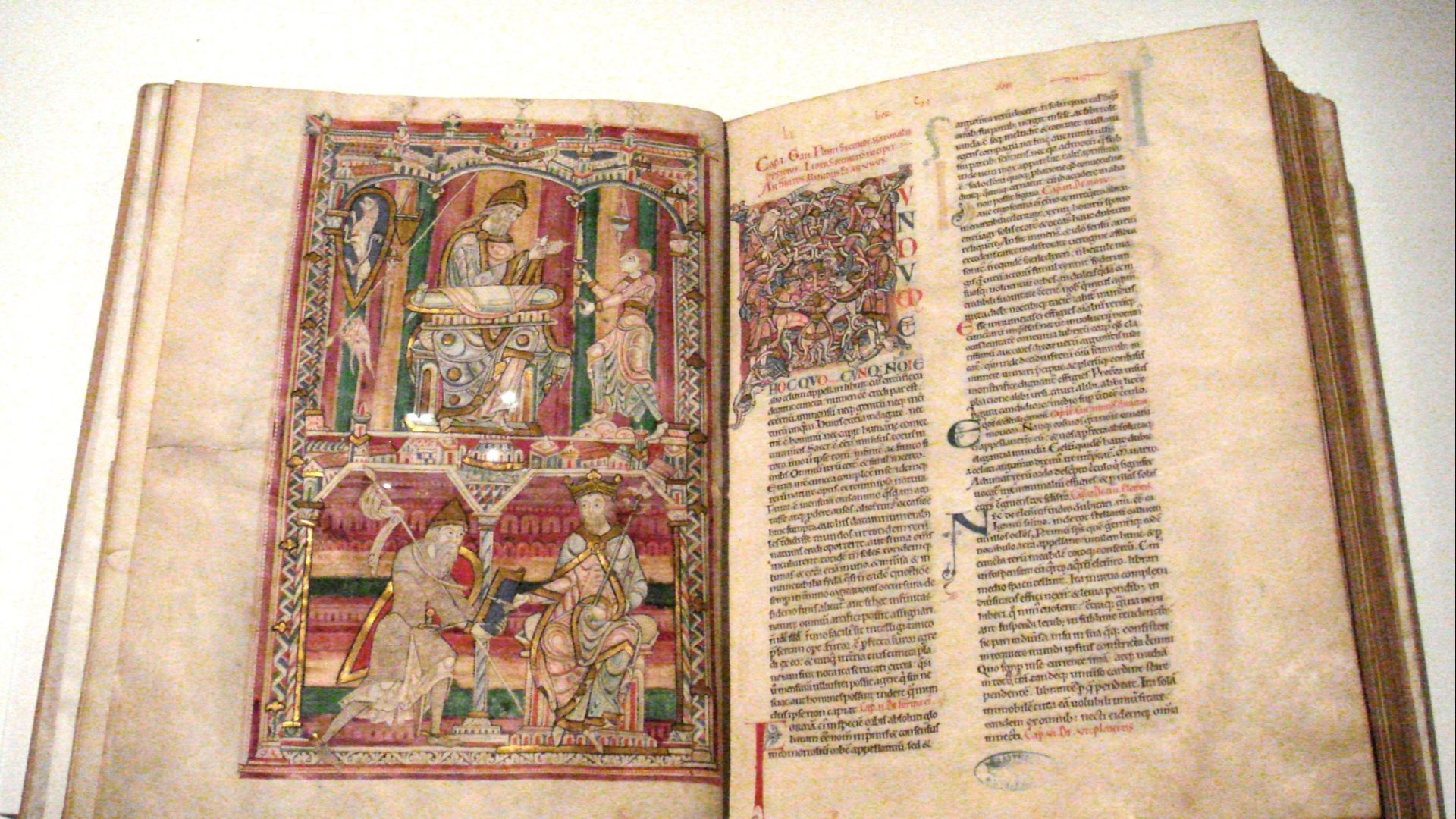
The Romans
Thanks to the Roman habit of absorbing the information they collected from other cultures, they are credited with inventing some of the earliest known encyclopedias. Pliny the Elder, a classical historian, compiled 20,000 facts from various cultures, on a variety of topics in his Naturalis Historia.
The Romans
The Romans weren’t without their talents, however. They may have absorbed knowledge from other cultures, but they always had the ingenuity to put their unique spin on that information, particularly when it came to their architecture.
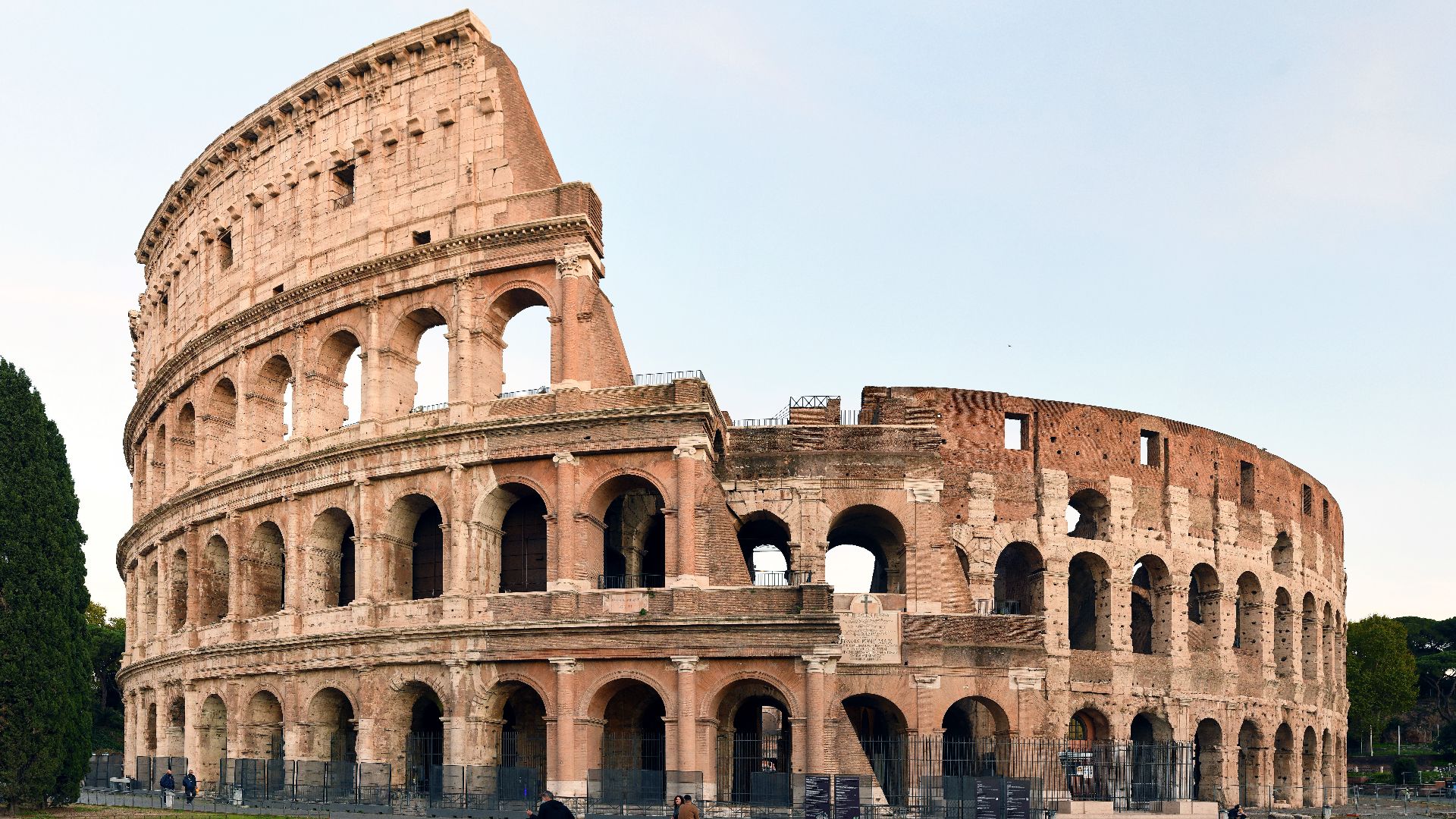 Utente:FeaturedPics, Wikimedia Commons
Utente:FeaturedPics, Wikimedia Commons
The Romans
Romans may not have invented the road, arch, or aqueduct; however, they perfected them. Their construction proved so sturdy, that many of their buildings and architecture still exist today (whereas those they sourced the knowledge from do not). They allowed these pieces of knowledge to be passed forward, enabling us to still use them today.
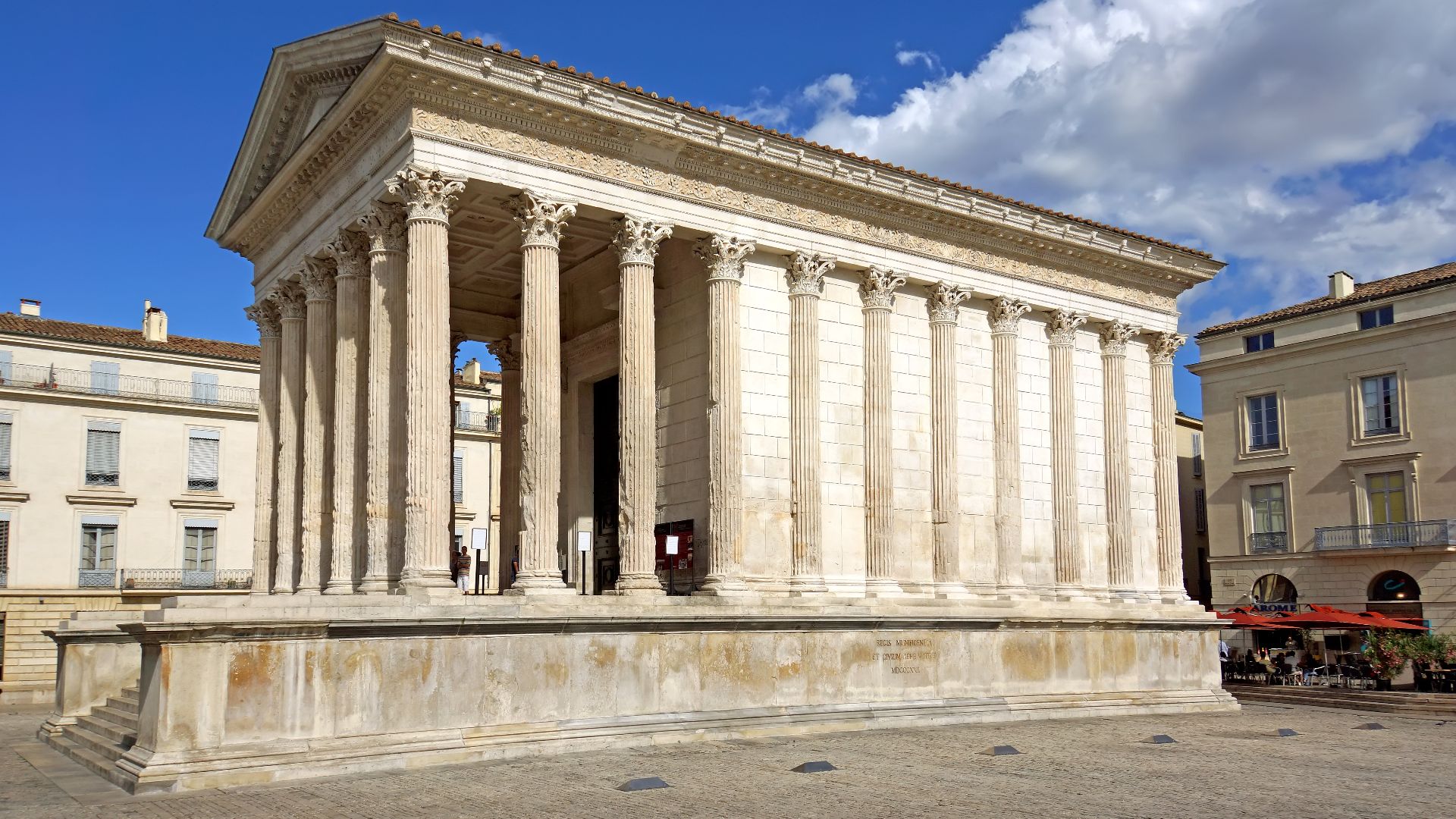 Dennis G. Jarvis, Wikimedia Commons
Dennis G. Jarvis, Wikimedia Commons
You May Also Like:
Secrets From The World’s Oldest Cities
Top 10 Ancient Cities To Discover Around The World
10 Everyday Things That Originated In Pagan Culture
Sources: 1