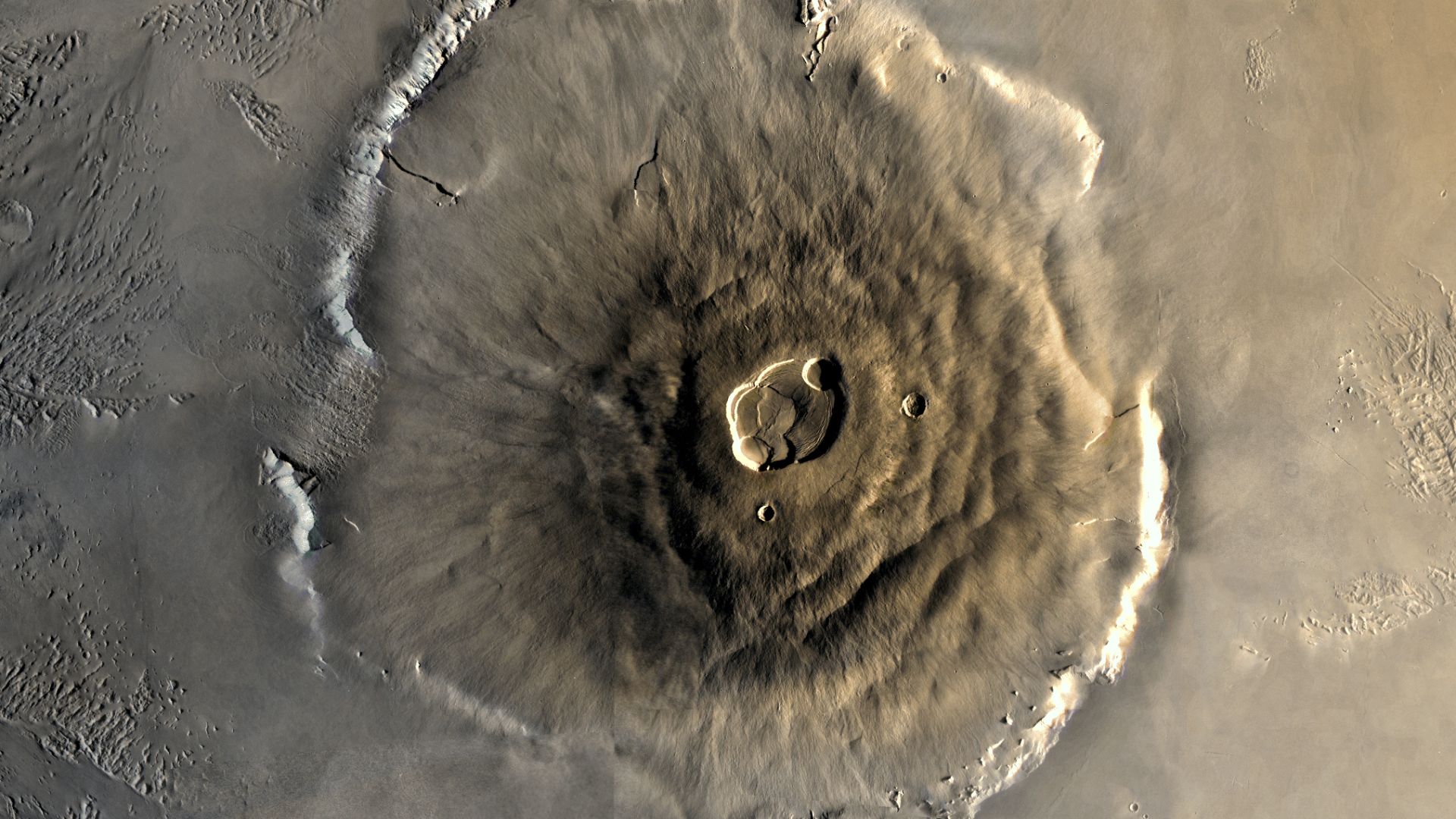
Mars Keeps Delivering Scenes That Raise Eyebrows
Over the years, Mars missions have returned more than data. They’ve brought strange discoveries that haven’t broken any scientific rules, but they’ve made people look (and think) twice.

The Face On Mars
In 1976, Viking 1 flew over Cydonia and captured a rock formation that looked like a human face. The image fueled global theories. However, by 2001, more explicit photos revealed a simple mesa, shaped by erosion and shadow, rather than alien design.
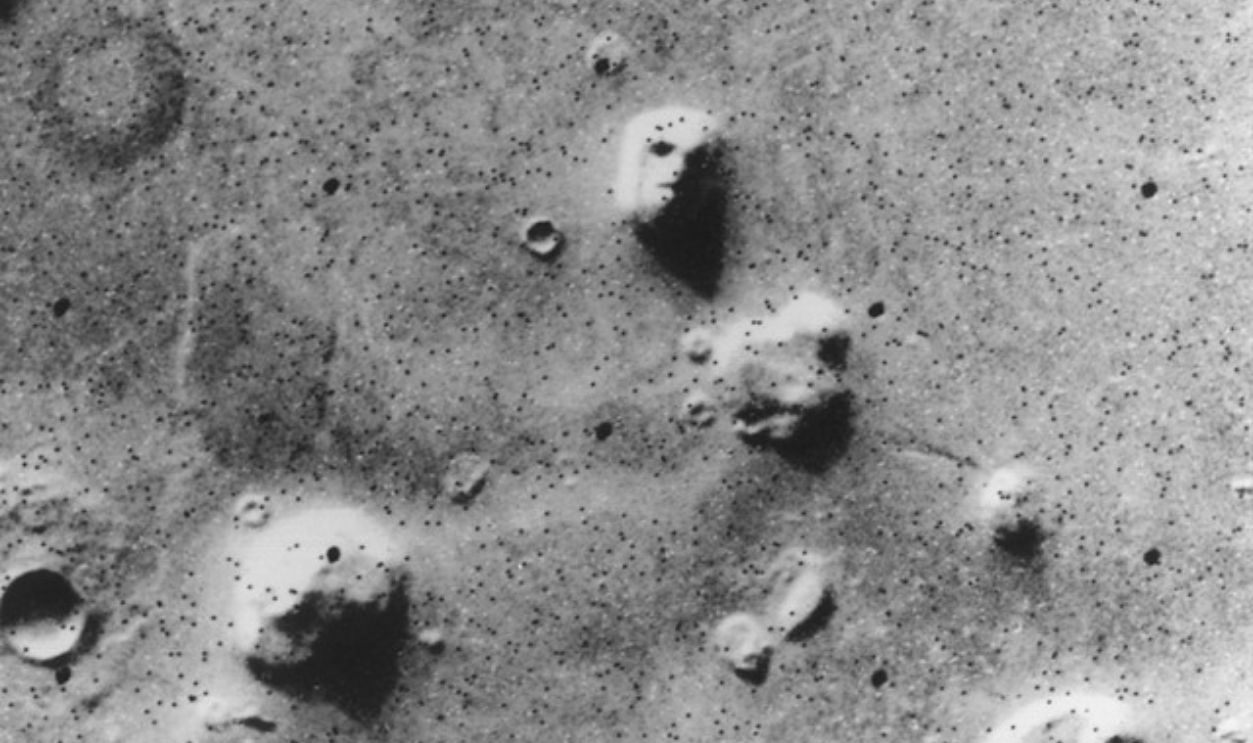 Viking 1, NASA, Wikimedia Commons
Viking 1, NASA, Wikimedia Commons
The Spoon Rock
It looked like a spoon hanging midair, but it wasn’t floating at all. On Sol 1089, Curiosity photographed a thin, curved rock protruding from the cliff. That odd shape formed as wind wore away the softer stone, gradually leaving behind that long, lifted edge now famous online.
The Doorway
Curiosity captured the image in 2022 while exploring a cliff on Mount Sharp. Online reactions took off quickly as the opening appeared to mimic a clean-cut doorway. Its edges looked sharp and symmetrical. However, NASA later cleared that it was just a 12-inch fracture, likely formed by seismic activity.
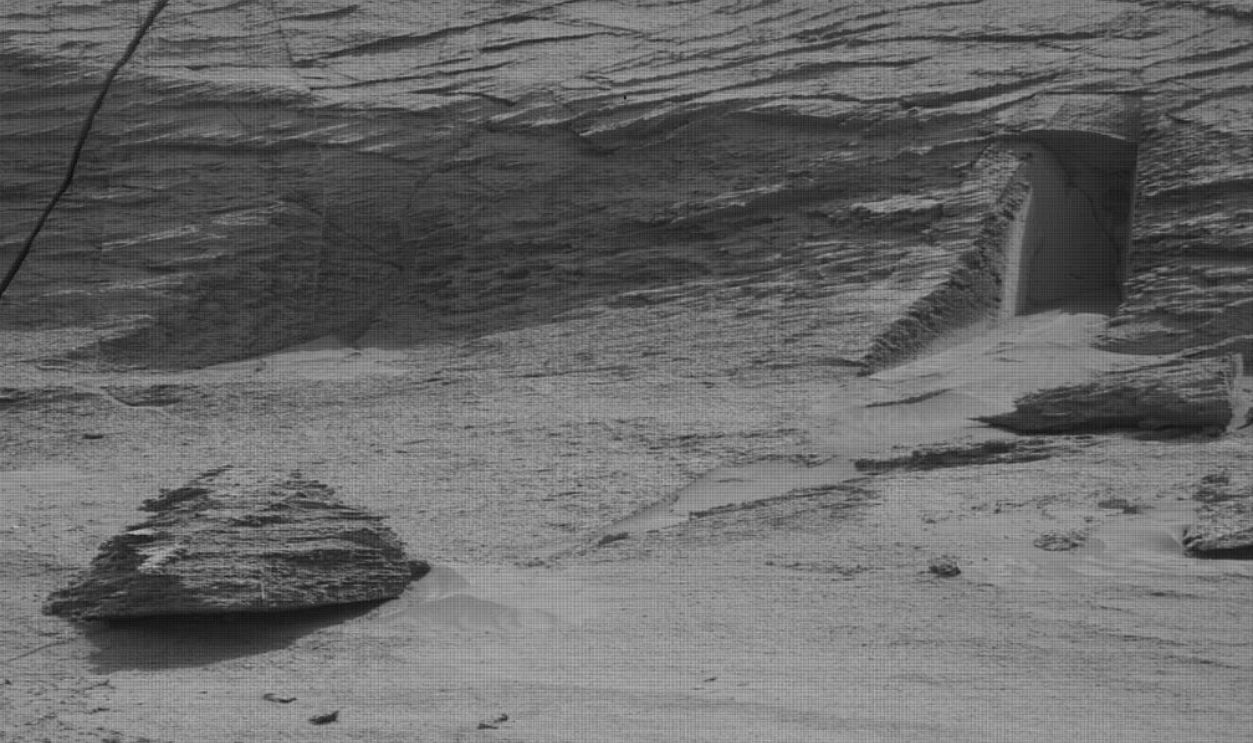 NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS, Wikimedia Commons
NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS, Wikimedia Commons
The Mars Squirrel
A 2013 rover photo stirred plenty of buzz when a rock appeared to resemble a crouching squirrel. It matched the dusty terrain and never moved. While NASA chose not to comment, scientists pointed to pareidolia—our brain’s habit of recognizing patterns that aren’t there.
 NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU/MSSS, Wikimedia Commons
NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU/MSSS, Wikimedia Commons
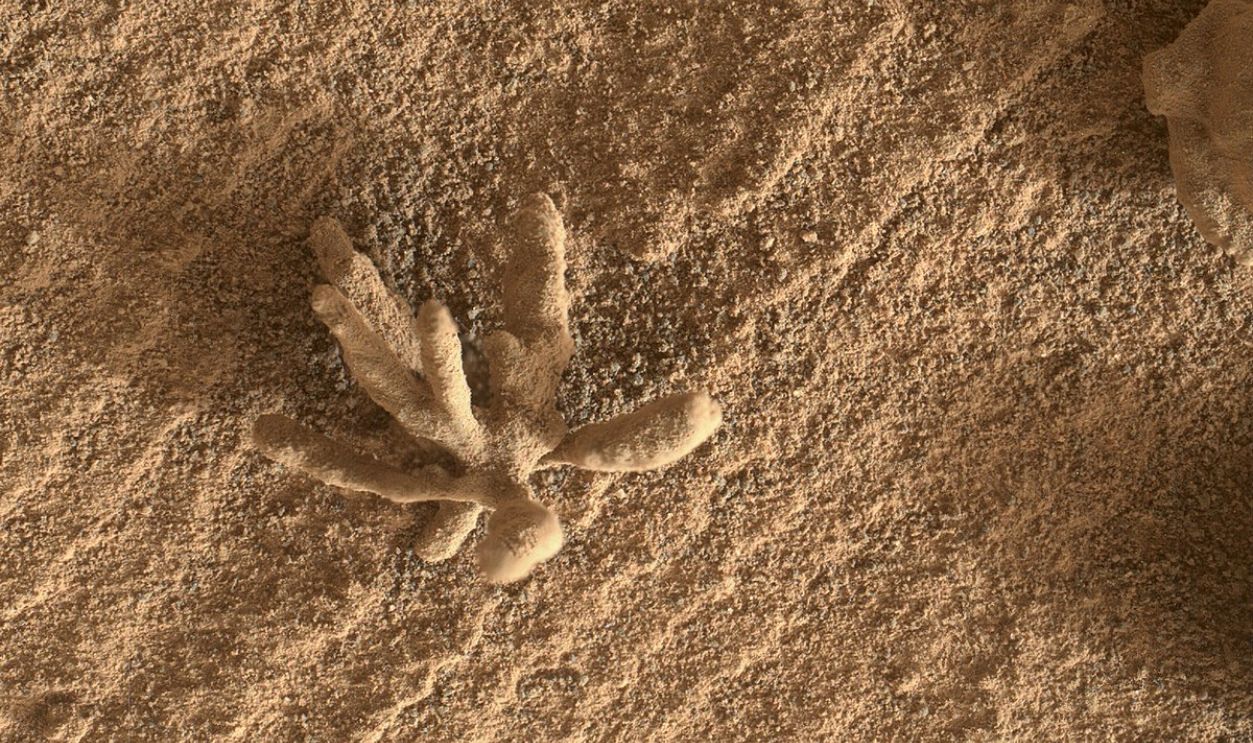
The Martian Flower
It looked almost glassy and was unlike the surrounding terrain. In 2013, Curiosity caught a strange, delicate formation later dubbed the Martian flower. The unusual shape was indeed baffling. Scientists later cleared the cloud, explaining that it was likely composed of calcium sulfate pushed up through the bedrock below.
 NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS, Wikimedia Commons
NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS, Wikimedia Commons
The Pyramid Formation
Its triangular shape led many to call it a Martian pyramid when Curiosity photographed the sharply angled rock in 2015. The formation stood about 1.5 meters tall. NASA’s response? It was joint fractures and slow erosion that could naturally carve symmetry into solid Martian stone over time.
The Cannonball
Near Fram Crater in 2004, Opportunity spotted a small, nearly perfect sphere sitting on the surface. It measured approximately 1.2 inches across. After assessment, it was identified as a hematite concretion—a type of concretion that forms in watery conditions. Its smooth roundness stood out in the jagged Martian geography.
 NASA Hubble Space Telescope, Wikimedia Commons
NASA Hubble Space Telescope, Wikimedia Commons
The Human Bone Illusion
In 2014, a photo showing a long rock stirred social media with claims of a Martian femur. NASA, however, clarified that the shape came from natural erosion. The rock looked convincingly bone-like, but to date, no fossils or skeletal evidence have ever been found on Mars.
 Liangtai Lin, Wikimedia Commons
Liangtai Lin, Wikimedia Commons
The Donut Rock
On Sol 3540, Opportunity’s camera picked up a strange new rock that hadn’t been in earlier images. It had a white rim with a dark red center and resembled a donut. Scientists believe the rover’s wheels flipped it. Later tests provided more information, indicating that it was just high levels of sulfur and manganese.
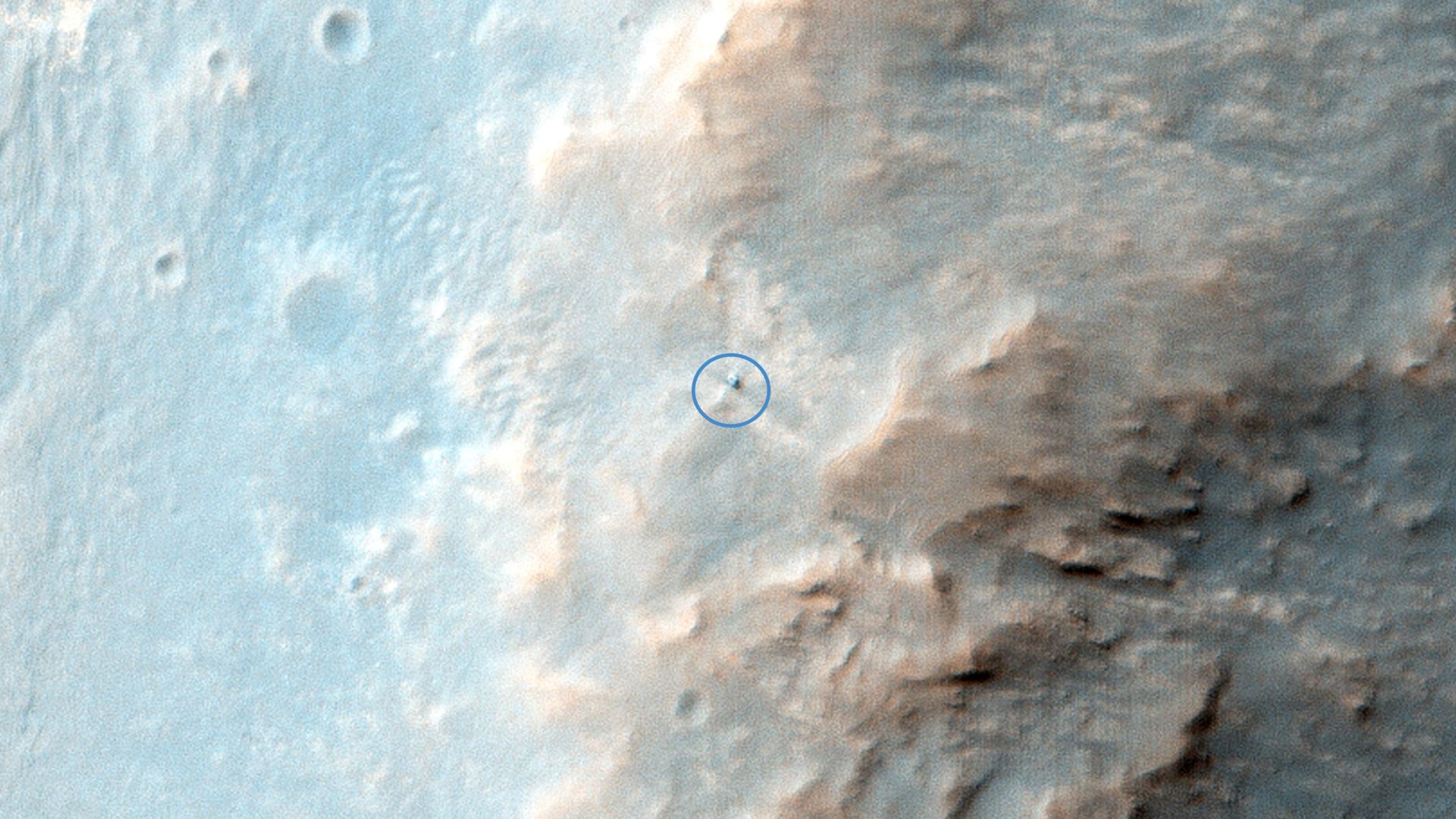 NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona, Wikimedia Commons
NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona, Wikimedia Commons
The Parachute Debris
Perseverance, while on its mission, captured a vivid scene in April 2021 as it traveled through Jezero Crater. Bright orange and white panels lay scattered across the ground. These fragments were parachute parts that helped NASA engineers assess how well the rover’s descent system handled the Martian atmosphere.
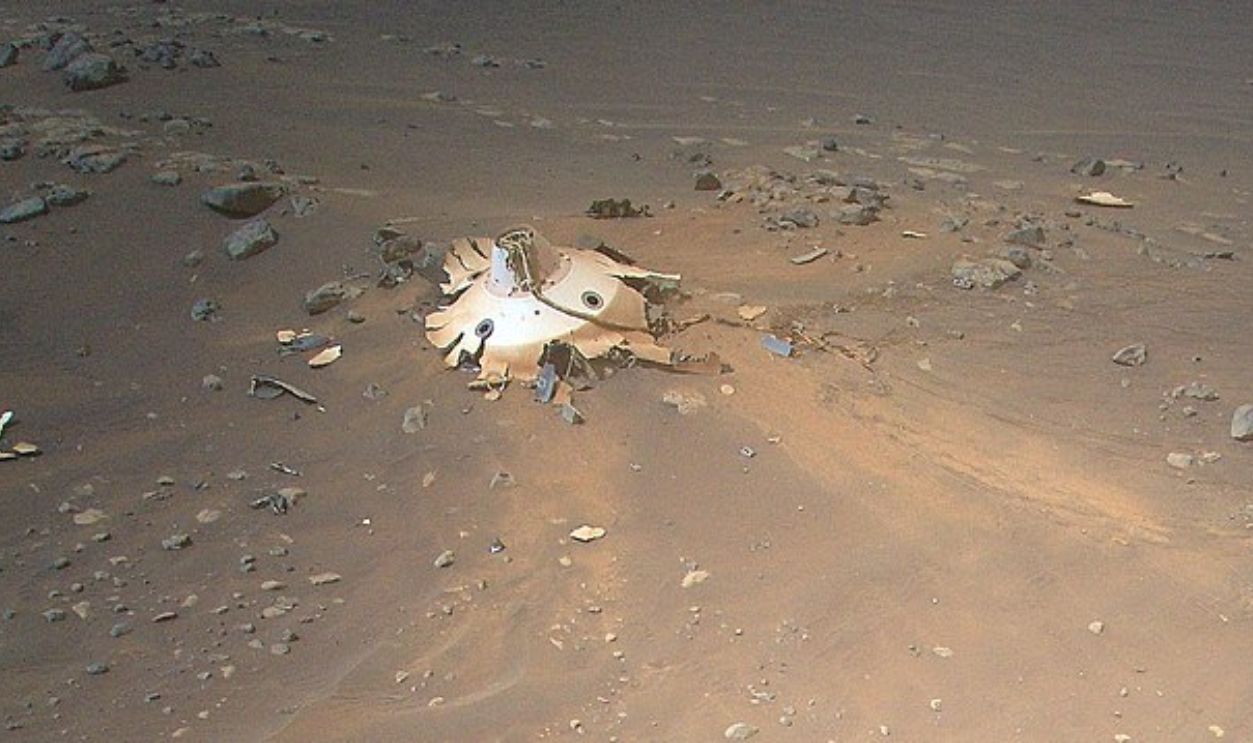 NASA/JPL-Caltech, Wikimedia Commons
NASA/JPL-Caltech, Wikimedia Commons
The Tower Spire
The structure stood long and upright, its silhouette cutting through the landscape near Vera Rubin Ridge in 2018. To clear the doubts, it was found that this structure wasn’t placed there, but was instead a result of wind erosion. Wind erosion carved away the softer rock, while the spire remained.
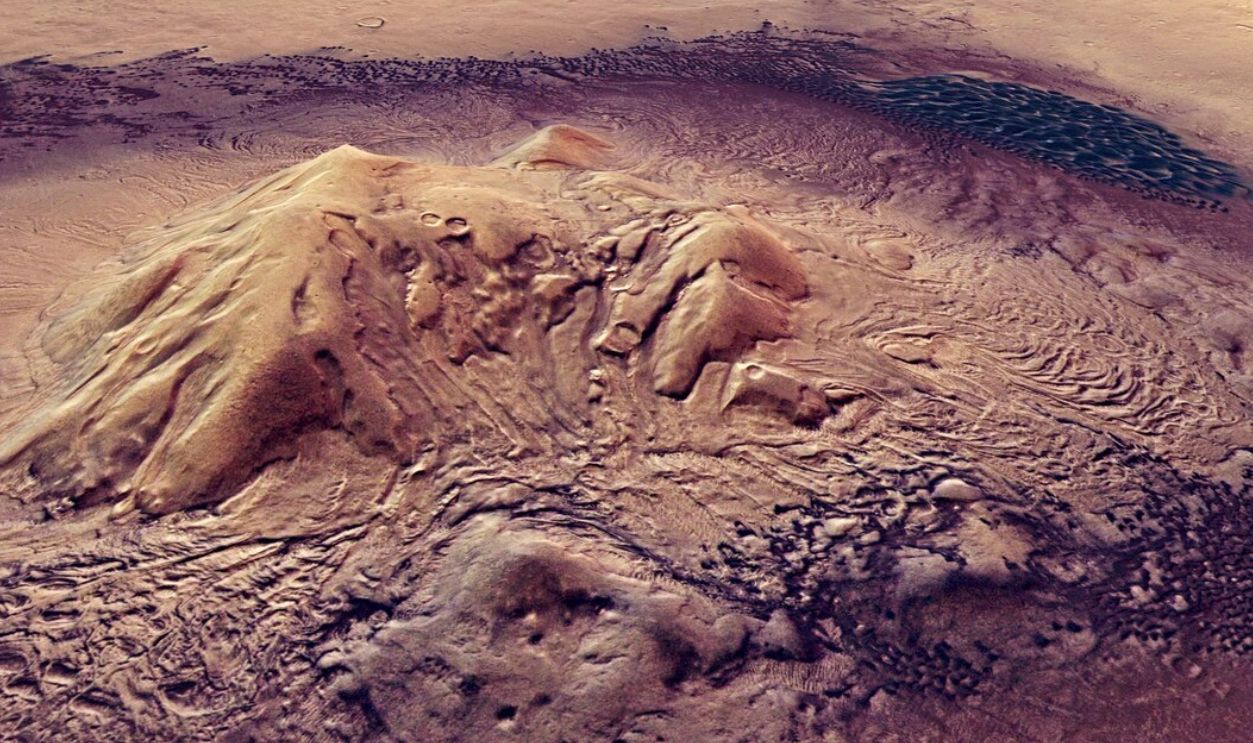 ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, Wikimedia Commons
ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, Wikimedia Commons
The Foil Fragment
Foil on Mars? How? Well, it turns out that the shiny fragment came from Perseverance’s descent stage in 2022, likely displaced by Martian winds. The torn material had been resting near the base of a rock, where its reflective surface stood out sharply against the dull terrain.
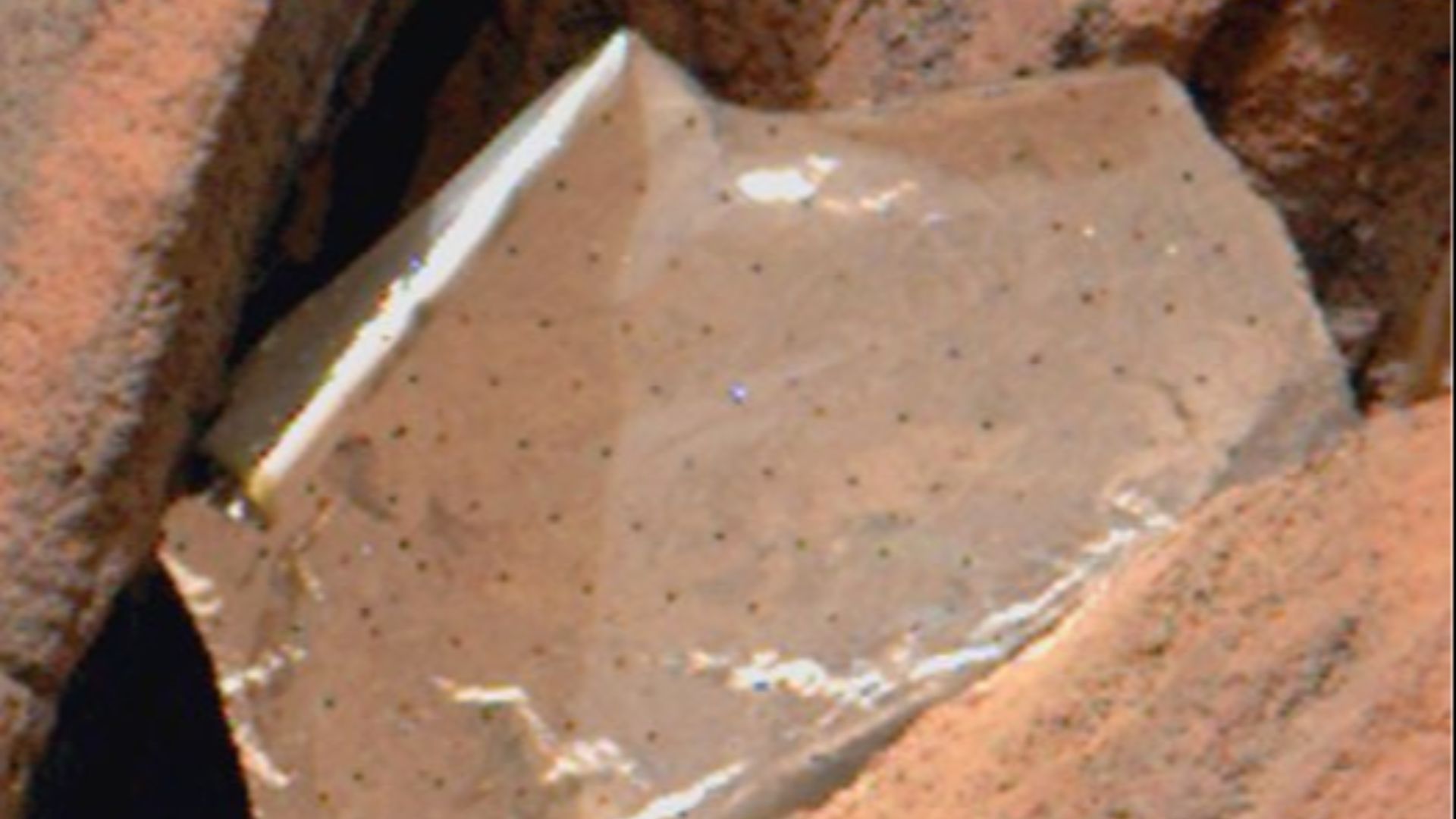 NASA/JPL-Caltech, Wikimedia Commons
NASA/JPL-Caltech, Wikimedia Commons
The Meteorite Fragment
Do you remember the first meteorite confirmed on another planet? Opportunity found it in 2005 and dubbed it Heat Shield Rock. Its pitted surface revealed signs of entry through the atmosphere. Later analysis confirmed it wasn’t Martian—a historic discovery that prompts further interplanetary exploration.
The Shadow Of Ingenuity
The image, taken in April 2021, showed a strange silhouette stretching across the surface. Ingenuity’s shadow appeared almost alien due to its narrow frame and rotor blades. As the first aircraft to fly on another world, it stood as a symbol of creative engineering and human ambition.
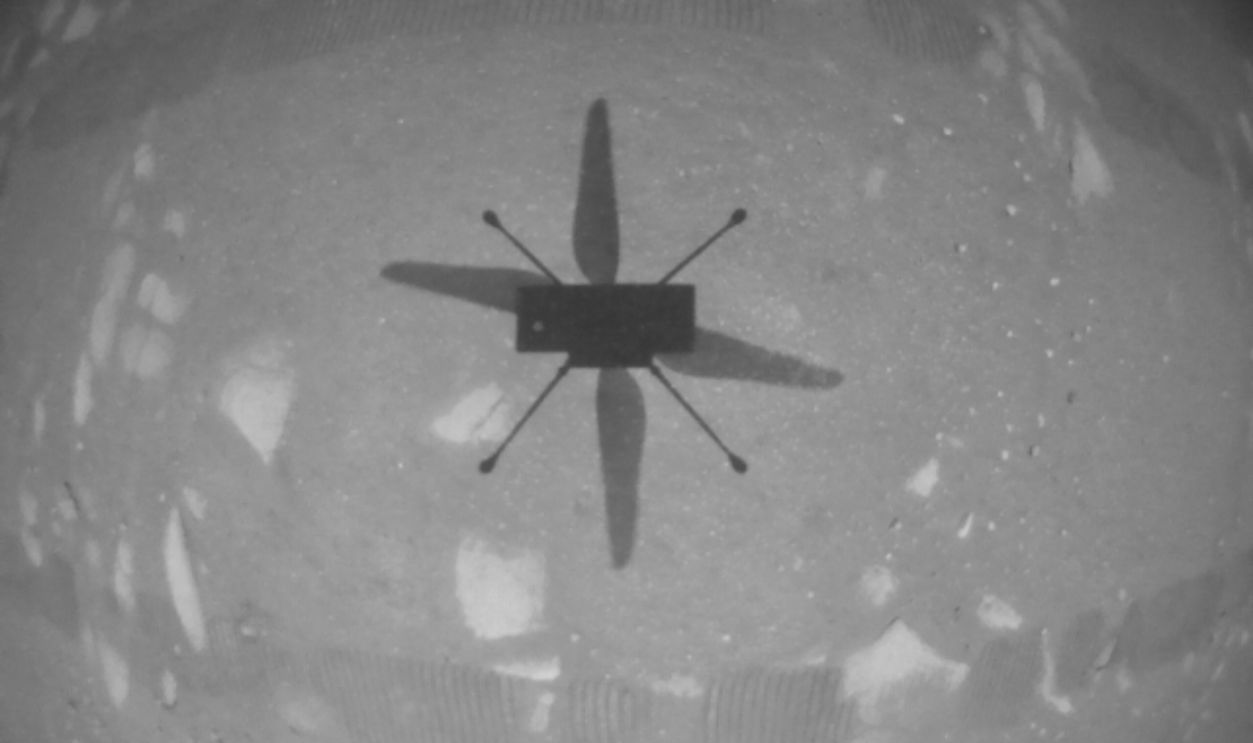 NASA/JPL-Caltech, Wikimedia Commons
NASA/JPL-Caltech, Wikimedia Commons
Martian Blueberries
Small and spherical, these curious formations were composed of hematite, a mineral rich in iron. Scientists believe they formed through water-related geochemical reactions. When Opportunity found them in 2004, it gave scientists even more confidence that water had once been a real force on ancient Mars.
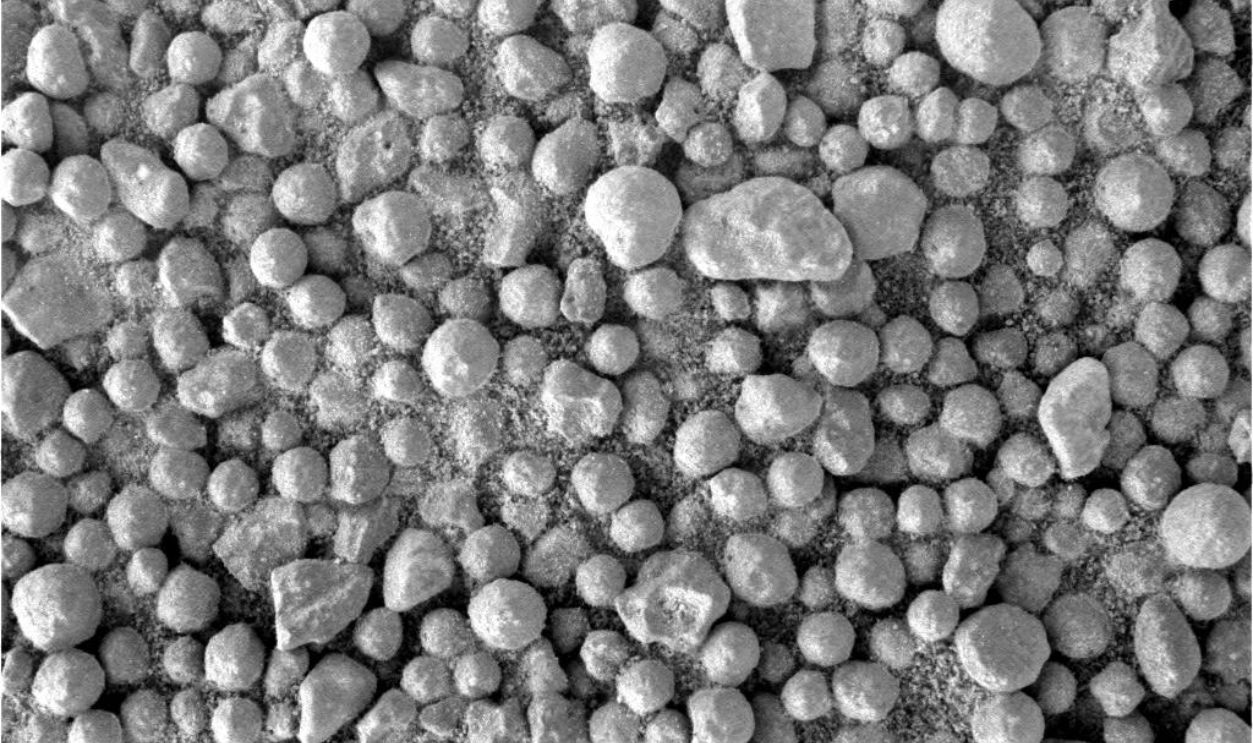 Opportunity rover's Microscopic Imager team, Wikimedia Commons
Opportunity rover's Microscopic Imager team, Wikimedia Commons
Ghost Dunes
Long ago, volcanic ash or sediment likely buried Martian sand dunes, protecting them from erosion. Seen in detailed images from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, the crescent-shaped marks left behind are traces of ancient winds. They are faint, yes, but they are lasting signs of a once-active atmosphere.
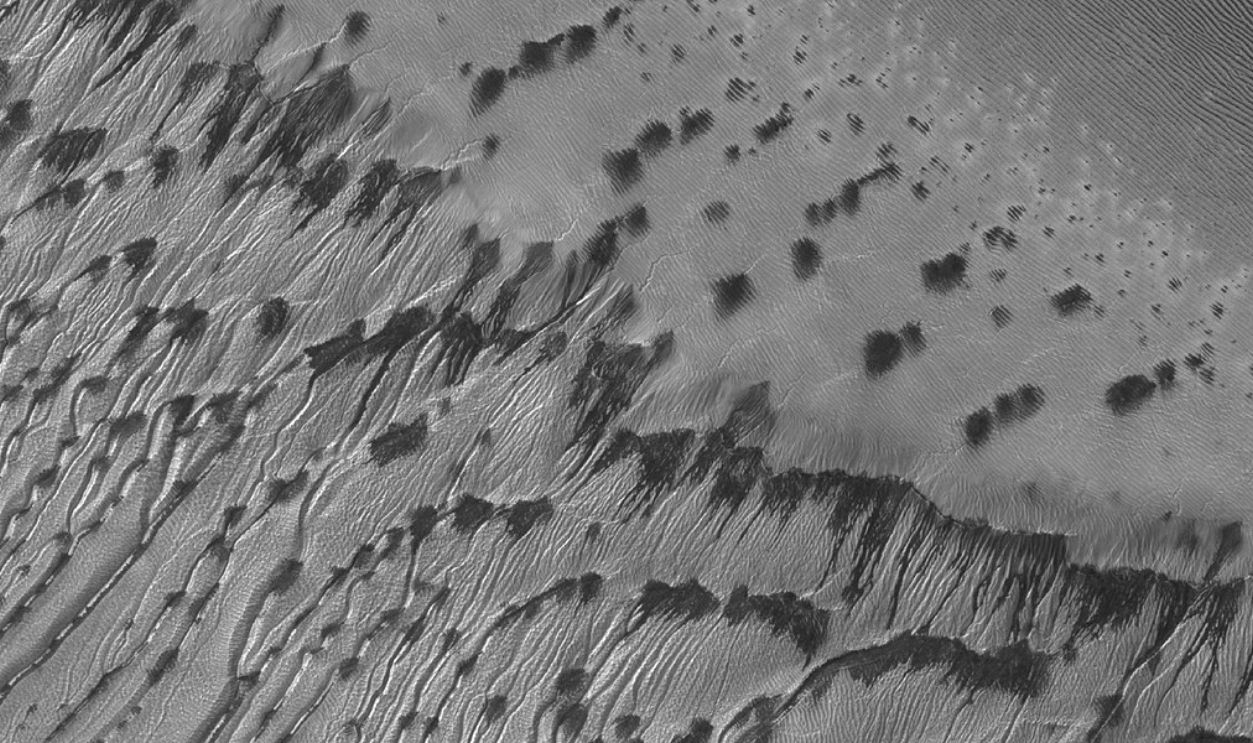 Jim Secosky modified NASA image NASA/JPL/University of Arizona, Wikimedia Commons
Jim Secosky modified NASA image NASA/JPL/University of Arizona, Wikimedia Commons
Recurring Slope Lineae (RSL)
HiRISE images from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter showed dark streaks that came and went on Martian hillsides. At first, people thought it was water, but now it looks more like dry sediment sliding downhill. Even so, some scientists think there still might be moisture hiding below the surface.
 UAHiRISE (NASA), Wikimedia Commons
UAHiRISE (NASA), Wikimedia Commons
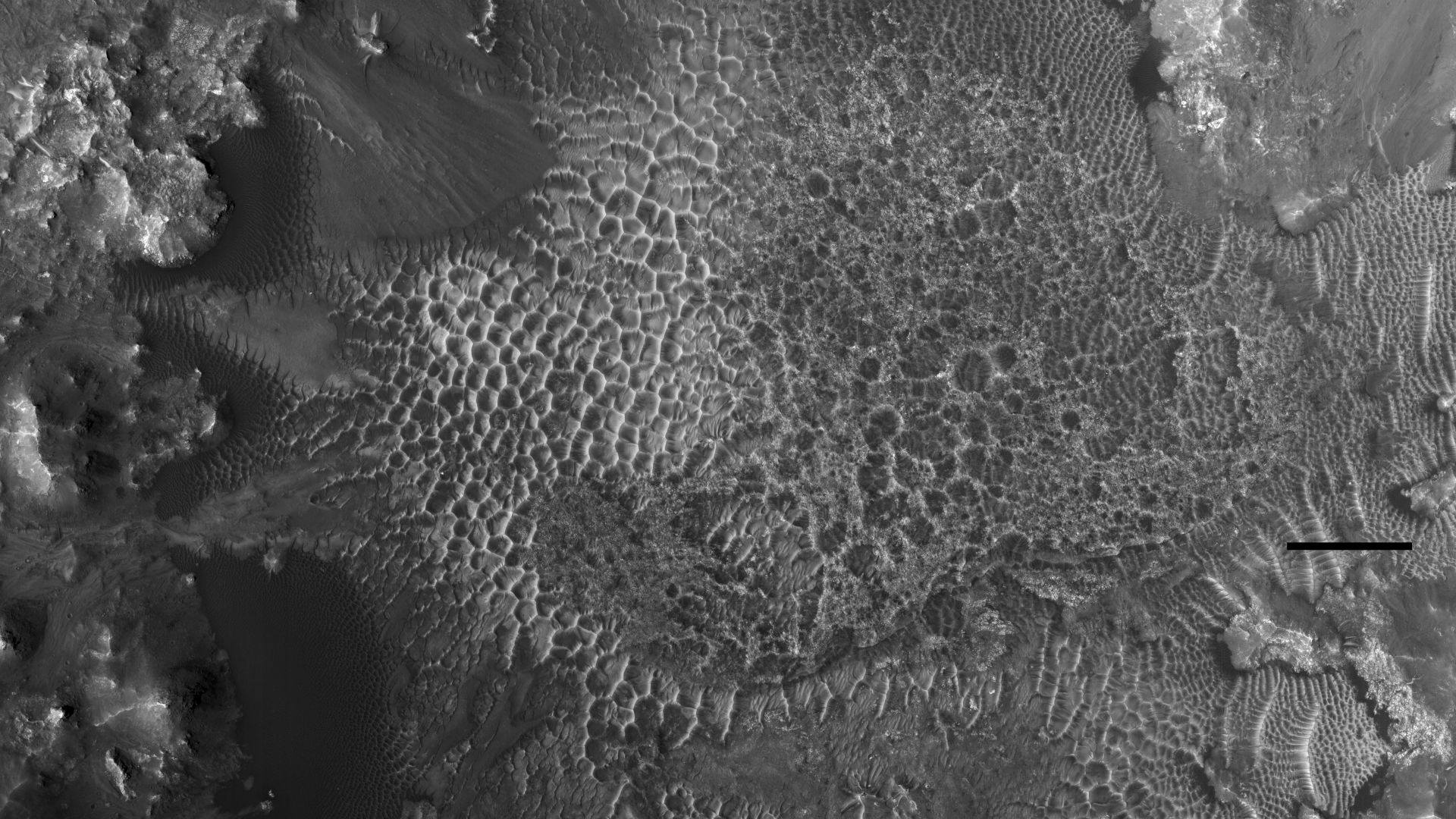
Honeycomb Terrain
This terrain features polygon-shaped textures that resemble a honeycomb. Experts suggest that this also indicates the presence of water on Mars, which leads to freeze-thaw cycles. The second theory posits that the salt crust fractures under varying Martian conditions—the third one suggests fluctuating climates or ancient processes beneath the surface.
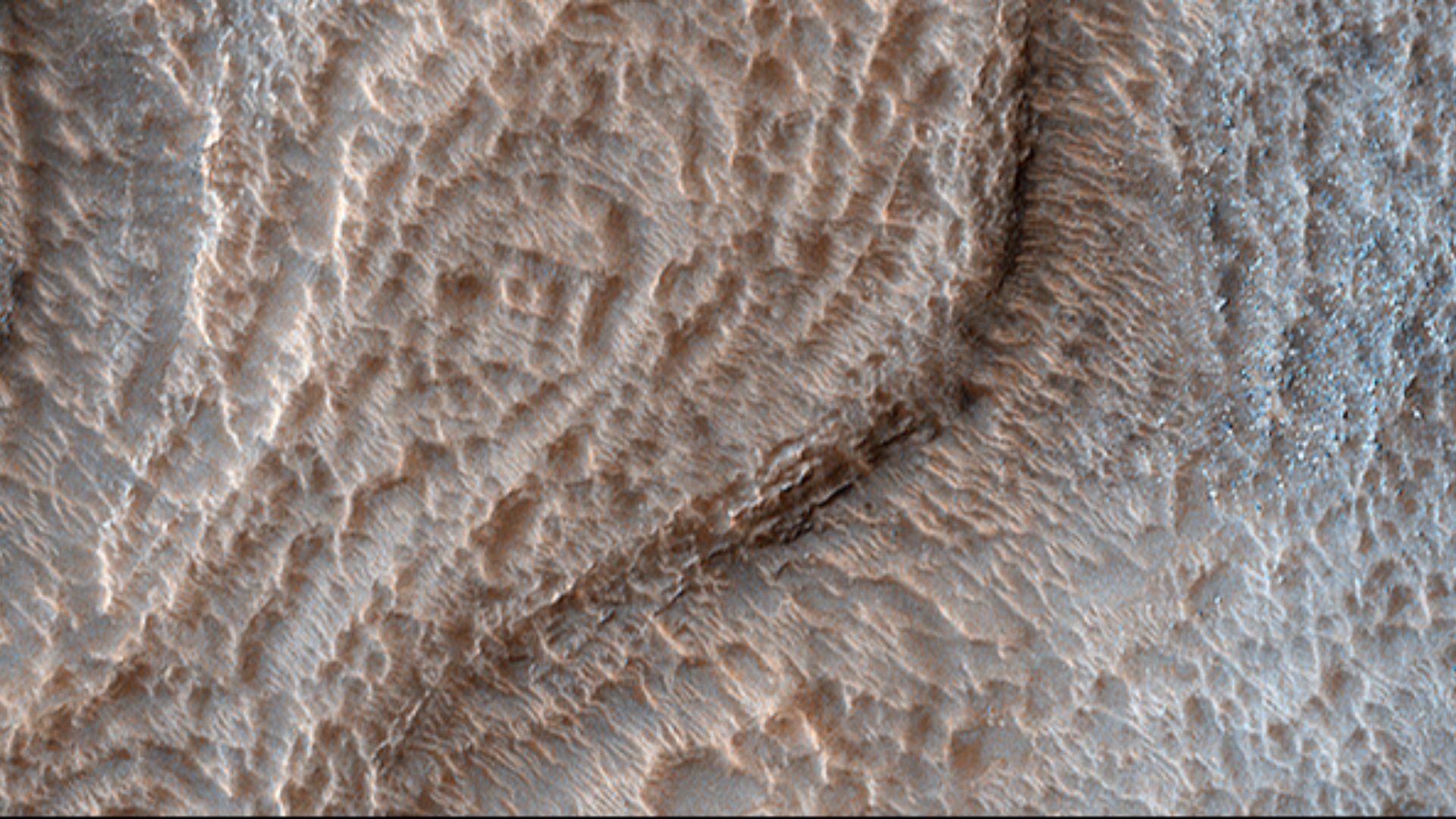 Jim Secosky modified NASA image. NASA/JPL/University of Arizona, Wikimedia Commons
Jim Secosky modified NASA image. NASA/JPL/University of Arizona, Wikimedia Commons
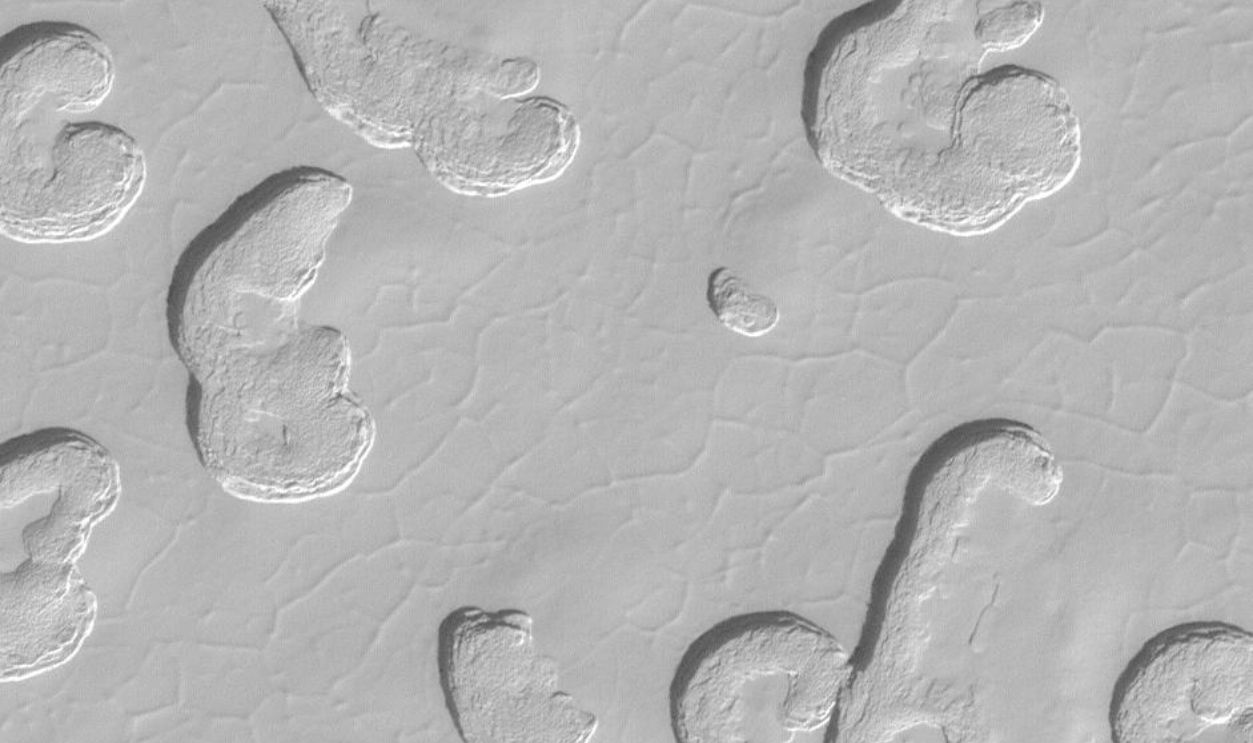
Swiss Cheese Terrain
Shifting around holes in Mars's icy surface indicates that change is underway, as observed through NASA's cameras. Patterns in the ice appear when frozen carbon dioxide turns directly into gas. Beneath the frozen layers, the planet's South Pole appears to harbor unexpected activity.
 Jim Secosky modified nasa image by Wikimedia Commons
Jim Secosky modified nasa image by Wikimedia Commons
Freya Castle Formation
Discovered by the Perseverance rover in 2024, this geological structure stood out with its unusual layered texture. Its fortress-like shape soon earned it the nickname "Freya Castle". Early on, scientists thought it might have formed through volcanic or metamorphic processes, which would explain its distinct look. Confirmation’s yet to come.
Bouncing Boulder Tracks
Using terrain mapping, researchers measured the displacement and length of tracks left by moving boulders. These marks, visible on Martian slopes in orbiter images, indicate paths left by rolling rocks. Experts think the motion resulted from seismic tremors or shockwaves from a distant impact event.
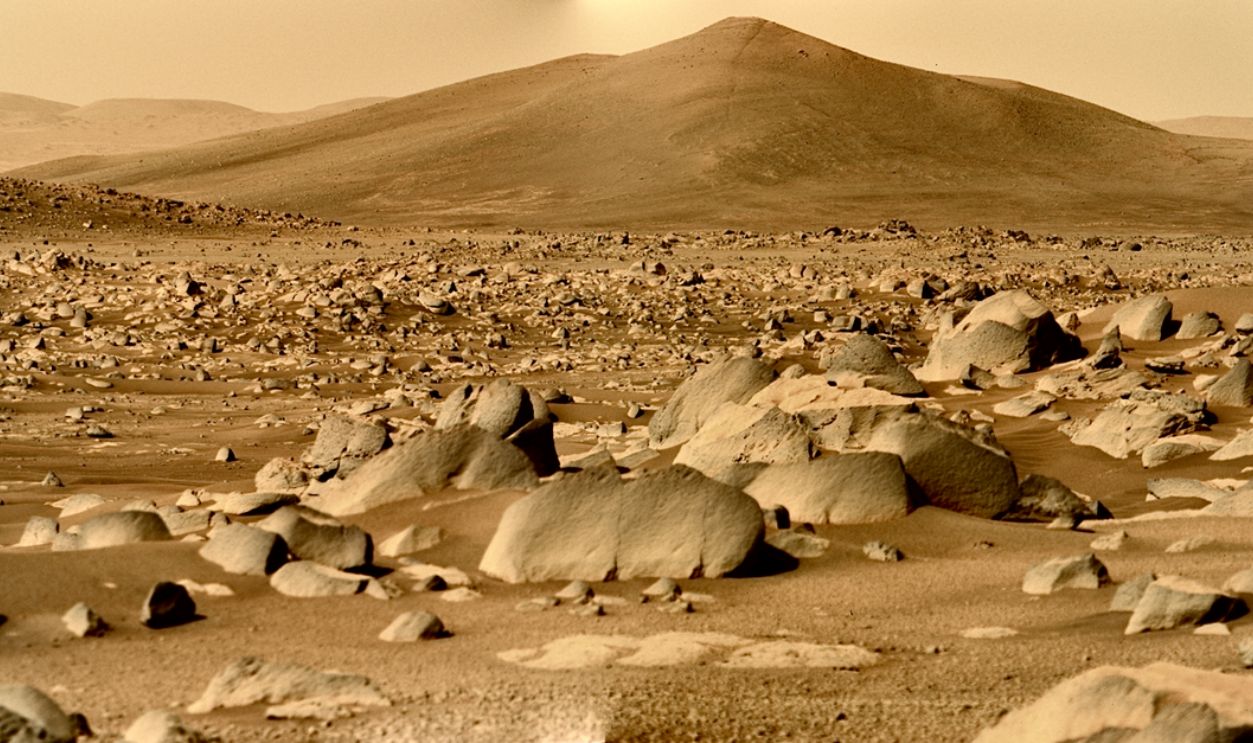 Raziel Abulafia, CCO, Wikimedia Commons
Raziel Abulafia, CCO, Wikimedia Commons
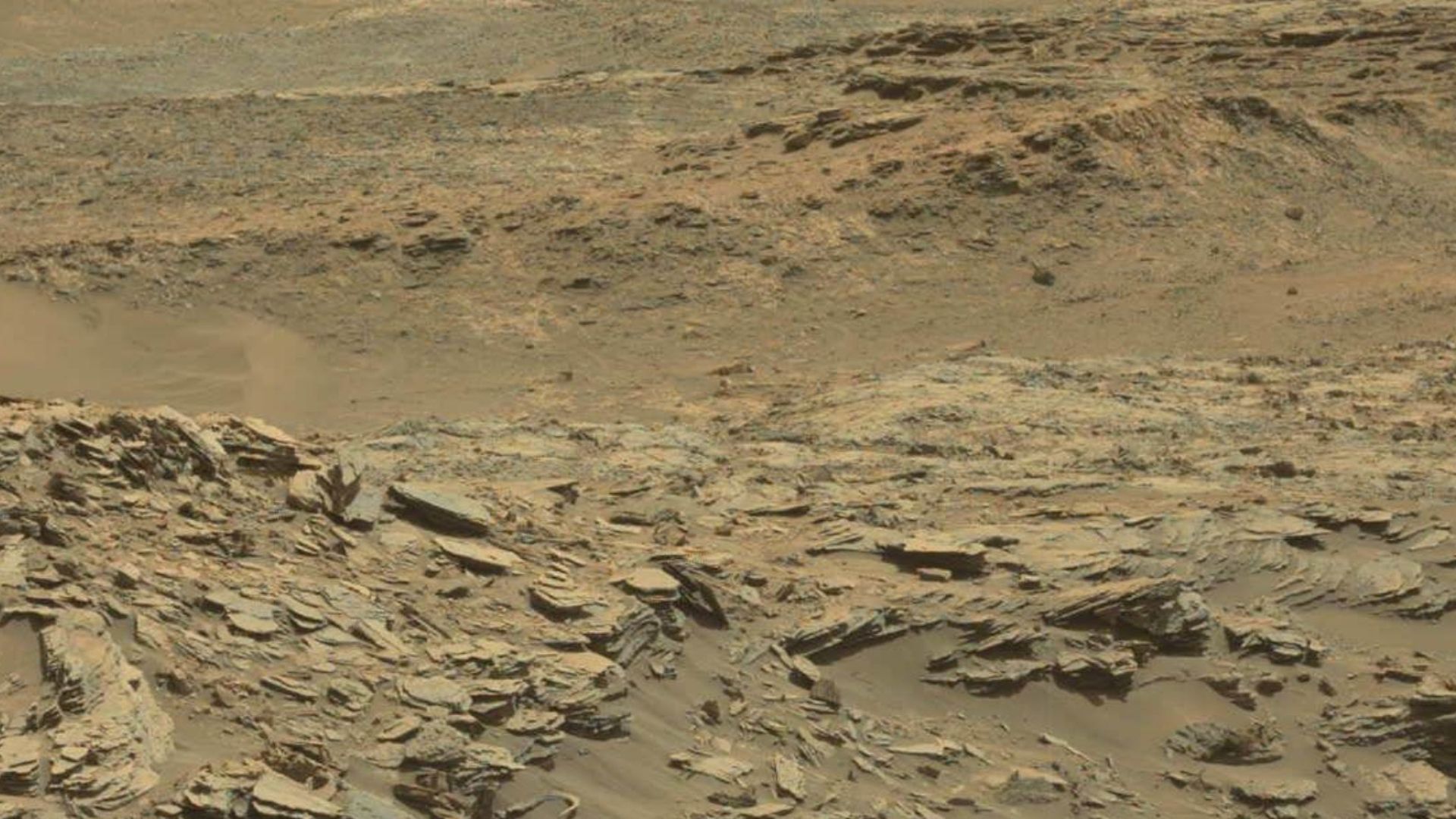
Mud Cracks
Curiosity came across dried-up mud cracks shaped like hexagons—almost like pieces of a puzzle. The pattern likely formed after repeated cycles of wet and dry conditions, much like puddles drying up on Earth. This is yet another strong hint that water once covered this area long ago.
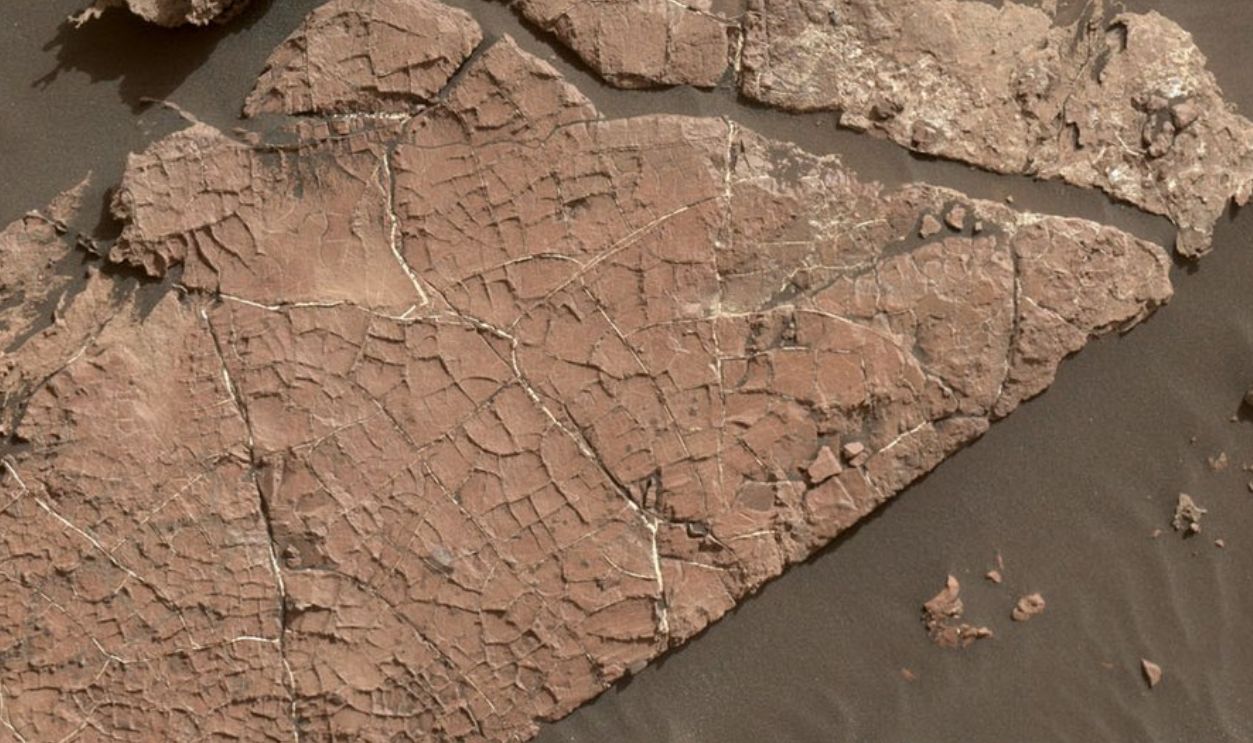 Jim Secosky selected NASA image. NASA/JPLJPL-Caltech/MSSS, Wikimedia Commons
Jim Secosky selected NASA image. NASA/JPLJPL-Caltech/MSSS, Wikimedia Commons
The Jagged Metal Fragment
Curiosity spotted the shiny fragment near a crater in 2012, its jagged edge catching the sunlight as it glinted on the ground. Scientists used ChemCam to scan it closely, and spectral results showed a high nickel content, which suggested that the object was likely a meteorite.
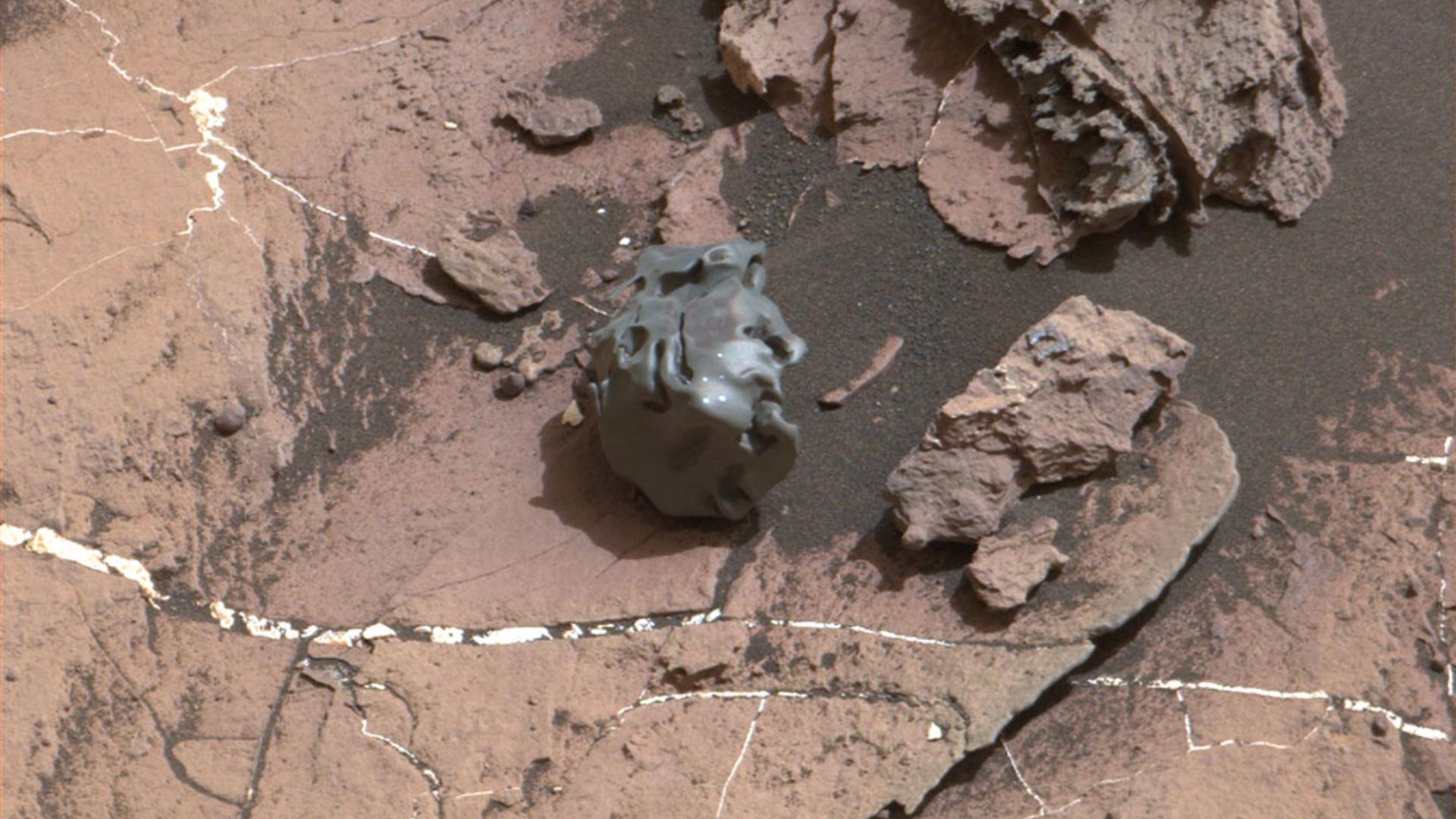 NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS, Wikimedia Commons
NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS, Wikimedia Commons
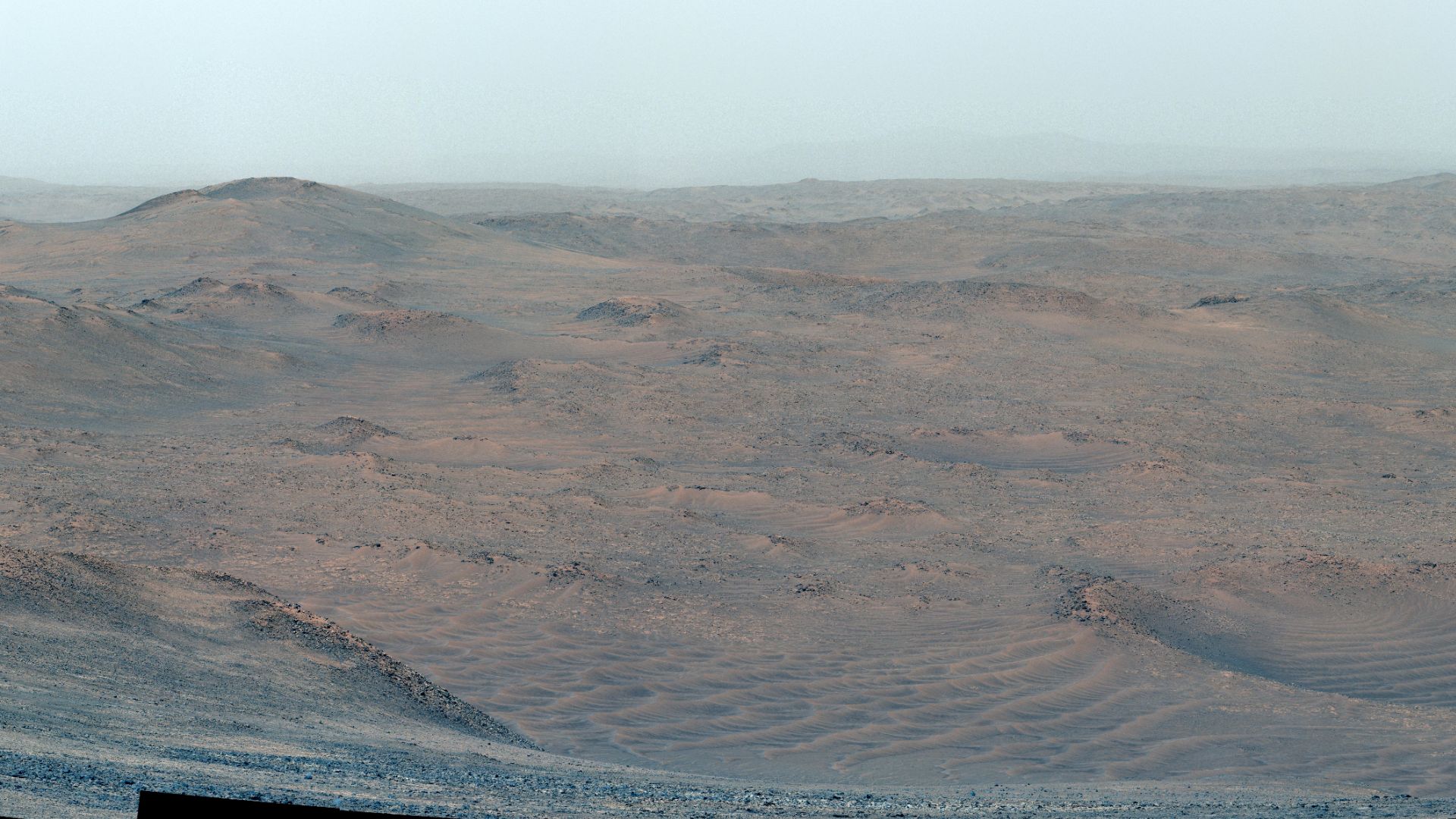
Layered Buttes (Murray Formation)
Apparently, Mars once had moving water and shifting weather patterns shaping this beautiful, strange terrain—at least that's what the signs suggest. The tall rocky towers, or buttes, show thin layers stacked like a cake. Curiosity spotted them and found slow deposits from ancient lakes and winds.
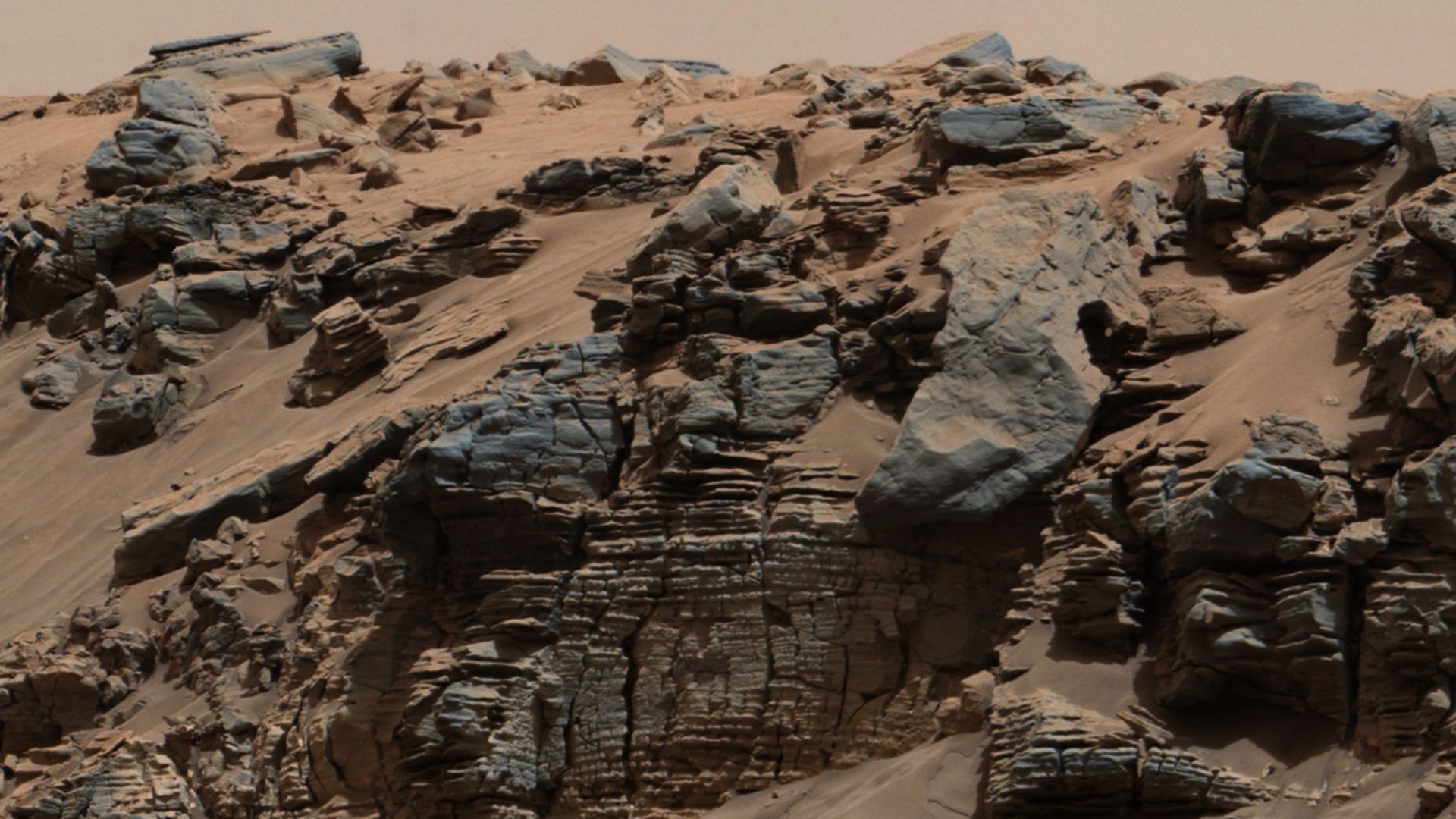 NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS, Wikimedia Commons
NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS, Wikimedia Commons
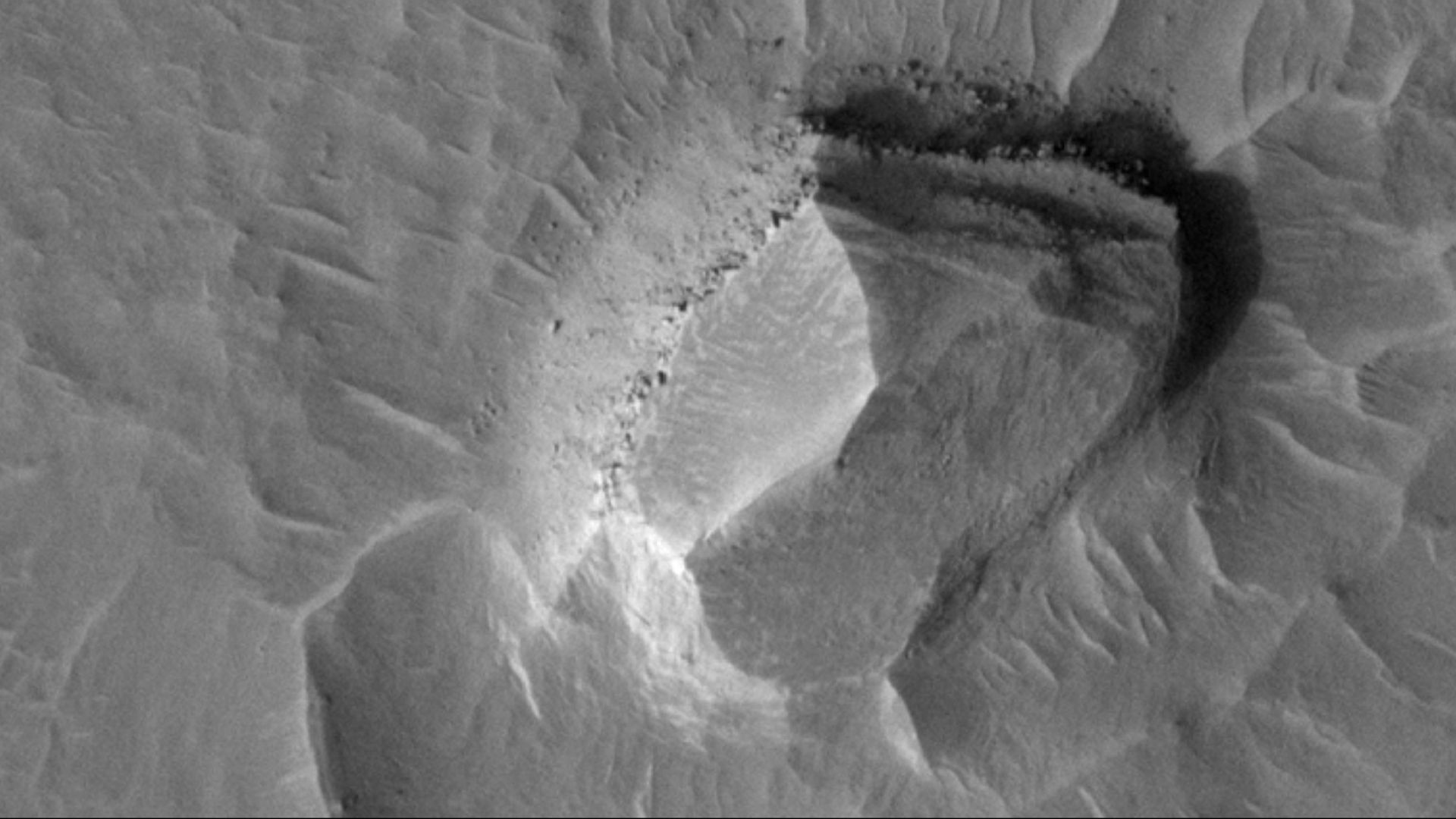
Bear Face Rock
A 2022 photo from NASA’s HiRISE camera stirred excitement for capturing what many saw as a teddy bear’s face. The visual effect, shaped by craters and erosion, fooled the brain into recognizing something familiar; a classic case of pareidolia seen on the Martian surface.