A discovery that changed Egyptology
A sealed doorway in 1922 opened far more than a tomb. It revived a young ruler’s world and reshaped how ancient Egypt is understood. More than 100 years later, the life and death of Tutankhamun still raise questions.

A Forgotten Boy King Returned To The Modern World
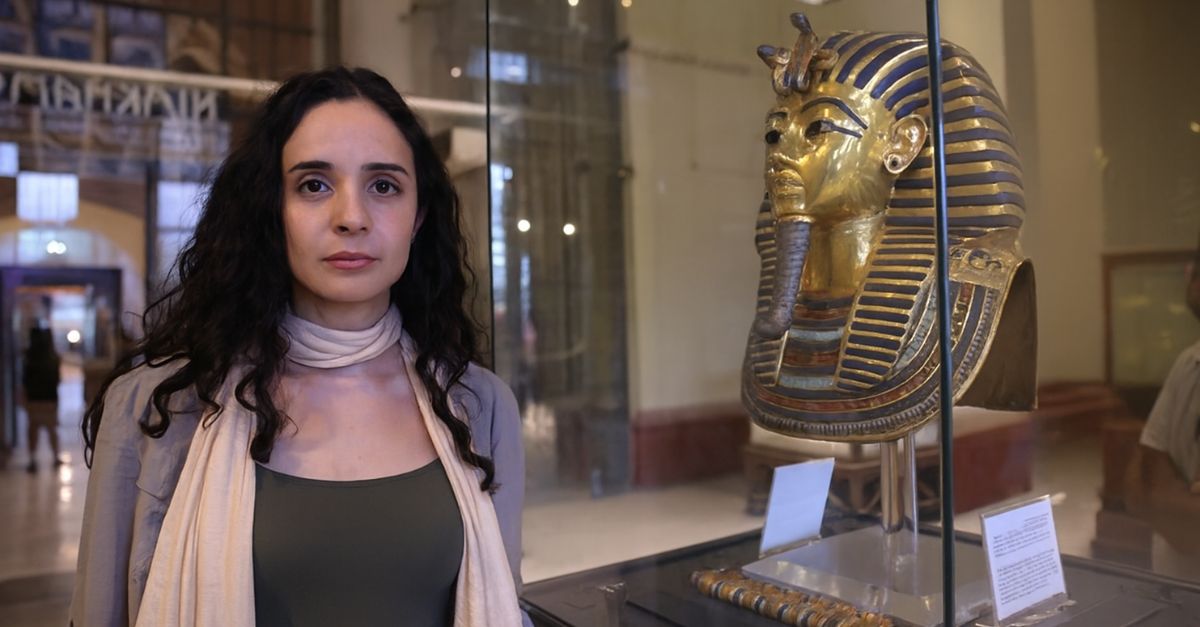
Tutankhamun lingered in obscurity for millennia until Howard Carter uncovered his nearly intact tomb in 1922. The discovery reintroduced a young pharaoh whose brief reign left faint political records but astonishing material evidence. That moment reshaped global interest in ancient Egypt and elevated archaeology into a disciplined science.
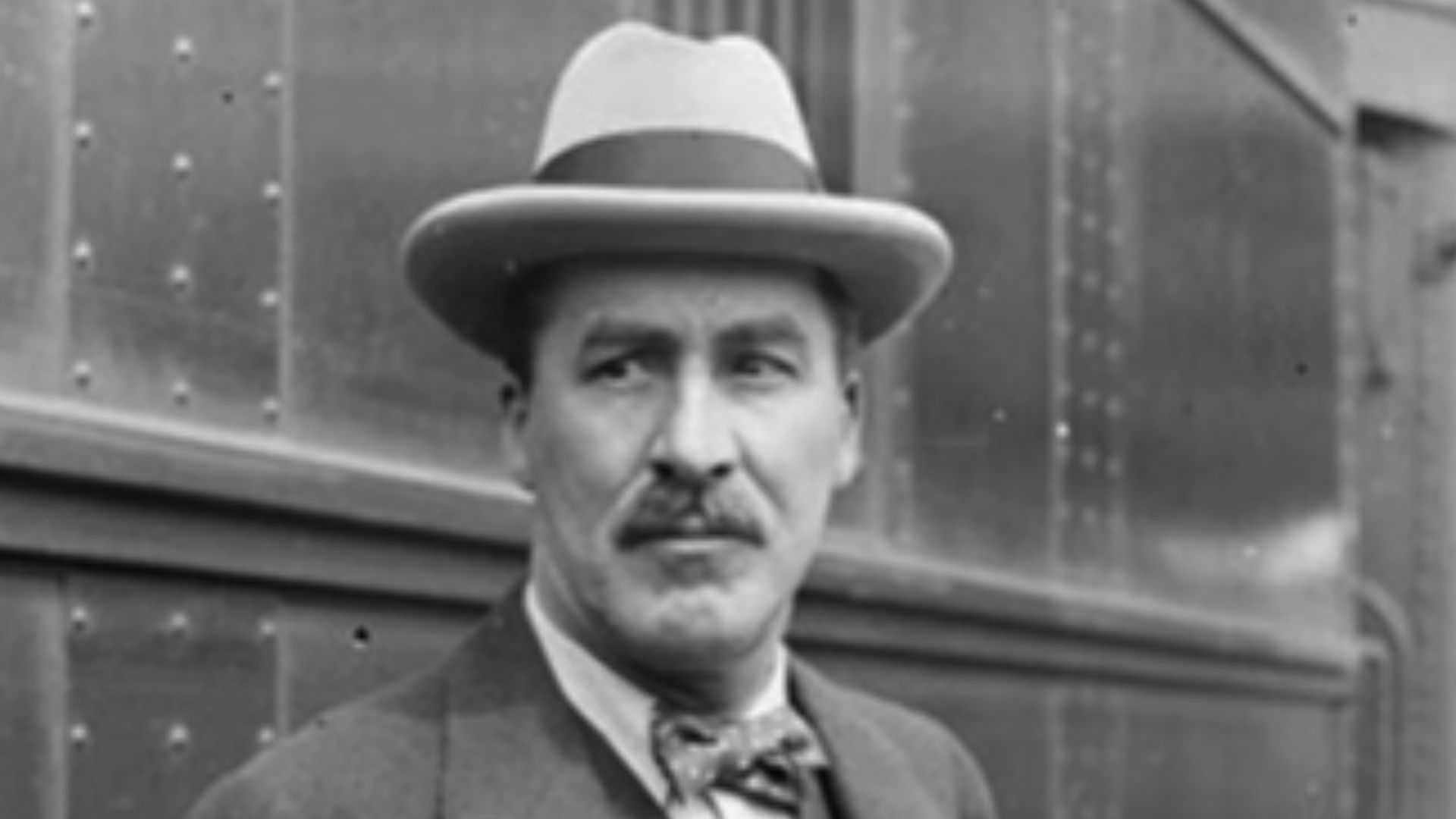 Chicago Daily News, Inc., photographer, Wikimedia Commons
Chicago Daily News, Inc., photographer, Wikimedia Commons
From A Dynasty Marked By Upheaval And Uncertain Beginnings
The young king emerged from a royal family going through instability created by Akhenaten’s religious changes. DNA studies confirm Akhenaten as his father and a close relative as his mother, revealing a dynasty strained by intermarriage. These conditions produced both political vulnerability and the fragile health observed in his preserved remains.
And A Childhood Framed By Akhenaten’s Radical Vision
Tutankhamun spent his early years within a court shaped by Aten worship, where traditional temples lost influence and royal culture shifted dramatically. Growing up in this experimental capital introduced him to beliefs unlike earlier dynasties, setting the stage for later decisions restoring long-standing customs across Egypt’s spiritual world.
The Meaning Behind The Name Tutankhaten
His birth name, Tutankhaten, signified “Living Image of Aten” and reflected his father’s devotion to the sun disk deity. Names carried ideological weight in ancient Egypt, so this title aligned the young prince with Akhenaten’s theological program.
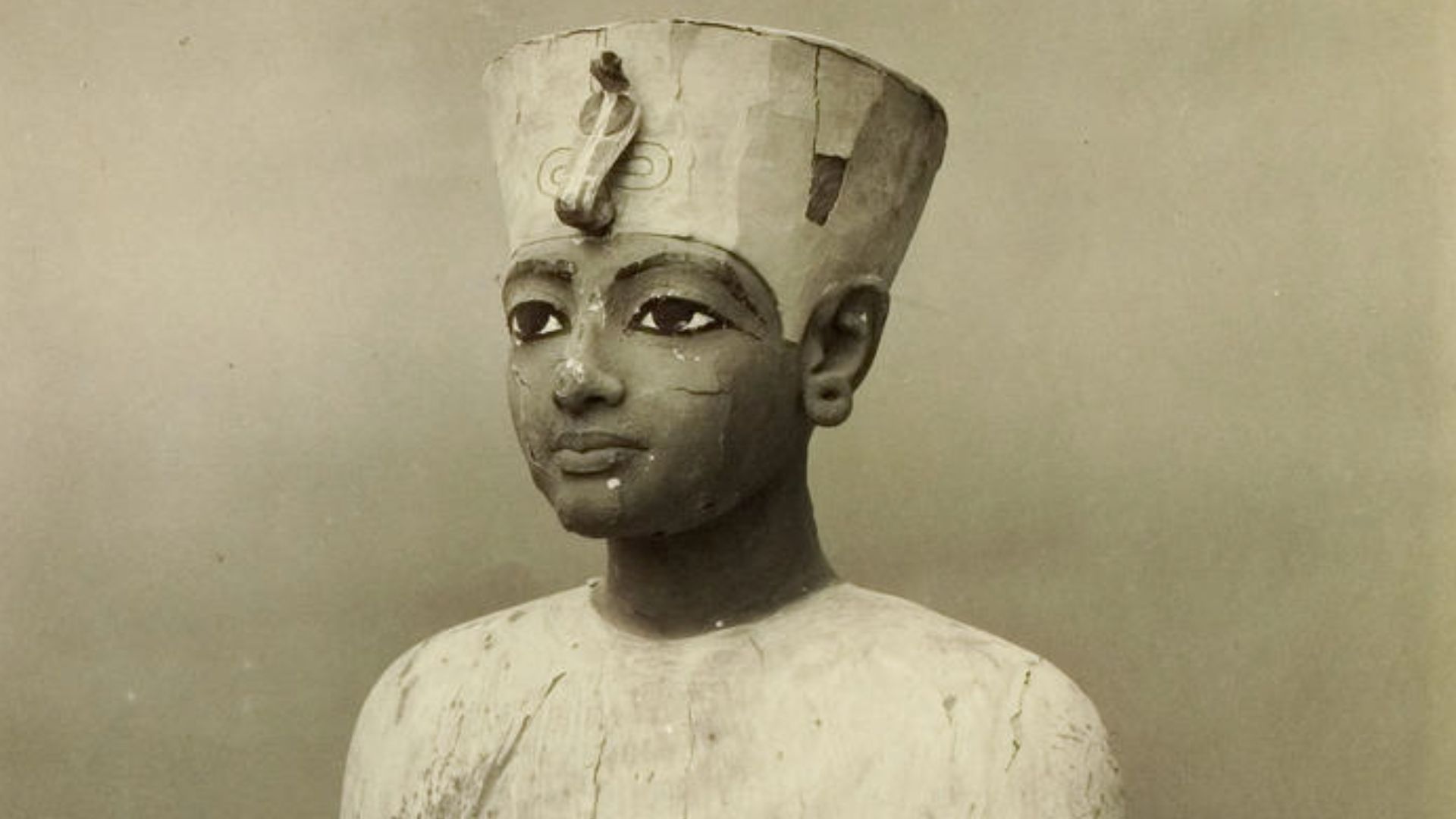 Harry Burton (1879-1940), Wikimedia Commons
Harry Burton (1879-1940), Wikimedia Commons
In A Kingdom Transformed By A Single Sun God
Akhenaten’s elevation of Aten reshaped artistic conventions and disrupted centuries-old religious networks. This overhaul weakened established priesthoods and altered administrative power, and the dramatic shift formed the backdrop of Tutankhaten’s early life.
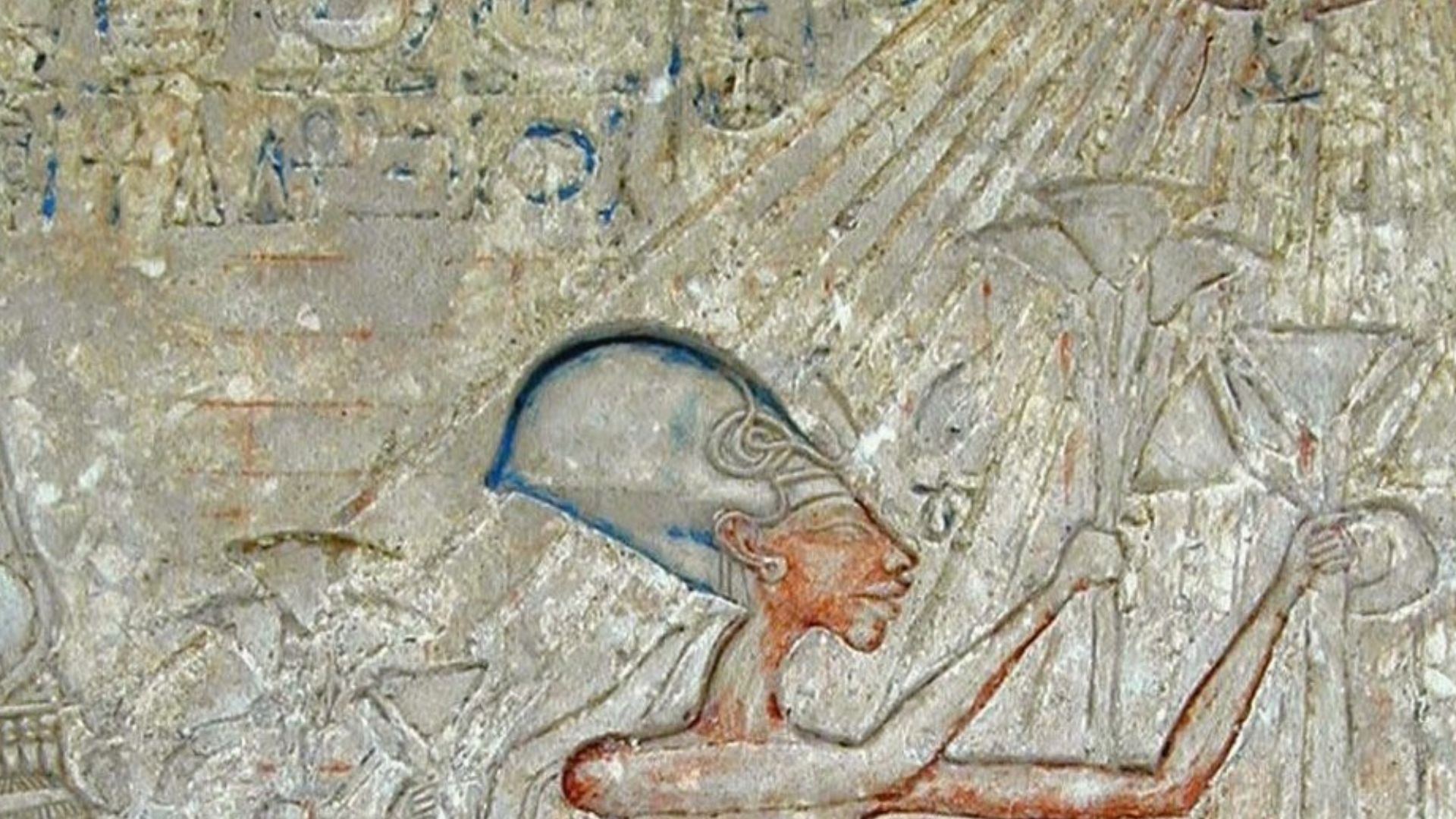 Jean-Pierre Dalbéra from Paris, France, Wikimedia Commons
Jean-Pierre Dalbéra from Paris, France, Wikimedia Commons
He Was Caught Between Two Worlds
After his father’s passing, Tutankhamun inherited a nation divided between Aten ideology and traditional worship. Advisors such as Ay and Horemheb guided him through competing expectations, as his position required balancing loyalty to his father’s legacy with growing pressure to revive earlier spiritual and political frameworks.
The Moment Tutankhaten Became Tutankhamun
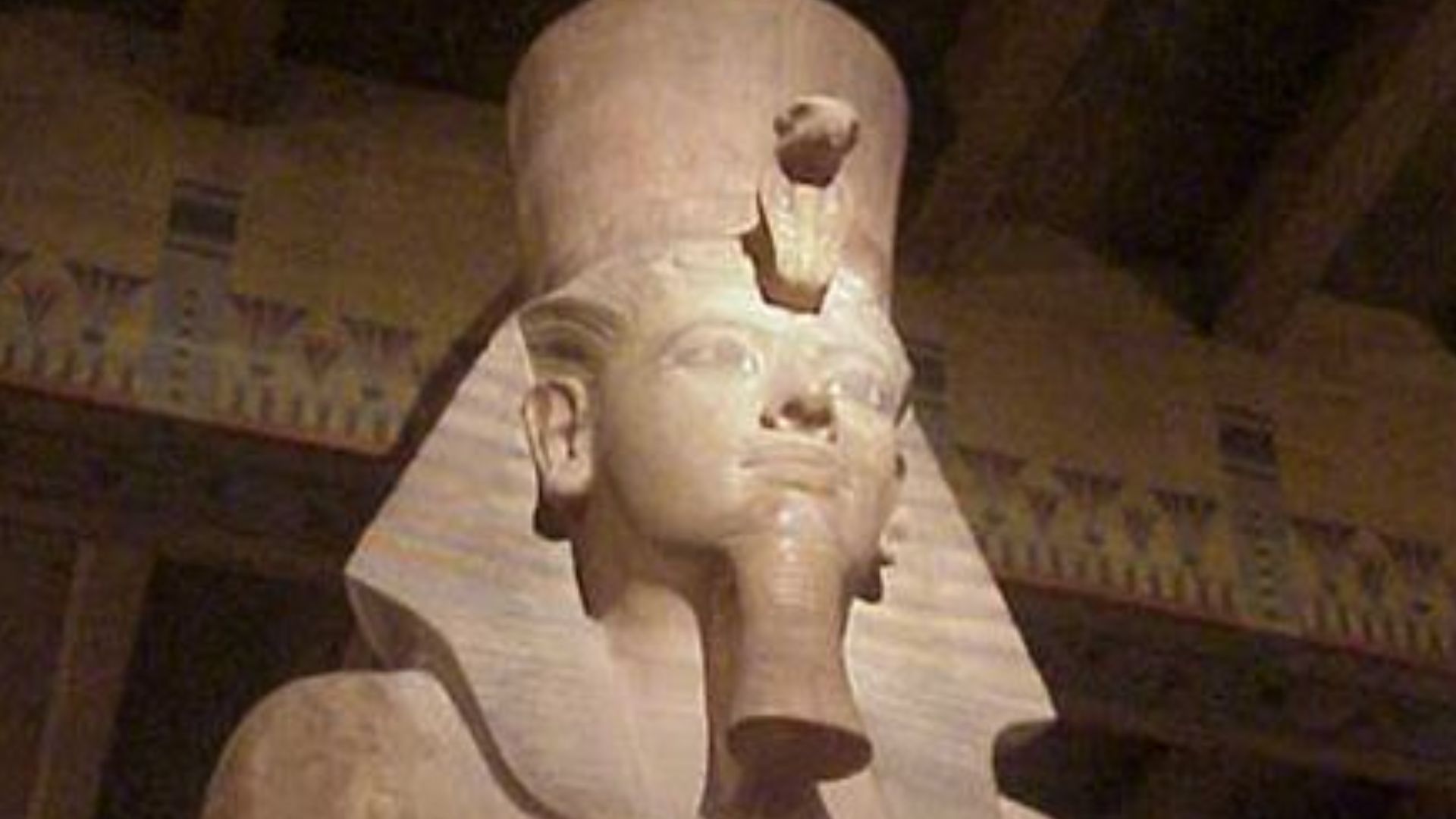
Changing his name to Tutankhamun signaled a deliberate return to Amun’s prominence. The decision restored confidence among the powerful temples marginalized under Akhenaten. This act did more than rebrand a ruler; it marked a national shift toward familiar rituals, renewing bonds between crown, priesthood, and communities unsettled by recent reforms.
What His New Name Signaled To A Troubled Nation
Tutankhamun’s new identity communicated stability during widespread uncertainty. Reestablishing Amun’s clergy revived institutional networks that supported local economies and civic life. The name change functioned as a political message, reassuring Egyptians that long-standing traditions would regain authority.
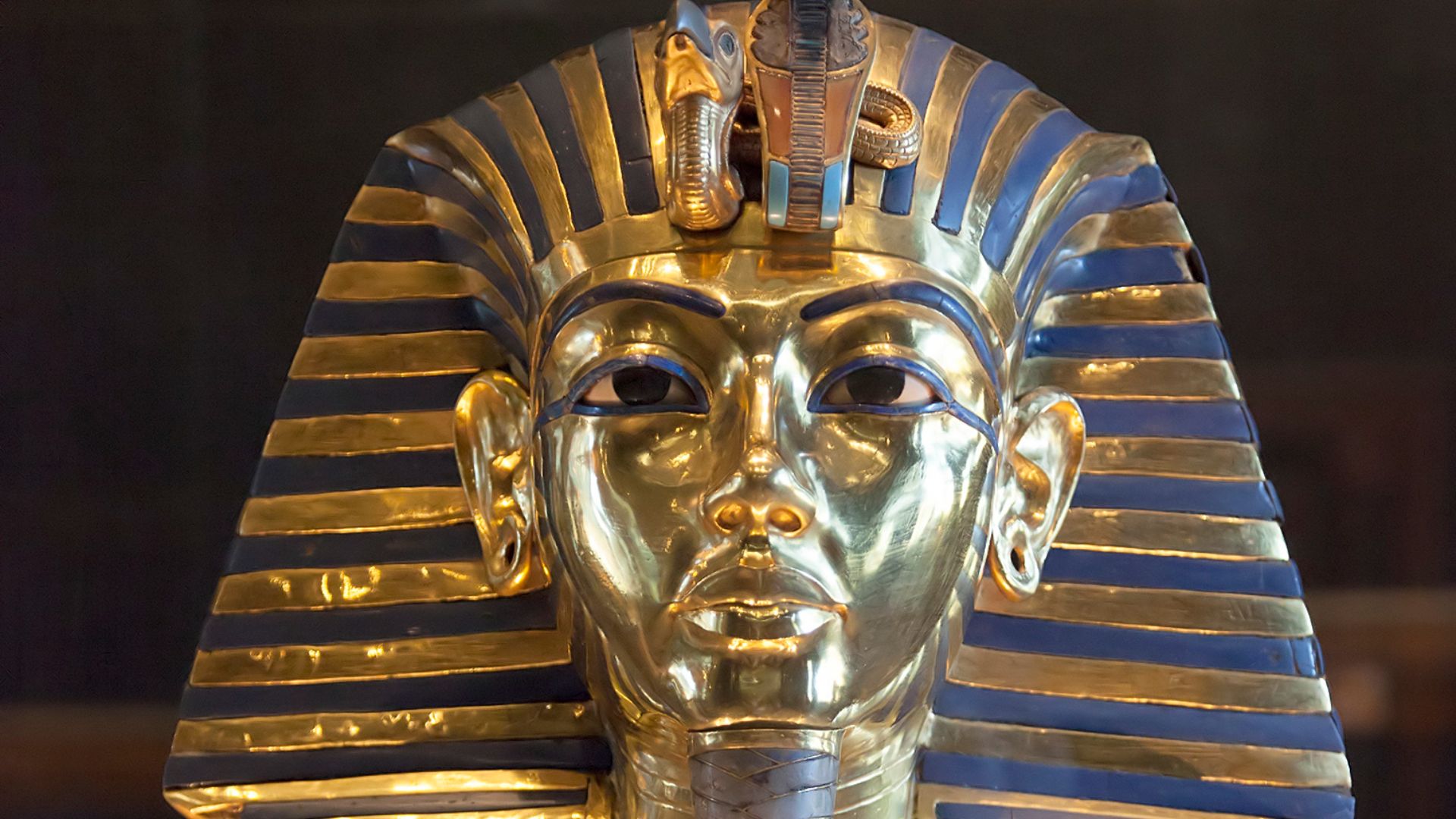 Roland Unger, Wikimedia Commons
Roland Unger, Wikimedia Commons
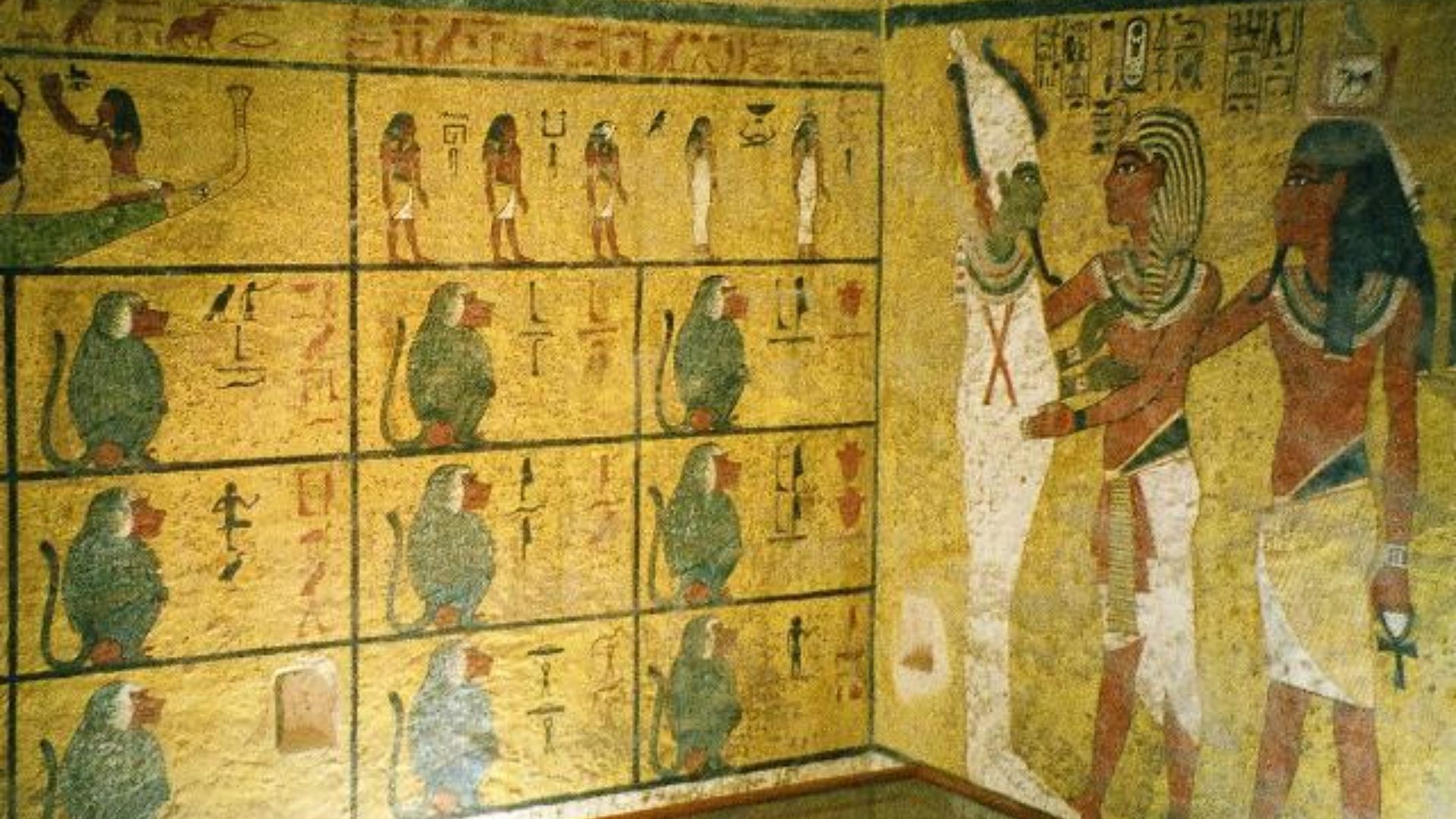
Inside The Daily Life Of Egypt’s Youngest Ruler
Objects from his tomb reveal glimpses of a teenager shaped by privilege and constraint. Fine linens, board games, ceremonial weapons, and numerous walking sticks show both comfort and physical challenges. These items document a ruler managing royal expectations while coping with health limitations.
 Hajor~commonswiki, Wikimedia Commons
Hajor~commonswiki, Wikimedia Commons
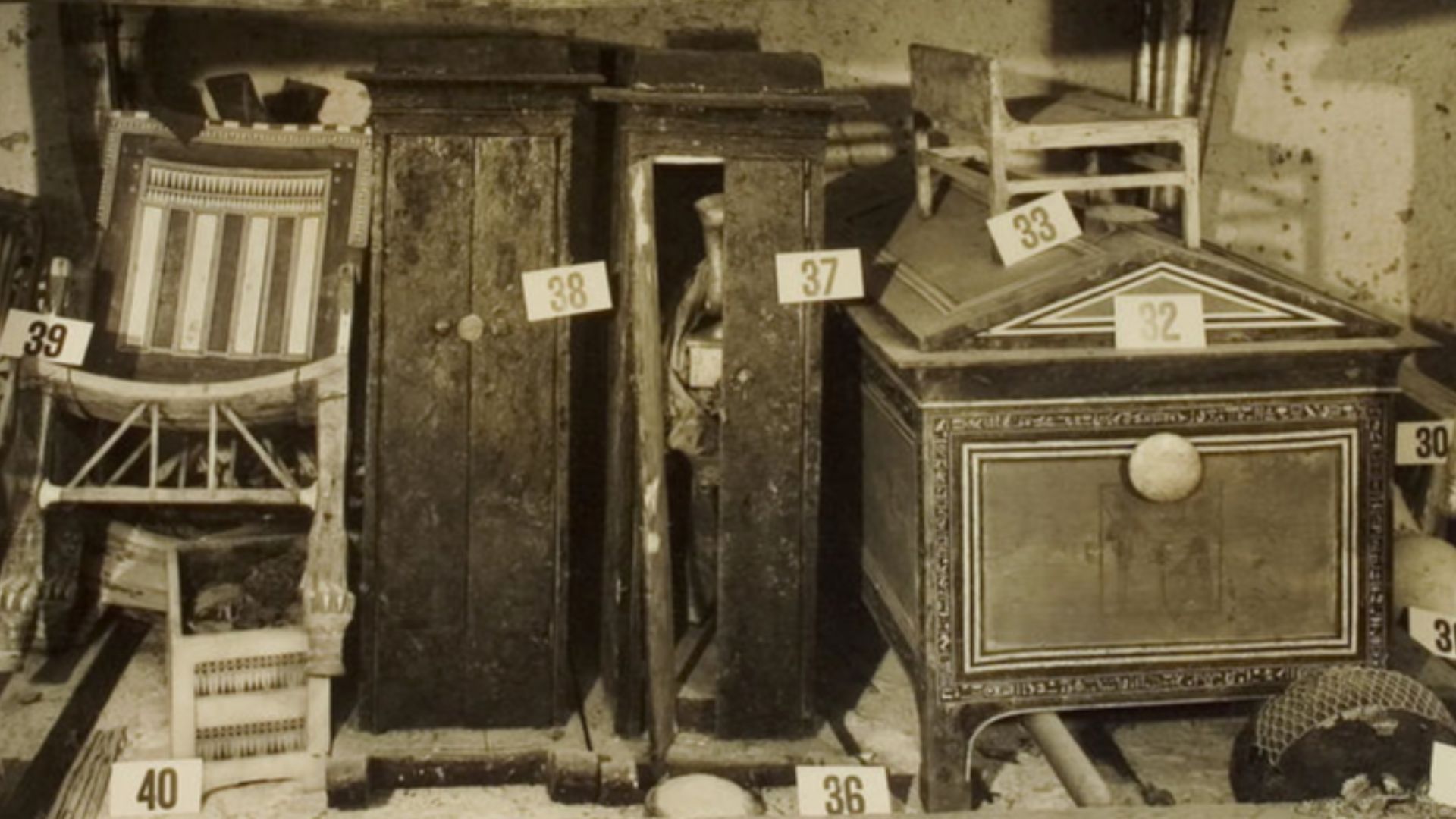
Thousands Of Objects Rebuilt His Lost Story
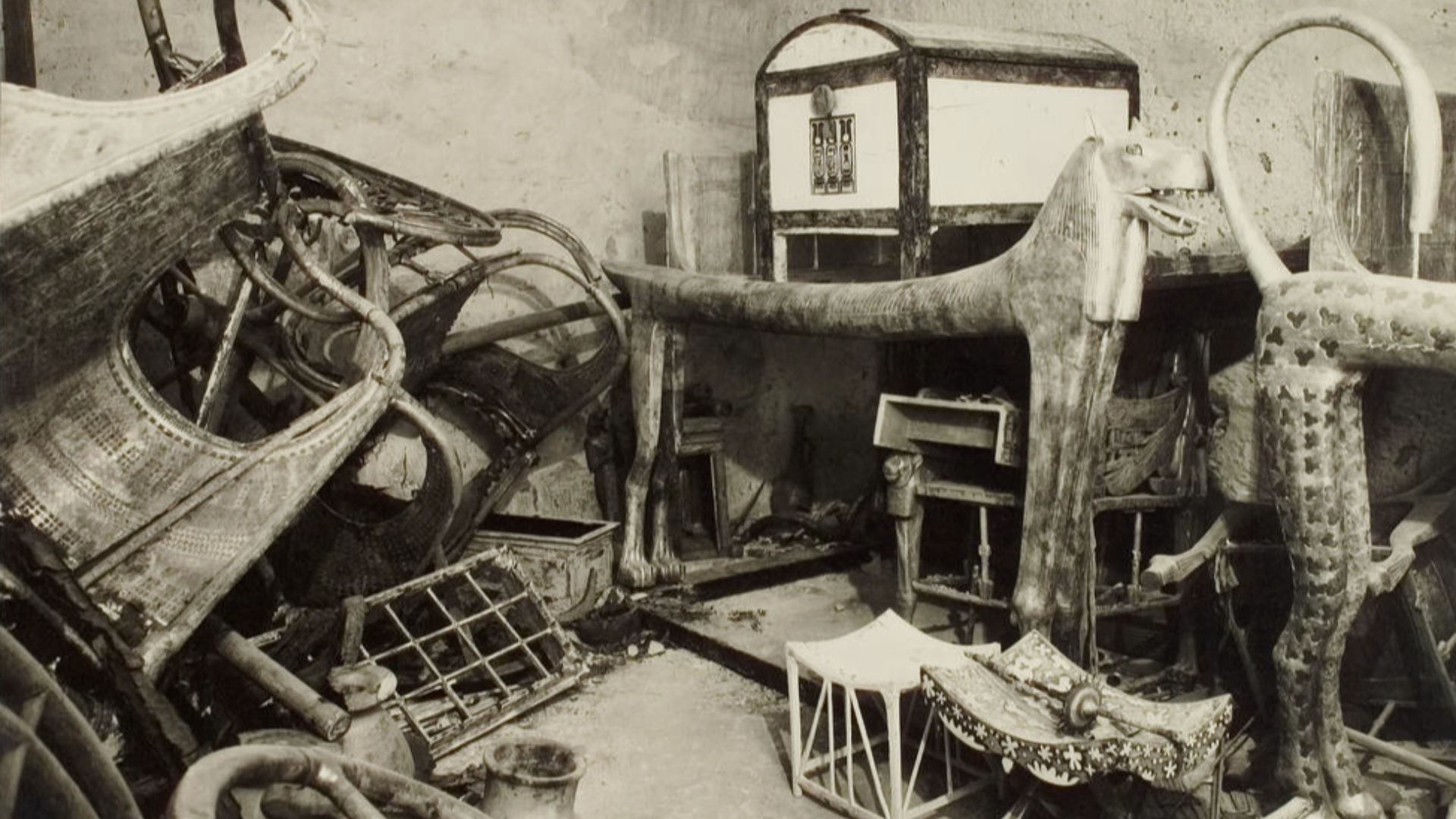
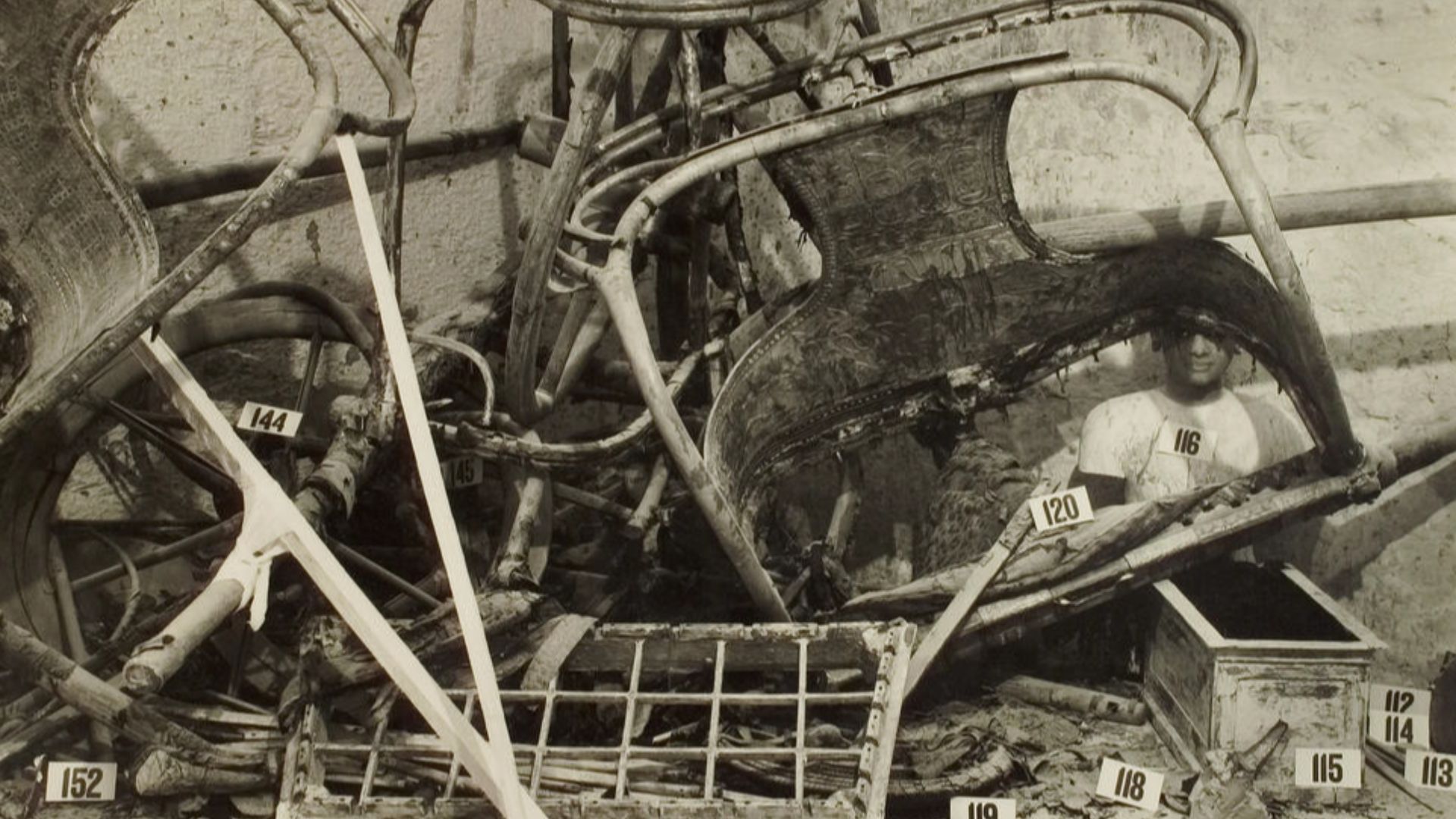
The tomb’s 5,398 catalogued items compensate for scarce written records about his reign. Furniture, clothing, chariots, jewelry, and ritual equipment offer a comprehensive portrait of royal life. Together, these artifacts allow researchers to reconstruct social dynamics, craftsmanship, religious practice, and the administrative realities shaping Egypt’s fourteenth century BCE.
 Harry Burton (1879-1940), Wikimedia Commons
Harry Burton (1879-1940), Wikimedia Commons
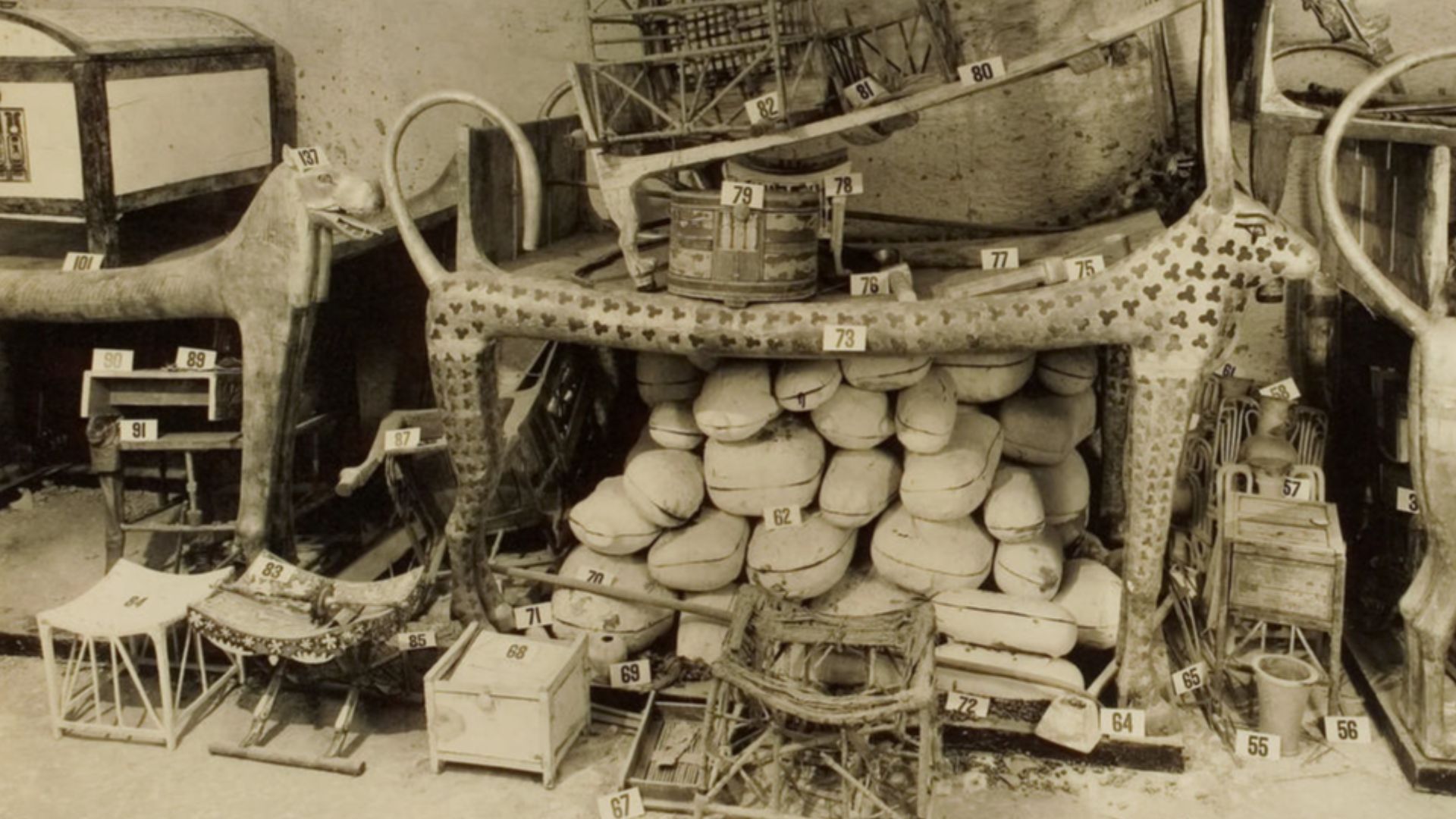
Ordinary Items That Revealed An Extraordinary Life
Sandals, cosmetic jars, stools, and linen garments uncovered within the tomb shed light on a ruler whose daily routines resembled those of elite households rather than distant legend. These familiar objects humanize him, illustrating how comfort, grooming, mobility, and leisure shaped existence inside a palace.
 Harry Burton (1879-1940), Wikimedia Commons
Harry Burton (1879-1940), Wikimedia Commons
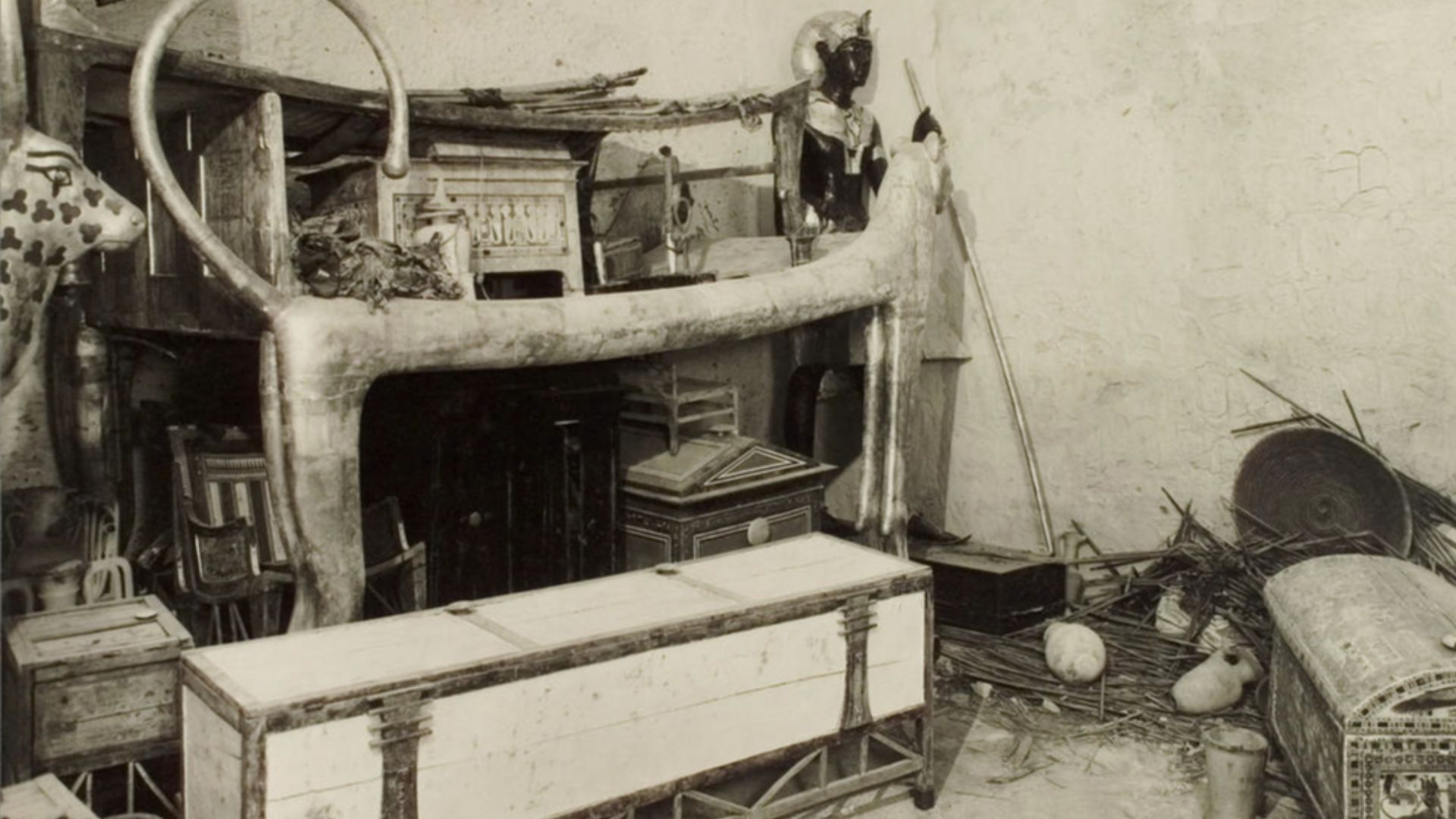
With Tools Designed For Eternity
Six chariots, nested gilded shrines, canopic equipment, and hundreds of shabti figures demonstrate how Egyptians envisioned a pharaoh’s journey beyond death. Their exceptional details reflect ritual expectations guiding burial preparation. These objects highlight beliefs linking earthly authority with cosmic renewal.
 Harry Burton (1879-1940), Wikimedia Commons
Harry Burton (1879-1940), Wikimedia Commons
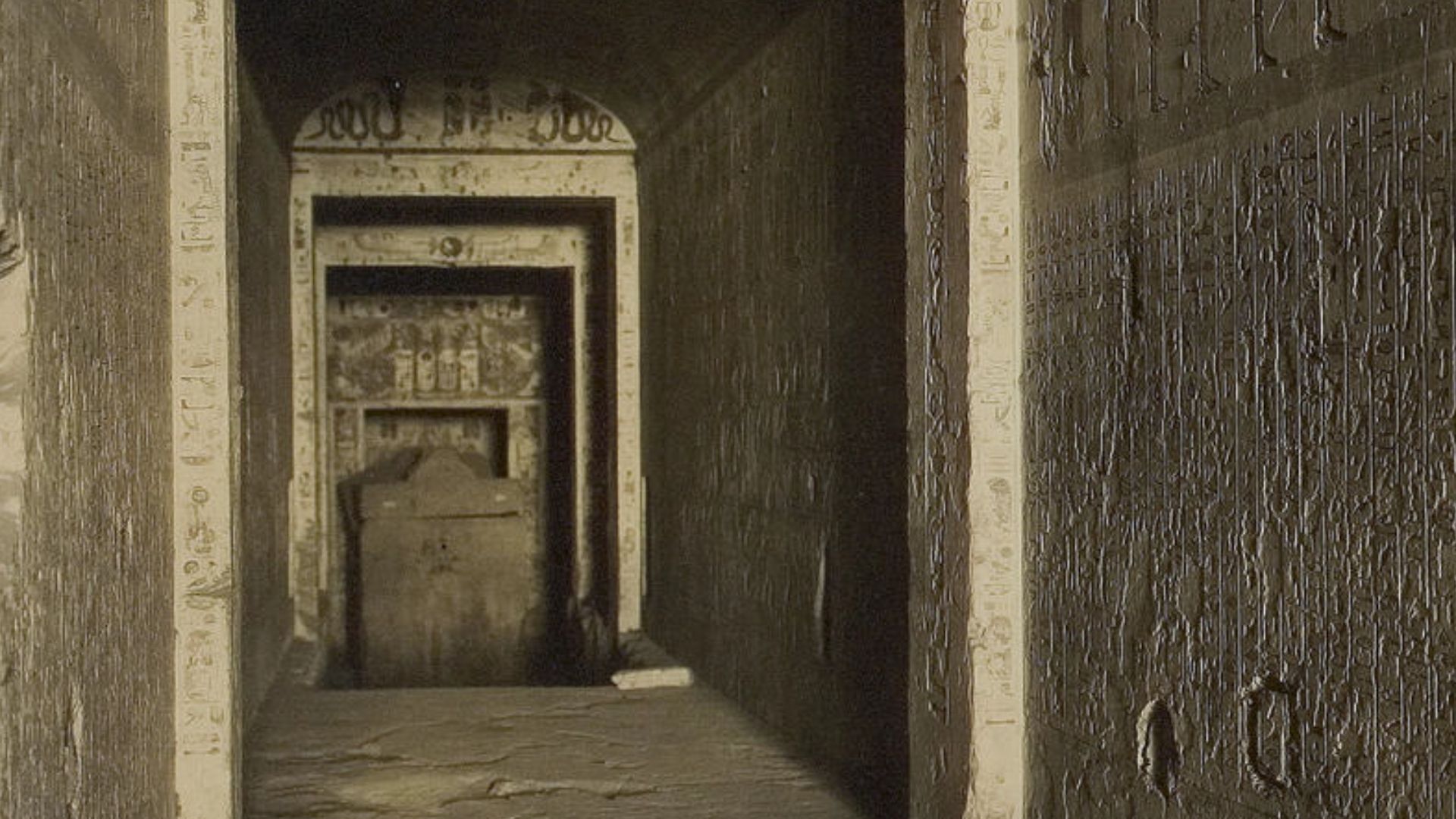
Mysteries Hidden In Gold And Sacred Artistry
Among the tomb’s wonders, the meteoric iron dagger stands out for its extraterrestrial origin confirmed through compositional analysis. Goldwork on coffins and jewelry displays advanced techniques rarely matched in later periods. Such materials symbolized divine association and an eternal presence grounded in religious ideology.
 Harry Burton (1879-1940), Wikimedia Commons
Harry Burton (1879-1940), Wikimedia Commons
Questions Surrounding His Final Days
Religious restoration defined Tutankhamun’s reign, yet his passing at approximately eighteen or nineteen remains unresolved. CT scans show fractures and illnesses, including malaria, complicating interpretations. Whether accidents or health conditions contributed, his burial materials emphasize rebirth themes central to traditional worship.
 Harry Burton (1879-1940), Wikimedia Commons
Harry Burton (1879-1940), Wikimedia Commons
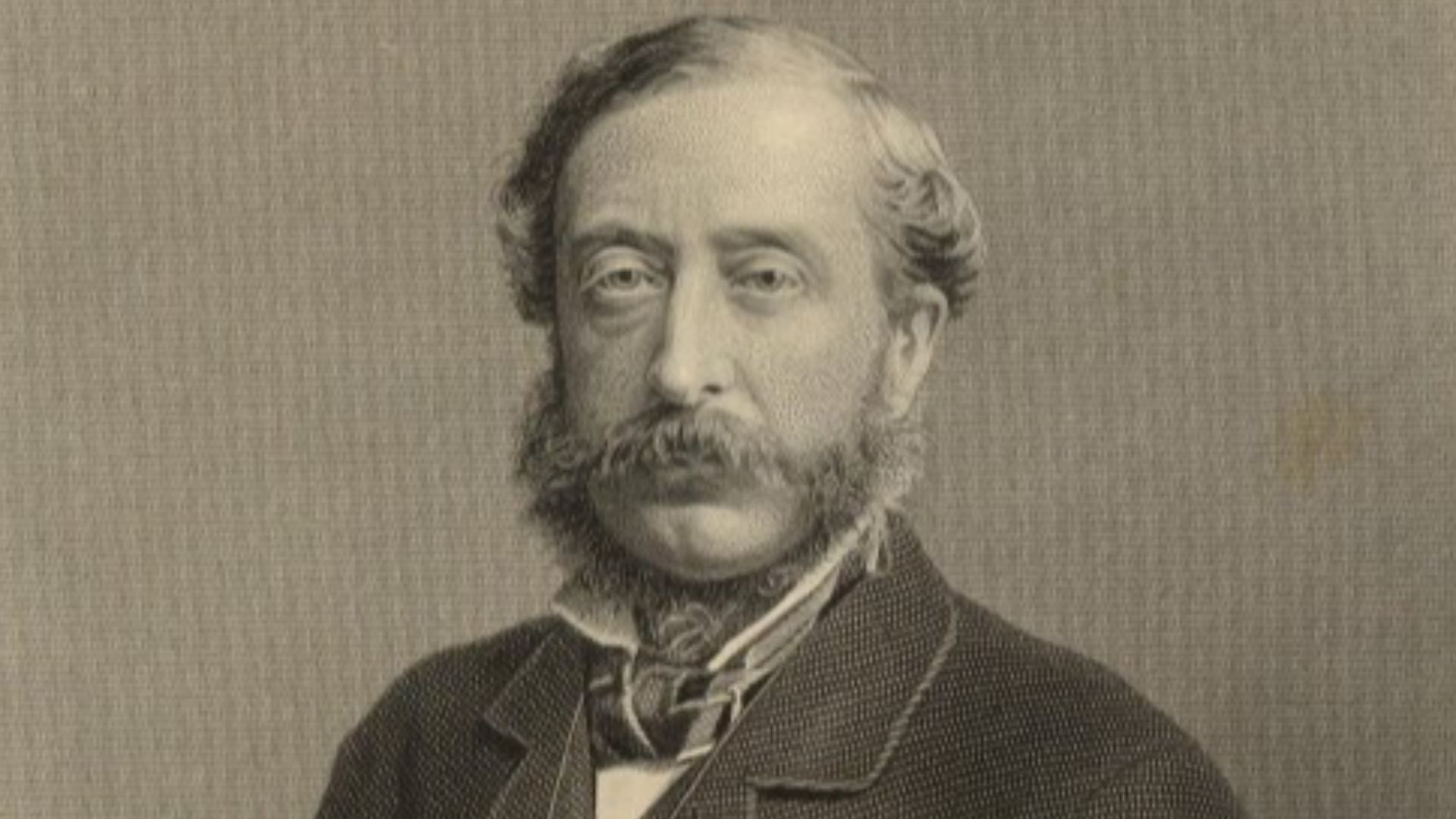
Legends That Rose From A Sealed Tomb
Stories of a “pharaoh’s curse” spread after Lord Carnarvon’s 1923 death, though no such inscription existed. Sensational reporting fueled enduring myths that overshadowed scientific work. Despite exaggerated claims, the fascination highlights public curiosity surrounding ancient burial practices and the dramatic circumstances surrounding the tomb’s unprecedented discovery.
 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/User:Ugen64, Wikimedia Commons
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/User:Ugen64, Wikimedia Commons
Early Archaeologists Who Paved The Road To KV62
Work by nineteenth- and early twentieth-century archaeologists refined excavation techniques long before Carter arrived. Their mapping and documentation narrowed possible burial locations across the Valley of the Kings. These foundational efforts created the methodological framework that ultimately enabled the accurate identification of Tutankhamun’s hidden resting place.
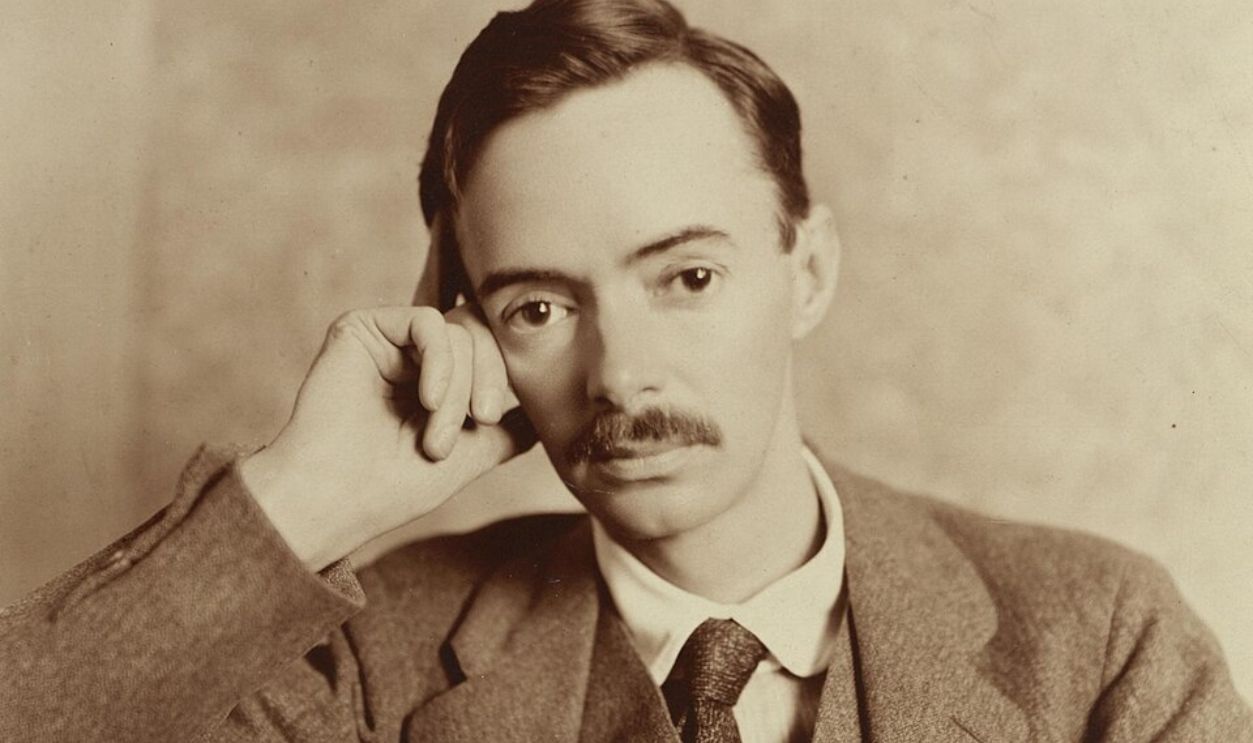
The Unheralded Contribution Of Ernest Harold Jones From Barnsley
Ernest Harold Jones, a skilled artist and archaeologist from Barnsley, documented finds with precision during early Valley of the Kings expeditions. His drawings and careful recording practices influenced evolving standards. Although his career ended prematurely, his groundwork strengthened the discipline Carter later applied.
 Welsh Portrait Collection, Wikimedia Commons
Welsh Portrait Collection, Wikimedia Commons
Howard Carter’s Long Search For A Missing Pharaoh
Carter spent years investigating abandoned clues, ancient workmen’s huts, and overlooked debris layers. Financial pressure nearly ended the project until renewed funding allowed deeper excavation. Persistence eventually exposed a staircase leading downward, confirming that the elusive burial he suspected lay concealed beneath relatively undisturbed valley strata.
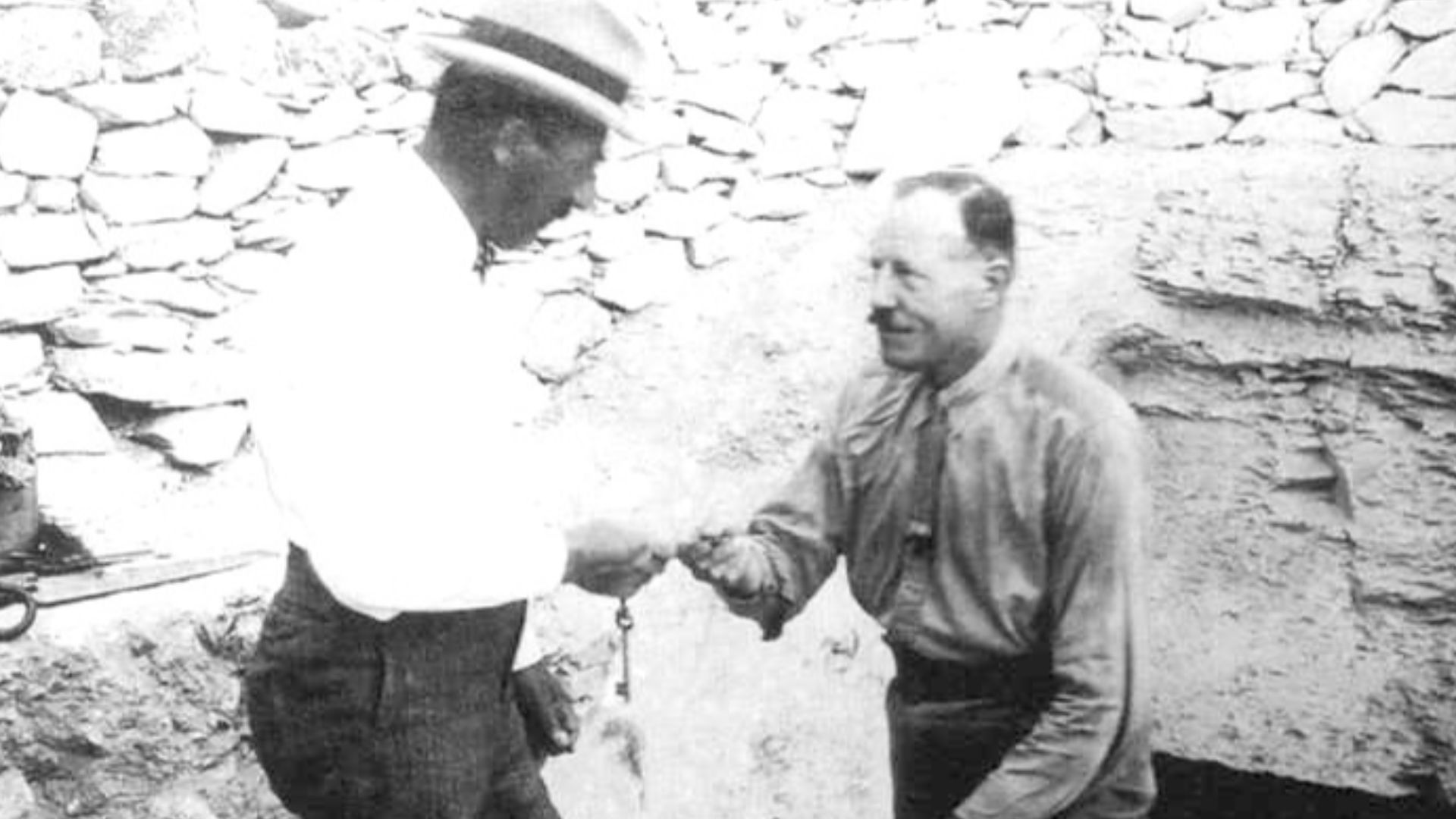 Harry Burton, Wikimedia Commons
Harry Burton, Wikimedia Commons
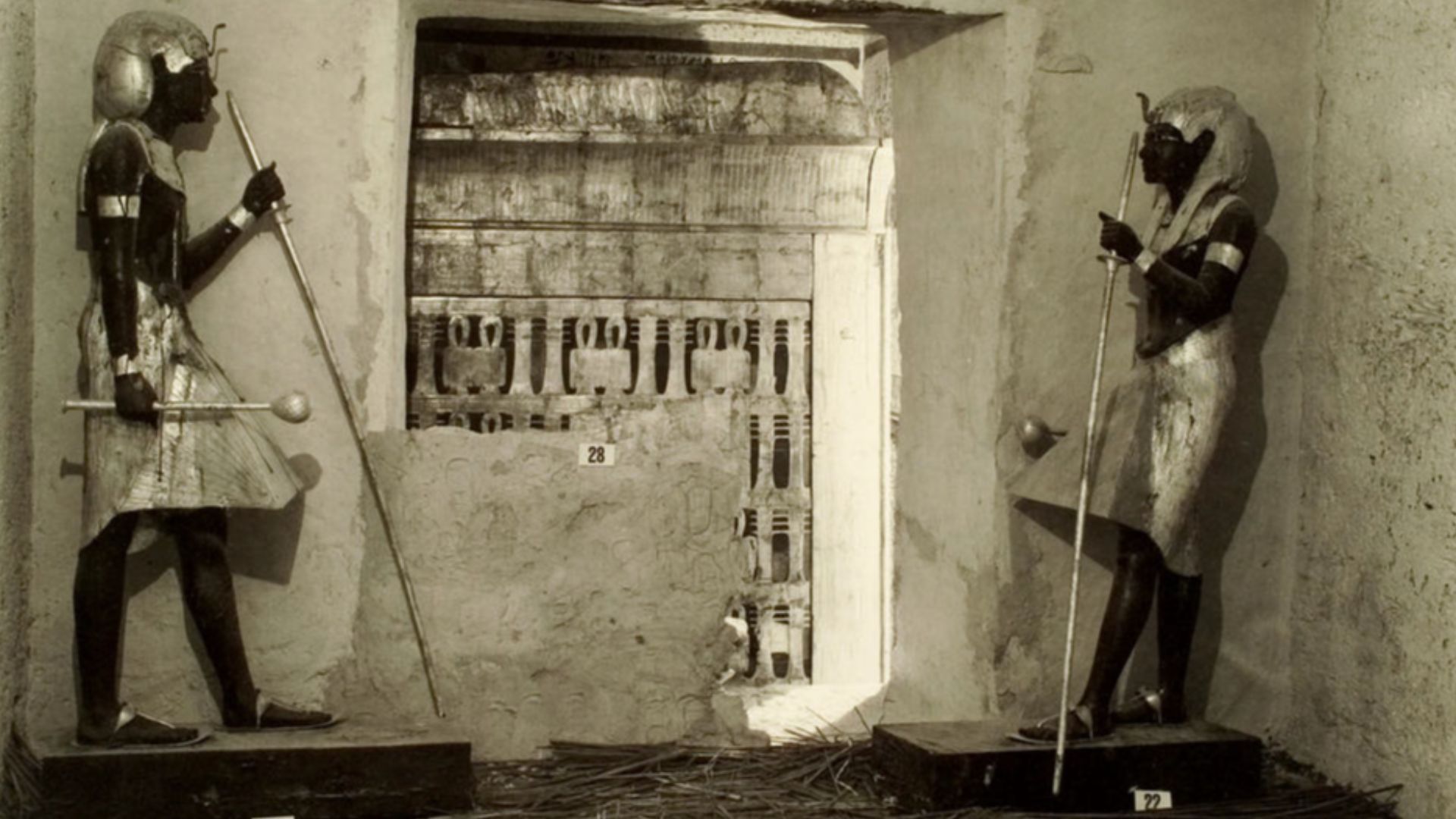
The Night “Wonderful Things” Shone In The Candlelight
Upon opening the sealed doorway in 1922, Carter glimpsed shimmering gold and densely packed objects untouched for centuries. His remark about “wonderful things” captured the moment’s weight. That initial view introduced a remarkably complete royal assemblage, offering unprecedented insight into Egypt’s 1400 BCE world.
 Harry Burton (1879-1940), Wikimedia Commons
Harry Burton (1879-1940), Wikimedia Commons
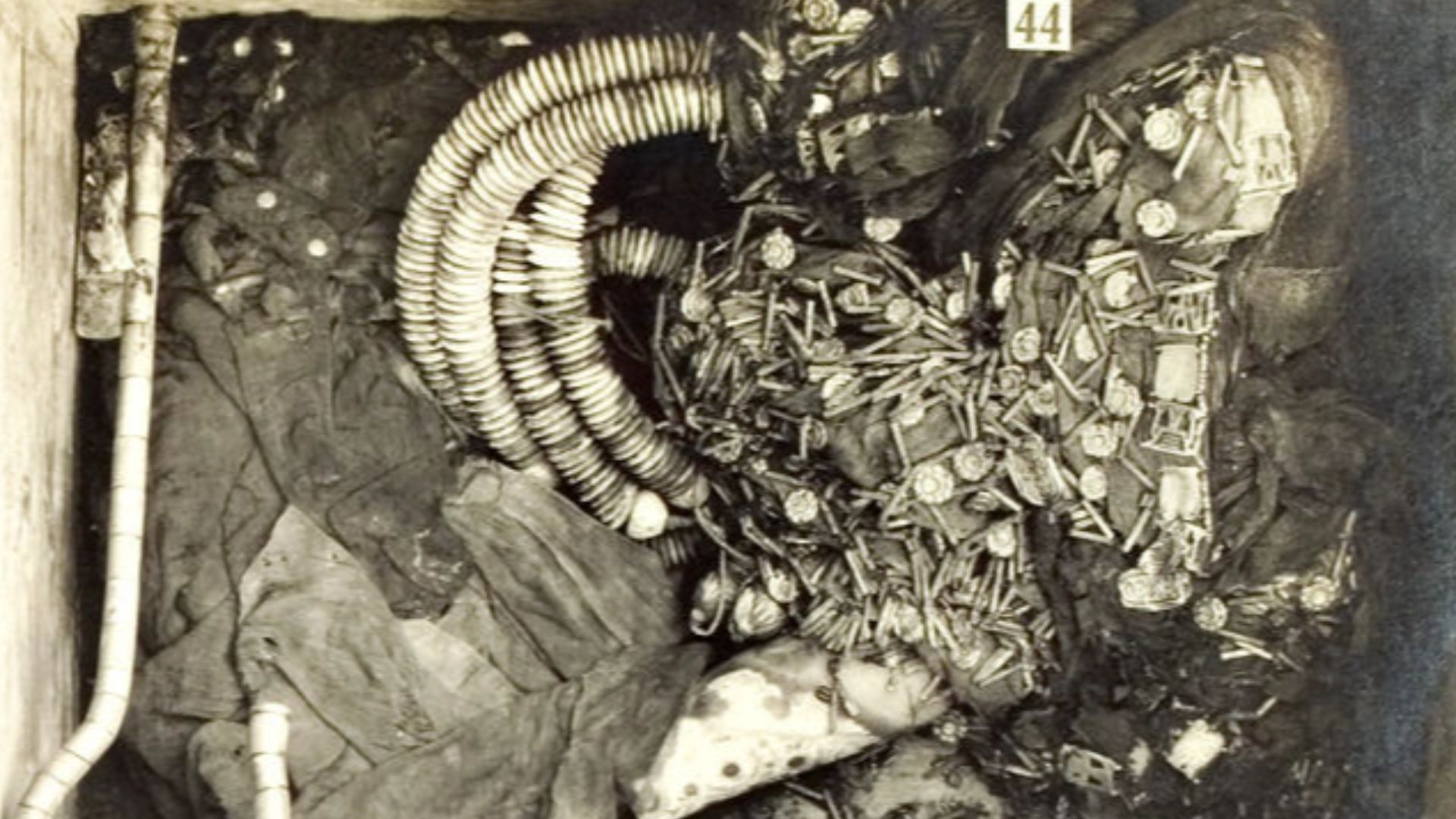
Why Did Tutankhamun’s Tomb Transform Egyptology Forever?
The tomb’s intact condition provided researchers with evidence unavailable elsewhere, with sealed containers and undisturbed ritual sequences. This completeness revolutionized archaeological interpretation by preserving context. Tutankhamun’s burial became a benchmark for studying Ancient Egyptian symbolism and funerary customs.
 Harry Burton (1879-1940), Wikimedia Commons
Harry Burton (1879-1940), Wikimedia Commons
How This Discovery Reshaped Museums And Scholarship Worldwide
The scale and preservation of Tutankhamun’s tomb encouraged museums to prioritize contextual displays rather than isolated treasures. Scholars adopted interdisciplinary methods by blending conservation science and textual study. These shifts broadened public understanding and established new expectations for presenting ancient cultures with accuracy.
 Harry Burton (1879-1940), Wikimedia Commons
Harry Burton (1879-1940), Wikimedia Commons
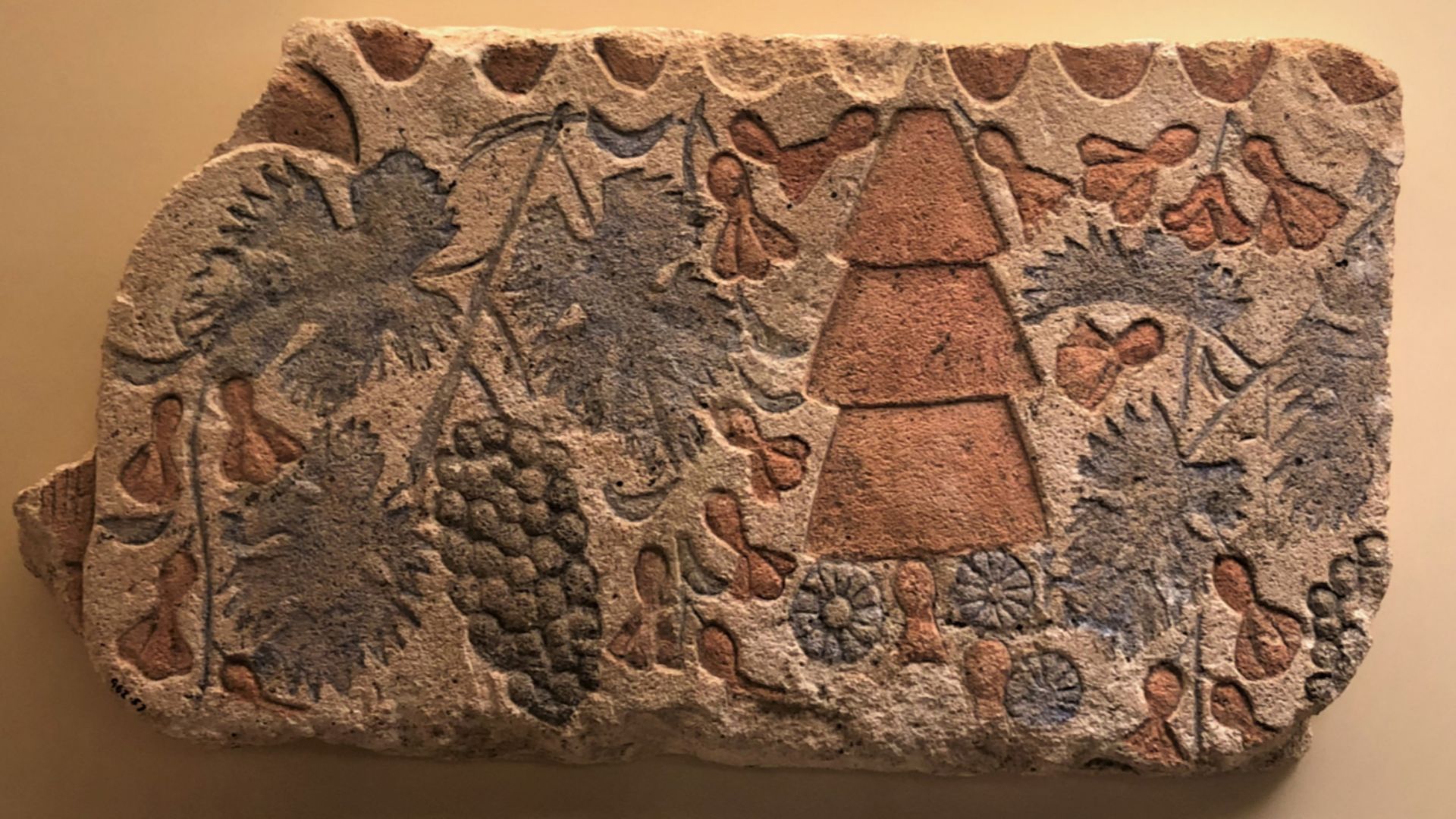
Revisiting A Century-Old Discovery
Barnsley marked the discovery’s centenary with an exhibition that blended original Amarna objects, modern reconstructions, and digital interpretation. The 2022 display echoed the excitement of 1922 by recreating the world surrounding Tutankhamun’s rise. Its focus on regional contributors highlighted the wider network that shaped Egyptology long before Carter opened the tomb.
 Maksim Sokolov (maxergon.com), Wikimedia Commons
Maksim Sokolov (maxergon.com), Wikimedia Commons
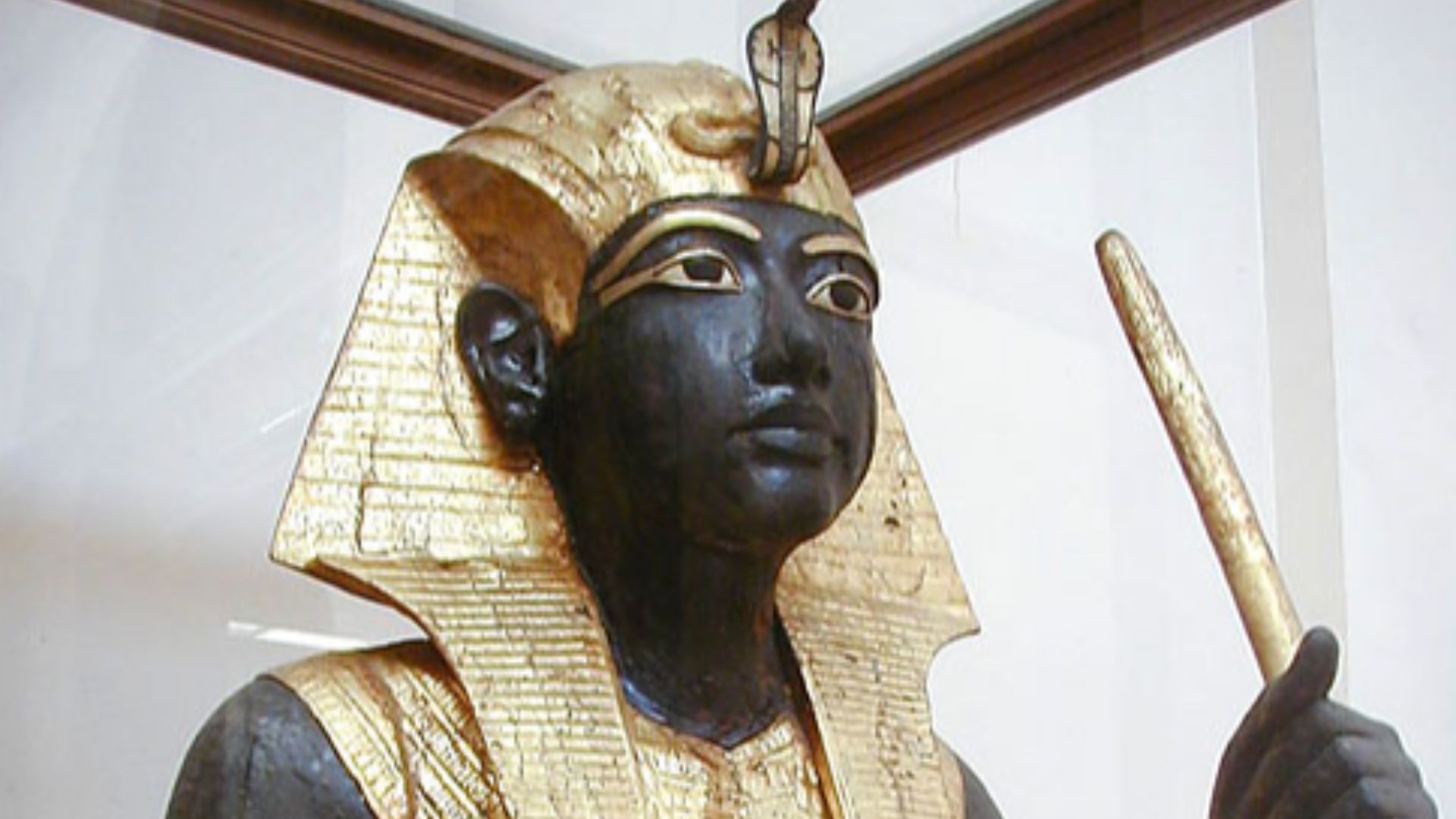
Tutankhamun’s Endless Influence On Culture And Science
Tutankhamun’s discovery shaped everything from art deco design to scientific innovation. His funerary goods inspired artistry studies, while analyses of his mummy expanded bioarchaeology. Exhibitions sparked global fascination, turning a once-obscure ruler into a cultural touchstone.
 Jon Bodsworth, Wikimedia Commons
Jon Bodsworth, Wikimedia Commons
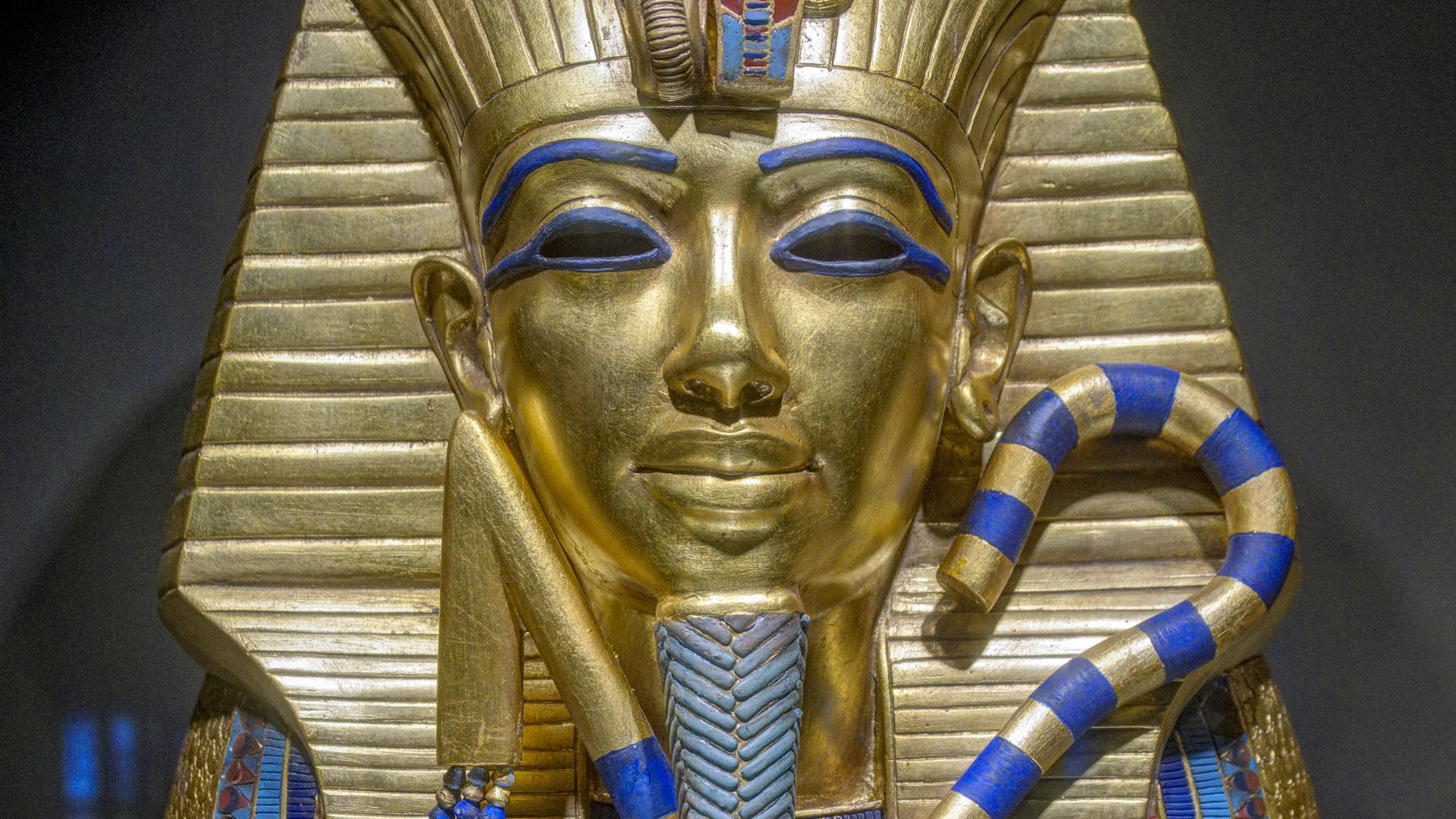
A Boy King Continues To Define Our Understanding Of Ancient Egypt
Tutankhamun’s preserved burial offers unmatched clarity about royal ideology and religious revival during the late Eighteenth Dynasty. His story forms a lens through which Egyptologists trace political restoration after Akhenaten. Through artifacts and context, his short reign continues to shape interpretations of an era once clouded by uncertainty.
 Kenneth C. Zirkel, Wikimedia Commons
Kenneth C. Zirkel, Wikimedia Commons












