A New Laser That Could Lead To A Lost World
For centuries, the Amazon rainforest was thought to be untouched: a green expanse teeming with wildlife but empty of complex human history. But a silent revolution in archaeology is rewriting that belief.
A Canopy Too Thick For Truth
For centuries, the Amazon’s dense tree cover acted like a natural vault that concealed thousands of years of human history. The sheer volume and height of its vegetation blocked aerial observation and satellite imaging and prevented archaeologists from detecting the patterned terrain and engineered structures just beneath the leaf-littered surface.
 Phil P Harris., CC BY-SA 2.5, Wikimedia Commons
Phil P Harris., CC BY-SA 2.5, Wikimedia Commons
Myths That Painted The Amazon Empty
Western explorers long believed the Amazon was a biologically rich but culturally void environment. This misconception, rooted in early colonial writings and reinforced by limited fieldwork, dismissed the idea of complex societies. Recent findings show thriving civilizations existed here, which contradicts outdated notions of an untouched, uninhabited wilderness.
 Alexey Yakovlev, CC BY-SA 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
Alexey Yakovlev, CC BY-SA 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
Why We Missed The Clues For So Long
The region’s inaccessibility and seasonal flooding delayed archaeological breakthroughs. Traditional excavation was slow and ineffective in thick rainforest environments. Combined with limited funding and a bias toward highland civilizations like the Inca, these factors kept Amazonian prehistory largely invisible until the 21st century.
 Expresso Futuro, CC BY-SA 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
Expresso Futuro, CC BY-SA 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
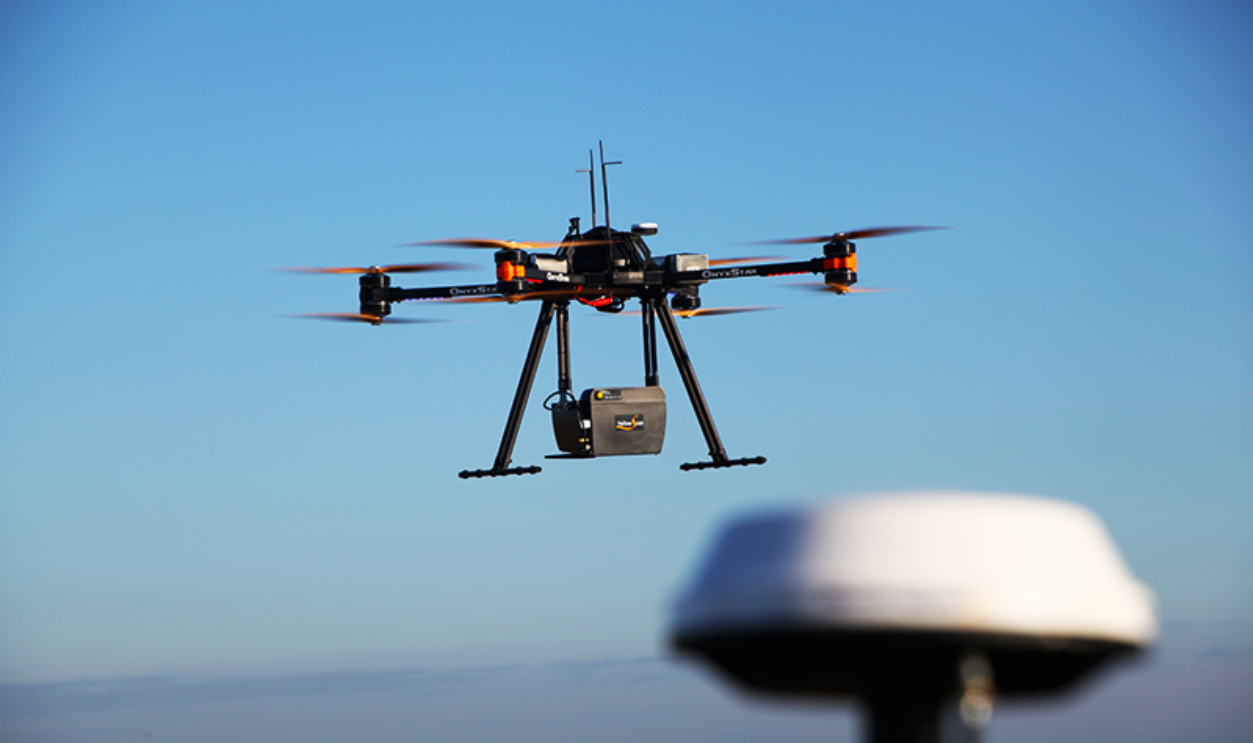
LiDAR: The Laser That Sees Through Trees
LiDAR, or Light Detection and Ranging, uses pulses of laser light from aircraft to create detailed 3D maps of the ground below. Unlike traditional imaging, it filters out foliage to reveal topography hidden beneath the forest canopy. This technology changed jungle archaeology by exposing earthworks and settlement layouts with centimeter-level precision.
 Cargyrak, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Cargyrak, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Archaeology Takes Flight Over The Amazon
Flying over regions like Brazil’s Tapajos basin and Bolivia’s Llanos de Mojos, researchers have recorded entire pre-Columbian lands with LiDAR. These scans confirmed that large, organized populations once thrived deep in the rainforest. This radically alters our understanding of Amazonian cultural development.
 Jonte, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Jonte, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
What A Laser Scan Can Reveal In Seconds
In just seconds, a single LiDAR scan can record millions of data points. These pinpoint subtle surface anomalies—like shallow ditches and buried enclosures—across wide areas. What once took archaeologists months to uncover with ground surveys now appears instantly to change both the speed and scale of archaeological discovery.
 Lost beneath the leaves: Lasers reveal an ancient Amazonian civilisation by nature video
Lost beneath the leaves: Lasers reveal an ancient Amazonian civilisation by nature video
Grids, Roads, And Geometric Wonders
Beneath the Amazon’s forest floor, LiDAR has uncovered carefully arranged grids, star-shaped enclosures, radial road systems, and polygonal causeways. These engineered designs suggest planning and communal labor. The symmetry and alignment rival that of ancient cities elsewhere and prove these societies were neither scattered nor technologically primitive.
 S. Winkvist, Wikimedia Commons
S. Winkvist, Wikimedia Commons
Villages That Once Buzzed With Life
Some of the newly discovered settlements housed thousands of people and featured plazas and defensive walls. These were vibrant hubs of trade and agriculture. Their density and layout hint at a deep social organization that operated in harmony with the forest ecosystem.
 Lost beneath the leaves: Lasers reveal an ancient Amazonian civilisation by nature video
Lost beneath the leaves: Lasers reveal an ancient Amazonian civilisation by nature video
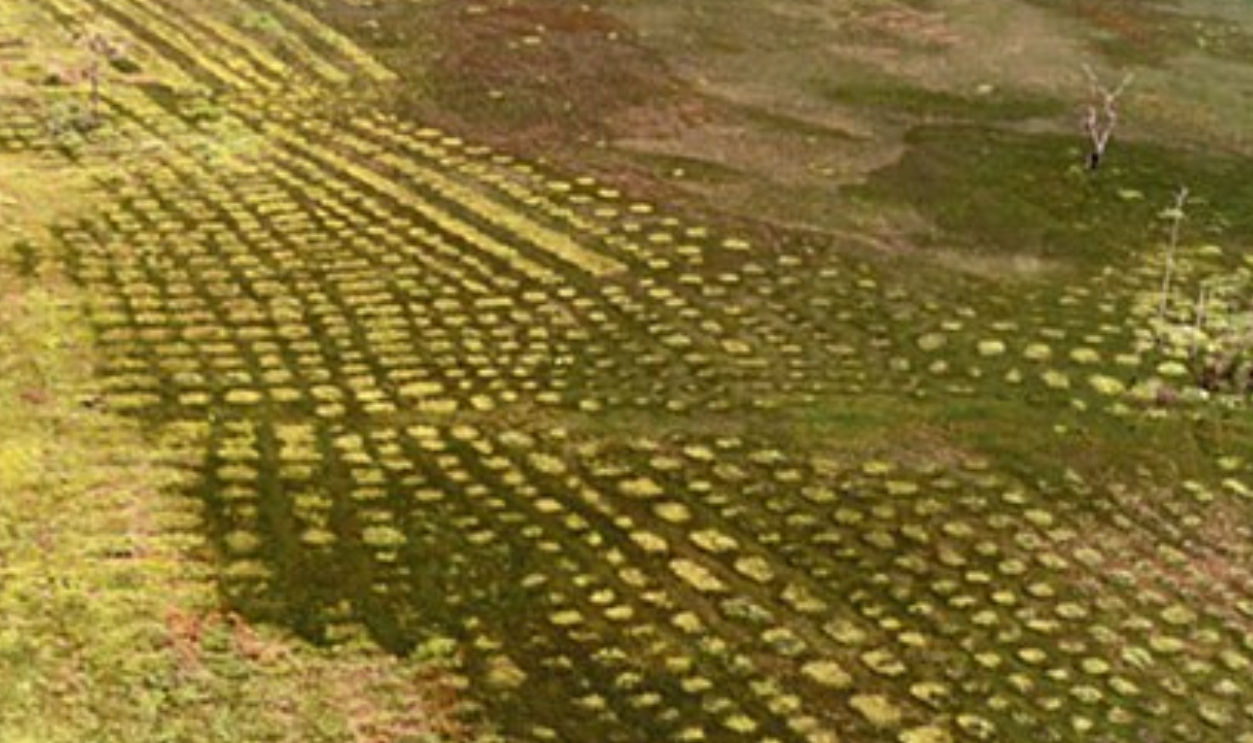
Geometry In Soil And Stone
Many archaeological features follow geometric designs—circles, squares, rectangles, and even compound shapes—that likely held ceremonial or cosmological meaning. These earthworks aligned with astronomical events or cardinal directions. Their precision implies sophisticated knowledge systems and cultural values tied deeply to the natural and celestial worlds.
 Lost beneath the leaves: Lasers reveal an ancient Amazonian civilisation by nature videoSacred
Lost beneath the leaves: Lasers reveal an ancient Amazonian civilisation by nature videoSacred
Earthworks That Defy Modern Assumptions
The sheer scale of raised causeways and monumental platforms suggests coordinated labor over generations. Their construction predates European contact and rivals engineering feats found elsewhere in the ancient world. These earthworks challenge assumptions that large-scale, permanent infrastructure couldn’t exist in tropical forest environments without metal or wheels.
 Lost beneath the leaves: Lasers reveal an ancient Amazonian civilisation by nature video
Lost beneath the leaves: Lasers reveal an ancient Amazonian civilisation by nature video
Bolivia’s Ancient Canals And Platforms
In the Llanos de Mojos, researchers found an intricate network of canals and settlement mounds spread across thousands of square miles. These engineered wetlands enabled intensive farming despite seasonal flooding. The complexity of this water management system highlights a better understanding of the region’s ecology and hydrology.
 Stephen Rostain, Doyle McKey, CC BY 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Stephen Rostain, Doyle McKey, CC BY 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
The Upano Valley’s Vast Urban Network
LiDAR revealed densely packed habitation mounds and wide roads connecting neighborhoods in Ecuador’s Upano Valley. Dating back over 2,500 years, this sophisticated system hosted thousands. It’s among the earliest large-scale urban developments in the Amazon basin and shows early city-building occurred deeper in the rainforest than believed.
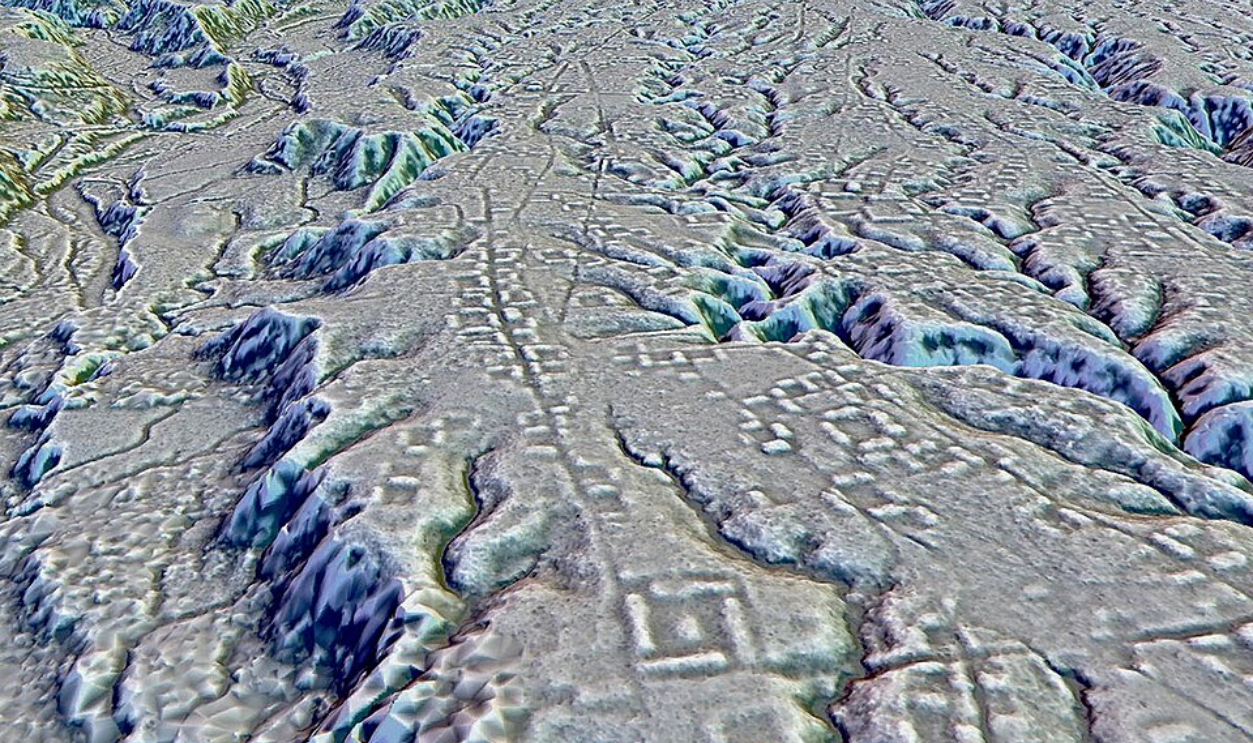 Antoine Dorison and Stephen Rostain, CC BY 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Antoine Dorison and Stephen Rostain, CC BY 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Connecting Civilizations Across The Amazon
Patterns in site orientation and agricultural engineering link settlements across distant Amazonian regions. These connections suggest cultural exchange and trade routes spanning hundreds of miles. The idea of isolated tribes gives way to a vision of interdependent civilizations connected by forest corridors and rivers.
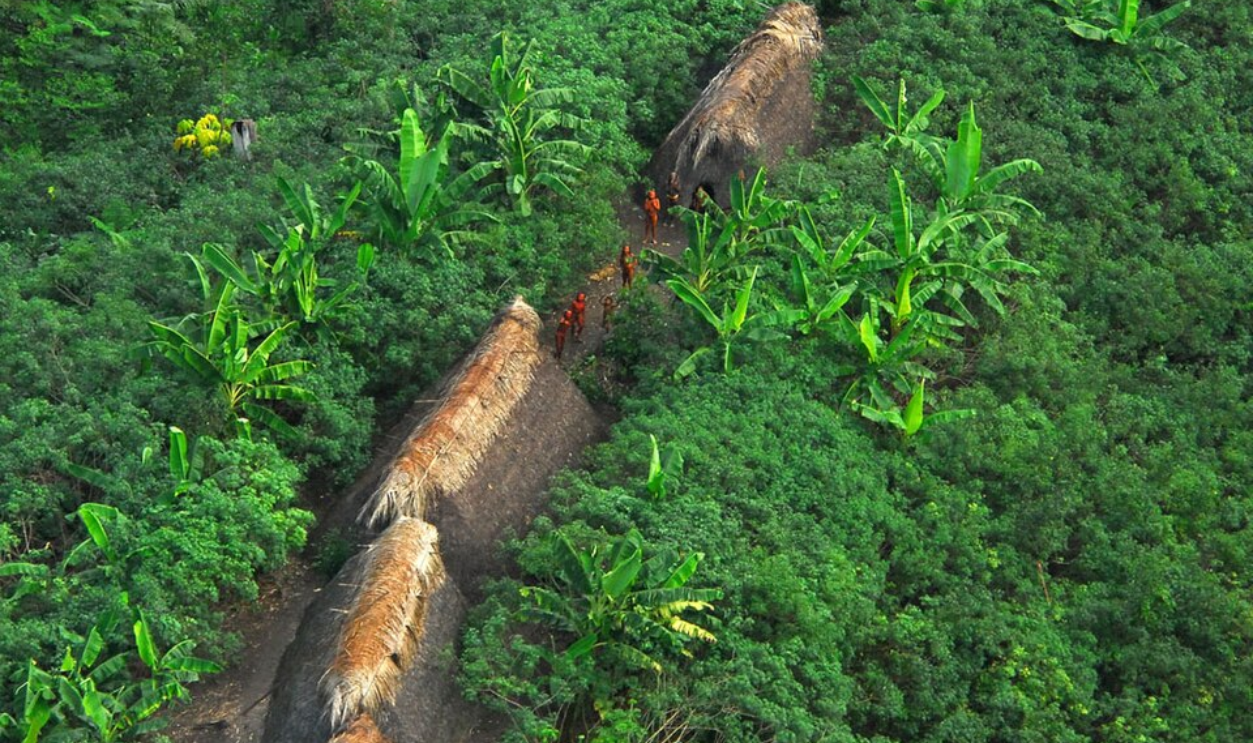 Gleilson Miranda / Governo do Acre, CC BY 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
Gleilson Miranda / Governo do Acre, CC BY 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
Terra Preta: The Amazon’s Engineered Earth
Terra preta, or “dark earth,” is a rich, carbon-enhanced soil created by ancient Amazonians through compost and organic waste. It has retained fertility for centuries and still supports farming today. Its existence proves these societies were actively enhancing the land with lasting agricultural innovations.
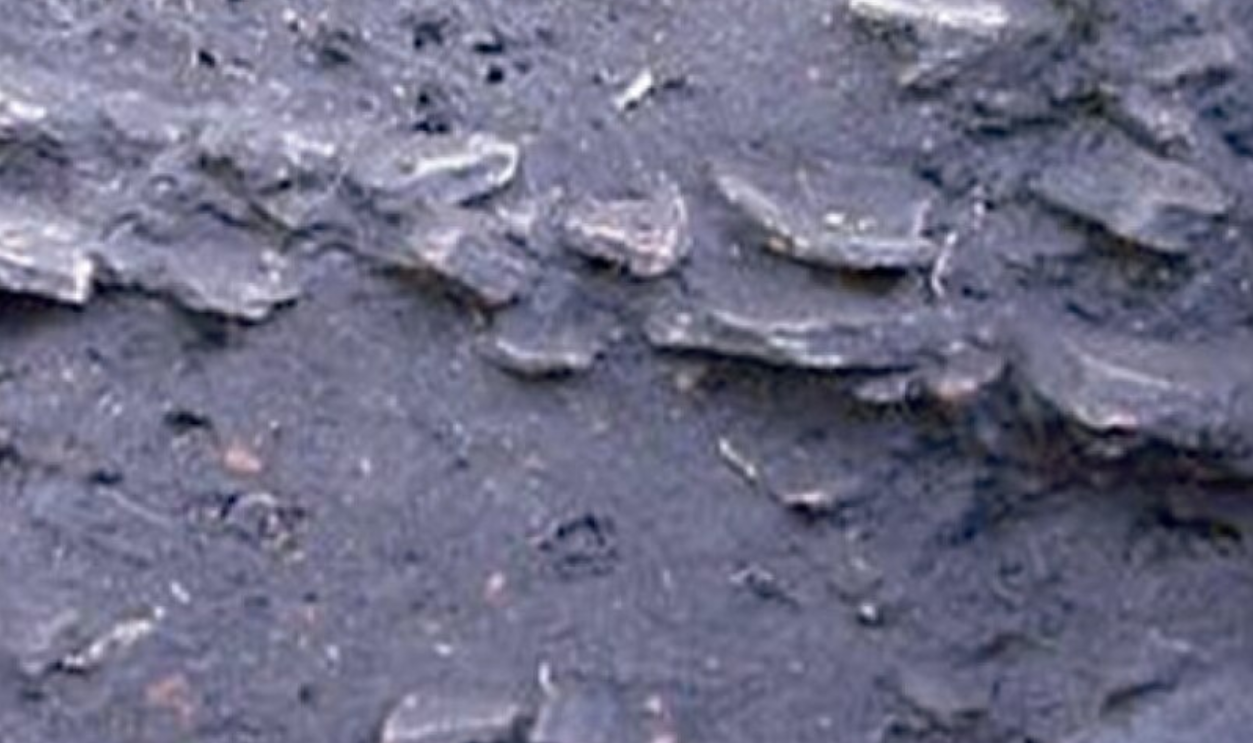 Bruno Glaser, CC BY 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Bruno Glaser, CC BY 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Finding Ruins Before The Bulldozers Do
Each new discovery has a race-against-time urgency. Expanding cattle ranches and road construction threaten to destroy ancient sites before they’re ever mapped. LiDAR allows researchers to locate and document cultural landmarks rapidly. It gives heritage protection agencies a chance to intervene before irreversible damage is done.
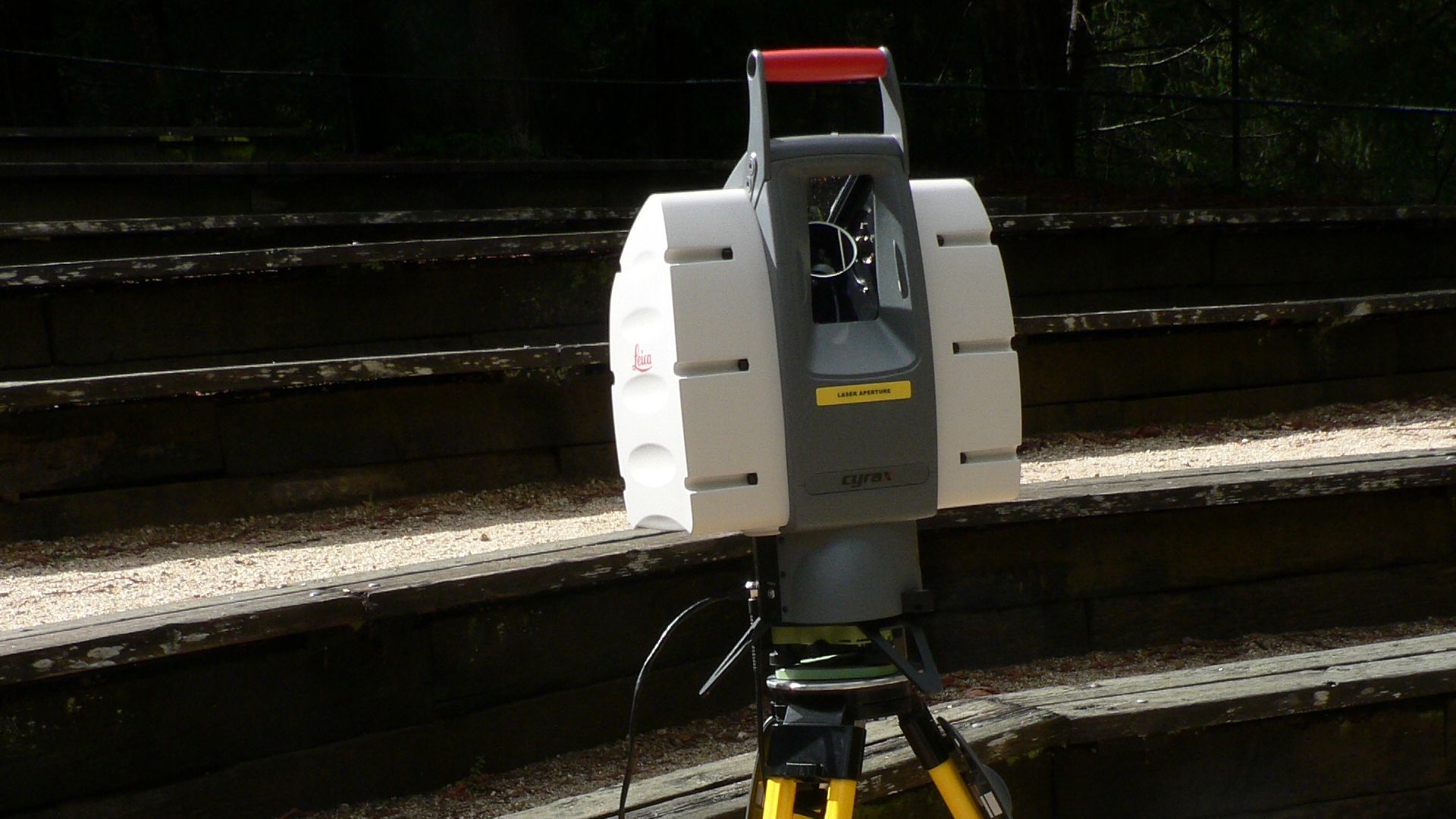 David Monniaux, Wikimedia Commons
David Monniaux, Wikimedia Commons
How Discovery Shields Land From Destruction
Official recognition of archaeological sites often leads to legal protection. In Brazil, mapping ancient settlements has helped designate conservation zones that stop land-clearing permits. These findings become tools in courtrooms and government offices. They give endangered ecosystems a second chance by proving their historical, and not just ecological, significance.
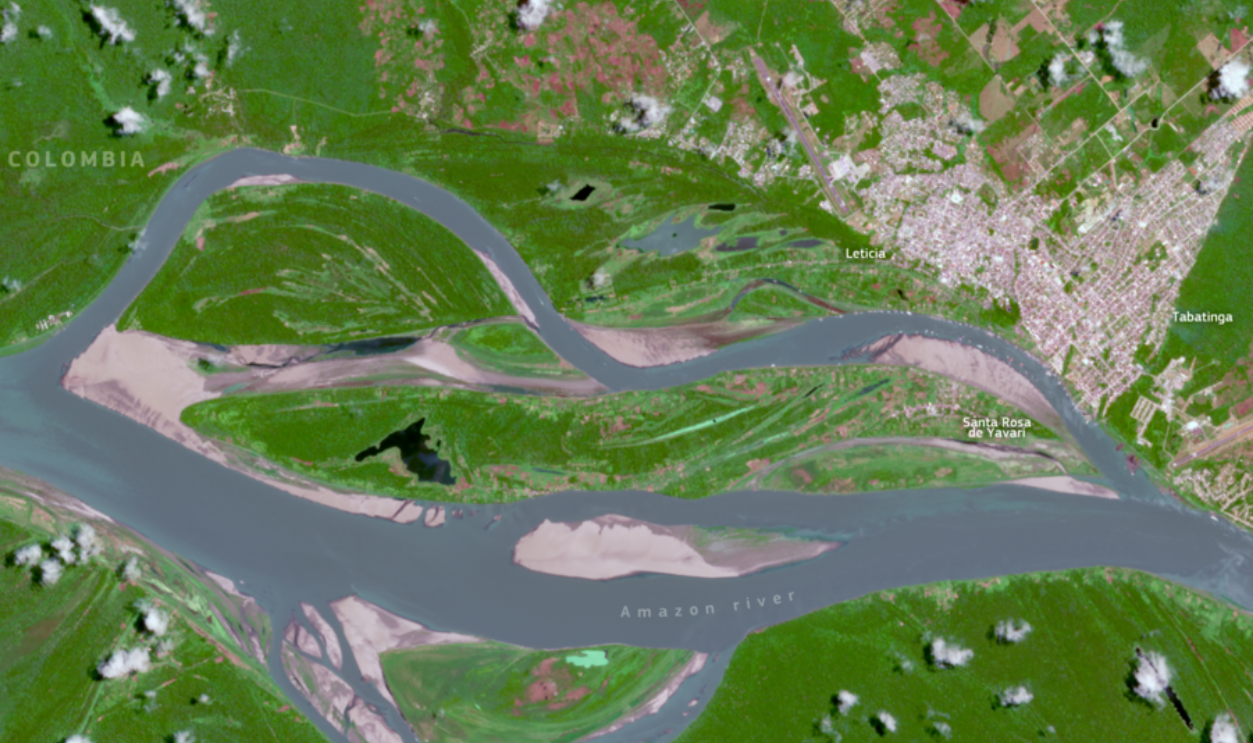 European Union, Copernicus Sentinel-2 imagery, Wikimedia Commons
European Union, Copernicus Sentinel-2 imagery, Wikimedia Commons
Saving History To Save The Forest
Preserving archaeological sites safeguards the future. Forests with cultural value attract research funding and sustainable tourism opportunities. When people see the Amazon as home to ancient cities, not just trees, it changes the conversation about what’s worth protecting and why.
 Artur Warchavchik, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Artur Warchavchik, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
The Myth Of Pristine Wilderness Falls Apart
LiDAR reveals that much of the Amazon was shaped by human hands. What was once considered untouched wilderness is now understood as a managed biome. This reframes the forest not as an untouched Eden but as a cultural milestone, altered and curated by generations of Indigenous inhabitants long before colonization.
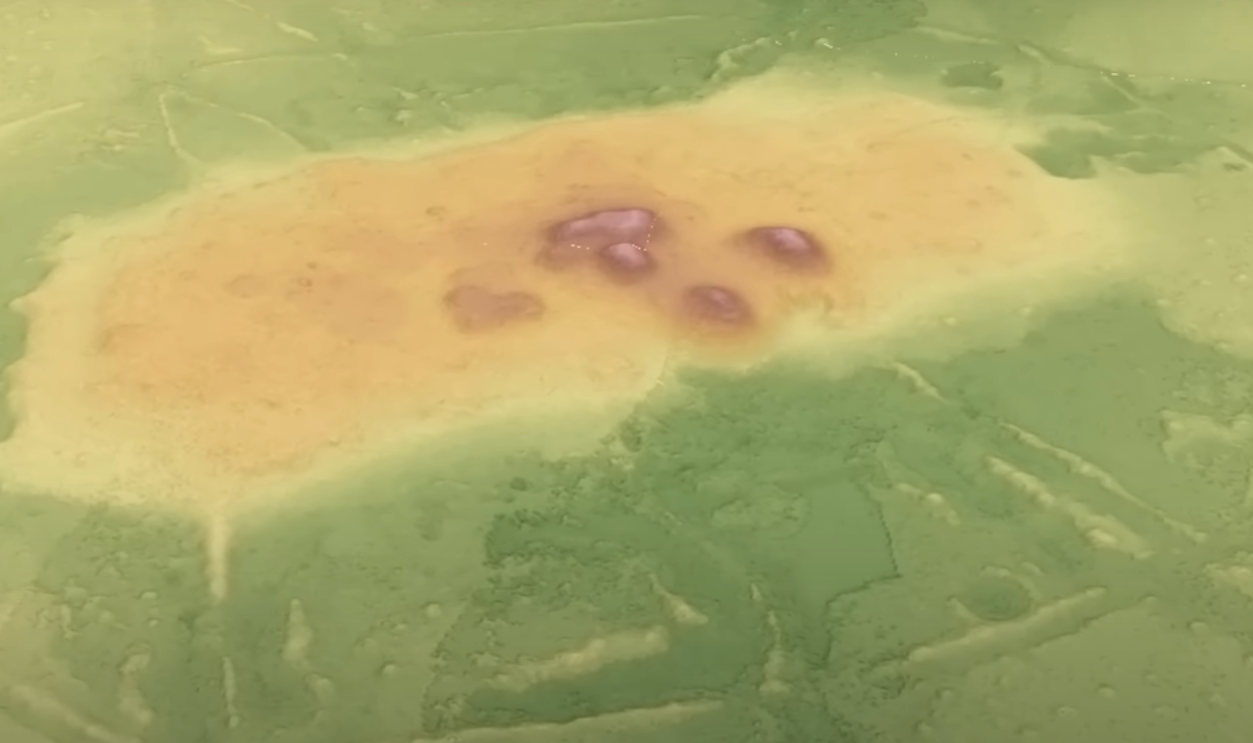 Lost beneath the leaves: Lasers reveal an ancient Amazonian civilisation by nature video
Lost beneath the leaves: Lasers reveal an ancient Amazonian civilisation by nature video
A Jungle Full Of People, Not Emptiness
Population estimates once capped Amazonian societies as scattered, small groups. Recent findings suggest regional populations in the hundreds of thousands. Settlement density and soil modification all point to thriving communities that are not actively designed to support complex and interconnected lives.
 Lost beneath the leaves: Lasers reveal an ancient Amazonian civilisation by nature video
Lost beneath the leaves: Lasers reveal an ancient Amazonian civilisation by nature video
Civilization Didn’t Begin With Europe
The traditional narrative places civilization’s origins in the Middle East, China, or Europe. However, the Amazon’s engineered lands show that urban planning and environmental mastery existed independently in the Americas. These discoveries demand a broader, more inclusive definition of what counts as a “civilization” in world history.
 Juan Carlos Fonseca Mata, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Juan Carlos Fonseca Mata, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Why This Changes The Way We See The World
Understanding the Amazon as a center of ancient innovation forces a paradigm shift in how societies are valued. These cultures were highly adaptive and advanced. Recognizing this rebalances global history and invites deeper respect for Indigenous knowledge as foundational, not secondary, to human progress.
Indigenous Knowledge Meets Aerial Mapping
Collaboration between archaeologists and Indigenous communities has become essential. Elders often recognize sacred spaces or ancestral territories that align with LiDAR data. Oral histories complement digital mapping to ground scientific findings in living memory. This respectful exchange deepens interpretation and ensures discoveries are understood within their cultural context.
 Anangu, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Anangu, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
How LiDAR Reshaped Angkor And Beyond
Over Cambodia’s Angkor Wat, LiDAR unveiled a vast suburban sprawl, grid-like infrastructure, and intricate canal systems that contradicted long-held assumptions about the temple’s isolation. These findings rewrote Southeast Asian history, much like it’s happening in the Amazon. They prove that forest-covered ruins often mask far more advanced urban planning than imagined.
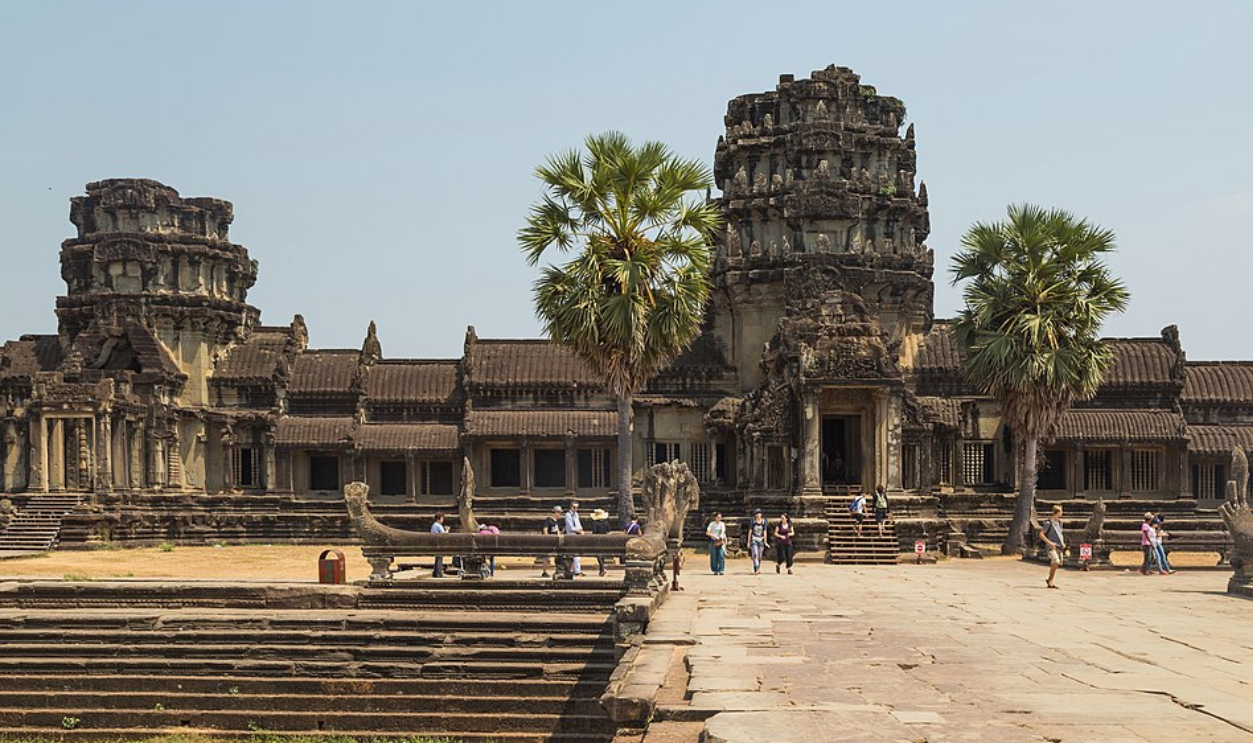 Photo: Marcin Konsek, Wikimedia Commons
Photo: Marcin Konsek, Wikimedia Commons
What We’re Still Blind To
Despite LiDAR’s power, many regions remain unmapped due to bureaucratic restrictions and difficult flight conditions. Moreover, LiDAR reveals shape, not function. It can’t decipher cultural meaning without excavation and context. Many discovered features are still unnamed and unprotected, which leaves key pieces of the human story in limbo.
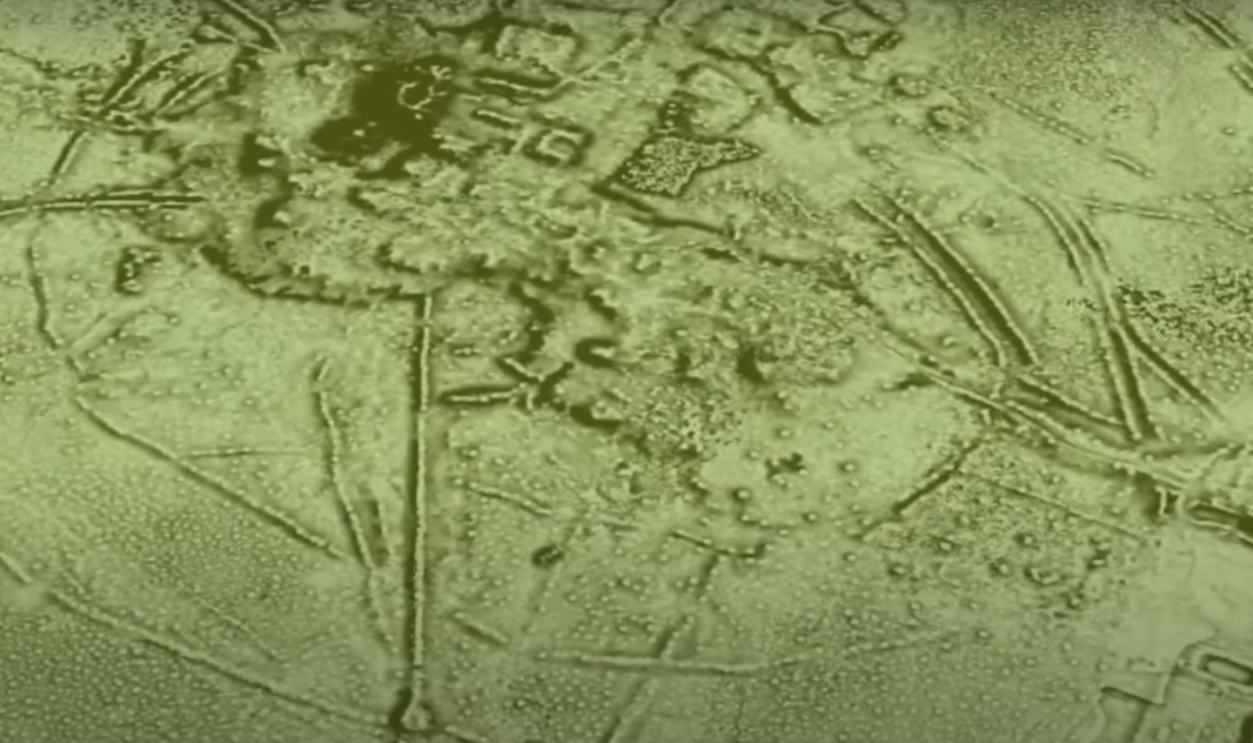 Lost beneath the leaves: Lasers reveal an ancient Amazonian civilisation by nature video
Lost beneath the leaves: Lasers reveal an ancient Amazonian civilisation by nature video
The Amazon’s Greatest Story Still Unfolds
What has emerged from the forest floor is just the beginning. Each scan adds new layers to Amazon's human history to make it more connected and dynamic. As technology advances and more regions are explored, this ancient rainforest continues revealing a legacy that reshapes everything we thought we knew.
 Artur Warchavchik, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Artur Warchavchik, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons