Introduction To Canopus
In August 2025, archaeologists announced an amazing discovery in the waters near Alexandria, Egypt: ruins of a possible extension of the ancient sunken city of Canopus. This once-bustling metropolis was well known in antiquity. This new discovery gives us an incredible look into the religious, cultural, and political world of ancient Egypt and the Mediterranean.
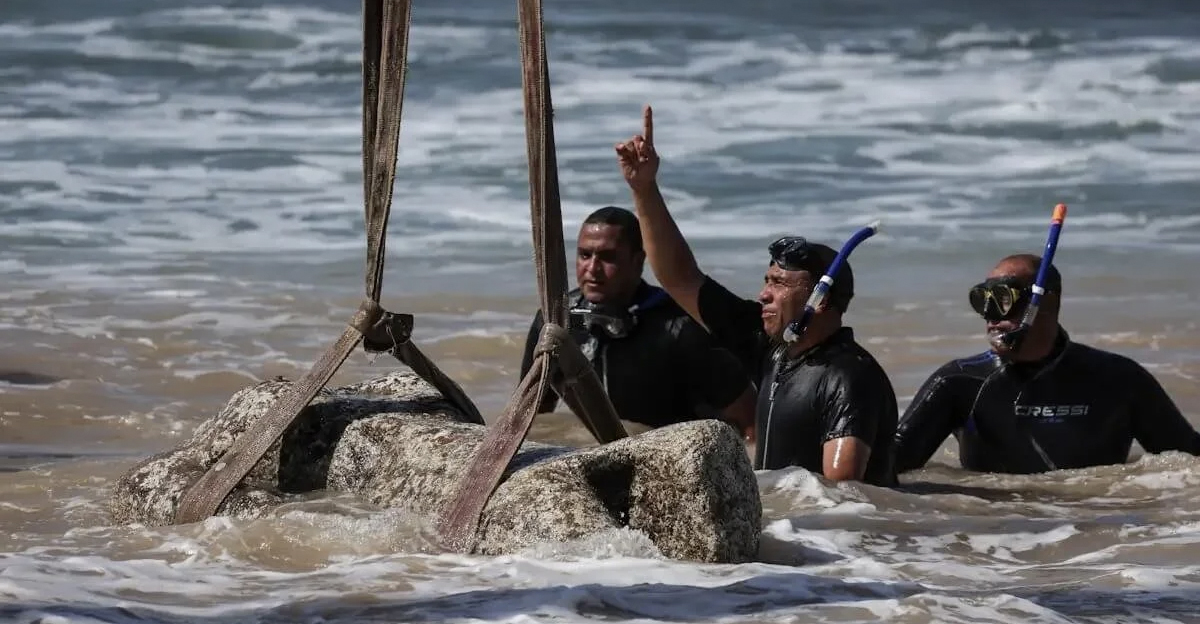

Treasures Hauled Out Of the Depths
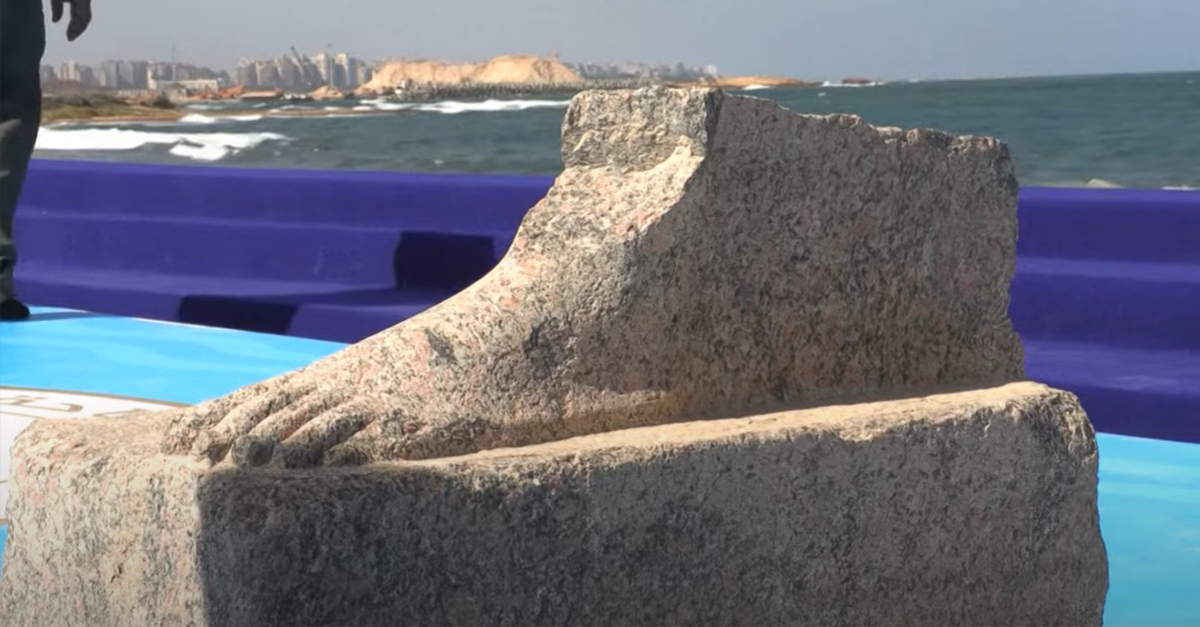
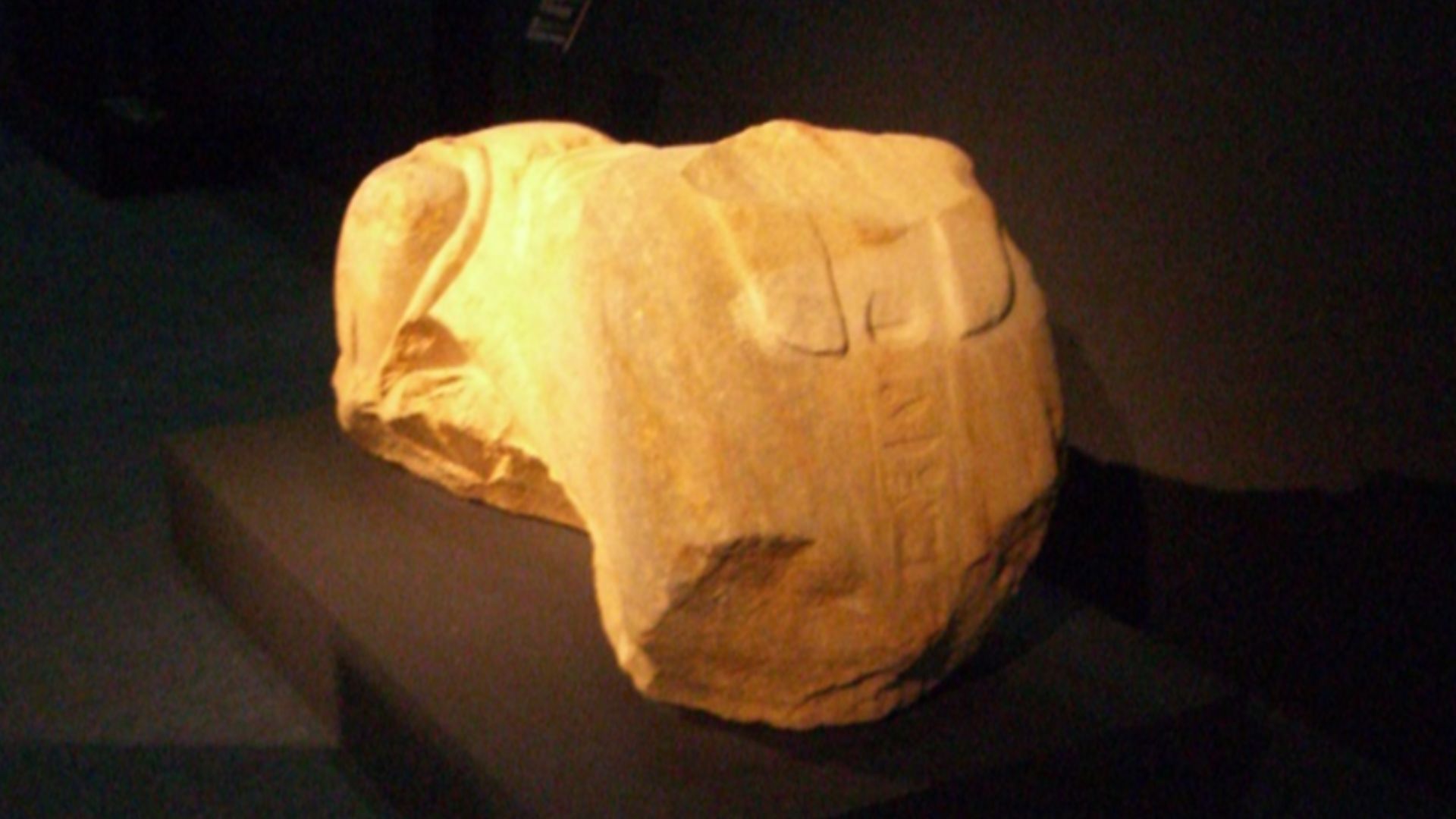
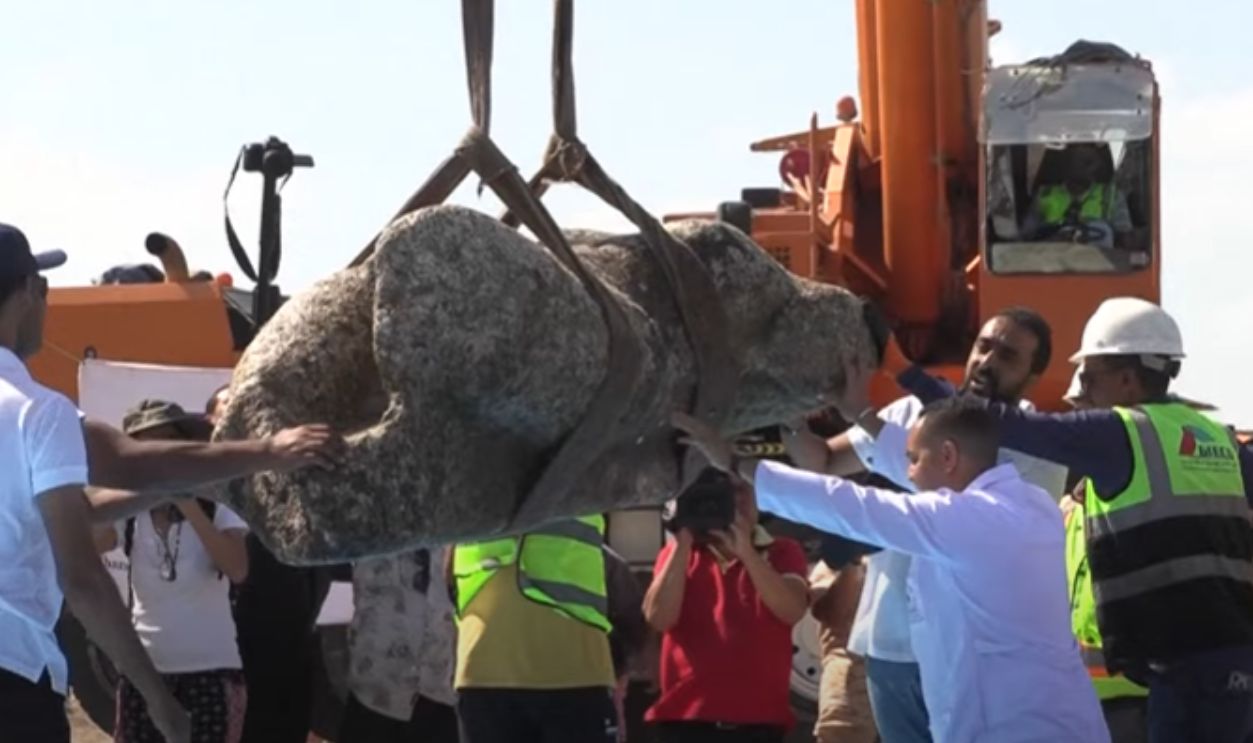
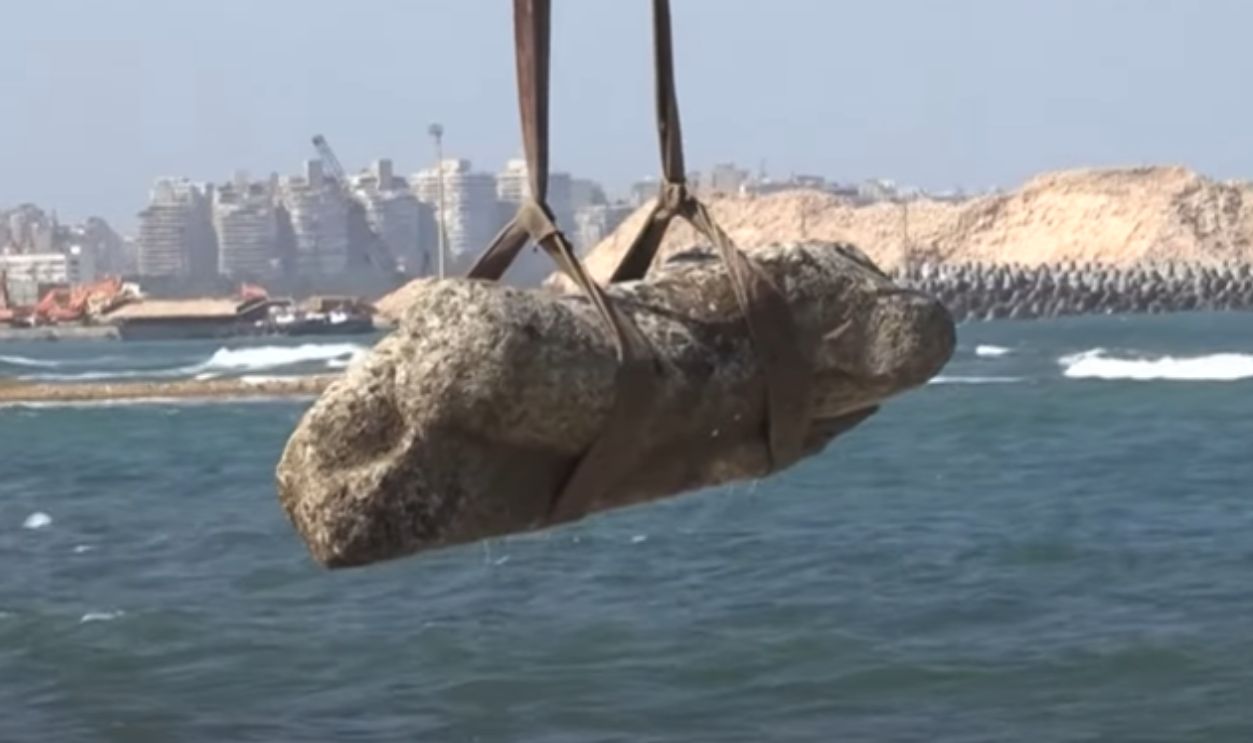
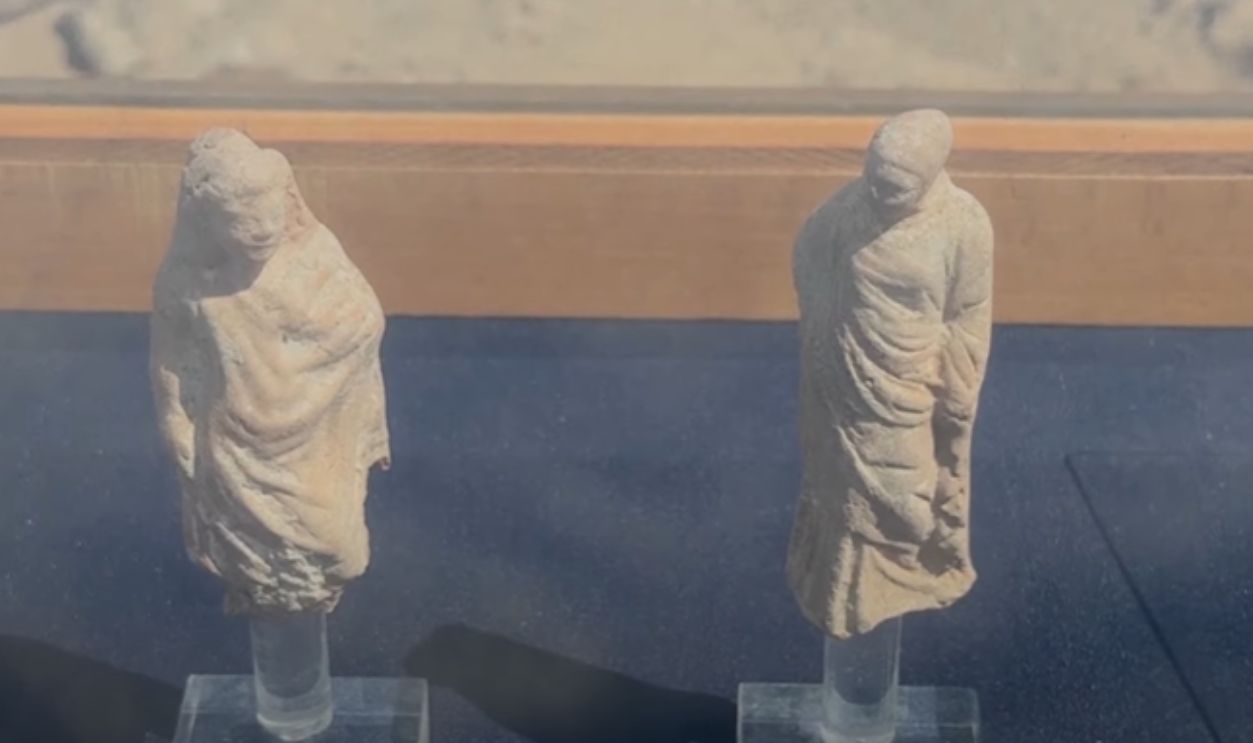
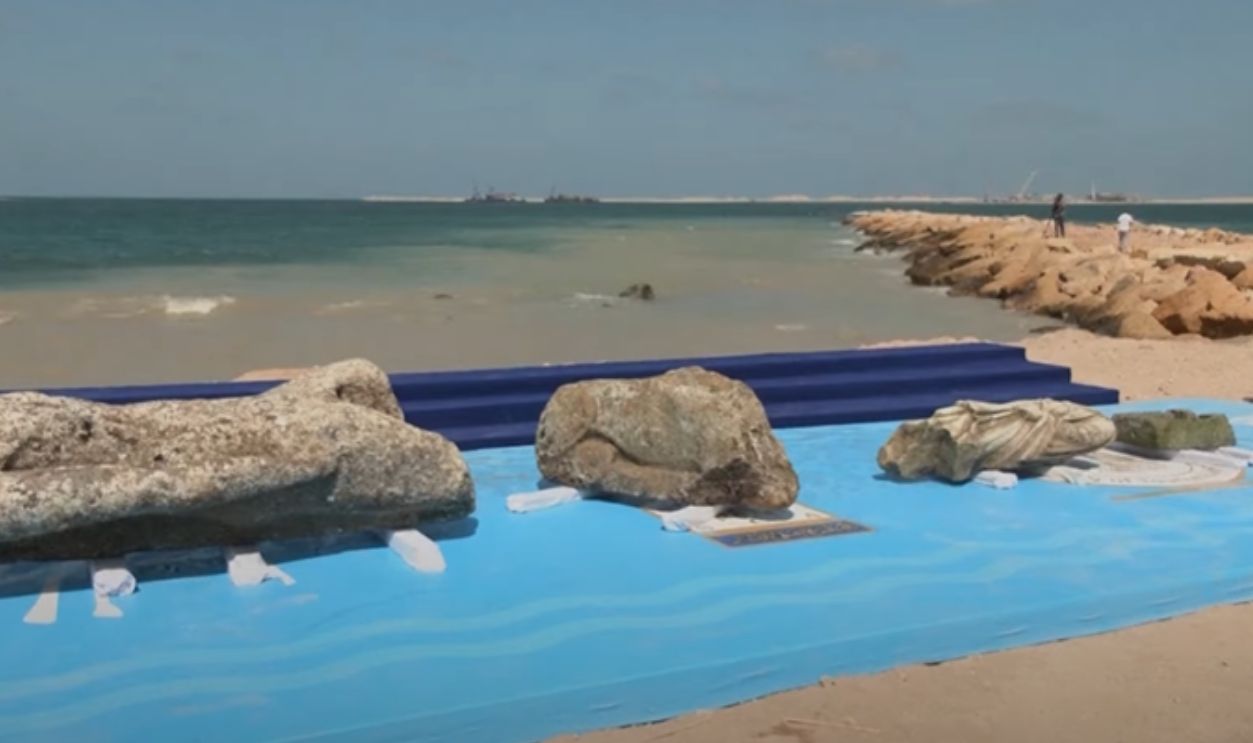
In August 2025, cranes hoisted statues, architectural fragments, and docks from Abu Qir Bay, including buildings, limestone structures, and water basins. These were carefully retrieved by divers from just off Alexandria’s shore. Among the stunning finds are royal and Ptolemaic statues, a quartz sphinx with Ramses II’s cartouche, and fragmentary figures: a headless granite Ptolemaic figure; and a marble Roman noble’s lower half.
Possible Extension Of Canopus
Egyptian authorities believe the submerged site could represent a previously unknown extension of the ancient city of Canopus. Discovered near its historically recognized area, the ruins, including residences, temples, reservoirs, and docks, lay concealed beneath the coastal waters of Abu Qir Bay, submerged under the sea by rising water and seismic shocks.
A City Lost To The Sea
Canopus, on the western Nile Delta, was at one time a thriving city. But as time inexorably marched on, natural disasters and rising waters caused its gradual submersion under the waves of the Mediterranean. Today, archaeologists are using advanced diving methods to explore its ruins, reconstructing the fragments of a society from 2,000 years ago.
 Jacques Descloitres, MODIS Rapid Response Team, NASA/sh, Wikimedia Commons
Jacques Descloitres, MODIS Rapid Response Team, NASA/sh, Wikimedia Commons
The 2025 Discovery
The August 2025 expedition revealed remarkably well-preserved ruins and artifacts. Temples, statues, and ritual objects lay hidden under layers of sand and silt. Each item hauled up off the sea bottom illuminates the daily life, spiritual practices, and international importance of Canopus at the cultural and geographic crossroads of Ptolemaic Egypt.
 James Byrum from Nowhere, Wikimedia Commons
James Byrum from Nowhere, Wikimedia Commons
The Importance Of Canopus
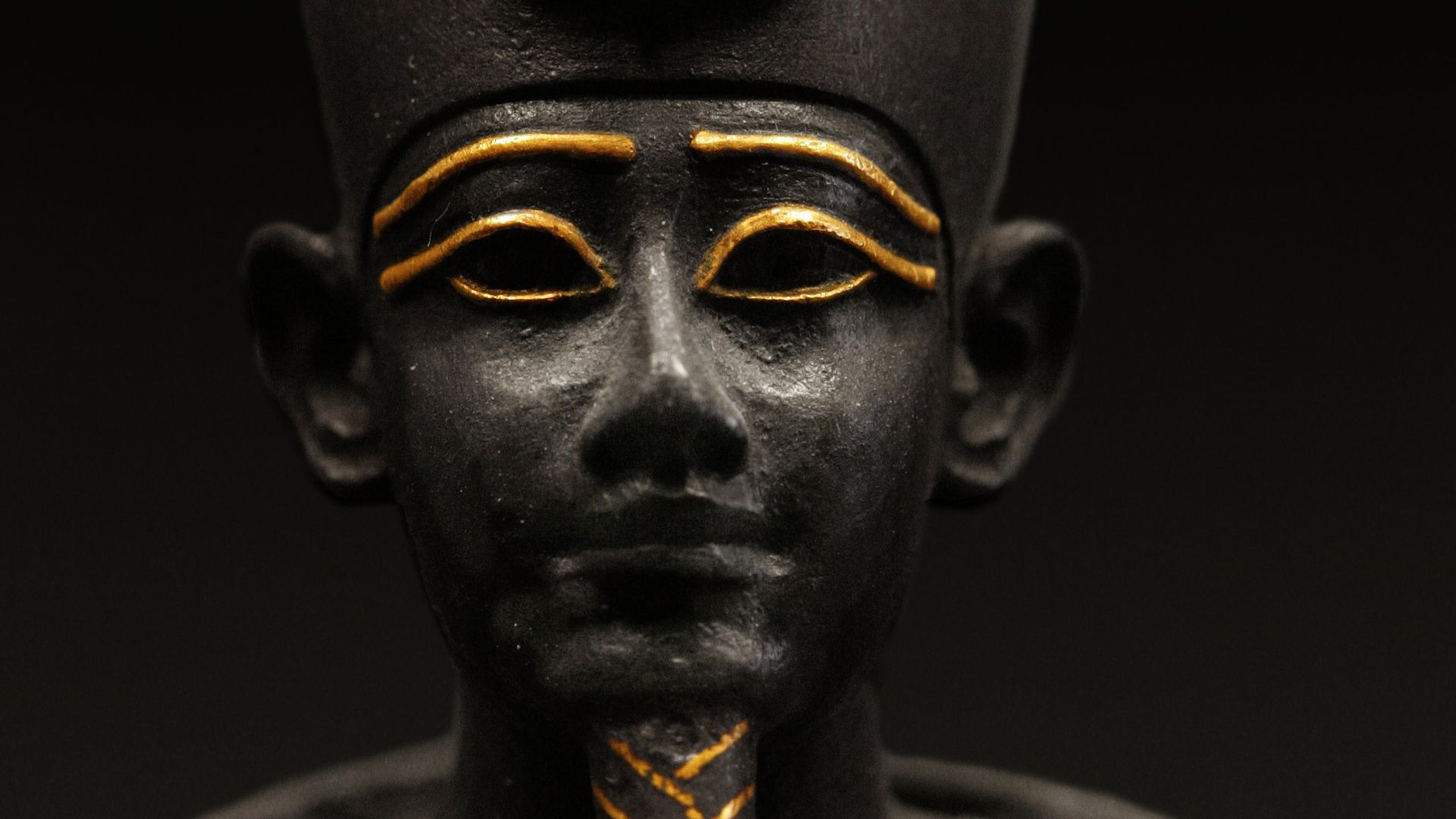
Canopus was famous in antiquity as a spiritual center dedicated to the Egyptian god Osiris. . Pilgrims traveled there from all across Egypt to take part in rituals. The city’s well-earned reputation for religious meaning was also matched by its role in trade routes, linking Egypt to the other civilizations of the Mediterranean.
The Role Of Osiris Worship
The spiritual lifeblood of Canopus was the Osiris cult. The city hosted sacred processions and ceremonies to honor the pivotal Egyptian god of the afterlife. The rituals drew many throngs of worshippers and elevated Canopus’s spiritual prestige to an international level. This made it one of Egypt’s most important religious centers during the classical Greco-Roman period.
Maritime Trading Hub
Aside from religion, Canopus thrived as a Mediterranean port. Situated strategically near Alexandria, it brought merchants, sailors, and travelers. Goods flowed in and out of the city from all over, as the city became a commercial gateway and center of cultural diversity.
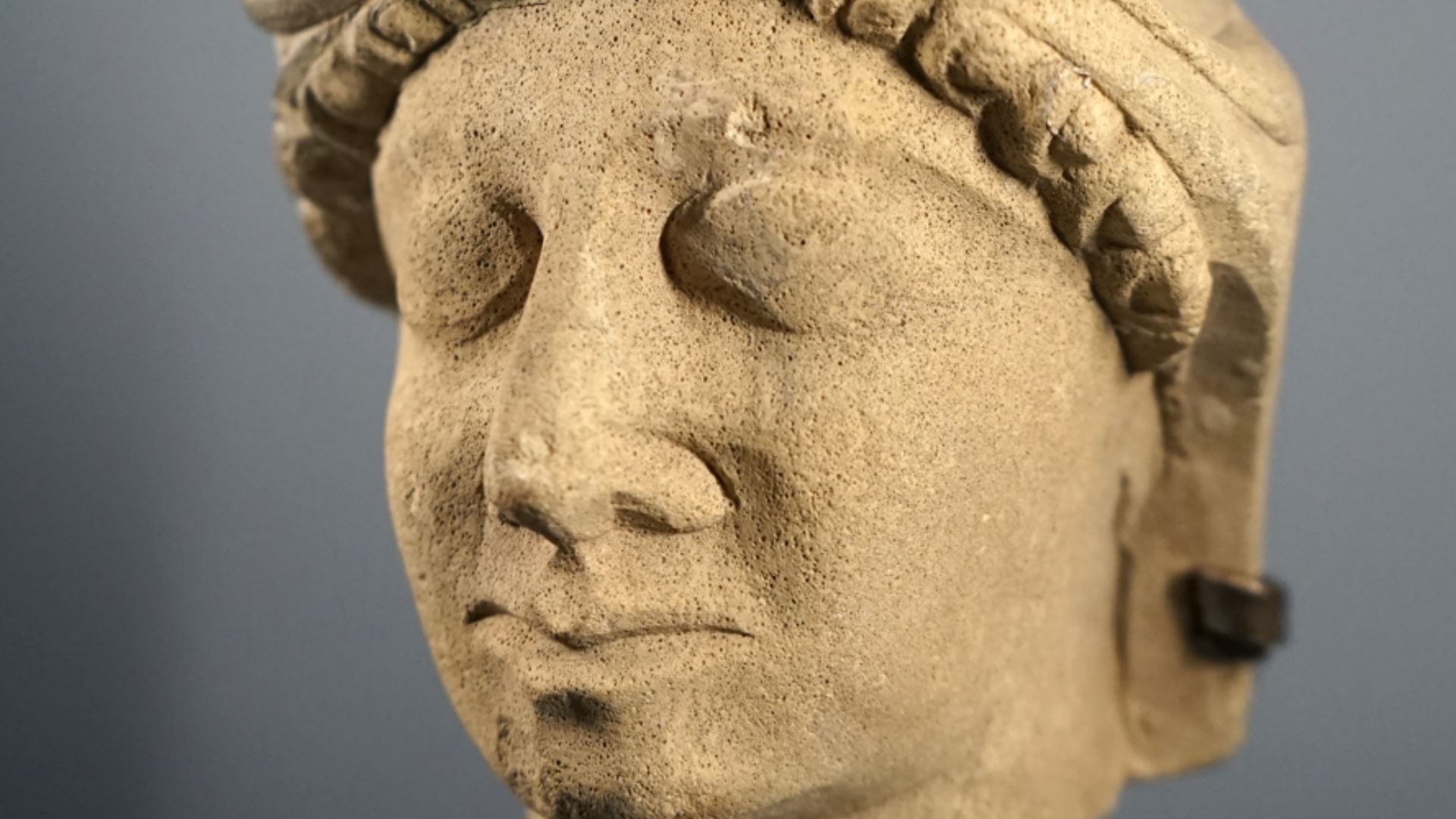 Jean-Pierre Dalbéra, Wikimedia Commons
Jean-Pierre Dalbéra, Wikimedia Commons
The Waters Rose
Historians believe a combination of earthquakes and rising sea levels were ultimately what led to Canopus’s submersion. The city gradually disappeared beneath the Mediterranean. For centuries its ruins were hidden, preserving temples, streets, and statues in a condition that modern divers are able to carefully document and recover.
A Trove Of Artifacts Large And Small
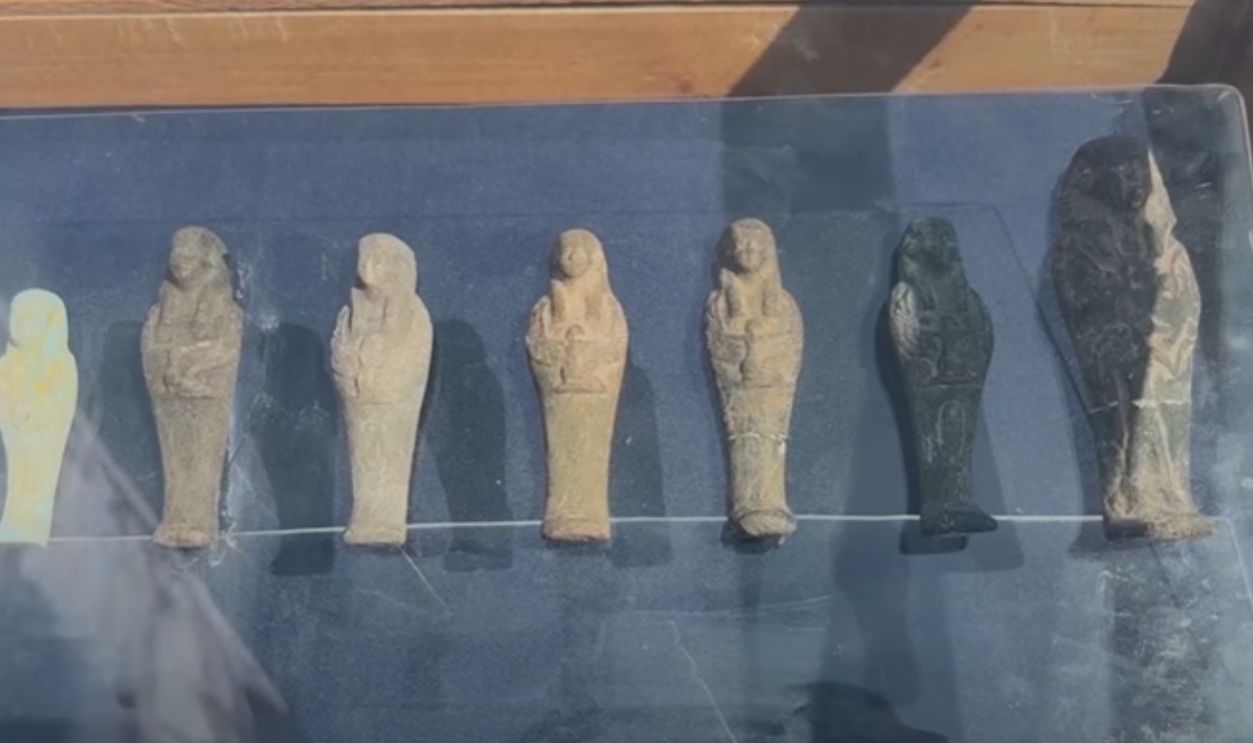
Among the greatest discoveries were massive granite statues of Egyptian deities and pharaohs. Ritual objects, jewelry, and household goods were also retrieved. Each piece adds more detail to what we know of the wealth and artistic sophistication of Canopus, telling the story of a society that was a fascinating mix of Egyptian traditions and foreign influences.
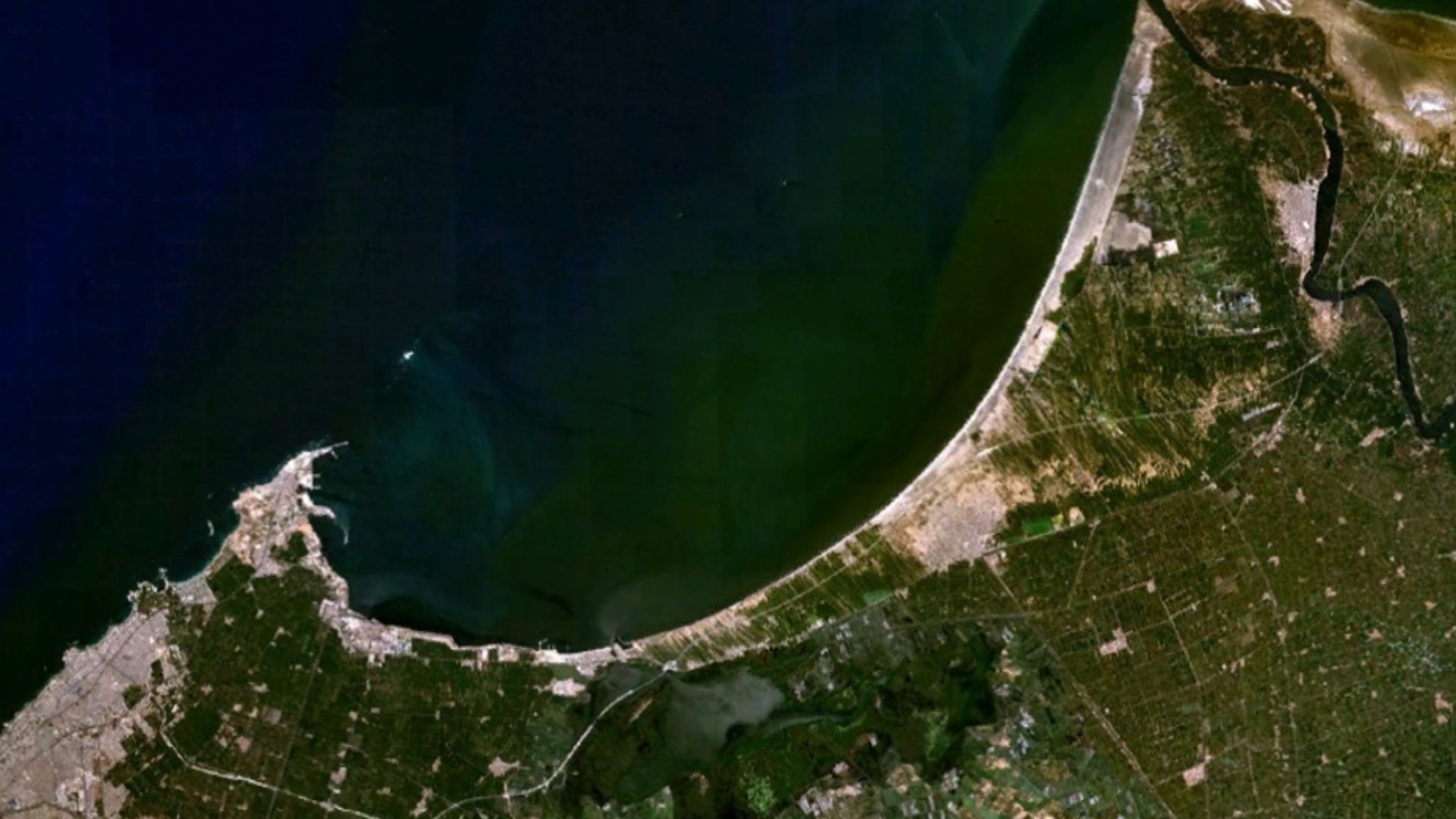 NASA World Wind (v1.4), Wikimedia Commons
NASA World Wind (v1.4), Wikimedia Commons
Greek And Roman Influence
Canopus flourished under Greek and Roman rule, essentially blending the cultures. Artifacts display a mixture of Egyptian religious symbolism with Hellenistic and Roman styles. The fusion reflects Canopus’s cosmopolitan nature; it was a meeting of East and West in art, commerce, and spiritual affairs.
International Importance
Canopus was internationally recognized in its time as a place of healing and pilgrimage. Ancient travelers praised its temples and sanctuaries, ensuring it an important place in classical literature and preserving its fame for eons after it slipped beneath the waves.
Temples And Religious Sites
Divers have revealed the remains of temples dedicated to Egyptian gods. Columns, altars, and sacred vessels are still scattered across the seabed waiting for discovery by enterprising underwater archaeologists. The sites testify to the grandeur of Canopus’s religious architecture that left ancient worshippers gaping in awe.
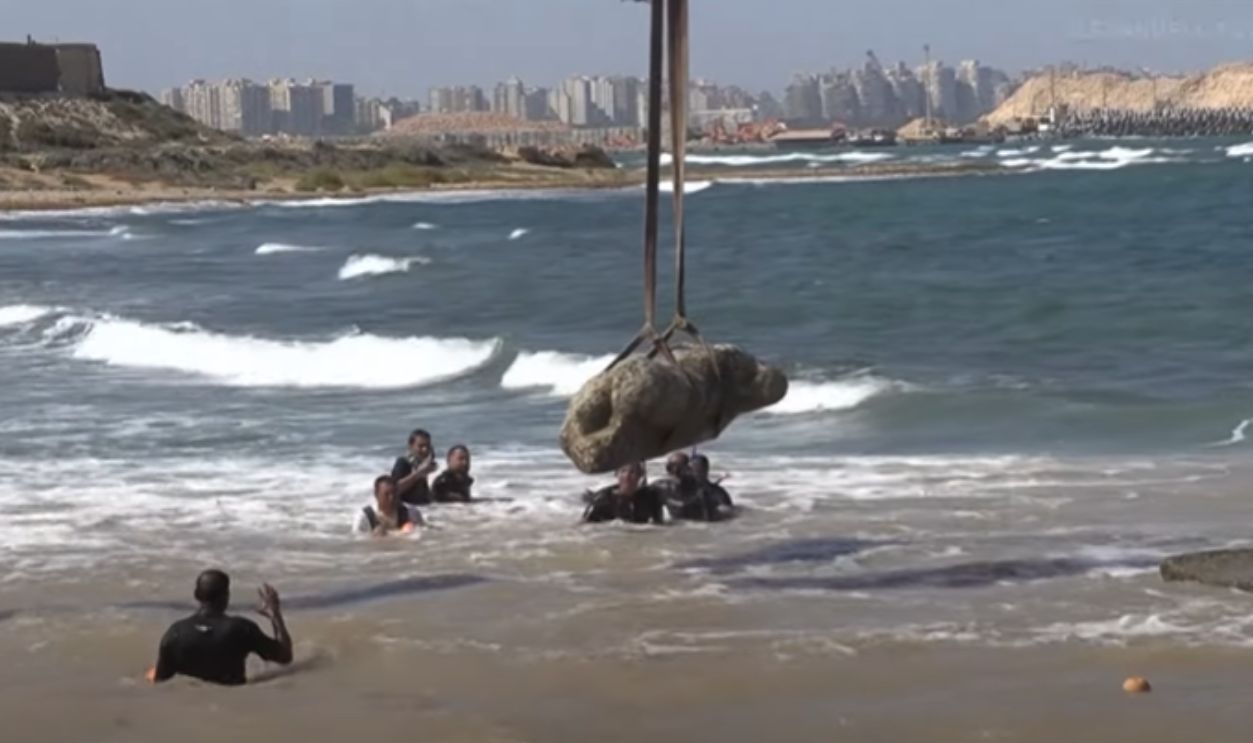 Egypt unveils 2,000-year-old sunken city • FRANCE 24 English, FRANCE 24 English
Egypt unveils 2,000-year-old sunken city • FRANCE 24 English, FRANCE 24 English
Treasures Of Everyday Life
The 2025 discoveries also included a wide range of pottery, jewelry, and everyday objects. These items offer us a rare glimpse into the routines of average Canopus residents. They show a wealthy and vibrant society shaped by artisans, merchants, and priests.
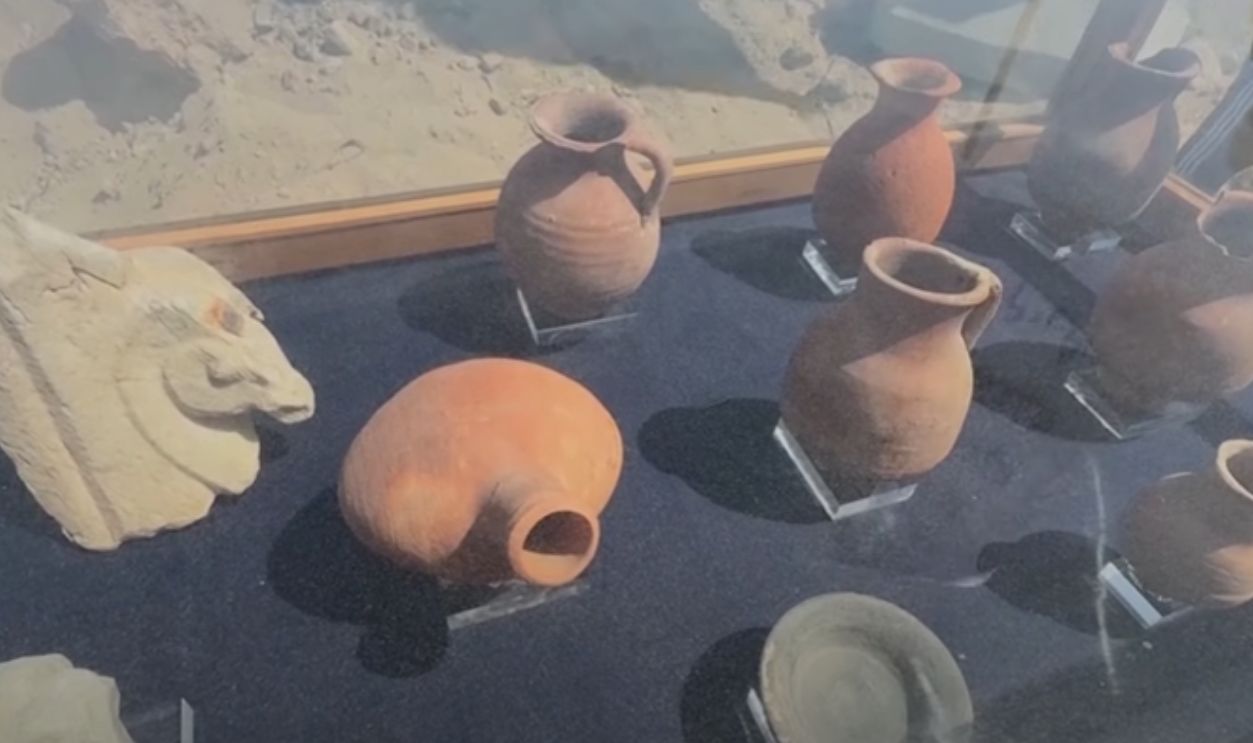 Egypt unveils 2,000-year-old sunken city • FRANCE 24 English, FRANCE 24 English
Egypt unveils 2,000-year-old sunken city • FRANCE 24 English, FRANCE 24 English
Underwater Archaeology Lends A Hand
Modern technology has enhanced the study of Canopus. Underwater archaeology combines diving expertise with digital mapping, sonar, and 3D modeling. These methods are integrated, allowing archaeologists to reconstruct the city on a virtual level. That way we preserve its memory while protecting its most delicate artifacts.
Partnerships In Discovery
The August 2025 mission was a joint effort between Egyptian authorities and international teams. The pooled collaborative expertise secured the careful recovery of artifacts and historically accurate interpretations. The partnership illustrates how global fascination with the ancient world continues to drive forward the preservation of Egypt’s vast legacy.
 Egypt unveils 2,000-year-old sunken city • FRANCE 24 English, FRANCE 24 English
Egypt unveils 2,000-year-old sunken city • FRANCE 24 English, FRANCE 24 English
Connection To Thonis-Heracleion
Canopus’s discovery is related to nearby Thonis-Heracleion, another sunken city. The two submerged cities together reveal a network of trade, religion, and culture, giving us unparalleled insights into the Nile Delta’s role in the ancient world.
 Jon Bodsworth, Wikimedia Commons
Jon Bodsworth, Wikimedia Commons
The Challenge Of Preservation
Hauling treasures up from the sands that veil Canopus poses major challenges. Saltwater corrosion, shifting sands, and fragile structures make preservation delicate, requiring infinite care and patience by archaeologists and technicians. As we speak, conservators are working tirelessly to stabilize artifacts for long-term survival as museum pieces for future generations of scholars and the public.
 Egypt unveils 2,000-year-old sunken city • FRANCE 24 English, FRANCE 24 English
Egypt unveils 2,000-year-old sunken city • FRANCE 24 English, FRANCE 24 English
Tourism And Global Interest
Egypt has plans to showcase these Canopus discoveries in museums and exhibitions. They’re exactly the kind of treasures that attract tourists from all over the globe, boosting Egypt’s cultural economy. Visitors can get a firsthand look at the grandeur of a city once lost beneath the waves.
 Egypt unveils 2,000-year-old sunken city • FRANCE 24 English, FRANCE 24 English
Egypt unveils 2,000-year-old sunken city • FRANCE 24 English, FRANCE 24 English
Cultural Significance Today
The rediscovery of these long-lost artifacts is a new chapter in the story of how civilizations change through time as they adapt, flourish, and eventually decline. IThe artifacts are yet another addition to Egyptian heritage and inspire pride in Egypt’s enduring contributions to human history.
 Egypt unveils 2,000-year-old sunken city • FRANCE 24 English, FRANCE 24 English
Egypt unveils 2,000-year-old sunken city • FRANCE 24 English, FRANCE 24 English
The Lessons Of Canopus
The sunken city tells us broader lessons about the power of nature and the transitoriness of man-made structures. It also shows us how interconnected all these ancient Mediterranean civilizations really were. Canopus thrived because of its spiritual life, trade, and cultural fusion, a newly reinvigorated legacy that can inspire into the future .
 Egypt unveils 2,000-year-old sunken city • FRANCE 24 English, FRANCE 24 English
Egypt unveils 2,000-year-old sunken city • FRANCE 24 English, FRANCE 24 English
The Rediscovery Of A Lost Jewel Of The Past
The August 2025 discovery of Canopus is another milestone in Egyptian archaeology. The recovery of its treasures revives the memory of a city that was celebrated across the ancient world. Canopus is now back in the public eye as a part Egypt’s glorious past.
 Egypt unveils 2,000-year-old sunken city • FRANCE 24 English, FRANCE 24 English
Egypt unveils 2,000-year-old sunken city • FRANCE 24 English, FRANCE 24 English
You May Also Like:
Ranking The Countries With The Most UNESCO Sites—According To Records
There's Way More To Egypt Than The Great Pyramids: The Explosion Of Egyptian Tourism















