Digging Into Biblical Times
What if a single trench could rewrite the story of Jerusalem’s past? Archaeologists in the City of David have uncovered a vast moat that once divided ancient Jerusalem, confirming details long recorded in sacred scripture.
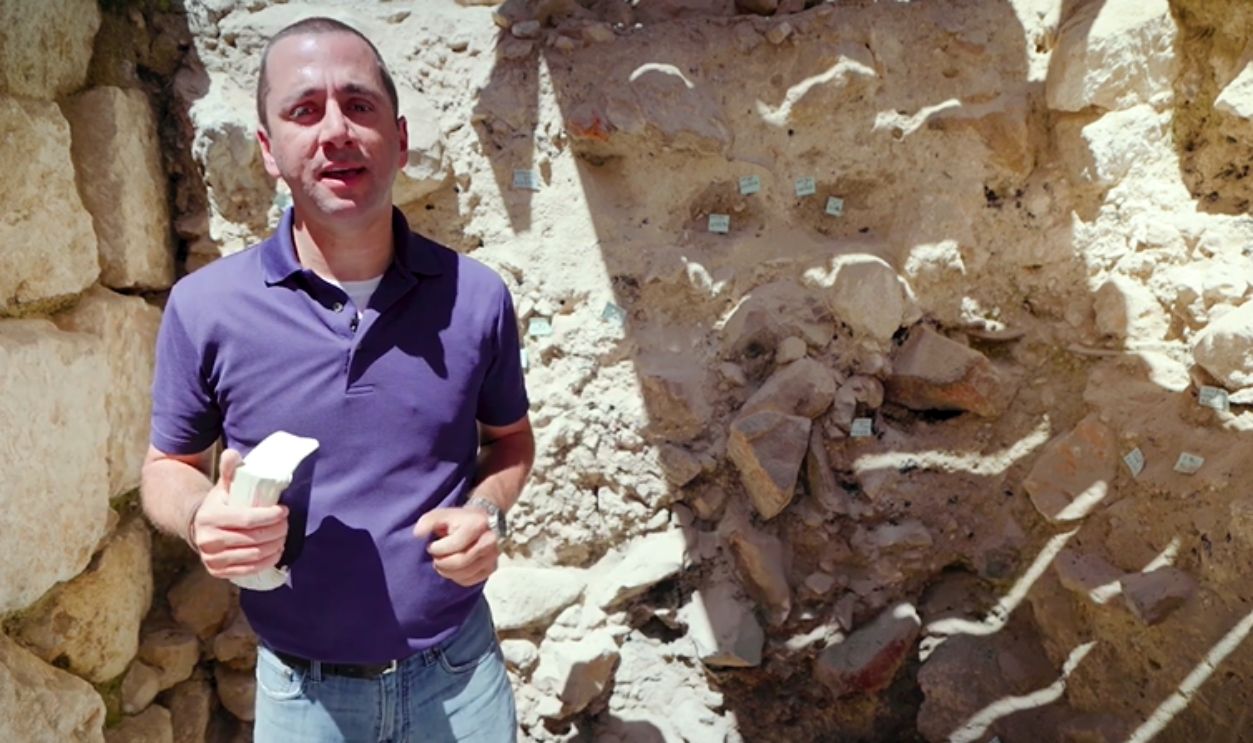

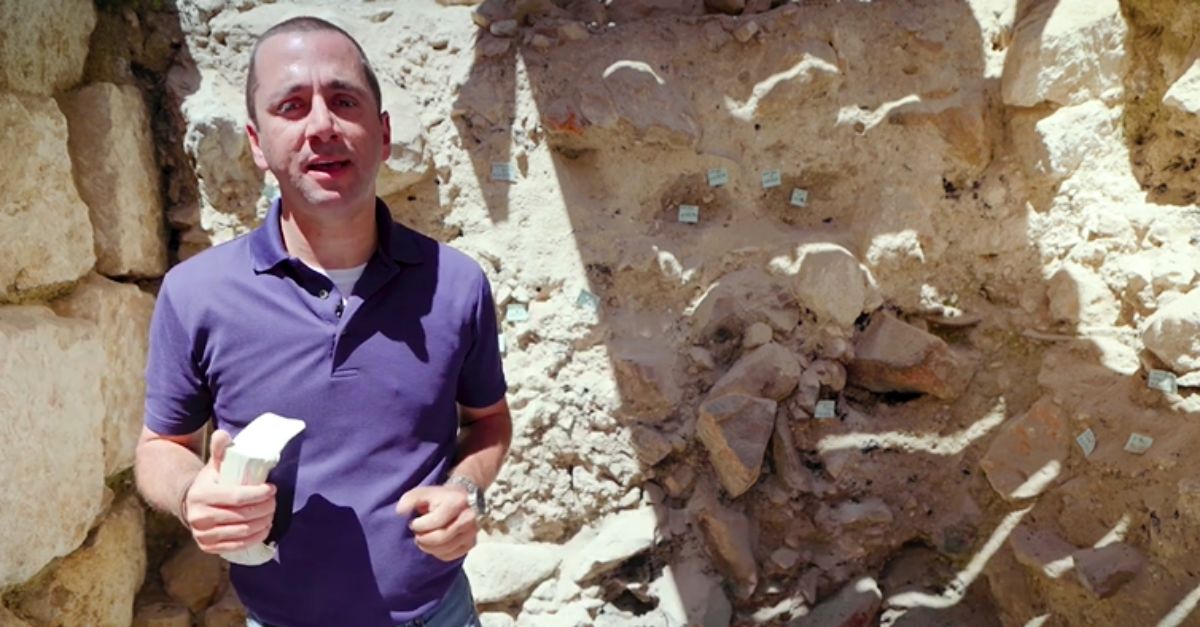
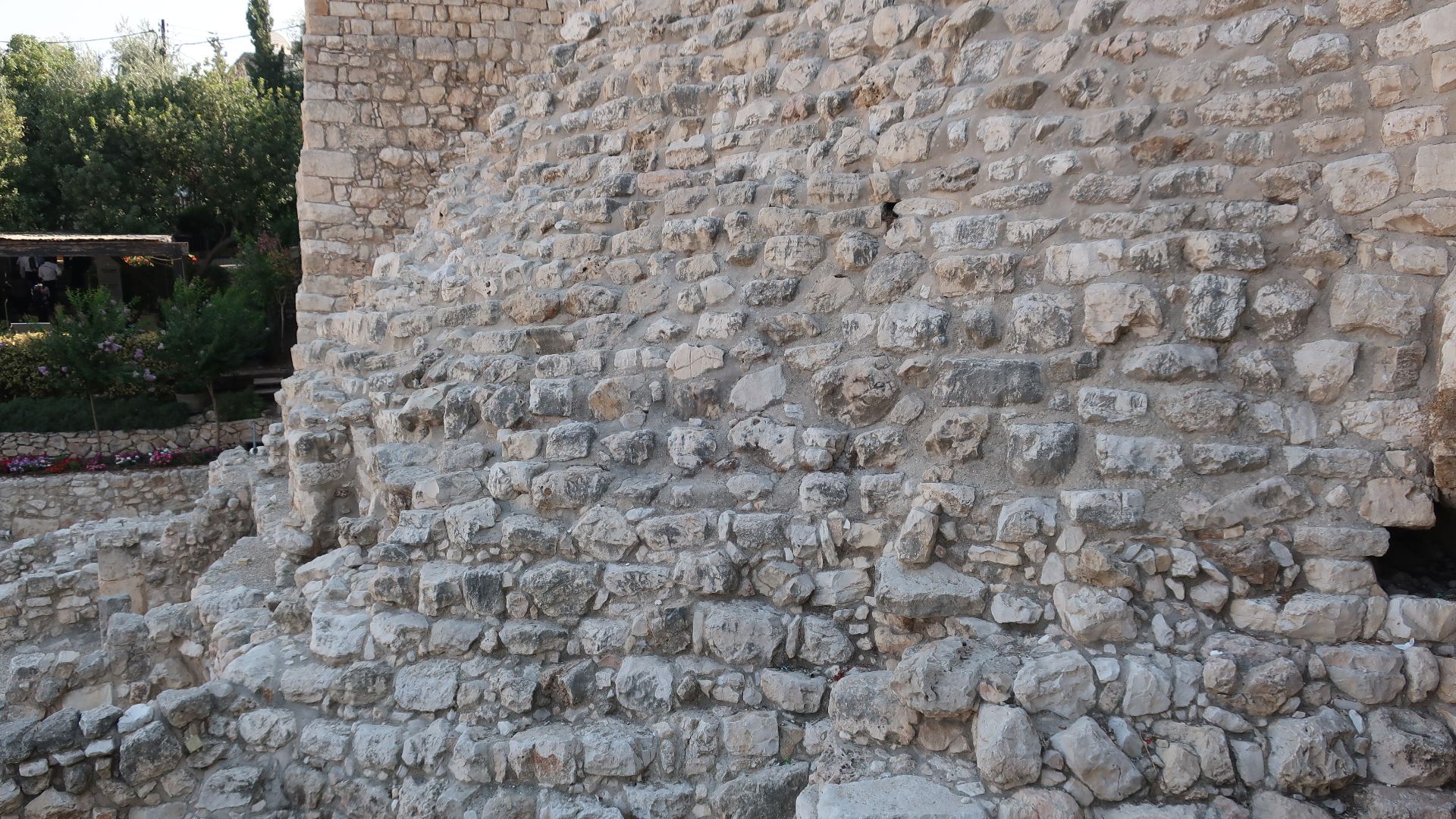
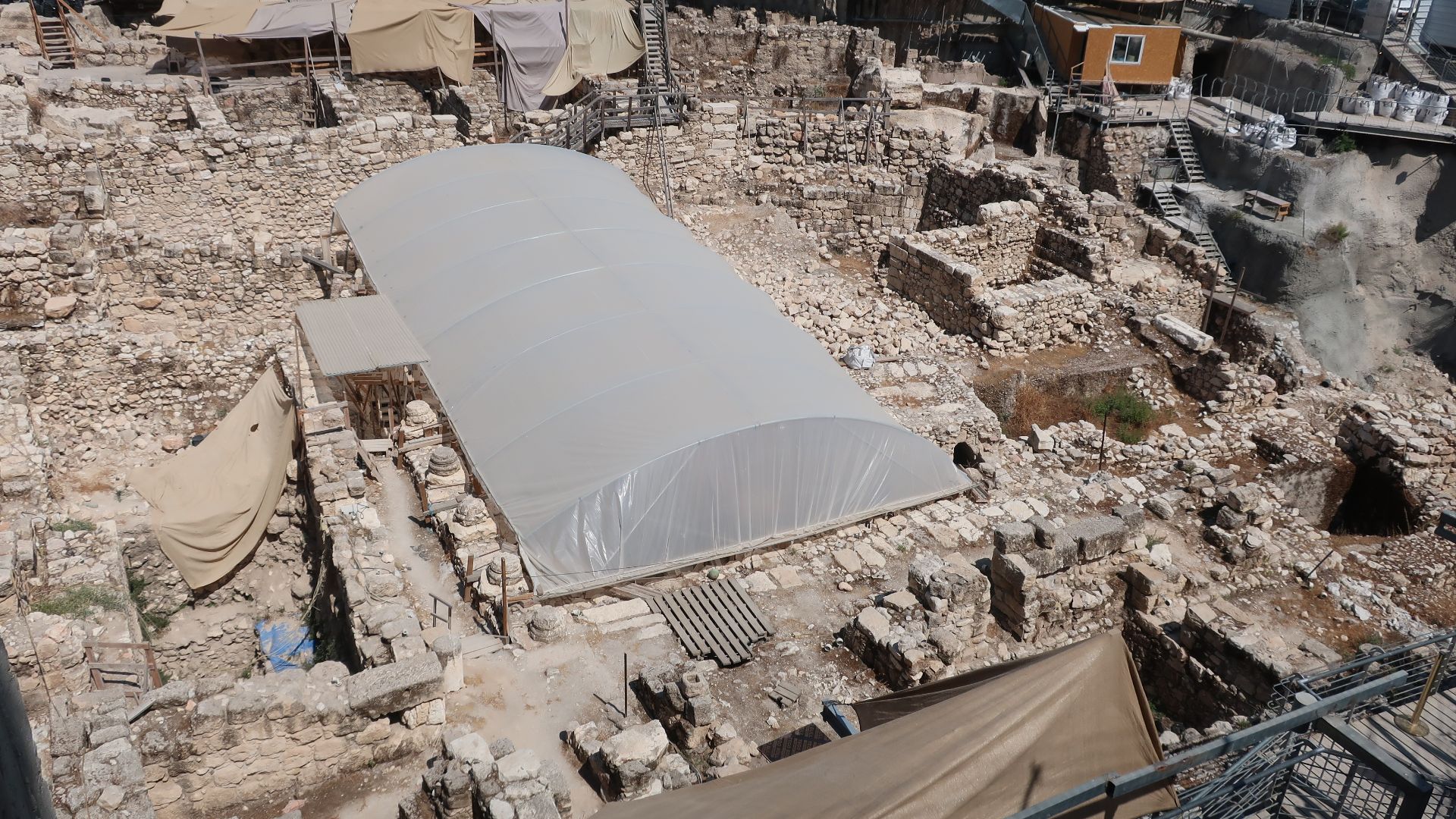
City Of David Moat
Hidden beneath the heart of Jerusalem’s City of David lay a massive trench no one expected to find intact. Excavation layers and dating evidence suggest it was already in use during the reign of King Josiah in the 7th century BCE. This offers a rare glimpse into the city’s ancient defenses.
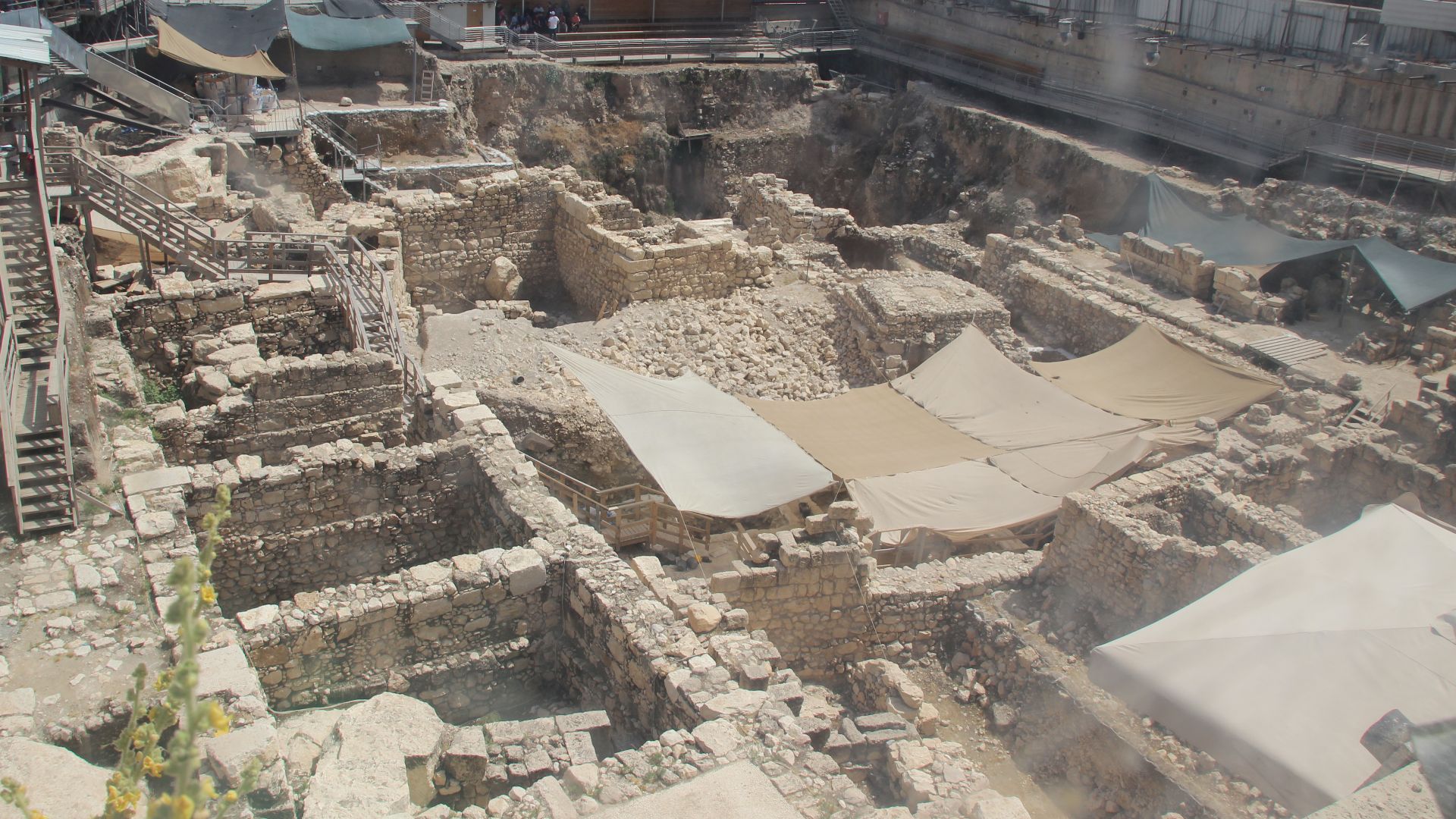
Giv’ati Parking Lot Site
Just uphill from the moat, the Giv’ati parking lot excavations continued the same story of a city built in layers. Archaeologists uncovered remnants spanning biblical ages, with artifacts from multiple eras revealing how Jerusalem evolved from its earliest settlements into the dense urban center recorded in ancient texts.
 Gary Todd from Xinzheng, China, Wikimedia Commons
Gary Todd from Xinzheng, China, Wikimedia Commons
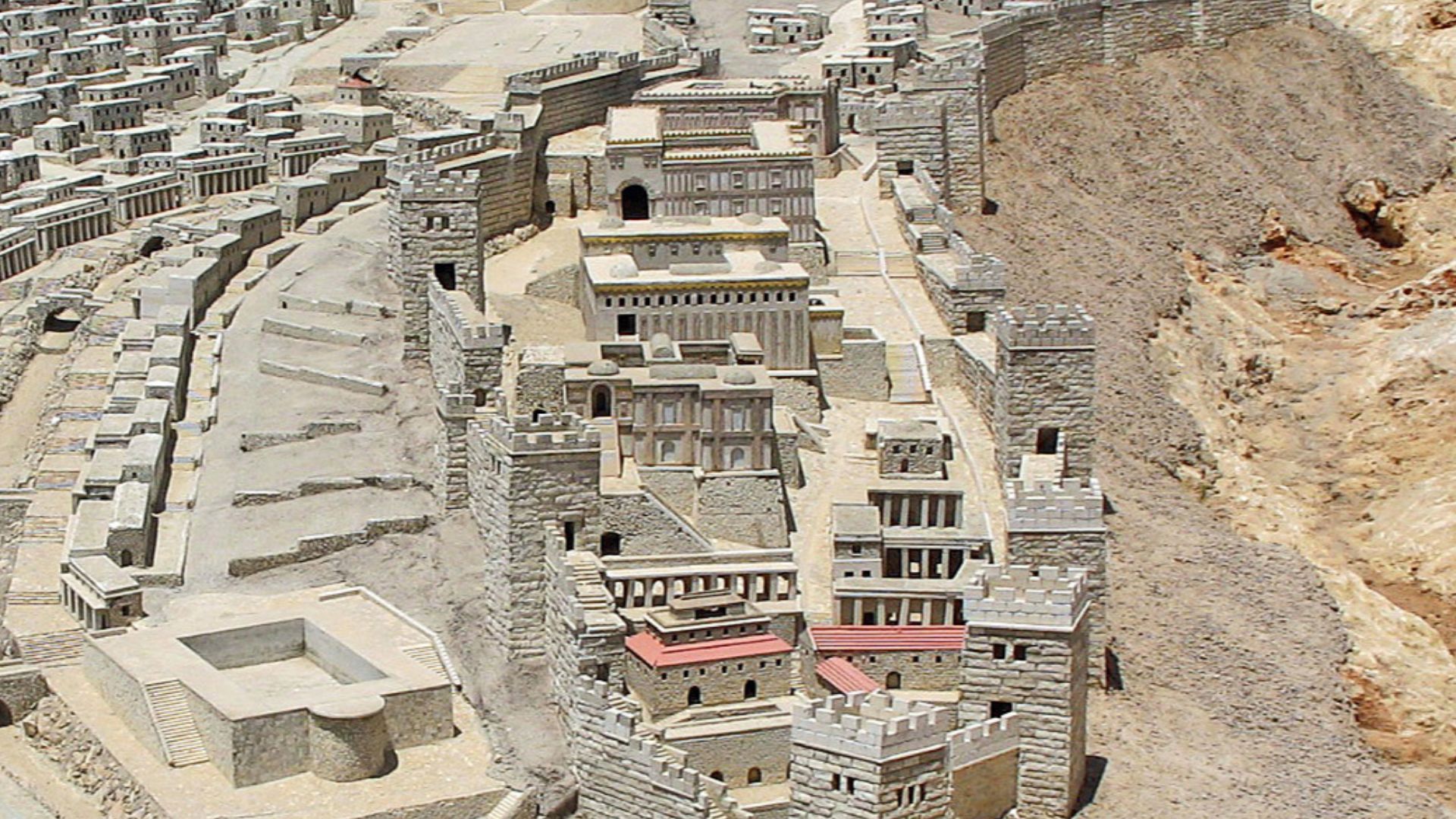
Dual Sections Of Jerusalem
Ancient texts often spoke of a divided Jerusalem, but until now, proof was scarce. Using 3D mapping, researchers visualized a massive trench cutting through the city’s old terrain. The feature likely marked boundaries between administrative or royal zones.
Israel Antiquities Authority’s Role
The Israel Antiquities Authority helped lead the excavation and, through their works, confirmed the moat’s age through standard archaeological methods. Researchers relied on stratigraphic layers and pottery typology to date the trench. When the findings were announced, the discovery quickly captured global interest and drew widespread media coverage.
 Gila Brand, aka Gilabrand at en.wikipedia, Wikimedia Commons
Gila Brand, aka Gilabrand at en.wikipedia, Wikimedia Commons
Tel Aviv University Collaboration
The story wouldn’t be complete without Tel Aviv University’s contribution. Their experts confirmed the moat’s strategic function and architectural purpose using precision dating tools. Every result went through peer review to ensure scientific credibility matched the excitement of the historical revelation.
City Of David Excavation History
The City of David has always been a magnet for discovery. Since the 19th century, its slopes have yielded walls, tunnels, and fortifications. The newly found moat now joins that lineage, adding depth to Jerusalem’s origin story.
 Joe Freeman , Wikimedia Commons
Joe Freeman , Wikimedia Commons
Biblical Mentions Of Fortifications
Scripture often referenced Jerusalem’s defenses, yet physical proof had remained elusive. The moat’s dimensions and placement mirror descriptions in the Books of Samuel and Kings. Scholars now compare terrain to text and, correspondingly, find a striking alignment that reinforces timelines from David’s reign.
Silwan’s Archaeological Riches
Silwan, where the City of David rests today, is no strange to discovery. Its homes lie on Canaanite foundations, Roman remnants, and now, the Iron Age moat. The district represents 3,000 years of layered civilization—so rich that residents sometimes uncover relics just by digging in their backyards.
Stonework From The Moat
Every stone in the moat’s wall hints at a workforce operating with practiced precision. Tool marks match Iron Age methods and point to trained masons working in coordination. Locally quarried limestone blocks add another clue, revealing a project organized and financed through official authority.
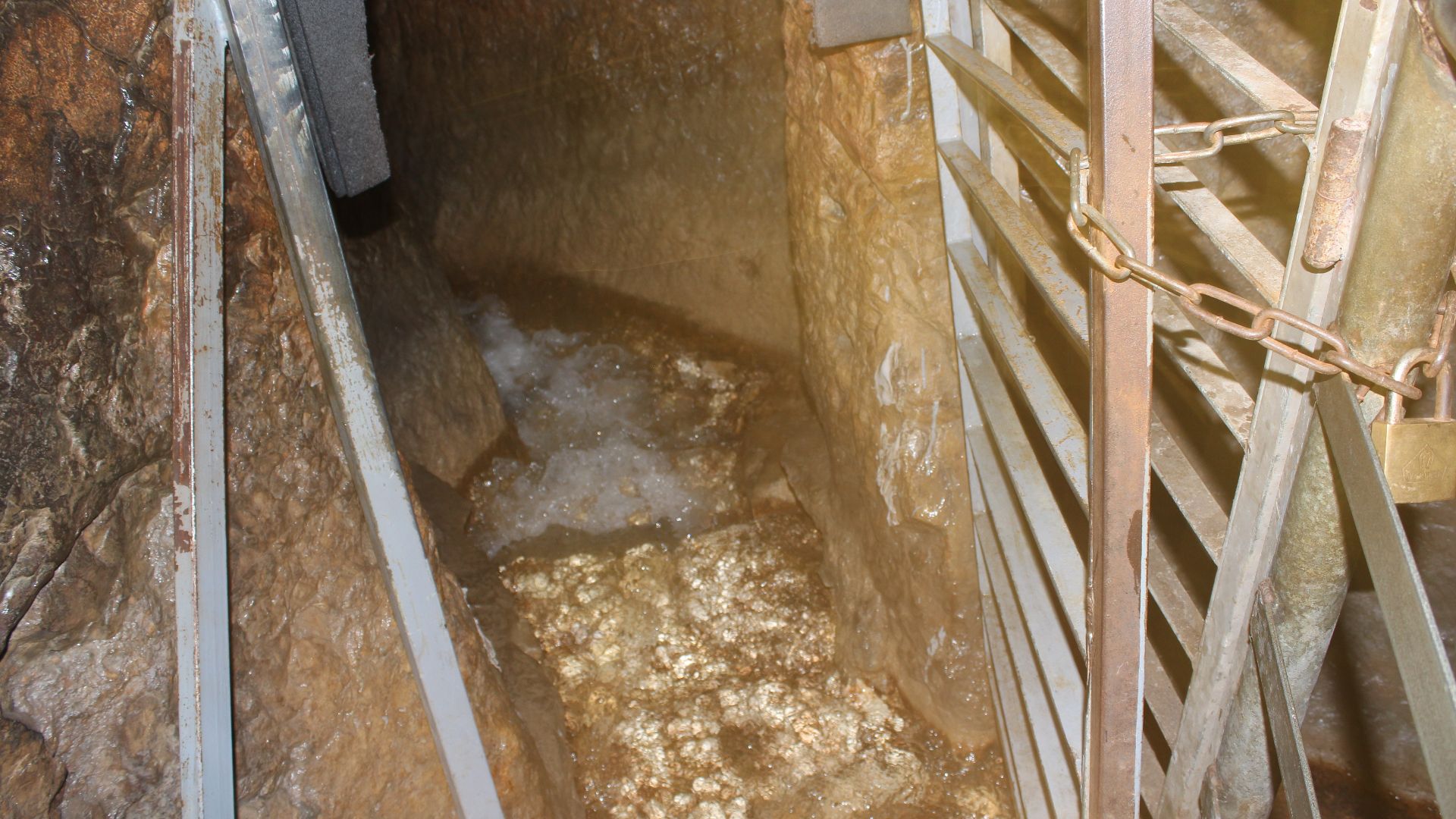
Evidence Of Water Systems
Near the moat, channels cut into bedrock hinted at ancient hydraulic planning. Engineers of the era likely used runoff from the Gihon Spring to reinforce defenses. Such ingenuity places Jerusalem alongside the great fortress cities of the Bronze and Iron Ages.
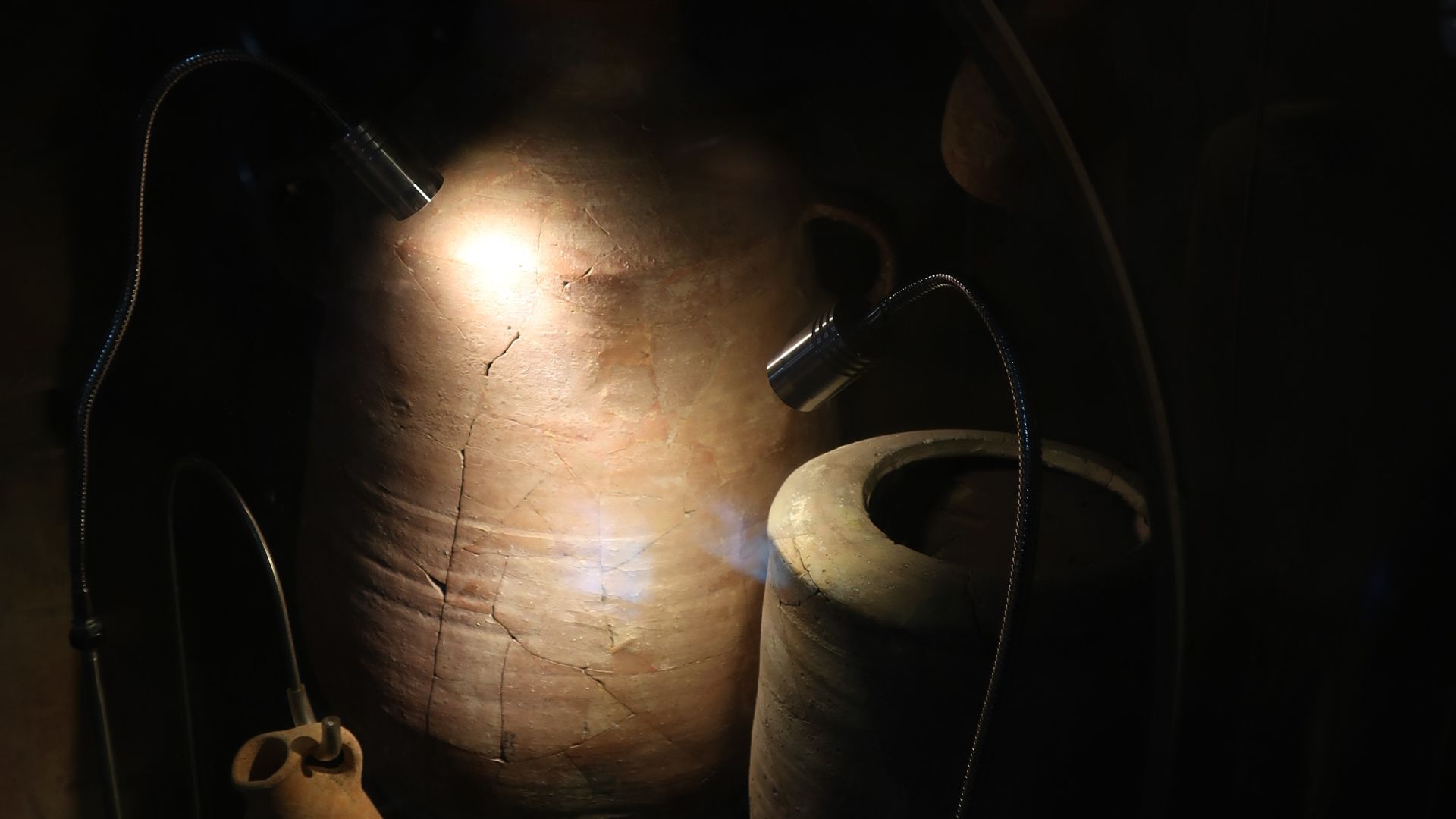
Pottery Shards Discovered
Ceramic fragments uncovered near the moat dated to Iron Age II, placing them around the 7th century BCE—closer to the time of King Josiah than to David. The pottery styles matched vessels from other biblical-era sites, and some jars may have held oil or grain.
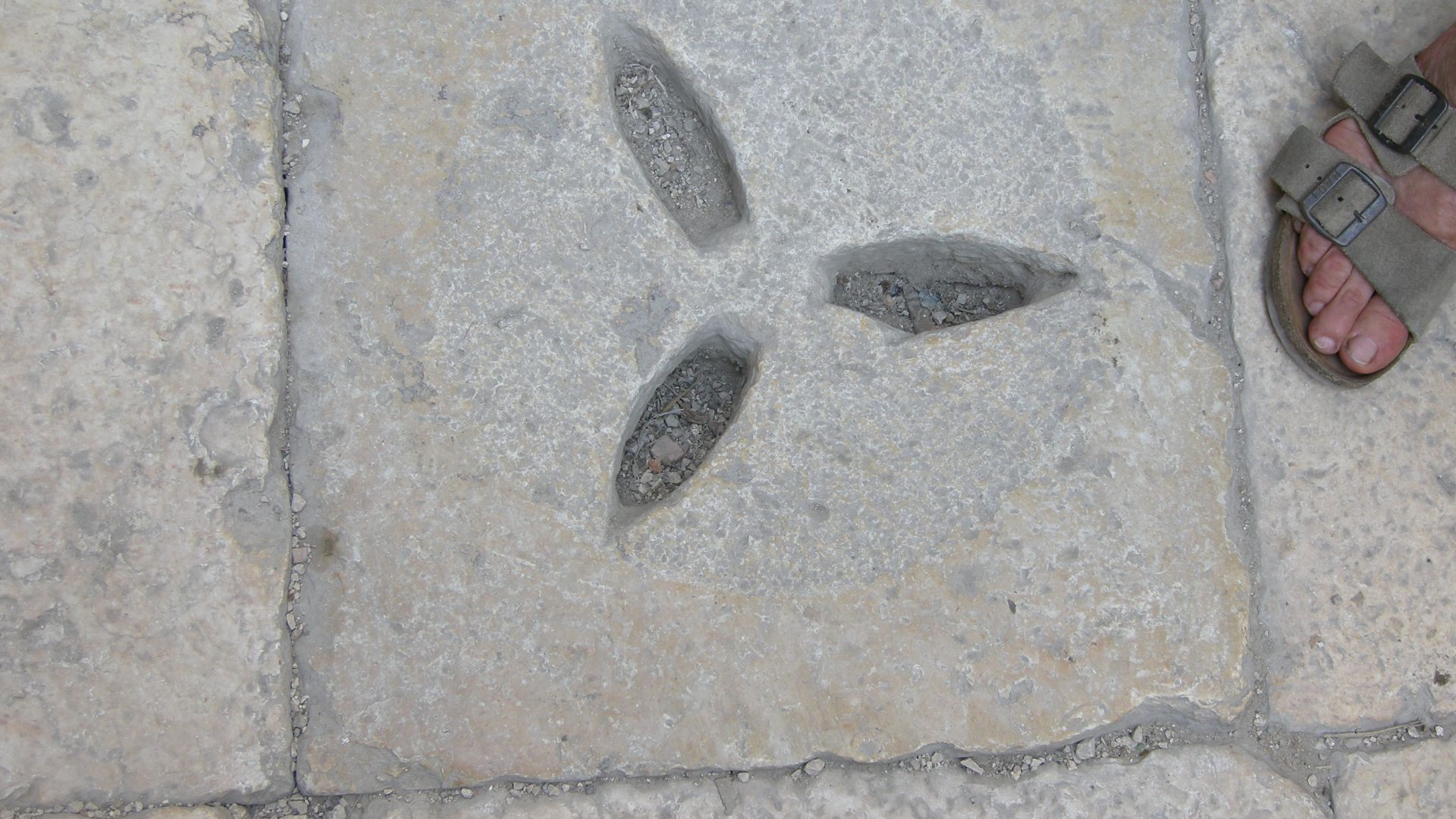
Tools Of Ancient Builders
The moat’s construction becomes clearer through the marks carved into its bedrock. Grooves and crushed-limestone surfaces reveal the extensive quarrying required to carve out the massive trench. The stone itself records the labor of the builders who removed an enormous volume of rock to shape Jerusalem’s defenses.
 Yoav Dothan, Wikimedia Commons
Yoav Dothan, Wikimedia Commons
Organic Remains Found
The soil around the moat was also home to preserved traces of seeds, pollen, and ancient burn marks. These clues help reconstruct the environment of Iron Age Jerusalem and offer insight into vegetation and moments of destruction, even without radiocarbon results tied specifically to this moat.
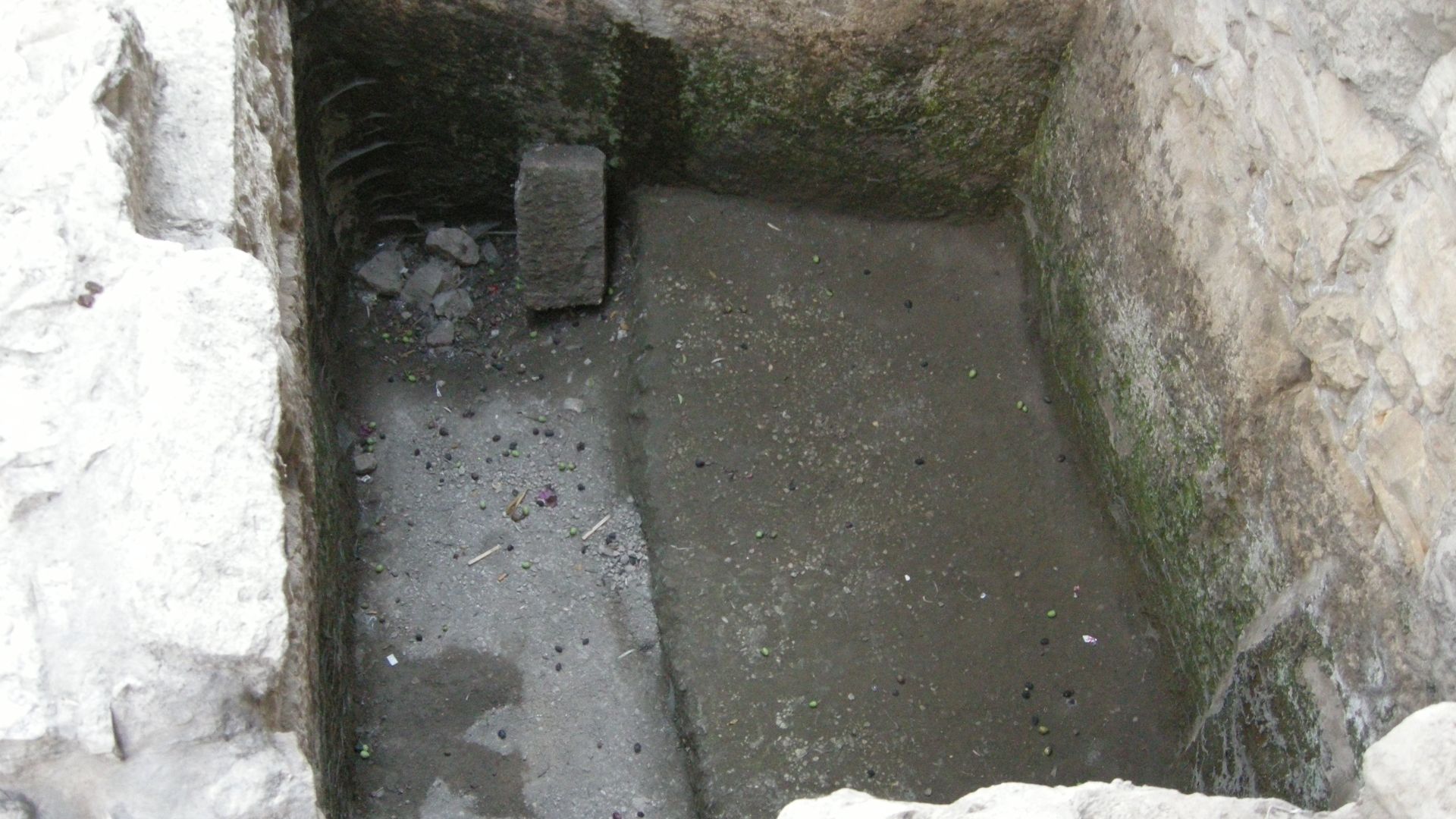 Yoav Dothan, Wikimedia Commons
Yoav Dothan, Wikimedia Commons
Defensive Purpose Confirmed
This moat was engineered for survival. Its sloped walls and remarkable depth reveal unmistakable military intent. With design elements echoing Canaanite fortresses, the trench transformed Jerusalem into one of the hardest strongholds to challenge in its era.
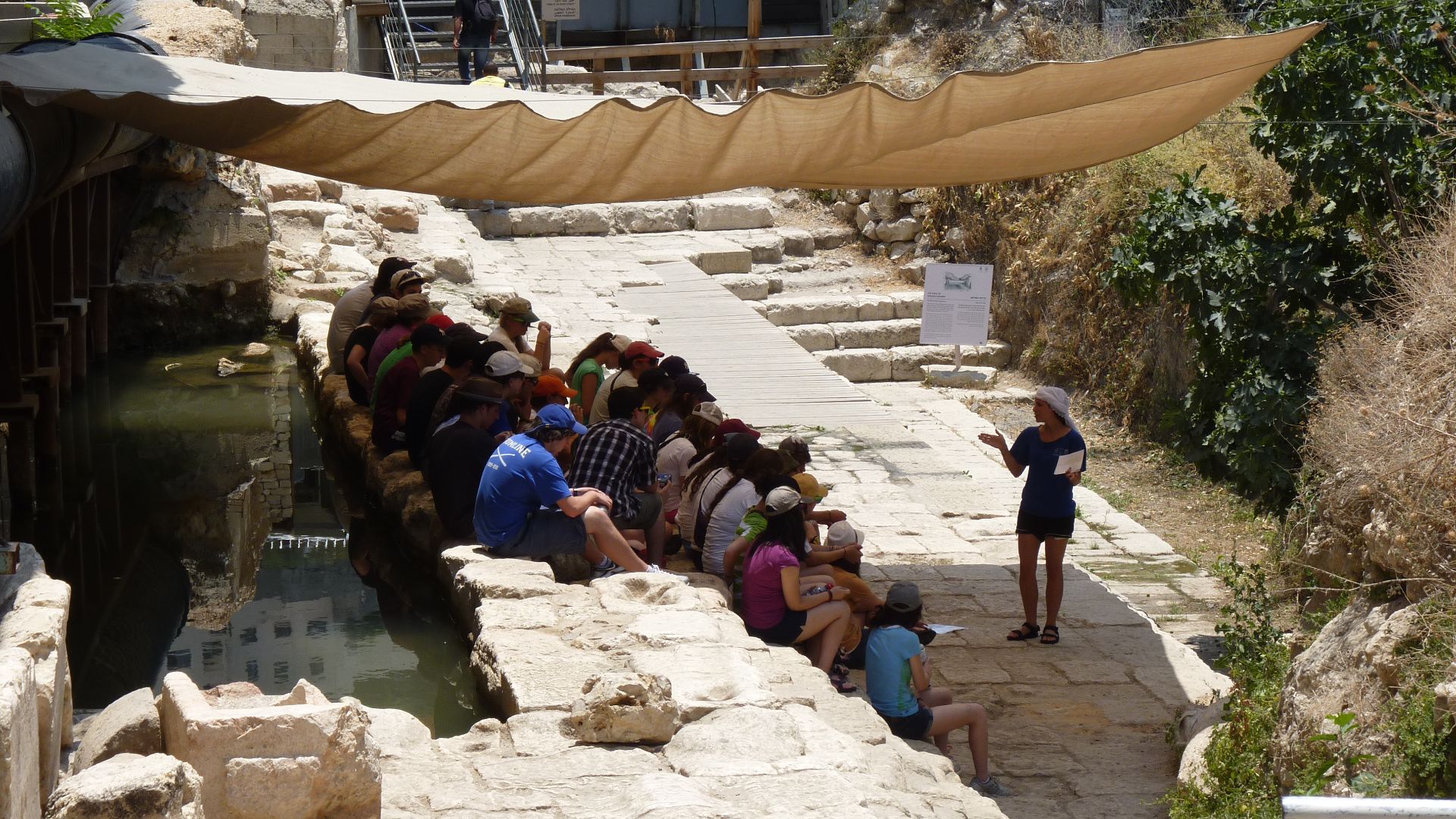 Ricardo Tulio Gandelman from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, Wikimedia Commons
Ricardo Tulio Gandelman from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, Wikimedia Commons
City Gate Proximity
If you walked toward ancient Jerusalem, the first thing stopping you would be the moat cut into the ridge just ahead of it. Nearby digs uncovered walls and higher defensive points. The whole layout shows how seriously the city guarded its front door.
Tracing Ancient Layers
You might picture high-tech tools doing the heavy lifting, but this find came from patient excavation and attention to stratigraphy. Each layer removed exposed another clue about the moat’s age and purpose. Gradually, the uncovered bedrock traced the outline of Jerusalem’s Iron Age defensive planning.
 David Monniaux, Wikimedia Commons
David Monniaux, Wikimedia Commons
The Moat’s Dimensions
Stand near the exposed trench, and the dimensions speak for themselves: almost 100 feet across and 30 feet down. Cut directly into the ridge, its angled walls hint at practical engineering choices. Few ancient structures in Israel match this scale, especially ones designed purely for defense.
Marks In The Bedrock
Instead of ornate carvings or inscriptions, the moat offered something quieter: the marks left behind by its makers. The bedrock holds long, deliberate cuts that trace the builders’s progress. These physical signs help researchers understand when and how the massive trench was created.
 Andrey Zeigarnik from Raanana, Israel, Wikimedia Commons
Andrey Zeigarnik from Raanana, Israel, Wikimedia Commons
Public Announcement Event
News of the moat spread quickly once the Israel Antiquities Authority and Tel Aviv University released their findings. Journalists arrived to photograph the exposed trench, and archaeologists such as Dr. Yiftah Shalev explained the results. The coverage turned attention toward a usually quiet corner of Silwan.
Academic Reactions
Scholars responded quickly. Some experts viewed the moat as an important addition to Jerusalem’s Iron Age record, while others urged caution about tying it too closely to biblical narratives. Coverage in regional and international outlets kept the discussion active within academic circles.
 Daniel Ventura, Wikimedia Commons
Daniel Ventura, Wikimedia Commons
Local Community Impact
Silwan residents became familiar with the activity as excavation teams worked through the season and news crews reported on the find. The City of David already drew steady visitors, and community outreach programs helped explain the moat’s significance without opening restricted areas to crowds.
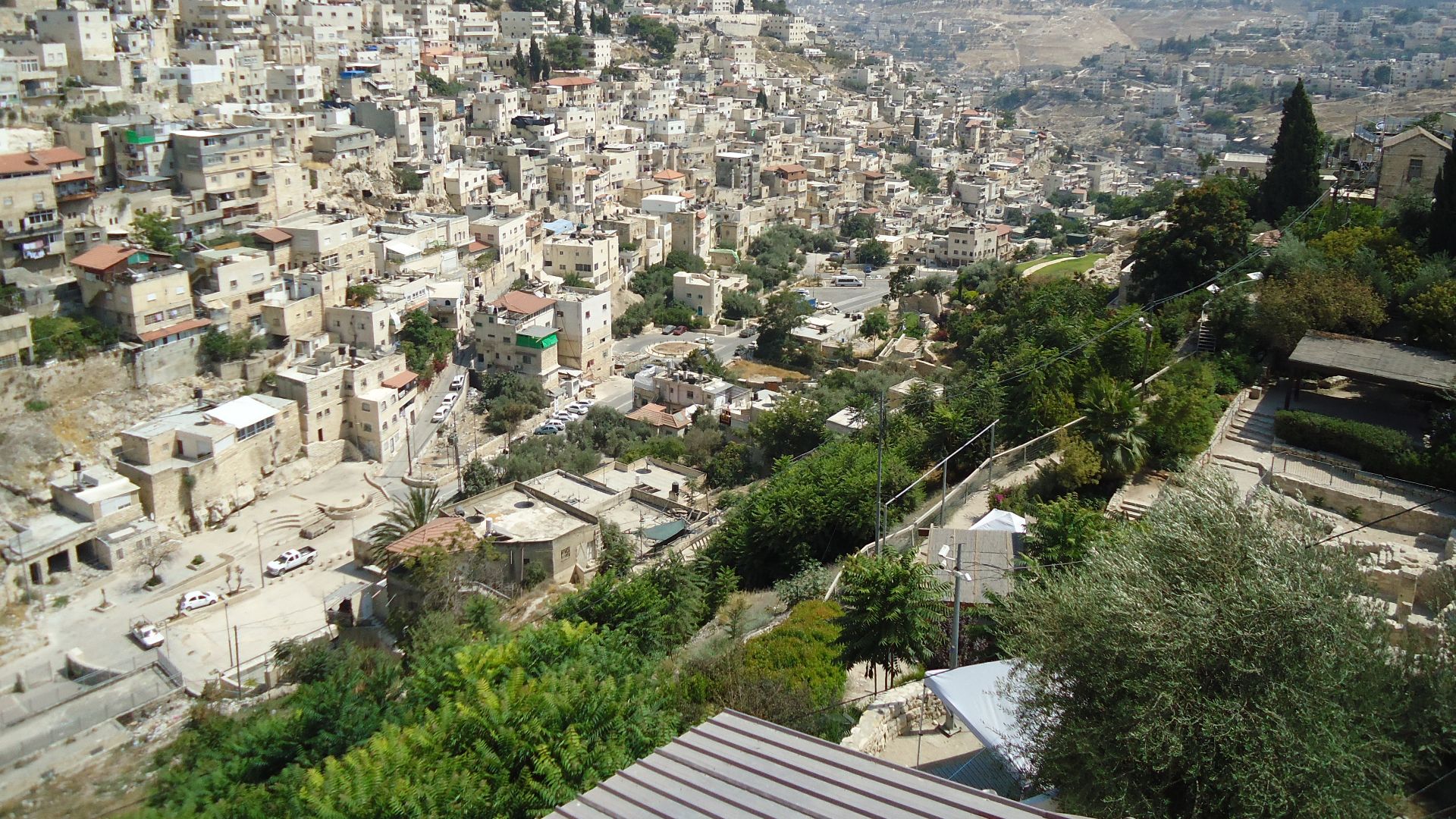 Meg Stewart from Poughkeepsie, NY, U.S.A., Wikimedia Commons
Meg Stewart from Poughkeepsie, NY, U.S.A., Wikimedia Commons
Artifacts Sent For Study
Once the excavation work was finished, the real sorting began. Thousands of items from the Givati layers were transferred to the Israel Antiquities Authority laboratories. Technicians cleaned and cataloged each artifact piece, adding new data that will shape future studies of Jerusalem’s Iron Age environment.
Comparison To Other Sites
Jerusalem’s moat doesn’t stand alone. Similar defensive structures appear in cities like Megiddo and Lachish, key centers of the Iron Age. The similarities hint at a regional network of military innovation stretching across ancient Israelite and Canaanite lands.
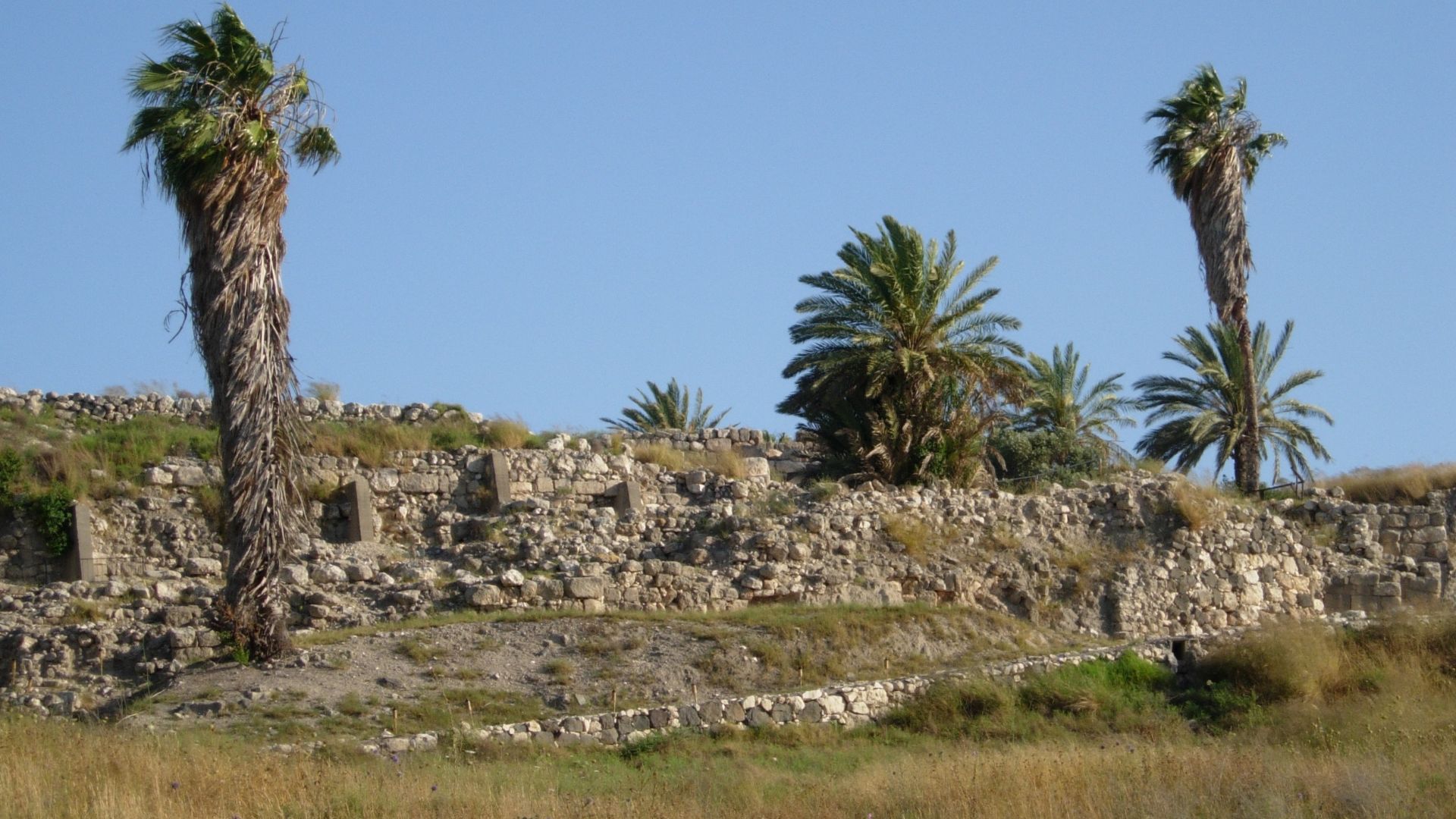 Wilson44691 at English Wikipedia, Wikimedia Commons
Wilson44691 at English Wikipedia, Wikimedia Commons
Tourism Boost Expected
Tourism at the City of David was already strong, but news of the moat encouraged many visitors to look more closely at the surrounding excavation zones. Existing digital reconstructions offered a broader context for Jerusalem’s early defenses. Turns out, the past still shapes Jerusalem’s future.
 Daniel Ventura, Wikimedia Commons
Daniel Ventura, Wikimedia Commons
Future Excavation Zones
Excavation teams know there is still much to uncover. Work in nearby areas has already revealed additional walls and architectural lines that hint at further buried structures. With each layer removed, Jerusalem’s early layout becomes clearer and better understood.
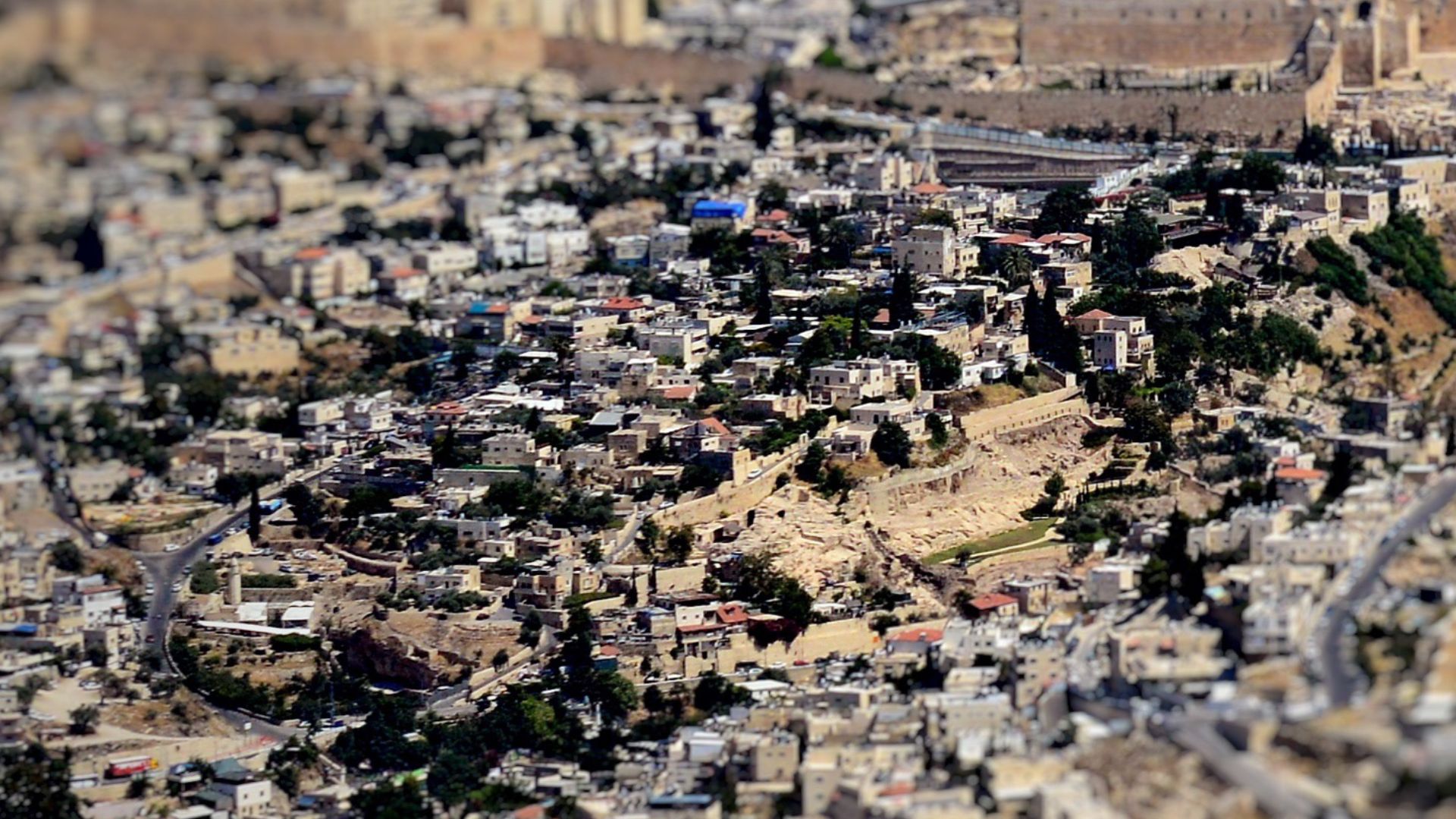 Avraham Graicer, Wikimedia Commons
Avraham Graicer, Wikimedia Commons