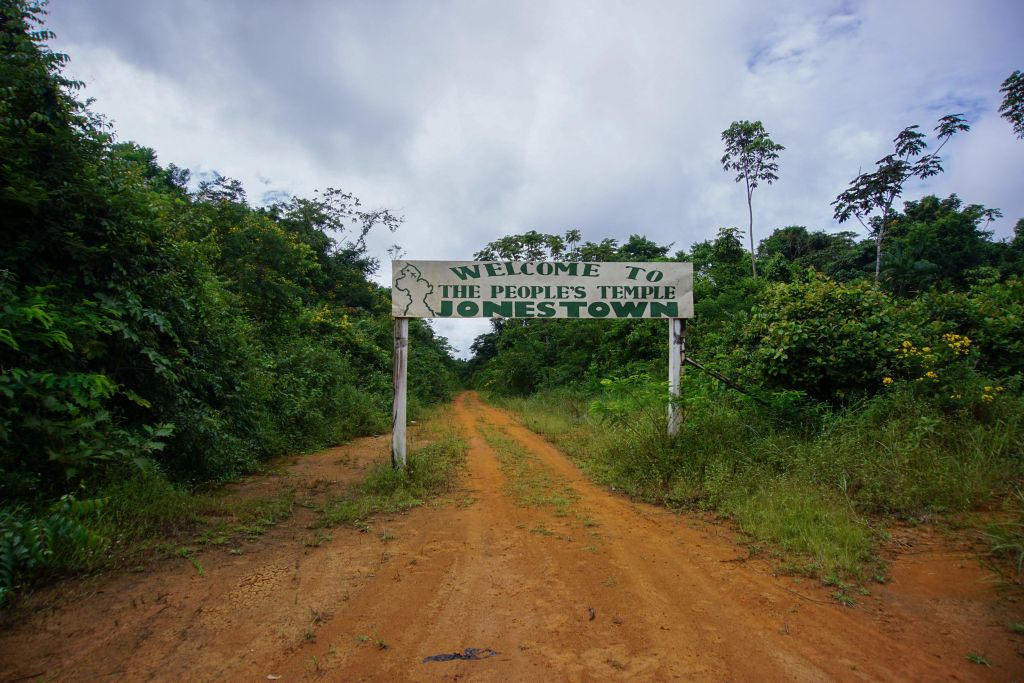
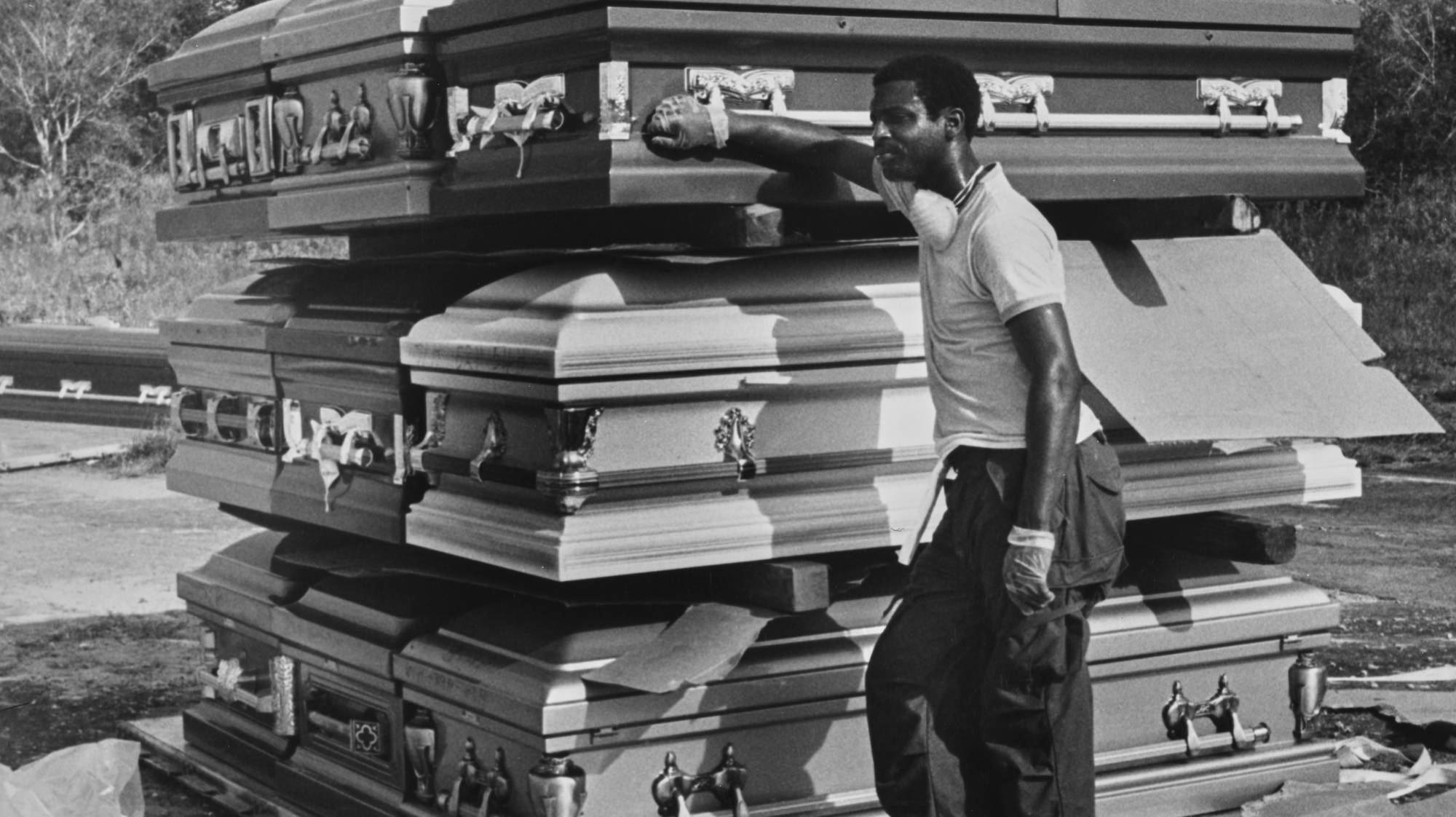
The Jonestown Massacre
The People’s Temple was an American new religious organization which existed between 1954 and 1978.
The group received international attention after over 900 of its members were involved in a massive act of persuasion to end their own lives. Often dubbed the "Kool Aid massacre"—it was the largest event of its kind in history.
From beginning to end, let’s find out how one man successfully brainwashed thousands of people, leading them to their demise.

The Temple’s Original Purpose
The People’s Temple was founded by Jim Jones in Indianapolis, Indiana.
The group spread a message that combined elements of Christianity with communist and socialist ideology, with an emphasis on racial equality.
Locations
Jones moved the group to California in the 1960s and establish several locations throughout the state, including its headquarters in San Francisco.
 Nicolas Martin, CC BY-SA 4.0 , Wikimedia Commons
Nicolas Martin, CC BY-SA 4.0 , Wikimedia Commons
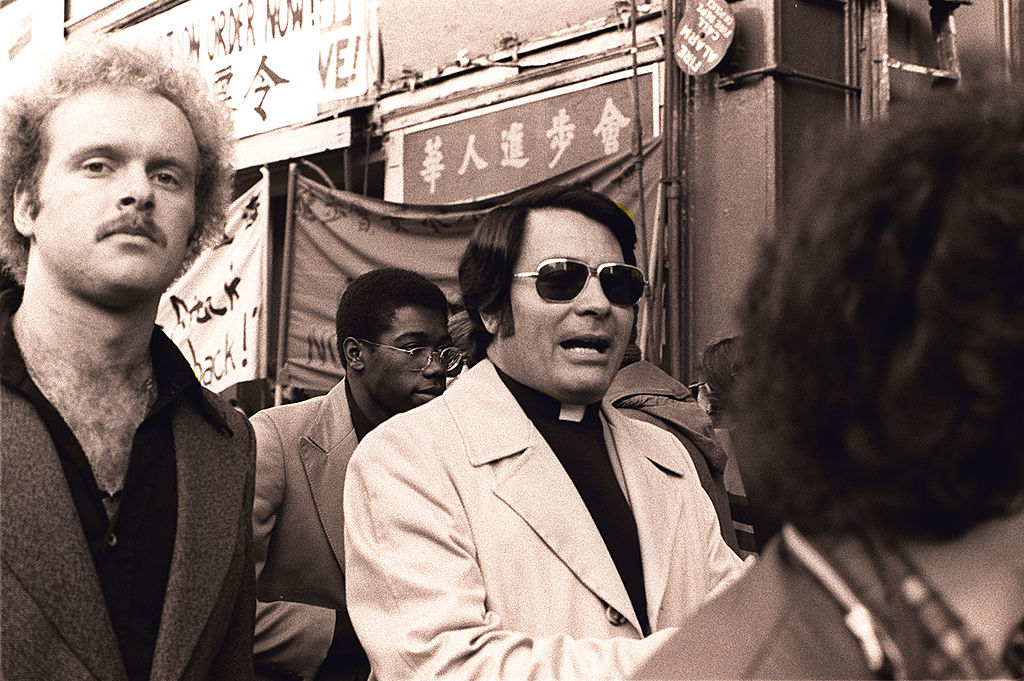
Members
The Temple created ties with many left-wing political figures and ended up claiming to have 20,000 members as a result.
This number steadily increased over the years.
 Nancy Wong, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Nancy Wong, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
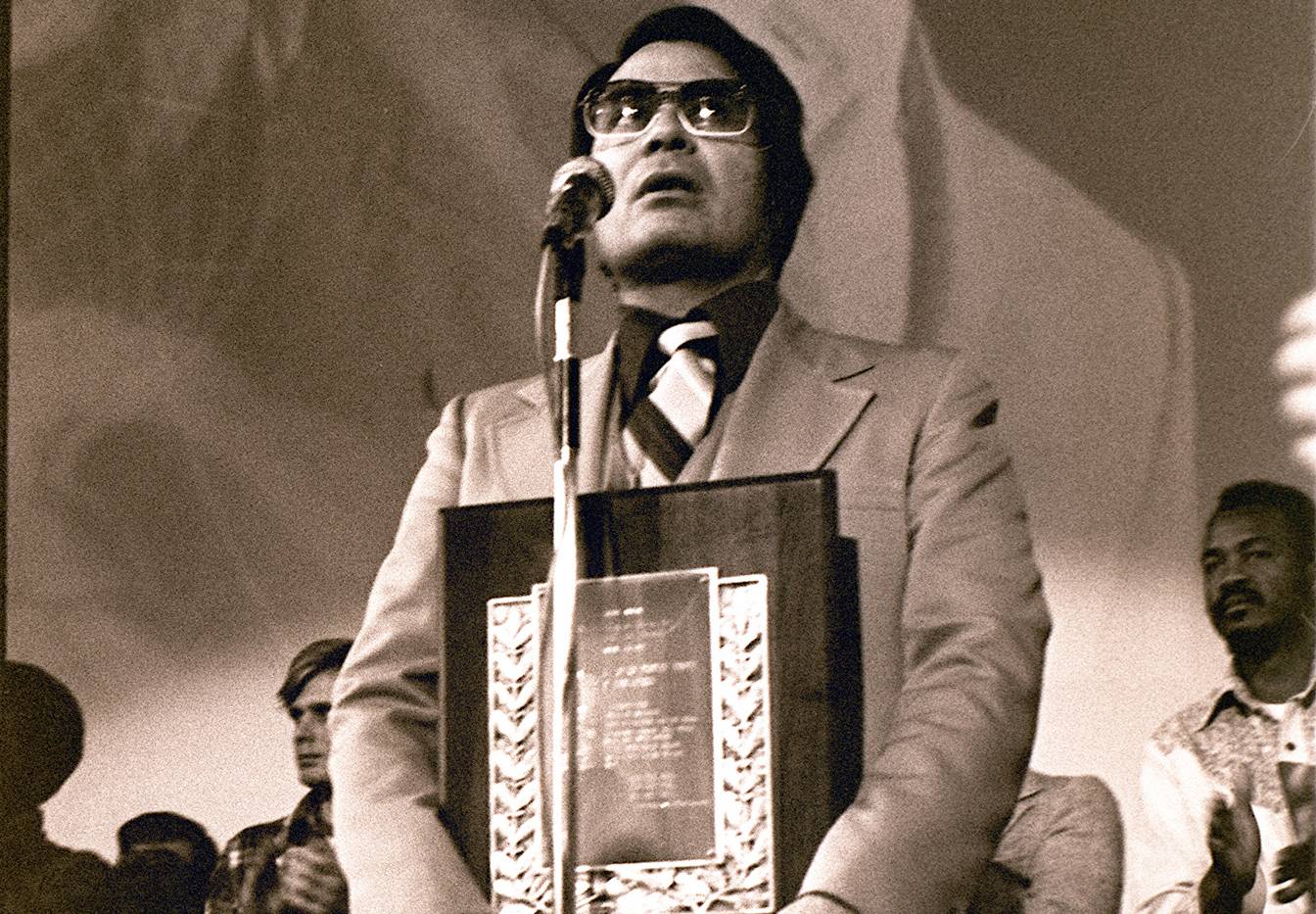
Founder: Jim Jones
Before he founded his church, Jim Jones was captivated by communism, even though it had a bad reputation at the time.
He was apparently “frustrated” by the harassment communists were being subjected to during the Red Scare.
This ultimately inspired him.
Jim Jones’s Vision
Jones reportedly recorded himself saying, “I decided, how can I demonstrate my Marxism? The thought was, infiltrate the church. So, I consciously made a decision to look into that prospect.”
And he set out to do just that.
 Nancy Wong, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Nancy Wong, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
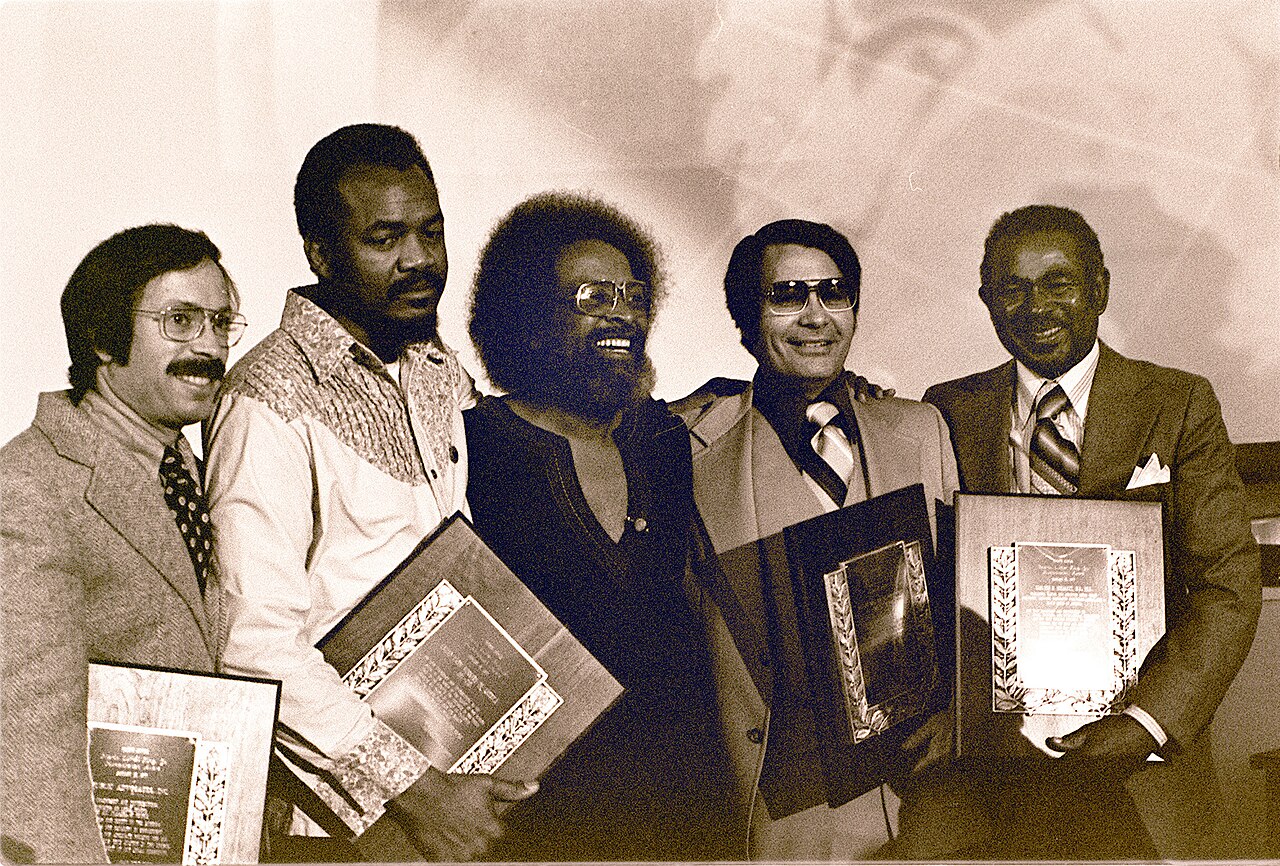
Jones Enters the Church
A Methodists superintendent helped him enter the church, despite knowing that Jones was a communist.
In 1952, Jones became a student pastor in Sommerset Southside Methodist Church in Indianapolis, Indiana.
Jones Leaves the Church
Jones ended up leaving that church because it did not allow him to integrate African-Americans into his congregation.
In 1954, Jones founded his own church in a rented space in Indianapolis, at first, he named it the Community Unity Church.
 Nancy Wong, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Nancy Wong, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
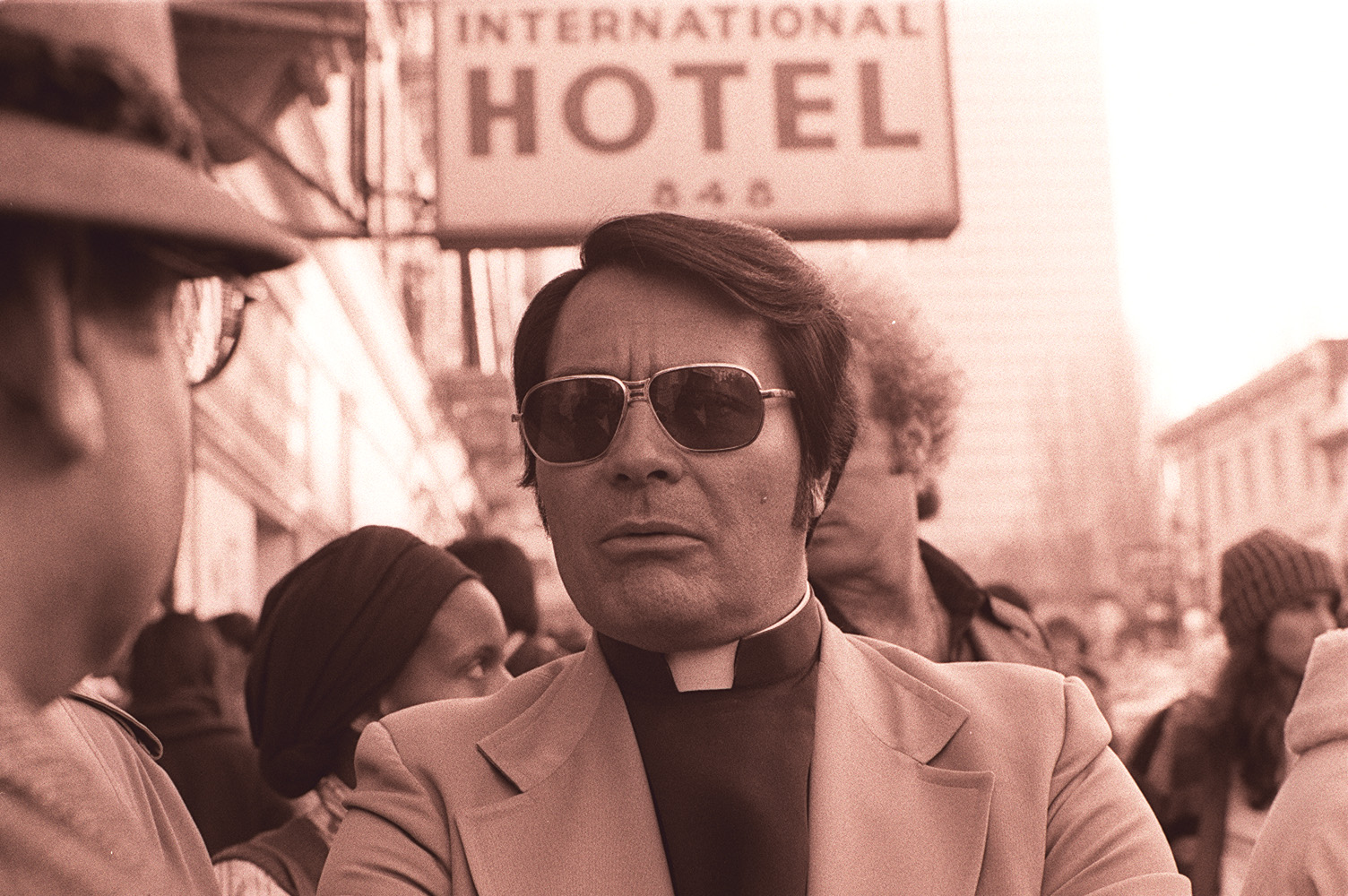
Jones’ Social Goals
Apparently, Jones had previously observed a faith healing service at the Seventh Day Baptist Church, which led him to believe that such healings could attract people, and generate income.
 Nancy Wong, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Nancy Wong, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Fake Healings
Jones and the Temple’s members started to knowingly fake healings because they found that the healings increased people’s faith—more importantly, they brought in a good chunk of money.
Healing Rituals
The “healing” services involved the use of chicken livers and other animal tissue, which Jones told his members were “cancerous tissues” that had been removed from the bodies of people who had been previously healed.
Gross, but effective.
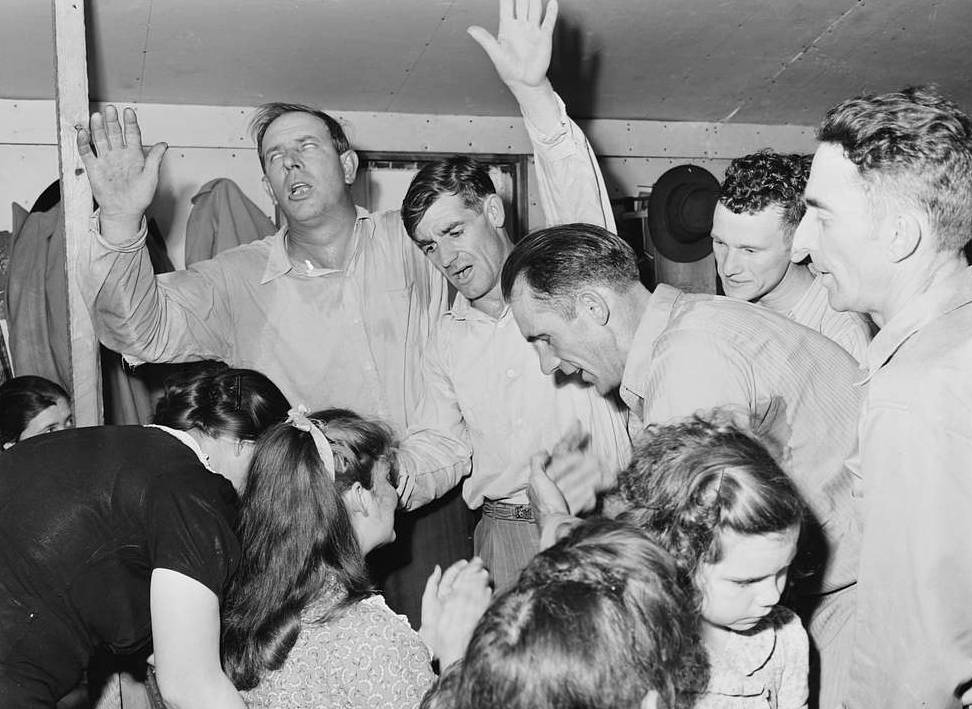 U.S. National Archives and Records Administration, Picryl
U.S. National Archives and Records Administration, Picryl
The First Building
In 1955, Jones bought his first church building, located in a racially mixed Indianapolis neighborhood. He initially named it “Wings of Deliverance”, but later renamed it to “The Peoples Temple Full Gospel Church.”
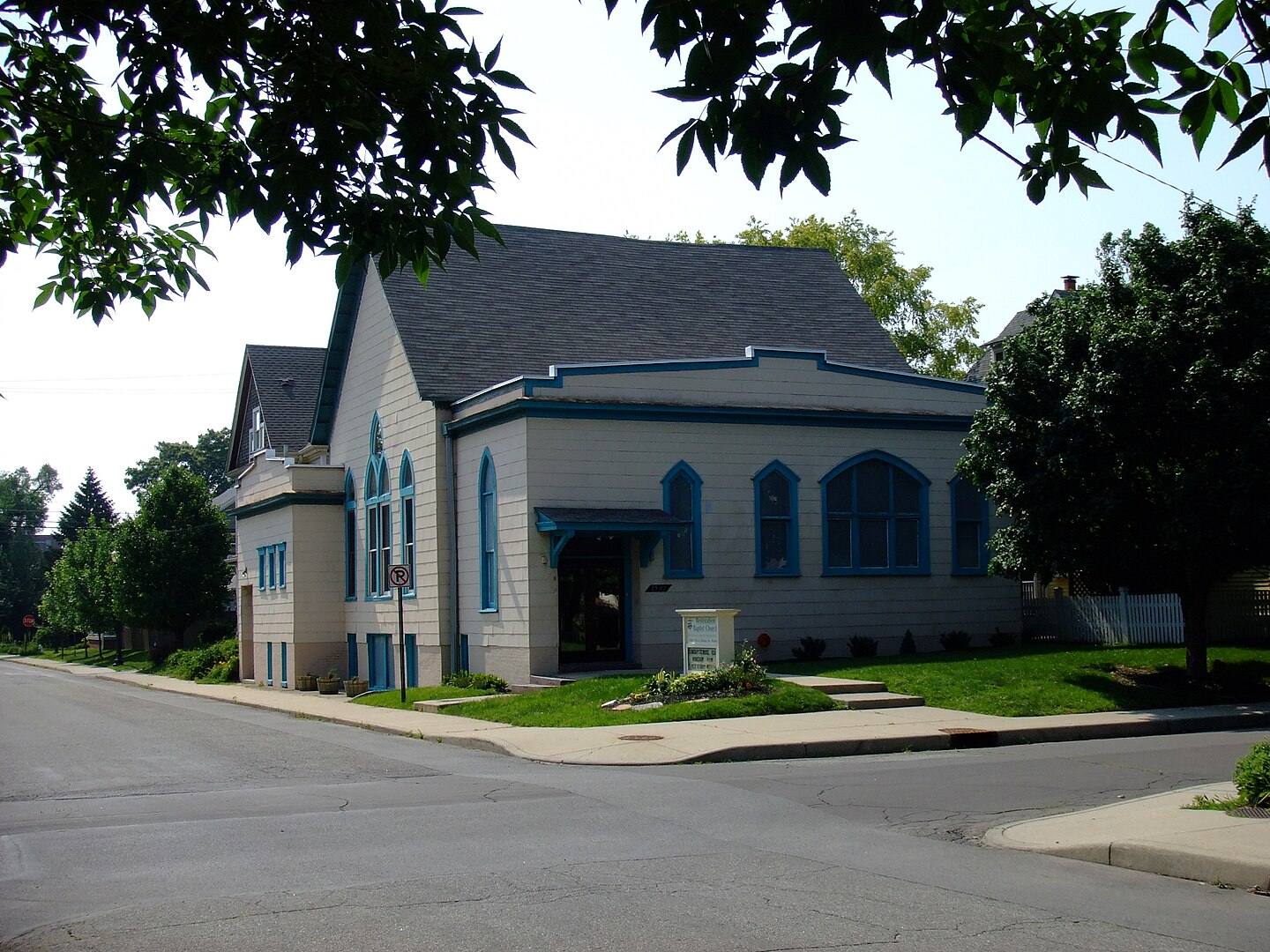 Indytnt, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Indytnt, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Spiritualists
Shortly after the name change, word spread about the healings and revelations and Jones’ church quickly attracted spiritualists.
He preyed on those who needed refuge and healing.
 Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
The Latter Rain Movement
Jones began associating with the Independent Assemblies of God (IAoG)—an international group who embraced the Latter Rain Movement.
In 1955, he became a minister as an IAoG, and he started planning a healing convention—which initially started his mass recruitment.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
The Healing Convention
Jones was intrigued by a fellow minister’s methods of pretending to know personal information about people (such as their name, address, and why they came for prayer) before pronouncing them healed—and he followed suit.
Together, the two of them attracted an audience of 11,000 people to their healings, and Jones’ reputation started to flourish.
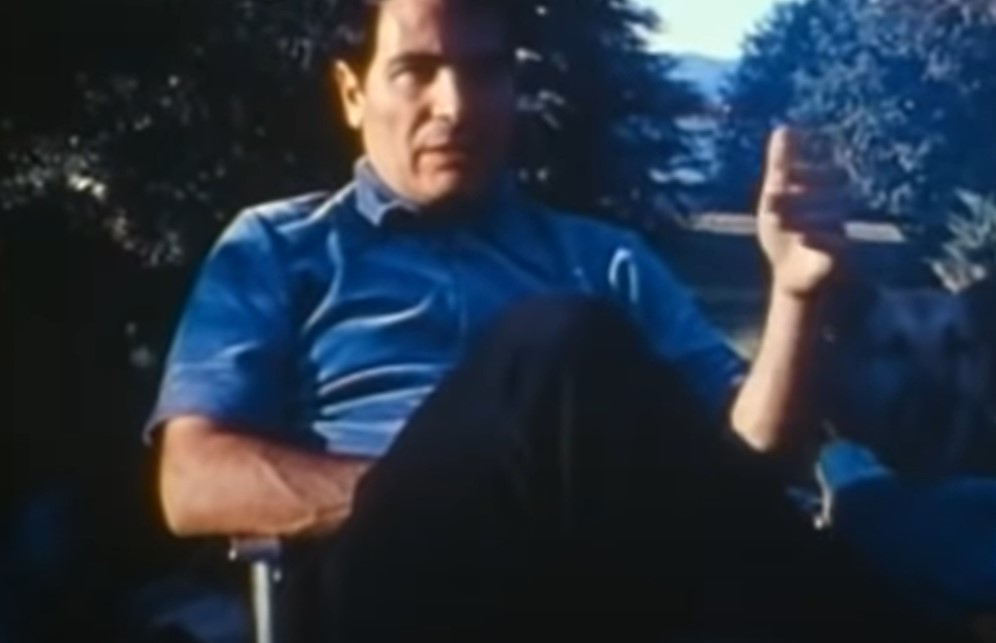 Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
A Supernatural Gift
Many people started to believe that Jones possessed a supernatural gift, which led to the rapid growth of Peoples Temple—especially African-American attendees.
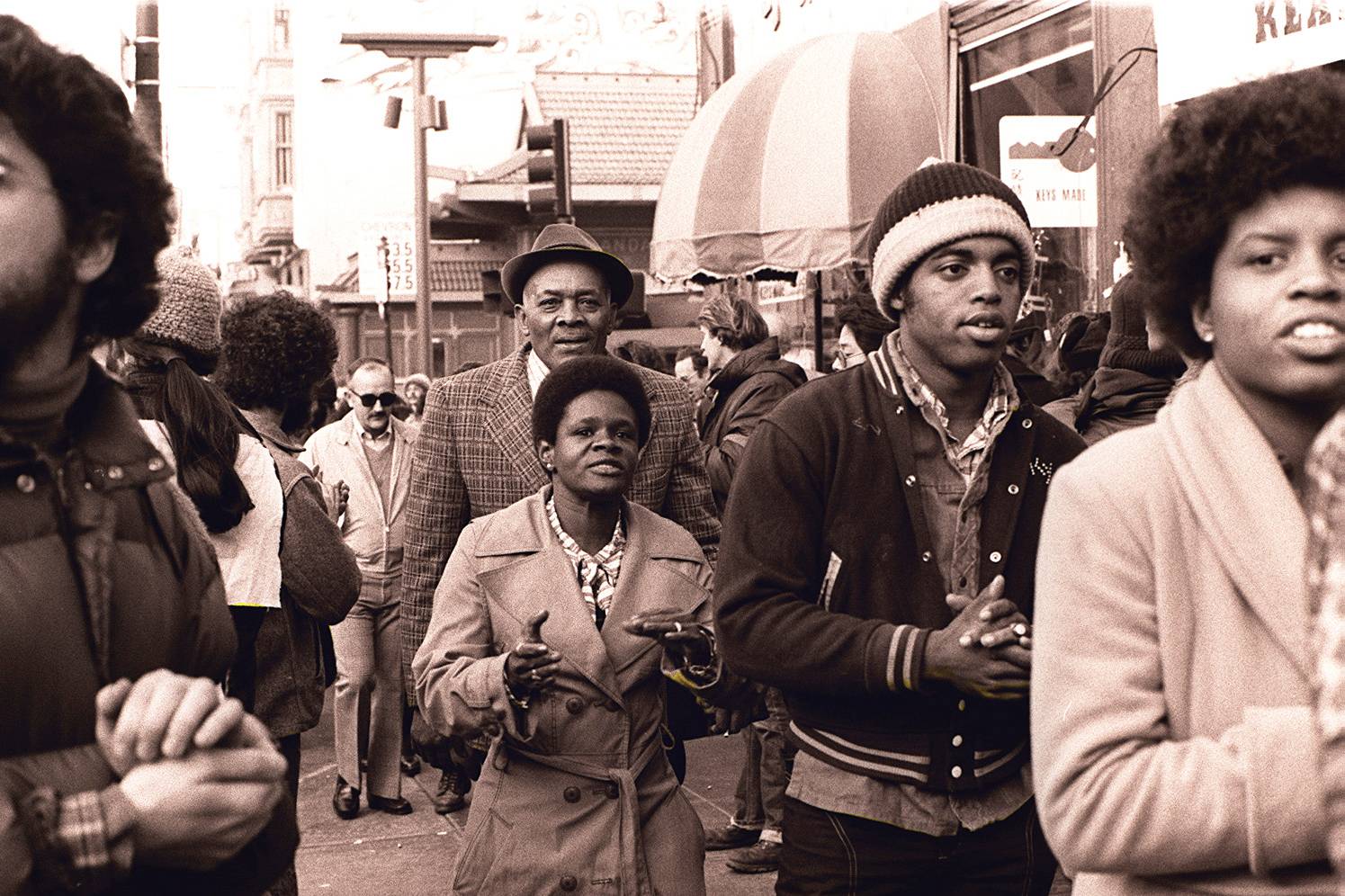 Nancy Wong, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Nancy Wong, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Connections
Over the next few years, Jones made multiple joint appearances with the other well-known ministers, gaining more and more followers each time, building connections all over the place and making his name known.
This was all part of his master plan. Jones continued to disguise the fact that he was using religion to further his political ideology.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
Building Trust
Jones continued to build trust with attendees by fooling them into thinking he knew everything about them using his “gift”—however, he actually used a private detective to uncover this information.
He was really good at faking his way to fame.
Recruitment
Jones and his close followers drove through various cities in Indiana and Ohio performing healing ceremonies to recruit more followers, and “earn” more money.
He built a trust with attendees, that strengthened his position of power.
 Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
The Temple’s Egalitarian Ideals
Jones’s church, the Temple, encouraged egalitarian ideals (all humans are equal), by asking members to attend in casual clothing so that “poor” members would not feel out of place.
That’s not all, though.
 Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
A Place for the Poor
In addition to a casual dress code, Jones also provided shelter for the needy, opened a soup kitchen and even provided social services such as rent assistance, job placement services, free canned goods, clothing, and coal for winter heating.
I suppose he wasn’t all that bad… or was he?
 Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Increasing the African-American Membership
All of Jones’s good deeds proved successful in his plan to gain more members—specifically the African-American member population which rose from 15% to 50%.
He furthered these gains by hiring an African-American preacher named Archie James—who actually previously gave up organized religion, but was convinced by Jones to join him.
 Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Jones’s Rise to Fame
All of this helped Jones rise in the community, and he was then appointed to the Indianapolis Human Rights Commission.
He regularly engaged in public attempts to integrate businesses and was often the subject of local media coverage.
 Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
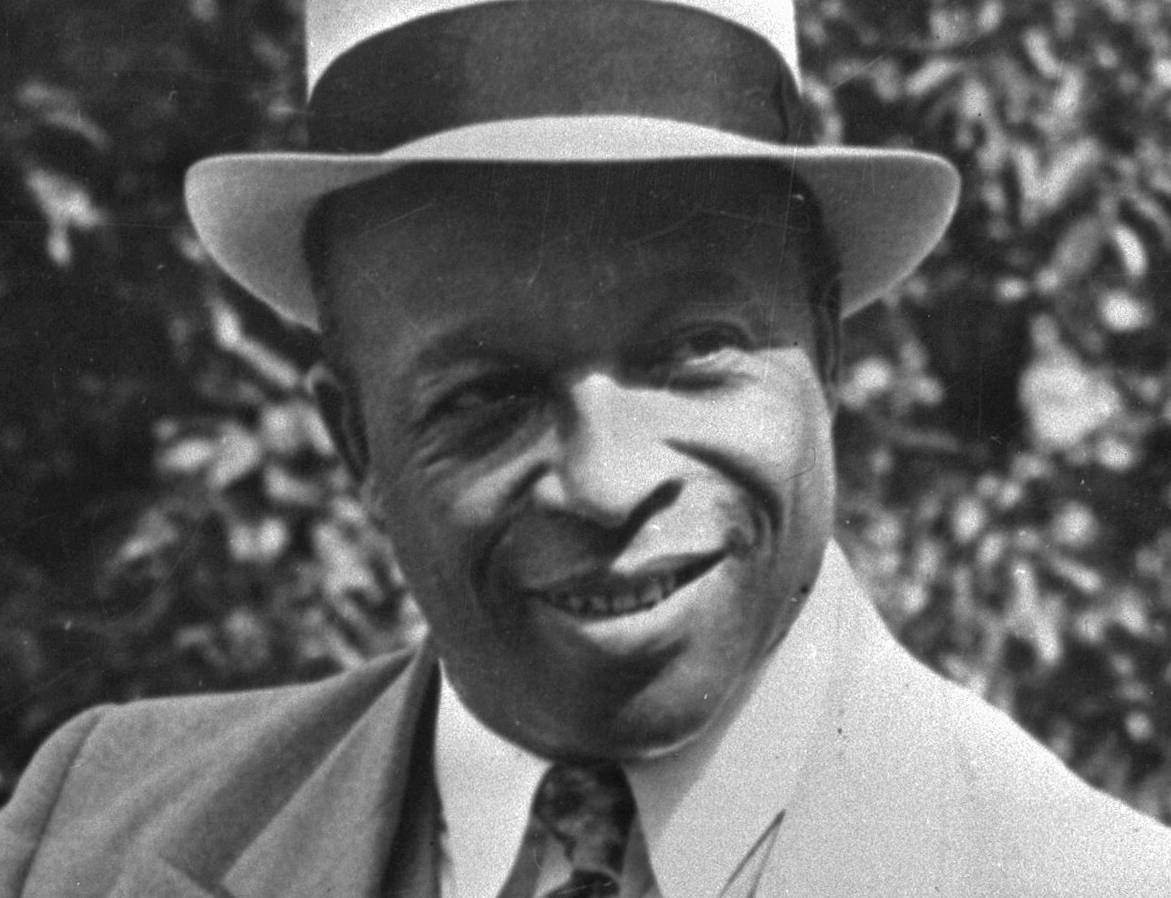
Father Divine’s Influence
Jones read extensively about Father Divine, the founder of the International Peace Mission movement.
He visited Father Divine many times with his close followers, and he studied Divine’s writings and tape recordings of his sermons.
 Los Angeles Times, CC BY 4.0 , Wikimedia Commons
Los Angeles Times, CC BY 4.0 , Wikimedia Commons
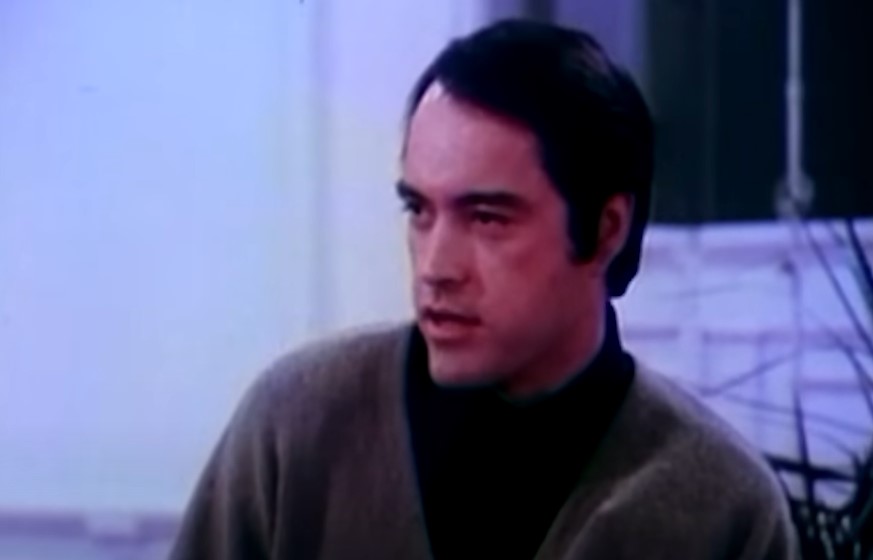
Father Divine’s Beliefs
Jones began fully following Father Divine’s teachings, and began to preach that his members should abstain from intimate activity and only adopt children instead.
This was only the beginning of what would soon become a serious power trip.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
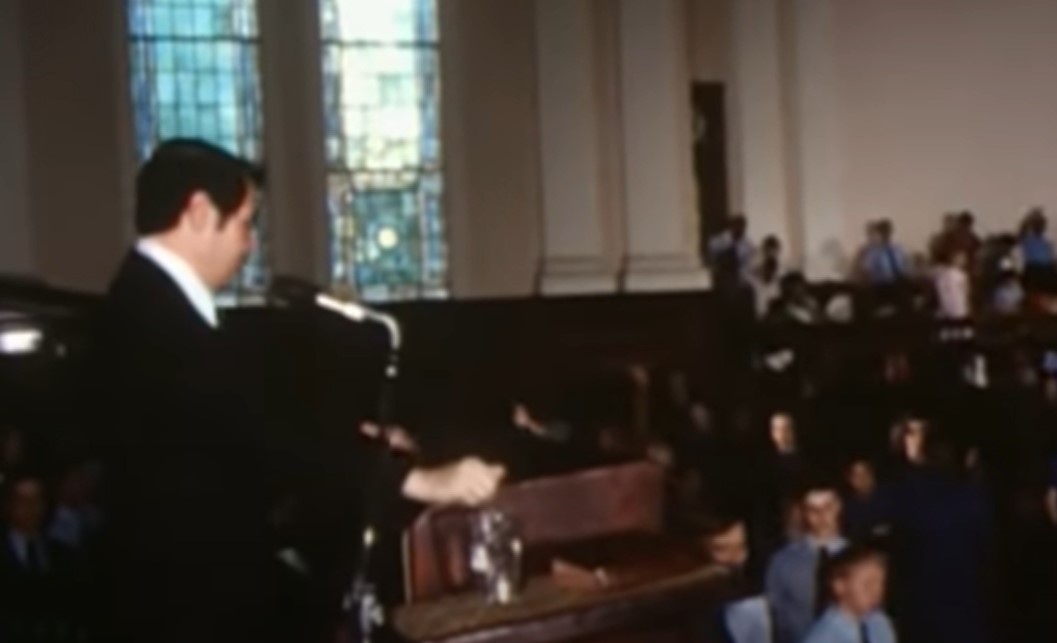
Us versus Them
Jones started to take things farther, quoting Karl Marx in his speeches, strengthening the “us versus them” message he was trying to send.
He repeatedly cited passages that painted Jesus as a communist, while at the same time attacking much of the text of the bible.
 Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
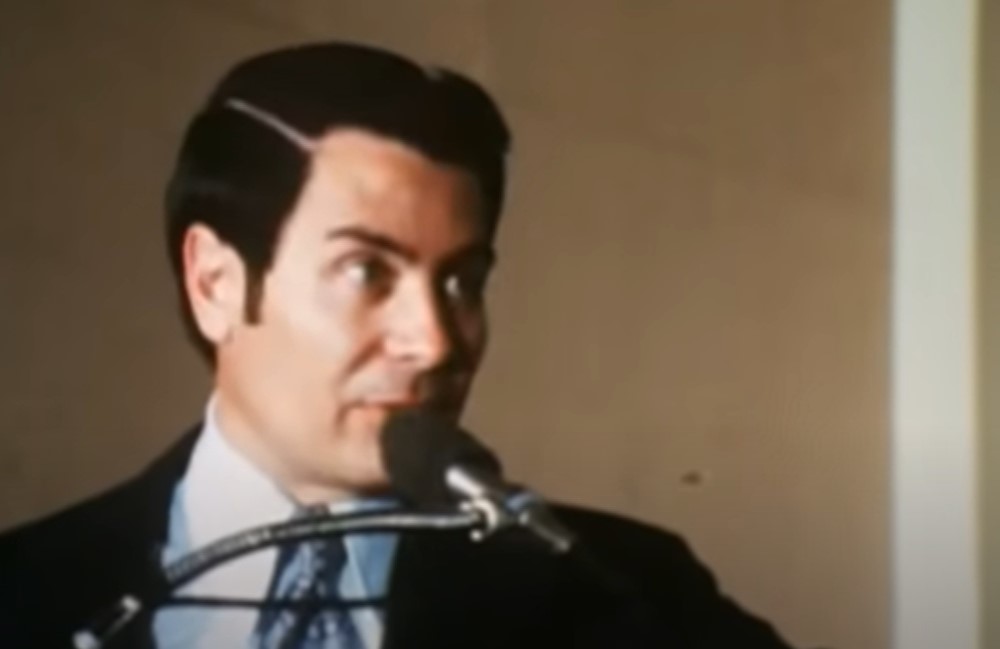
Tightening Control
The Temple started tightening the control of its organization, asking more from its members than most other churches did—specifically requiring that members spend Thanksgiving and Christmas with its Temple family rather than blood relatives.
This was how the Temple started to wean their members of outside contact.
 Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
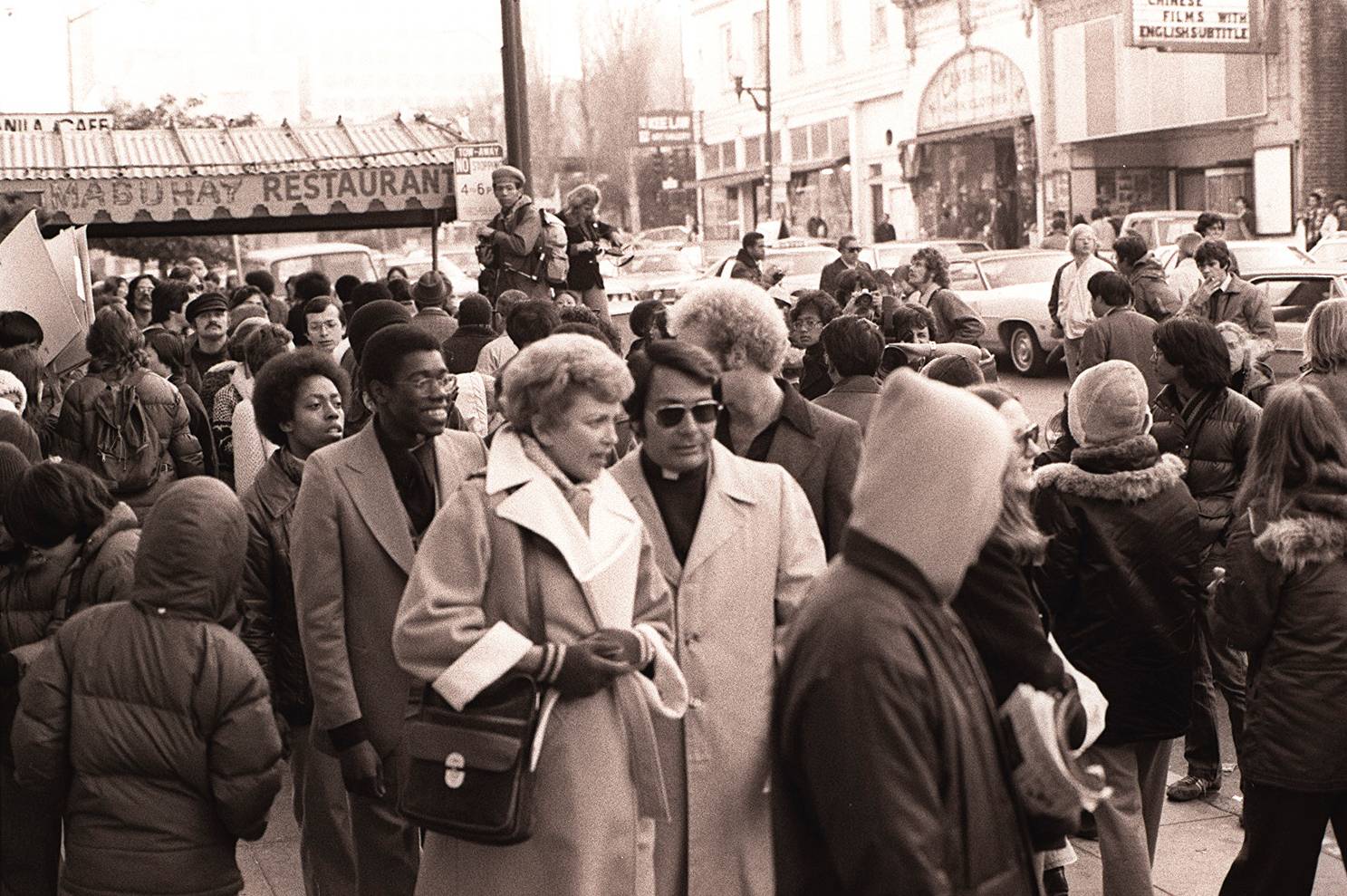
Commitment to the Temple
Jones had now built a loyal group of followers, and he knew he could get them to do anything he wanted.
He started to redirect his members toward a total commitment to the Temple.
 Nancy Wong, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Nancy Wong, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Religious Communalism
Once he had his members blindly following his every suggestion, he took things a step further and offered them a deal, which he called “Religious Communalism”—where members would donate their material possessions to the Temple in exchange for the Temple meeting all of their needs.
Pastor James was the first to commit.
 Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Jones’ Vision
In 1961, Jones claimed he had had a vision in which Indianapolis and Chicago would be destroyed in a nuclear attack.
This vision convinced his members that the Temple needed to look for a new location.
 Carol M. Highsmith, Wikimedia Commons
Carol M. Highsmith, Wikimedia Commons
Jones’ Trip to Brazil
After reading that Brazil was apparently a good location for avoiding nuclear attacks, Jones set off on a year-long trip to check out Brazil as a possible next location.
But this actually created a set-back for Jones.
Trouble in the Temple
While he was gone, the church significantly lost financial security, so he sent a new Brazilian follower back home to stabilize the Temple.
But he wasn’t prepared for what he would later return to.
Jones’s Return
Upon his return from Brazil, Jones found the Temple bitterly divided.
Financial issues, and a much smaller congregation forced Jones to sell the Peoples Temple church building and relocate to a smaller building close by.
 Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
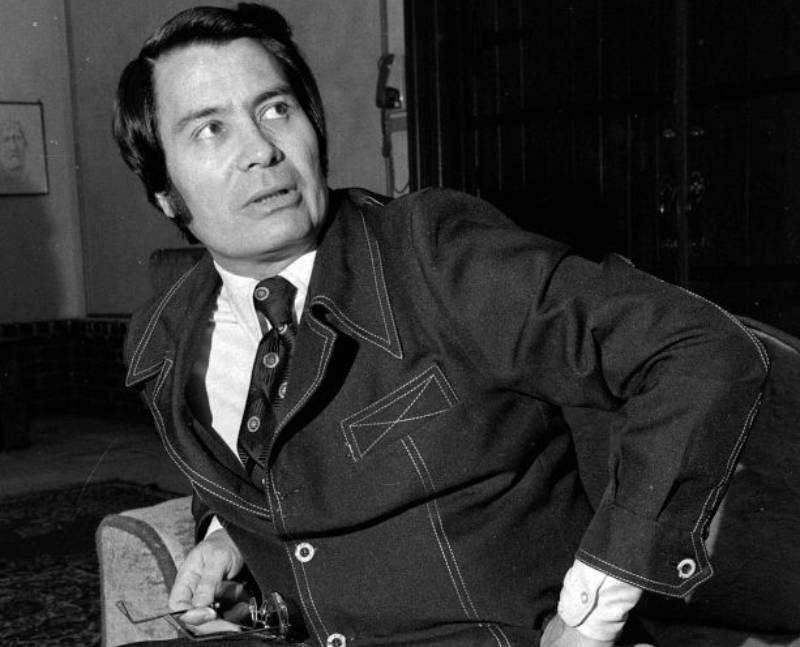
A Comeback Attempt
Jones began traveling for healing rituals, hoping to make more money and stabilize his church once again.
But it didn’t fare well, and he now had to convince his congregation to move once again—this time, to California.
 San Francisco Chronicle, Getty Images
San Francisco Chronicle, Getty Images
Trusting Jones
Jones told his members that that a nuclear war was approaching and that they must move to Northern California for safety.
As people had a lot of trust in Jones, he relied on this to call upon more members, slowly growing the congregation once again.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
The Big Move
In 1965, Jones and his followers moved to their new location in Redwood Valley, California. However, his assistant pastor was feeling uneasy and began resisting Jones’s efforts to move.
 Redwood National and State Parks, Flickr
Redwood National and State Parks, Flickr
The Resistance
Jones’s assistant pastor, Russell Winberg, strongly resisted Jones’s plan and warned members of the People’s Temple that Jones was “abandoning Christianity”.
Winberg stayed behind and took over leadership in the Indianapolis church when Jones moved.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
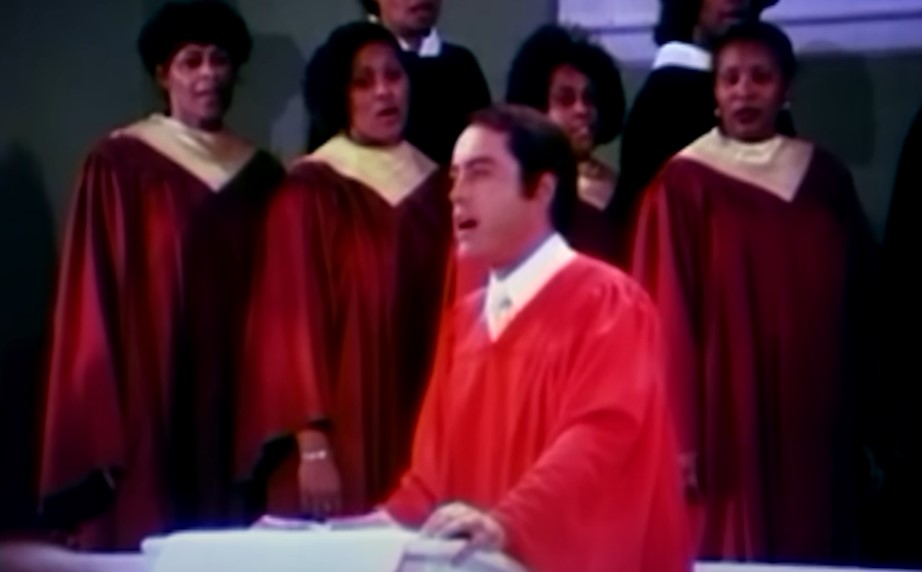
Jones’s Followers
Jones had about 140 of his members make the move to California to follow him, while the rest of his congregation stayed behind in Indianapolis.
He then had to find a way to gain followers once again.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
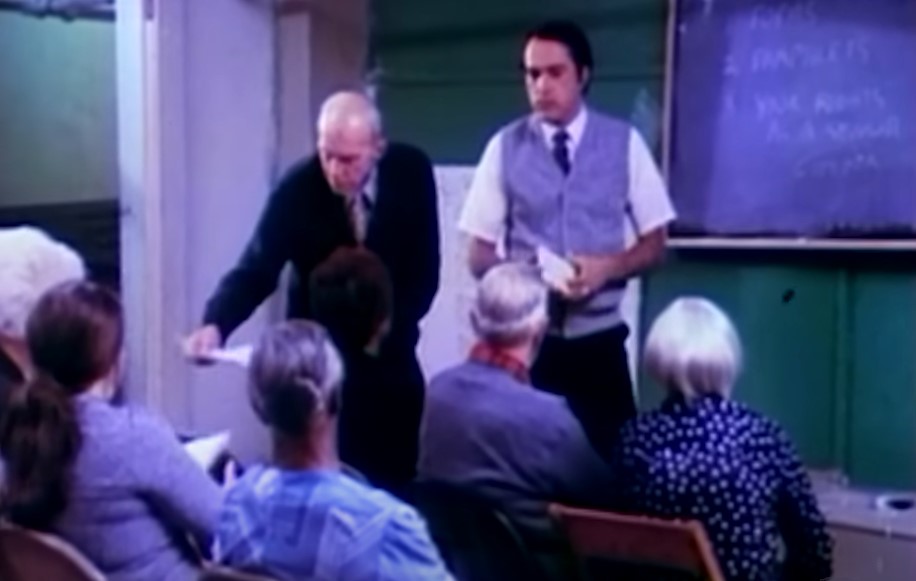
Professor Jones
Jones happened to have a degree in education, so he secured a job as a history teacher at an adult school, where he used his position to recruit for Peoples Temple, teaching his students his beliefs.
He even planted his own members in his class to secretly influence his students.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
New Members
His plan worked, and he recruited 50 new members to People’s Temple within only a few months.
By this time, his followers were successful at coaxing his old congregation in Indianapolis, and by 1967, about 75 of his previous congregation made the move to California to follow Jones.
He took it a step further.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
Building Connections
In 1968, the People’s Temple in California was admitted to the Disciples of Christ—a Protestant Christian denomination.
This was good news for Jones as he can now use this connection to promote the People’s Temple as part of the 1.5-million-member denomination—making the People’s Temple more desirable to unsuspecting prospects.
 San Francisco Chronicle, Getty Images
San Francisco Chronicle, Getty Images
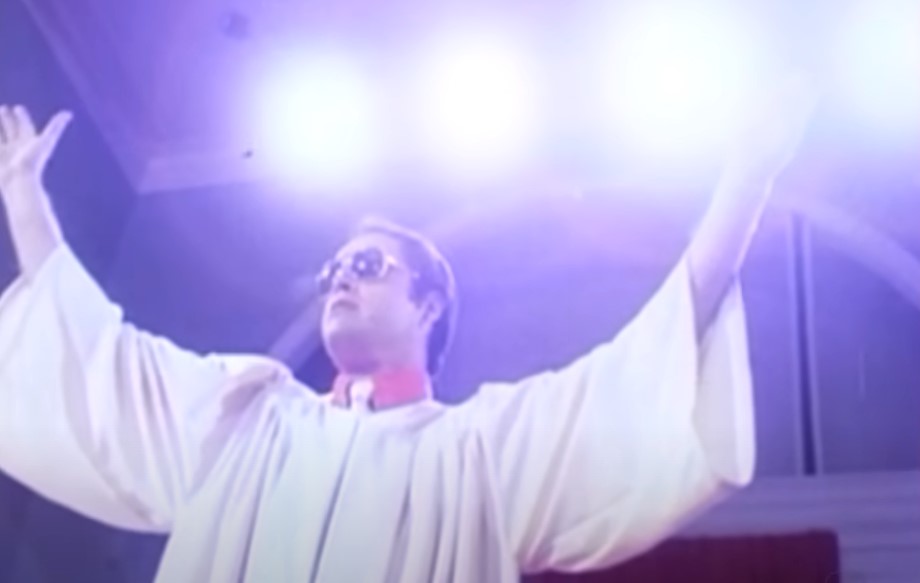
Abusing His Power
Now that Jones had a connection to one of the biggest religious denominations in the nation, he used it to lure in new members.
Jones greatly misrepresented the nature of his position in the denomination—but somehow it brought in another 300 members.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
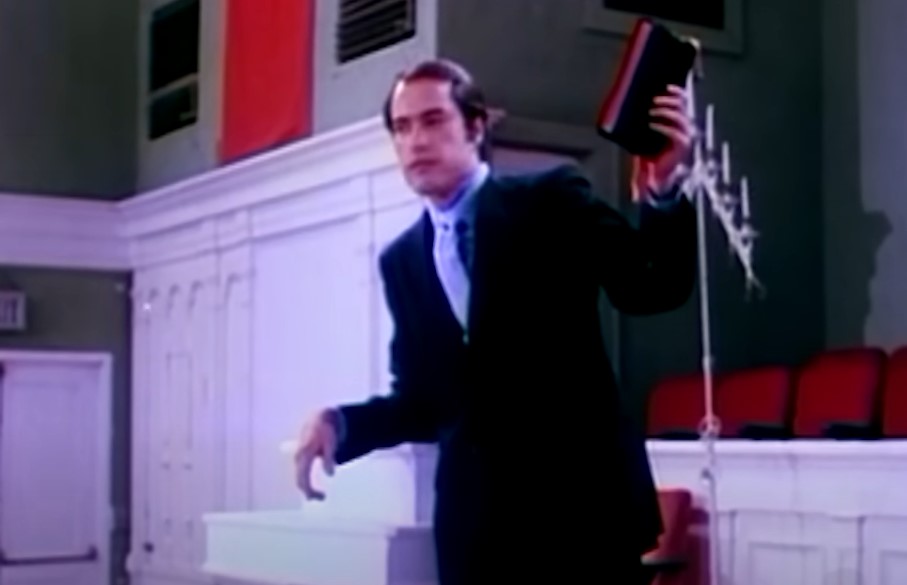
Gradually Swaying Beliefs
Now that Jones had an even bigger following, he started gradually introducing a new concept to his followers.
He referred to this concept as, “Apostolic Socialism”—which was a blend of the teachings of the Latter Rain movement and Jones’s personal communist worldview.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
Jones’s Teachings
Jones taught that "those who remained under the influence with the opiate of religion had to be brought to enlightenment", which he defined as socialism.
He also emphasized that “traditional Christianity had an incorrect view of God.”
He had a different idea of “God.”
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
The “Fly Away Religion”
By the early 1070s, Jones began mocking traditional Christianity as a “fly away religion”, rejecting the Bible as a “tool to oppress women and non-whites.”
He often referred to Christianity’s view of God as a “Sky God” who was “no God at all.”
The Divine Principle
Jones claimed to be following the “true God who created all things”—called the “Divine Principle”. He associated the principle with love, and he associated love with socialism.
He then proclaimed why he was here.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
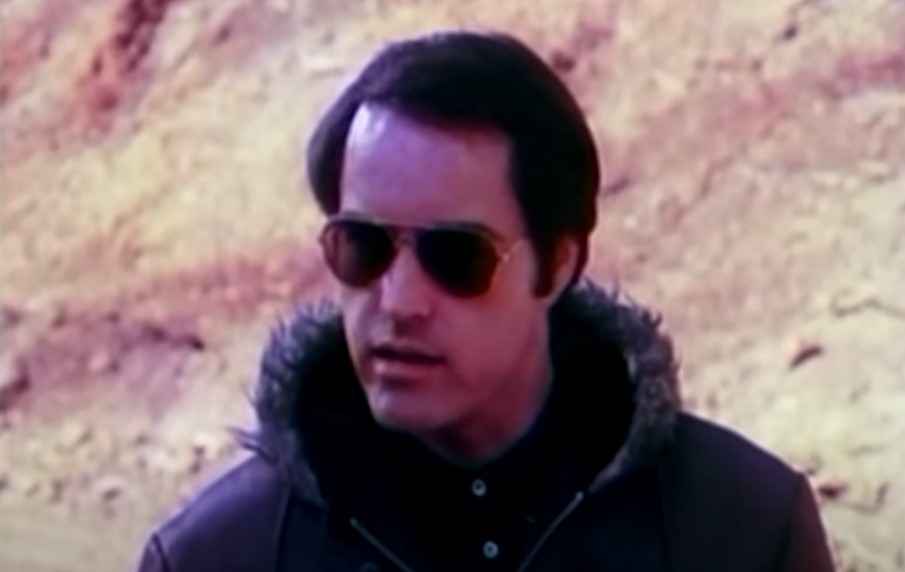
Jones’s Purpose
Jones convinced his followers that he was a “savior” sent by the true God, to rescue humanity from their sufferings.
He insisted that accepting the Divine Principle was the same thing as being “crucified with Christ”.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
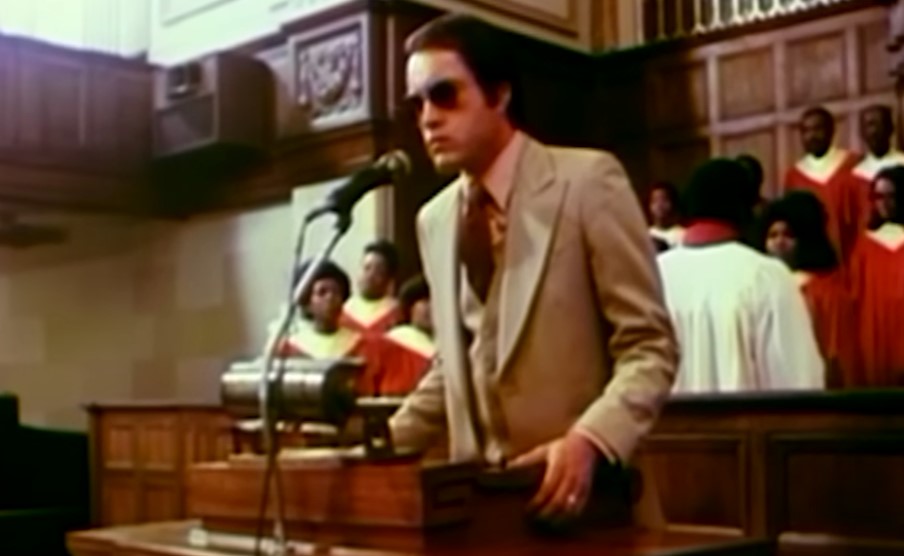
Jones’s Followers
By this time, Jones’s followers were so brainwashed by his teachings and healings that they were receptive of everything he taught.
They treated Jones as though he was God himself—which is exactly what he wanted.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
Jones’s Rising
Jones used this to his advantage, and continued to attack traditional Christianity and replace its teachings with his own, claiming that he was “sent to share the true meaning of the gospel, which had been hidden by corrupt leaders.”
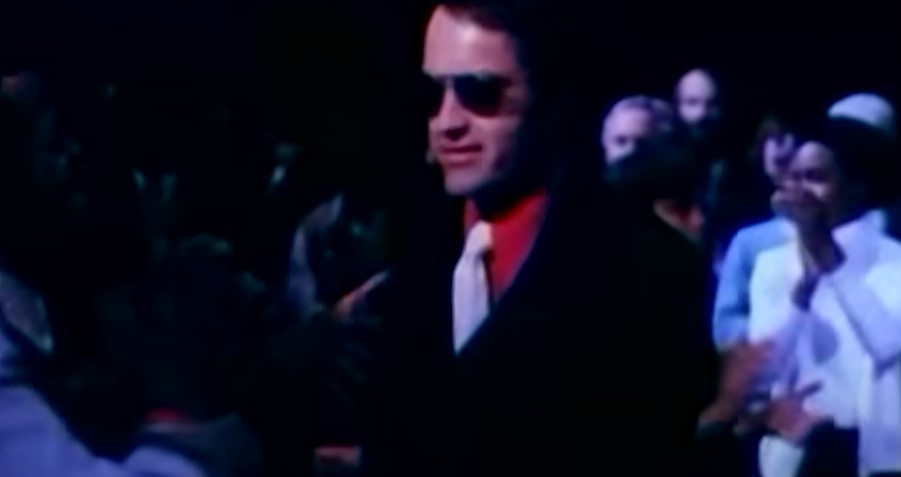
Baptisms
Jones rejected the required teachings of the Disciples of Christ denomination and instead created his own baptismal formula—baptizing his converts “in the holy name of Socialism.”
Even though he was pushy with his beliefs within his congregation, he was secretly fearful of the public’s reaction.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
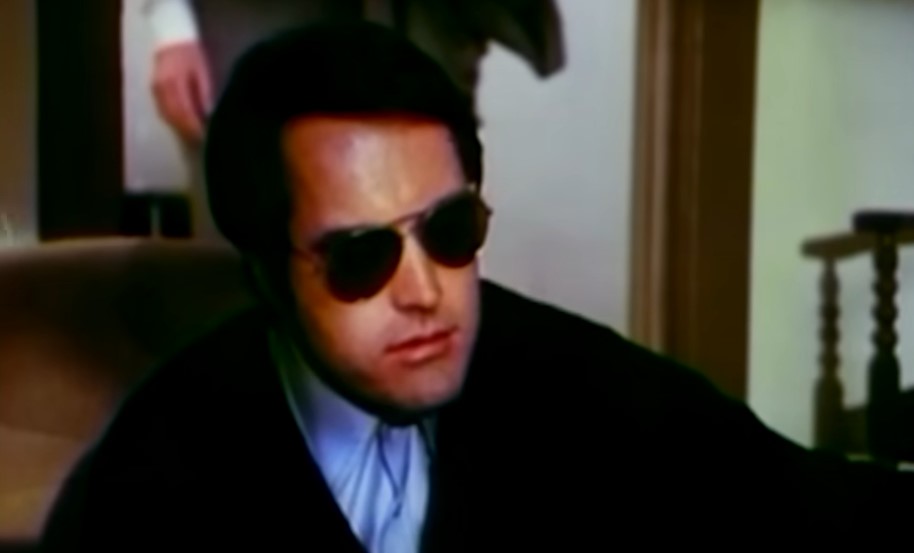
Consequences of His Teachings
Jones believed that if the true nature of his views became widely known, he would quickly lose the support of political leaders and even face the possibility of Peoples Temple being ejected from the Disciples of Christ—which would drastically reduce his credibility.
He had to make sure he didn’t lose his power.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
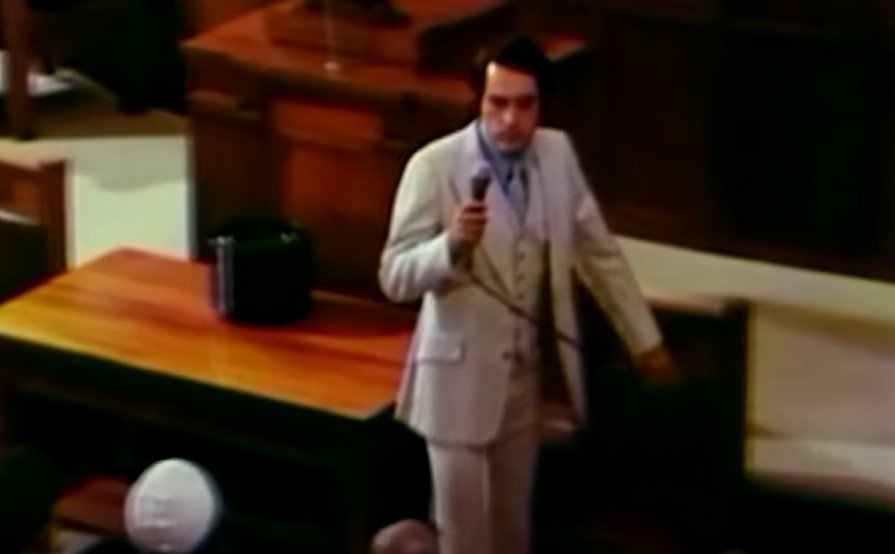
Strategy
Jones was careful to cover up his socialist views by using religious terms such as "apostolic social justice".
But he also had to keep up a certain level of fear in order to keep his followers.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
Fear of the Future
Jones often warned his members of an imminent apocalyptic genocidal race war and nuclear war. He told his non-white followers that they would be put in concentration camps if they were not careful.
He reminded them that he was their messiah, giving them refuge within his church.
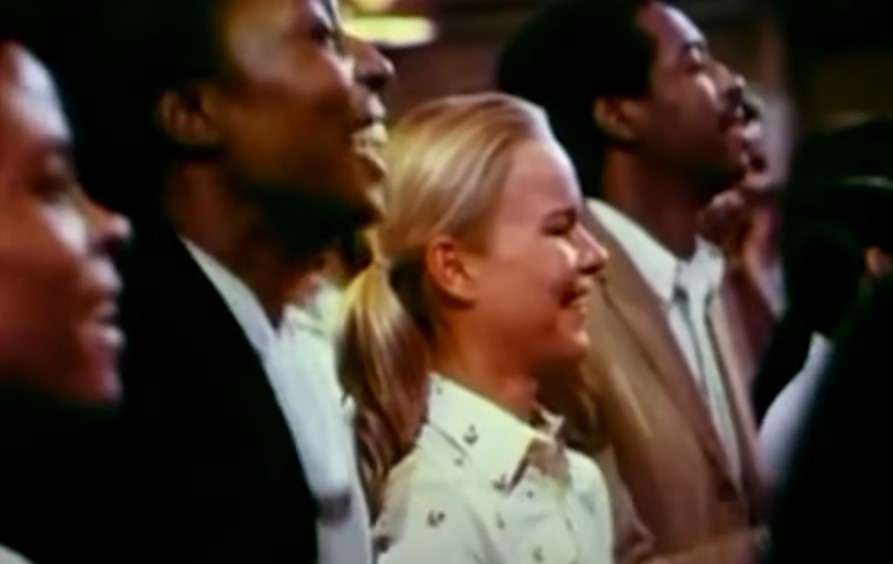
Their Safety Net
Jones ensured his followers that they’d be safe with him during the apocalypse, and that they’d be the only group to be saved.
He promised them that after it was all over, they would emerge to establish a perfect communist society.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
Control
Jones’s followers were terrified of what was to come, and felt no choice but to trust in him for the sake of their lives.
He now had complete control over them.
 Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
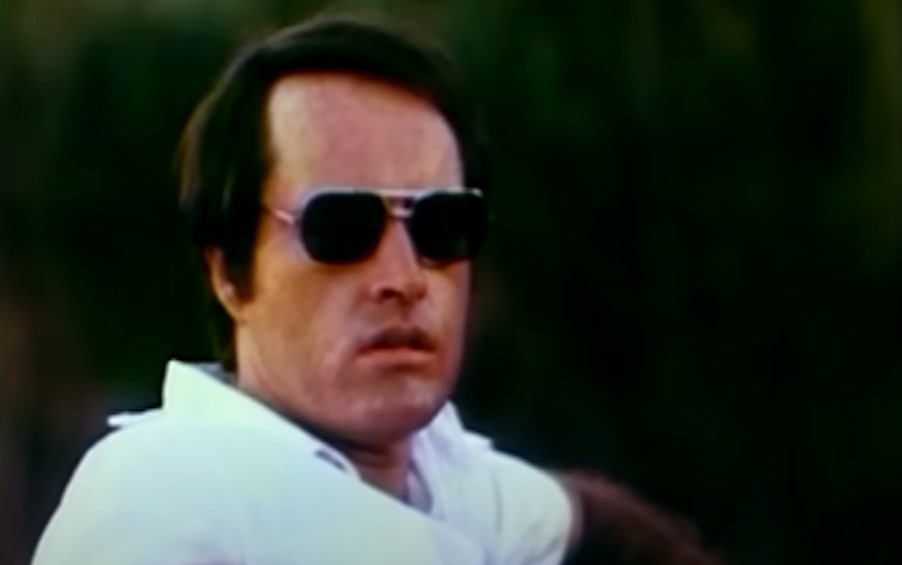
As His Ego Grew, So Did His Paranoia
At some point, Jones had begun misusing unlawful substances, which further heightened his paranoia. Which in turn, increased his use of fear to control and manipulate his followers.
He regularly warned his followers of an evil enemy looking to destroy them. The identity of this enemy was ever-changing.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
The Enemy
Jones convinced his followers that many different racial hate groups were after them, making them fearful of anyone outside their community.
Eventually, he added the American government to the list of enemies—taking things to the next level.
 Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Complete Fear of the Outside World
At this point, Jones just kept going. Not only were his followers afraid of literally anyone outside their group, they were now afraid of everything.
Jones had convinced them that bad things would happen to them (such as car accidents, fires, and injuries) if they were not faithful to him.
Forced Communal Lifestyle
Jones now implemented a communal lifestyle among his followers—members were required to turn over all of their assets to the church in exchange for free room and board.
Anyone who worked outside the Temple was required to give him all of their income to be used to benefit the community.
Things only got worse from there.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
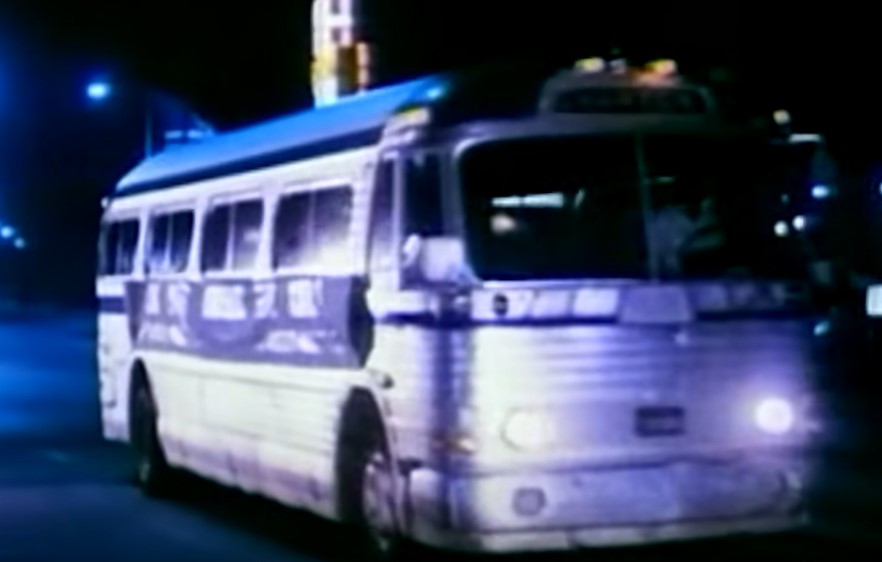
The Community
Jones assigned his followers jobs within the communal living spaces, and he transported them by bus to various places in the region to perform community service.
Not only did he control where and how they worked, he began taking away their rights to their own bodies.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
Misuse of Power
The People’s Temple was now a full-blown cult. His followers were so brainwashed that they did everything he told them to do.
This included marriages, and intimacy. Jones had rules on who can do what with whom, and when. He even decided which pregnancies would be allowed and which would be terminated.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
Forced Intimacy
At this point, Jones treated his followers like slaves. He started requiring intimate favors from the wives of some members of the church.
He even forcibly helped himself to whichever young woman he desired.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
Consequences for Non-Compliance
If any of his members rebelled against his control, they were punished with reduced food rations, harsher work schedules, public ridicule and humiliations, and even physical violence.
Jones even established an armed security crew, to keep his members in line.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
The People’s Temple Expansion
By this time, Jones had several committees within the People’s Temple that helped continue to successfully recruit members.
By the early 70s, they expanded the church to an urban area, holding large services in San Francisco and L.A. Their pure purpose was to recruit, and make money.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
Increasing Memberships
Implementing these recruitment strategies increased their membership from a few hundred to a few thousand by the mid-70s.
Most of them were African-American.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
Organizational Structure: Mind Control
Although the focus has been on Jones, the true control of the Temple was unevenly dispersed among its members.
This led to members being subjected to sophisticated mind control and behavior modification techniques similar to post-revolutionary China and North Korea.
 (stephan), CC BY-SA 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
(stephan), CC BY-SA 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
Organizational Structure: The Secret Police
The Temple had a group of people that were often referred to as “the Secret Police”—a group of predominantly college-educated white women that undertook the Temple's most sensitive missions.
This group followed the “ends justify the means” philosophy.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
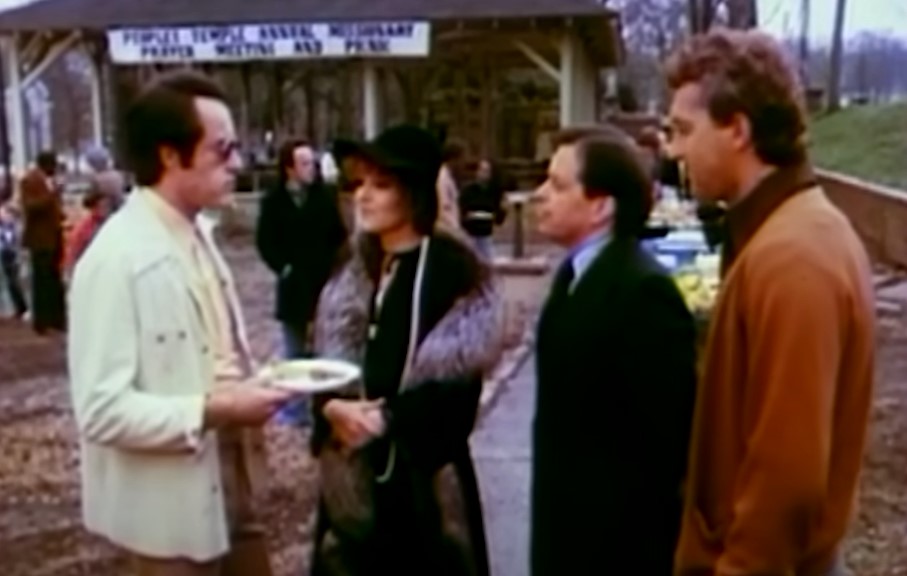
Organizational Structure: Committees
The Temple had various power groups, including a Planning Commission, a Diversions Committee, a Mertles Committee, and a group referred to as the “troops”—which consisted of working-class members who were specifically 70-80% black.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
Financial Goals
The Temple kept strict financial goals. They turned their recruitment efforts to people who had high-paying salaries. Once they joined the church, their salaries were handed over.
They were now targeting people with money and assets.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
Recruiting & Fundraising
Jones was shuttling 10-15 buses each week up and down California for recruitment and fundraising. He told members that the Temple would not schedule a trip unless it could net $100,000 minimum.
His annual net goal from bus trips alone was $1 million.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
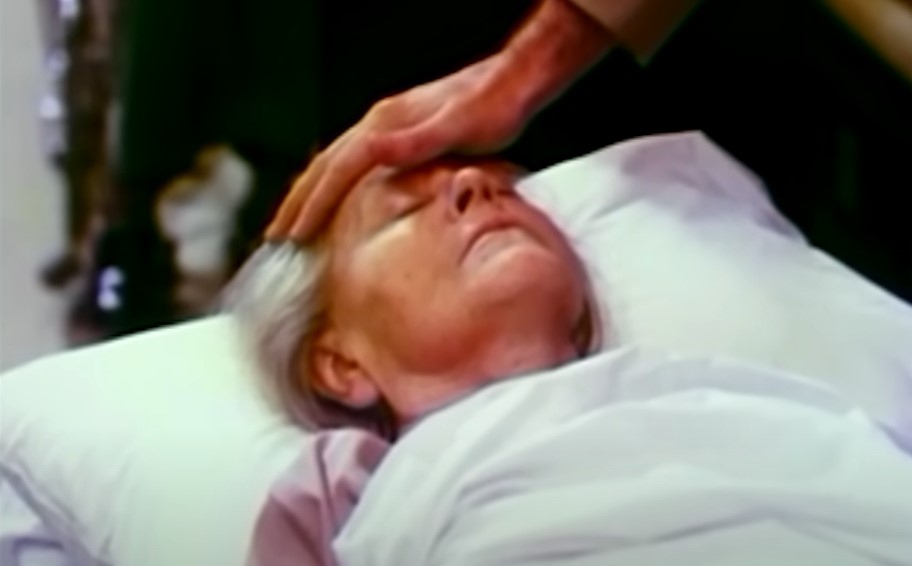
Their Disguise
Even though the People’s Temple sounds anything but appealing, it is important to remember that Jones was able to continue recruiting because he was still lying to prospects—promoting “spiritual healing” (which was all fake) and avoiding mentioning their Marxist goals.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
Con Artists
The Temple used their members to con people into joining. They did this by posing as locals in the audience, subjecting themselves to the spiritual rituals, pretending to be healed.
Each event brought in close to $40,000 in donations and collections alone.
But it didn’t stop there.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
International Donations
Somehow, the influence of the Temple was magnifying. They now set up “Truth Enterprises”—a direct mailing branch that sent out 50,000 donation requests to people who had attended their services.
Believe it or not, it worked, and donations flooded in from all over the U.S., Hawaii, South America, and Europe.
More and More Money
The Temple found more and more ways to make money, including selling merchandise and opening up a record label called “Brotherhood Records”, which produced music from the Temples “large interracial youth choir and orchestra.”
The Temple was taking over.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
Taking Over
With an influx in money and power, the Temple continued to expand. They established satellite congregations all over California, and implemented a college tuition program and dormitory at Santa Rosa Junior College.
At this point, the Temple had close to 5,000 members and it was growing daily.
 Dominik Martinez, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Dominik Martinez, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
The Temple’s Image
The Temple was careful in maintaining their positive image. They had earned a reputation for helping the poor, as well as racial minorities, addicts, and the homeless.
They made strong connections in the state’s welfare system, opening up even more for them.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
A Bureaucratic Social Service Organization
Continuing in the social service direction, the Temple owned and ran at least nine residential care homes for the elderly, six homes for foster children, and a state-licensed 40-acre ranch for developmentally disabled persons.
From the outside, the Temple’s reputation was still very positive. But inside members knew differently—and eventually, people woke up.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
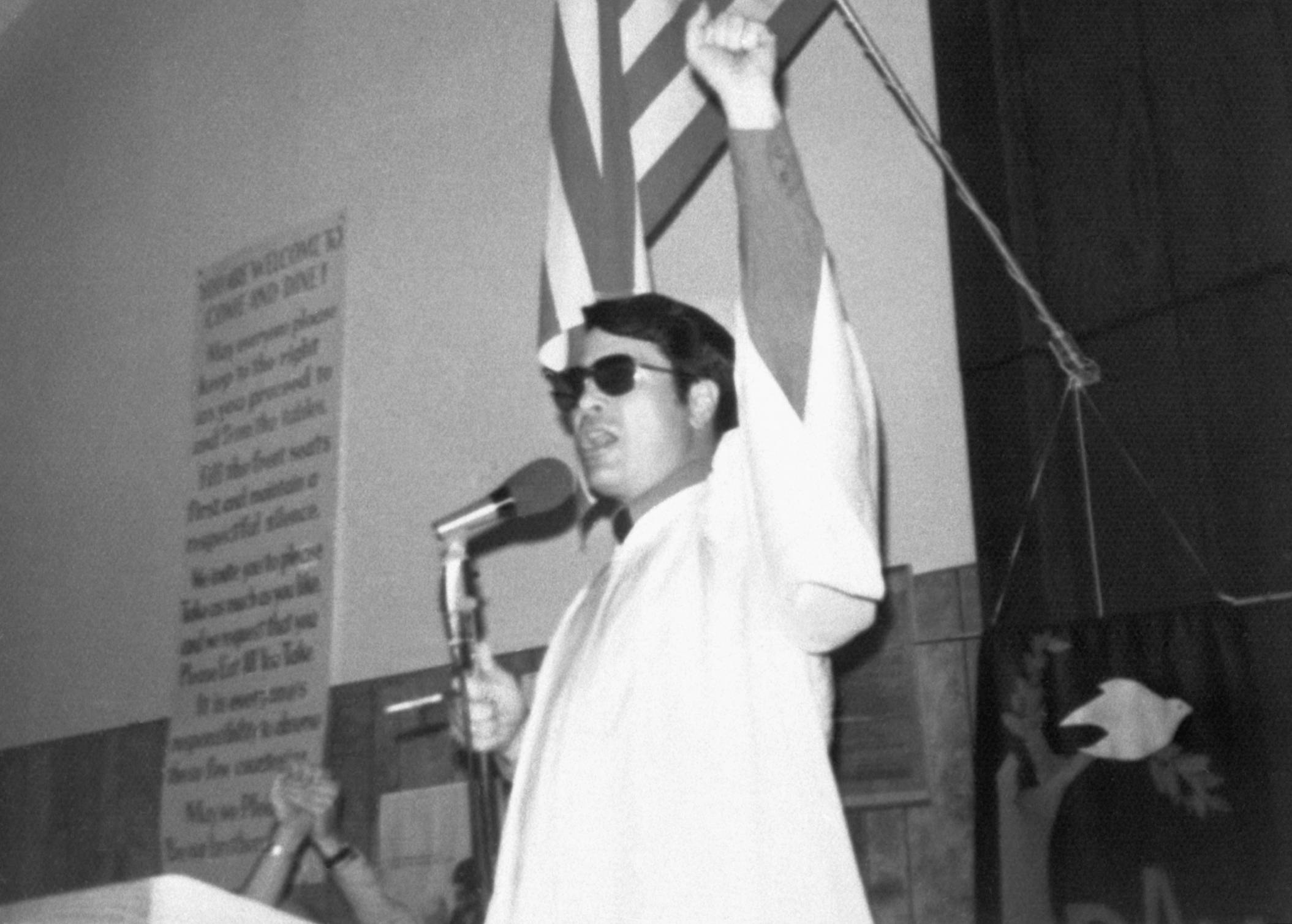
The Group of Eight
In 1973, a group of eight young members decided to leave the Temple. They were aware of the possible consequences if they were found—but they left anyway.
Jones, angry at their defiance, sent out search parties to look for them.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
The Search
Jones’s search was extensive. He had a private plane scanning the highways to look for them.
The group had planned on fleeing to Canada, but their trucks were loaded with firearms, so they went to the hills of Montana and made a plan for outing the Temple for what they truly were.
The Letter
The Group of Eight wrote a long letter documenting all of the bad things that went on inside the Temple.
Even though Jones did not find them, he knew what it was they would do, and he made a drastic decision.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
The Plan
Jones frantically called 30 members to his home and threatened his sinister plan—in order to keep their apostolic socialism, everyone should end their lives and leave a note stating that because of the harassment, “a socialist group cannot exist at this time.”
During this meeting, Jones grew increasingly angry.
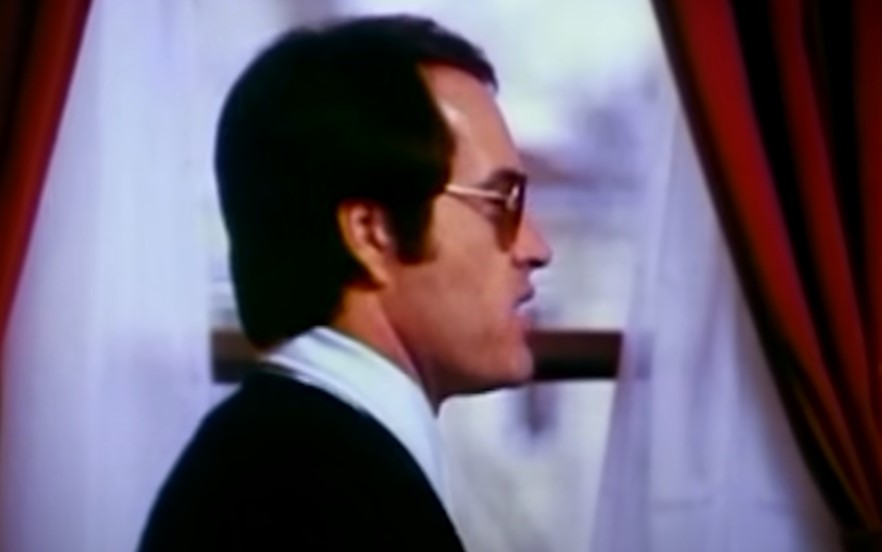 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
The Plan’s Execution
Luckily, the Temple did not execute Jones’s end of life plan at that time, but it did perform fake end-of-life rituals in the years that followed, eventually leading up to something more horrific than ever imaged.
 Don Hogan Charles, Getty Images
Don Hogan Charles, Getty Images
Suspicion Arose
While more and more people started leaving the church, Jones grew angry again. He was committed to his political views, and hated the negative attention that was following.
Authorities began to notice more after a man was mysteriously slain after his wife reportedly left the church.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
The Move to Guyana
In 1974, the People’s Temple signed a lease to rent land in Guyana. They established a community on the property dubbed "Jonestown.”
Jones saw this place as a “socialist paradise” and a “sanctuary” from the increasing media scrutiny, and what Jones believed was an increase in fascism and racism.
 Treez44est, CC BY-SA 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
Treez44est, CC BY-SA 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
The Reason for Guyana
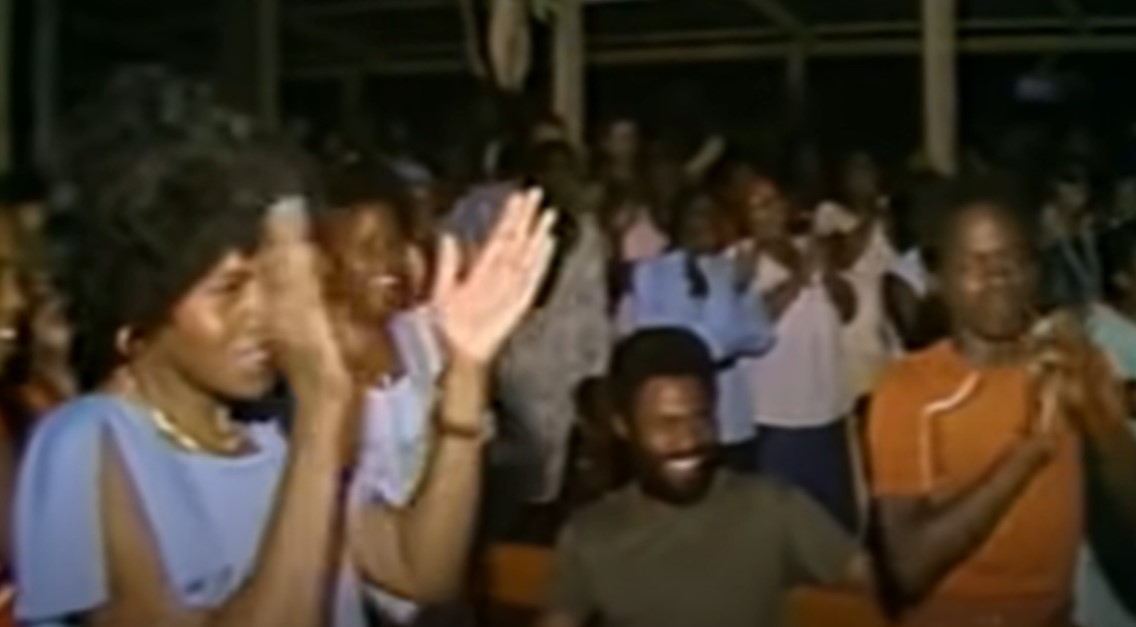
The Temple had concluded that Guyana was “a place in a black country where our black members could live in peace,” and that it was “a socialist government”, and “the only English-speaking country in South America.”
Only about 50 members lived there at this point, but this would soon change.
 Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
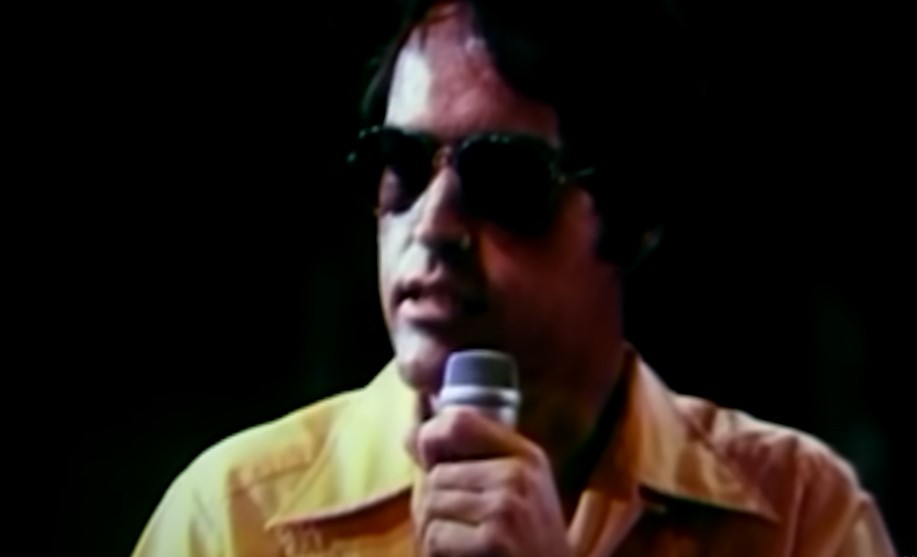
Media Scrutiny Continued
The People’s Temple was under serious media scrutiny now, as former members were speaking up about the church’s abusive lifestyle.
Shortly before a news article was scheduled to publish, the editor called Jones to give him a heads up. In fear of what was to come, Jones hatched a plan.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
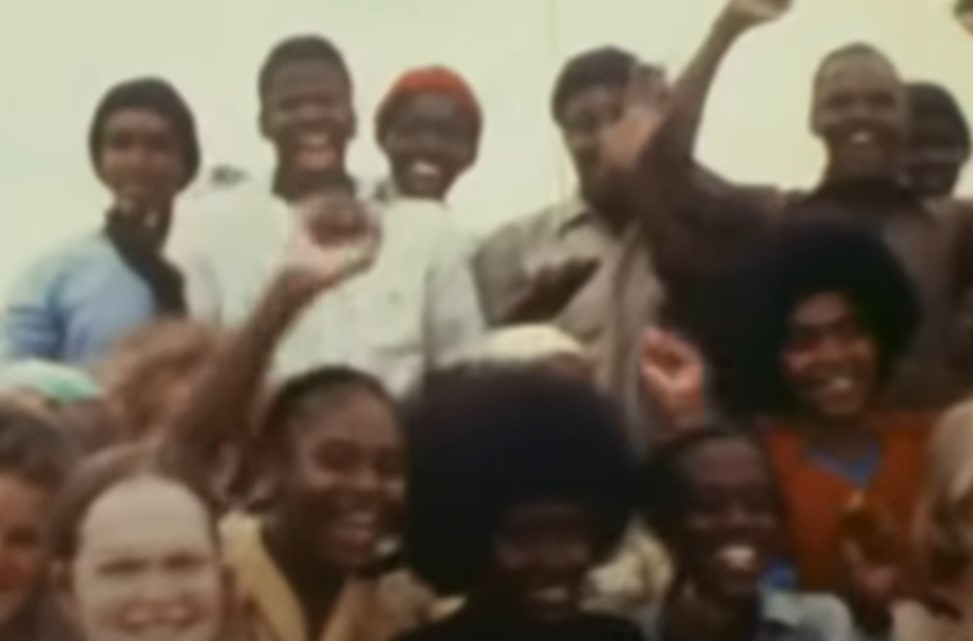
The Final Move
Jones, who was still in California at the time, immediately decided that all and every remaining member in the U.S. would move to Jonestown in Guyana.
He convinced 900 people to follow him, promising them a tropical paradise free from the “wickedness of the outside world.”
 Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
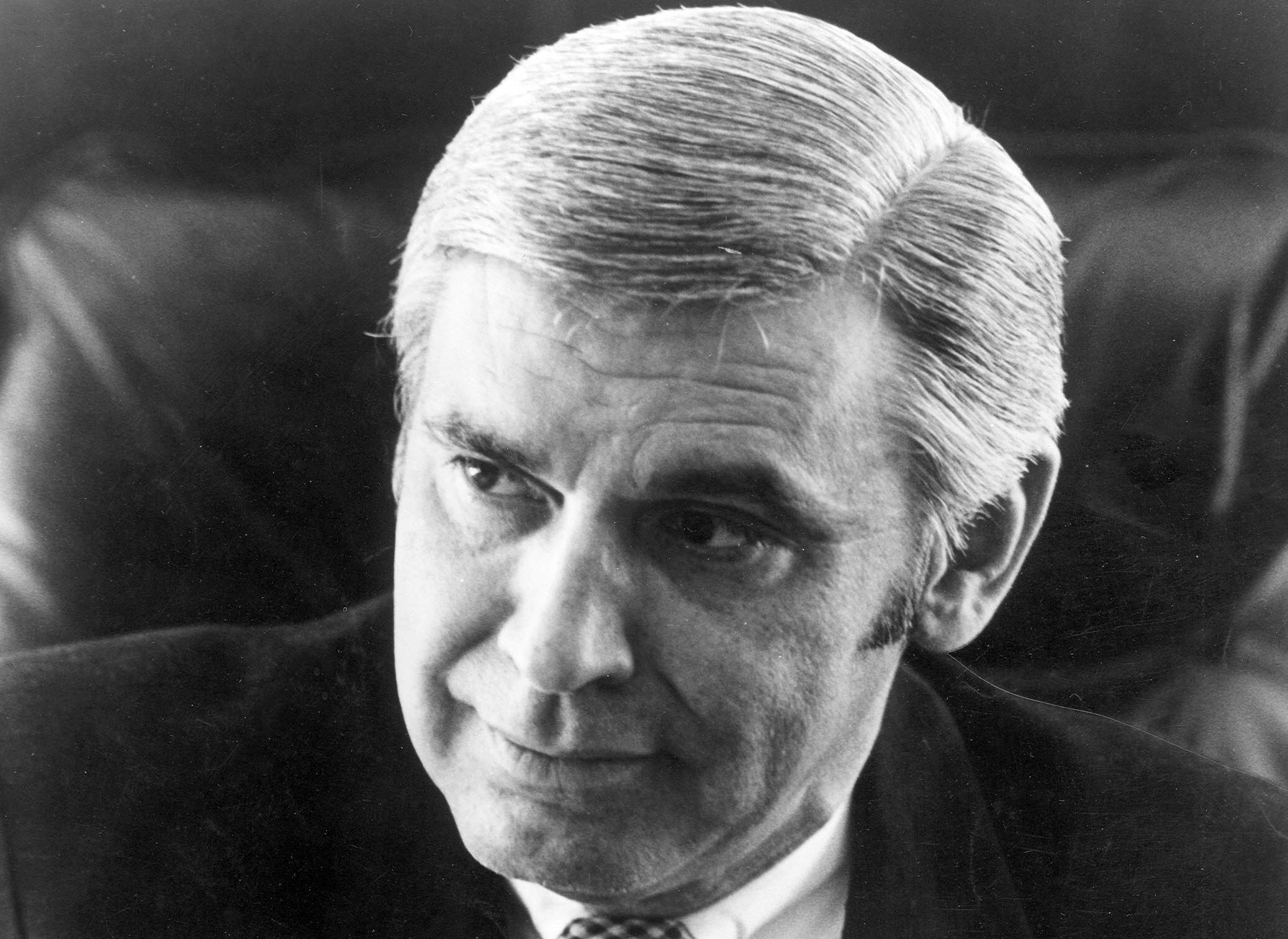
Investigations
Not long after Jones and his followers got to Guyana, a political representative named Leo Ryan, who was investigating the Temple, visited Jonestown.
During his visit, a number of members begged him to take them with him when he left. But this was not a smart move.
 U.S. House of Representatives, Wikimedia Commons
U.S. House of Representatives, Wikimedia Commons
Interception
The members who wanted to flee left with Ryan to the local airstrip, but were intercepted by the Temple’s security.
The security opened fire on the entire group, which ended the lives of Ryan, three journalists, and one of the church members. Several others were severely injured.
However, one of the journalists kept his camera rolling.
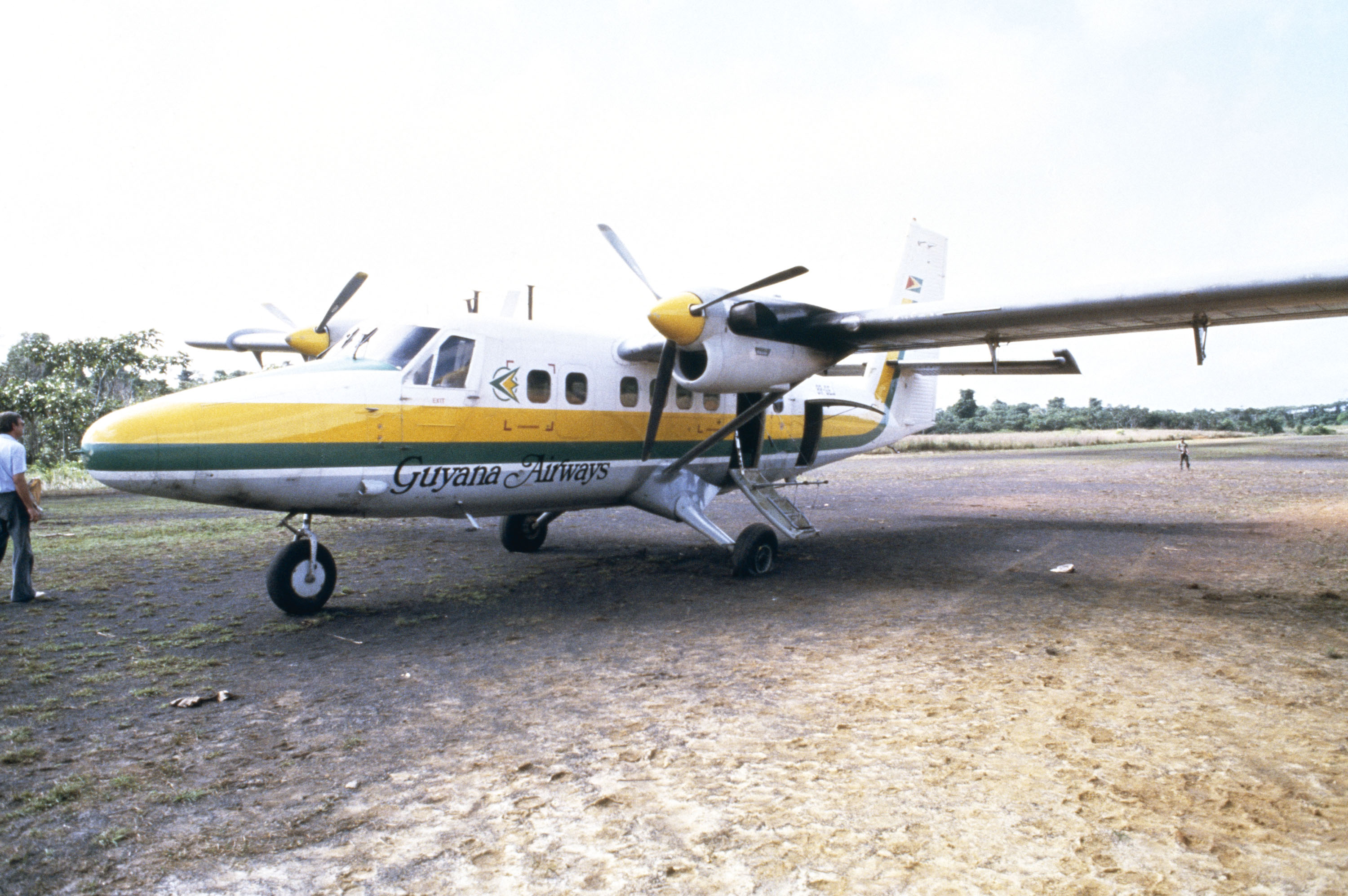 David Hume Kennerly, Getty Images
David Hume Kennerly, Getty Images
Caught on Tape
One of the journalists who lost his life in the attack, Bob Brown, captured a few moments of the incident on video. Although he didn’t make it out alive, one of the other journalists who did, grabbed Brown’s tape.
At this point, Jones knew he was in serious trouble, and made a life-changing decision.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
The Escape Plan
Fearing the repercussions that were about to come his way, Jones introduced his plan that would help his entire congregation “escape”.
The most important part of the plan—absolutely no one is to be left behind.
The Kool-Aid
That evening, on November 18, 1978, Jones ordered his congregation to drink a concoction of cyanide-laced, grape-flavored Flavor Aid, that would “free them” of this life.
The congregation was so brainwashed that compliance was fairly easy.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
The Aftermath
In all, 918 people lost their lives that night, including 276 children. People were given the drink and dropped to their demise wherever they were standing. Bodies scattered across the compound.
Some members resisted committing “revolutionary loss-of-life”, but were once again met with forced compliance.
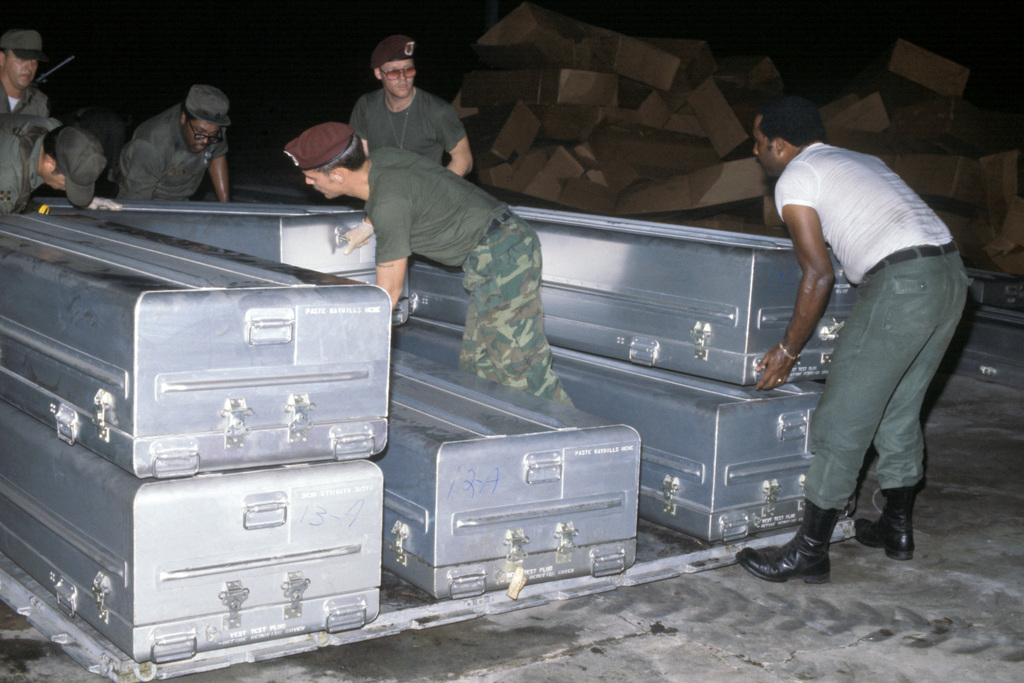 The U.S. National Archives, Picryl
The U.S. National Archives, Picryl
Forced Compliance
Anyone who fought back, resisting the drink, were tied down and injected with fatal doses of cyanide. This method was also used on infants, and members who initially survived by fleeing through the jungle.
But it didn’t end there.
 CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
CBS, Guyana Tragedy: The Story of Jim Jones (1980)
Survivors
Temple members that were in the United States were now fearful of possible “hitmen” that would come looking for them.
One insider survivor, who had been tasked with delivering a suitcase full of money to the Soviet Union, instead wrote a 30-page statement about the Temple, and then ended his own life. His note highlighted his fear of survival.
More survivors emerged, but met the same fate.
The Fate of the Supporters
One of the Temple members had married Guyana’s ambassador to the U.S., and had a child together. But after the incident, the ambassador fatally shot both his wife and child, and then did the same to himself.
It is assumed he had felt guilt for his support in the Temple, or perhaps he was brainwashed enough to join them.
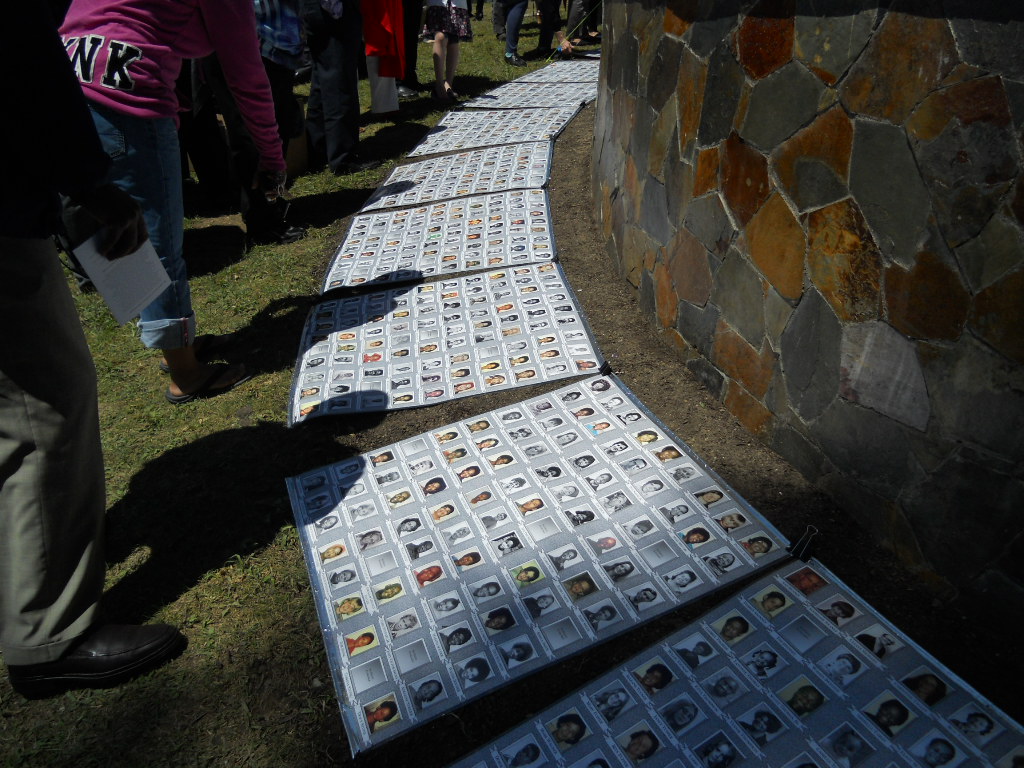 Symphony999, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Symphony999, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Dissolving the Temple
At the end of 1978, the Temple declared bankruptcy, and its assets went into receivership. In light of an abundance of lawsuits, a petition to dissolve the Temple was granted in 1979.
 Los Angeles, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Los Angeles, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Final Thoughts
This event was the greatest single loss of American civilian life in a deliberate act until the events of September 11, 2001.
It became one of the most-known events in U.S. history, and appeared in several media outlets for months afterward.
 Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Firelight Media Inc., Jonestown: The Life and Death of Peoples Temple (2006)
Source: 1






















