Ancient Planetary Remains
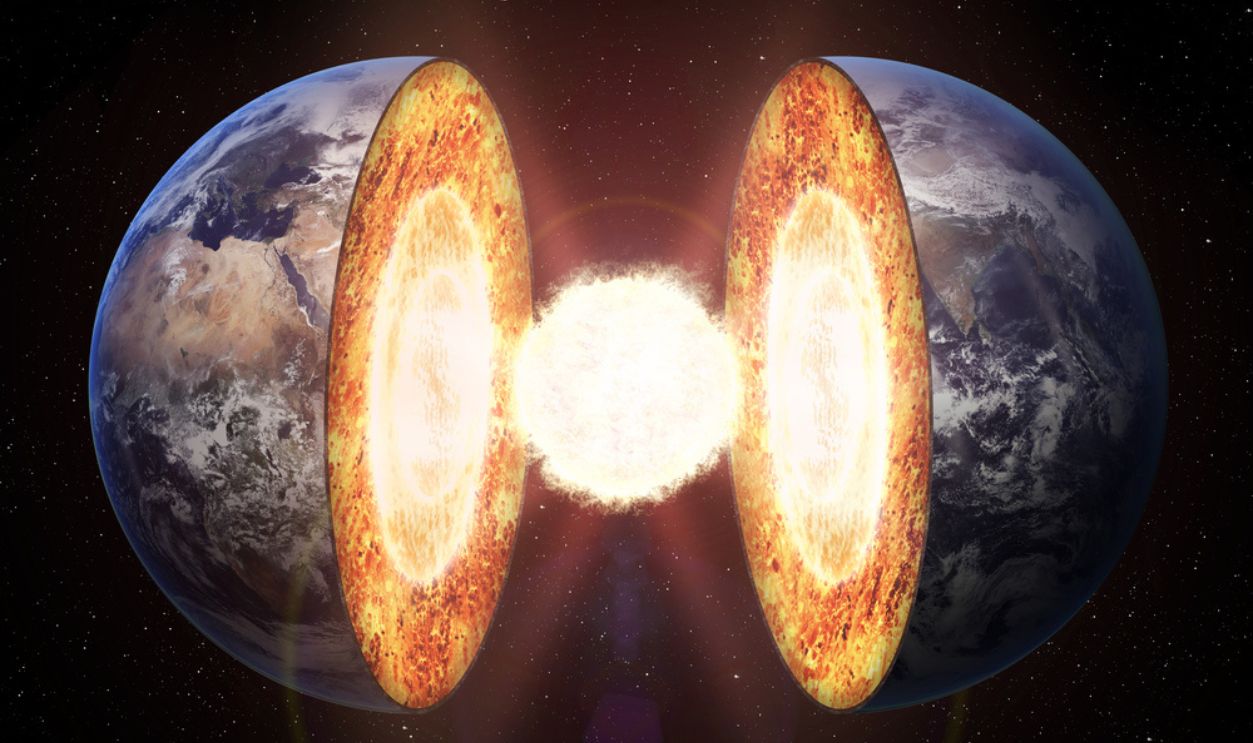
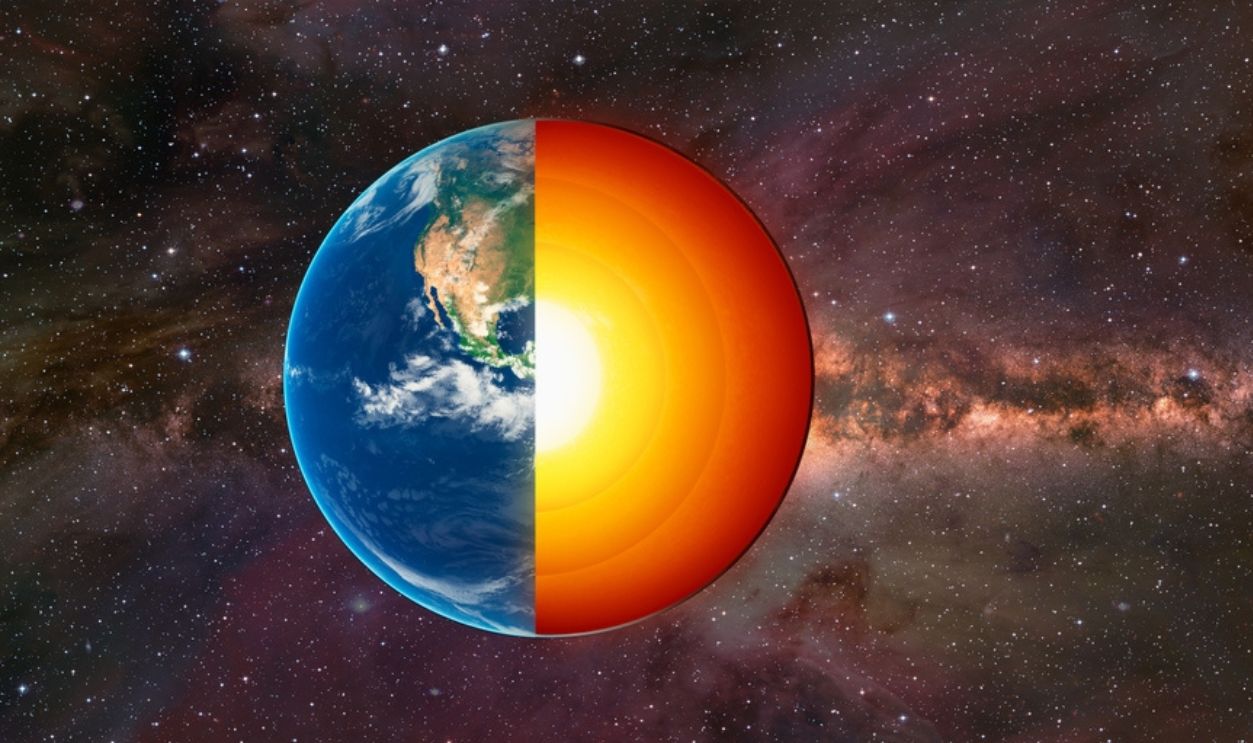
Scientists have been puzzled by the Earth’s origins for centuries and searched for answers buried deep within its layers. Could there be a secret buried deep inside its mantle?

What Lies Beneath
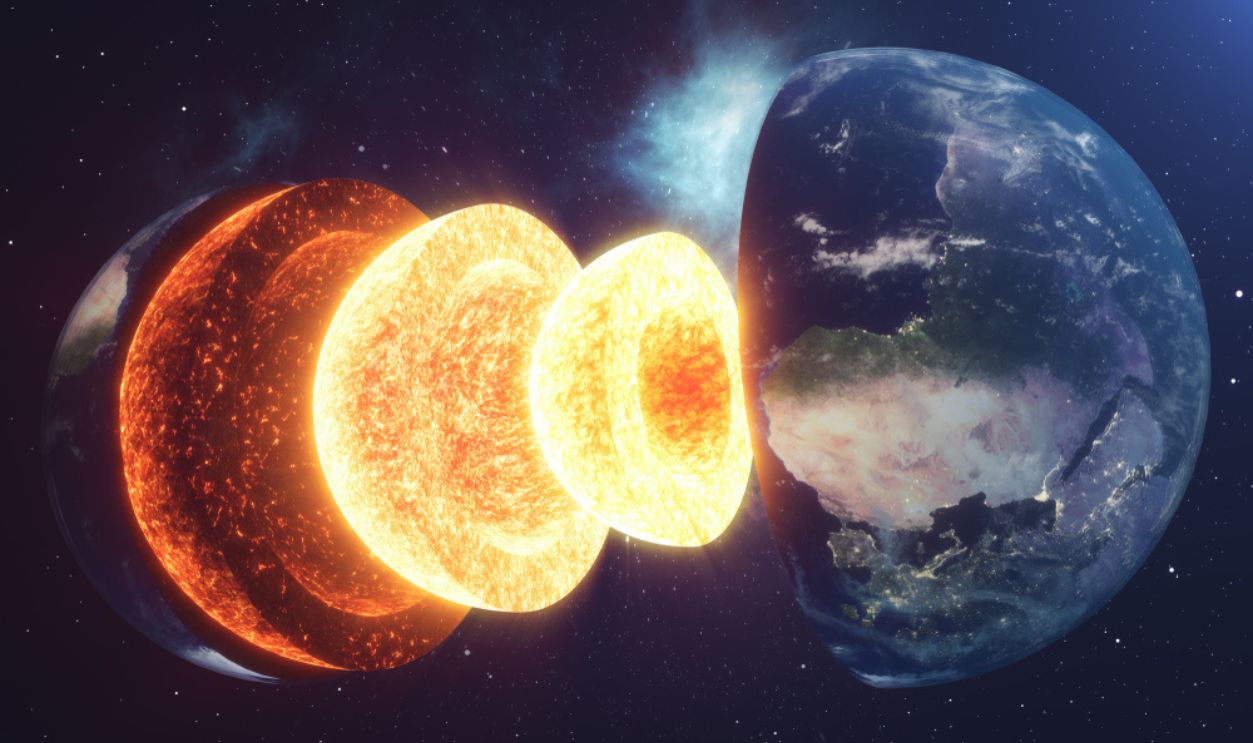
Without the right tools and equipment, it was impossible to determine what could have been buried within the Earth’s mantle. Thanks to new advancements in seismology, we can have more answers now. And great new discoveries.
A Solid Interior
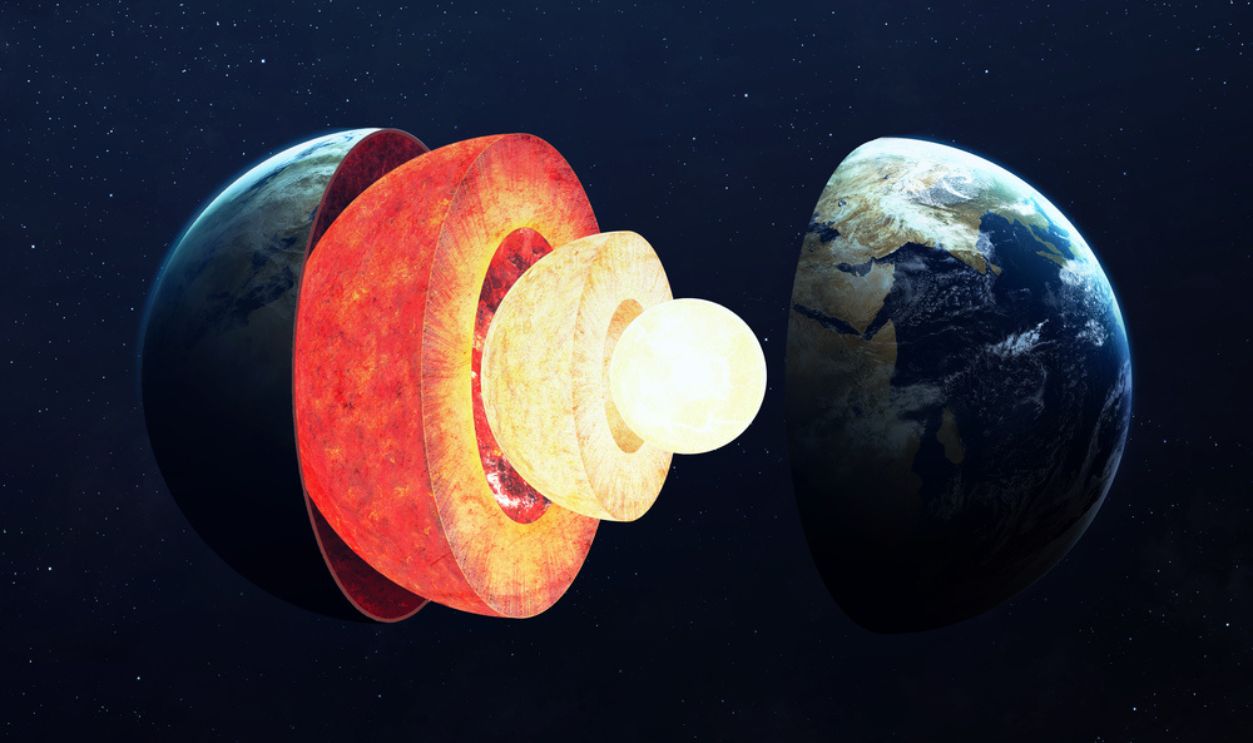
Seismic waves move through the Earth and have told us a lot about its interior. It’s mostly made of silicate rock but it behaves like a viscous liquid. However, studies showed mysterious masses that made scientists question their findings.
 Rob Lavinsky, iRocks.com, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Rob Lavinsky, iRocks.com, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Mysterious Structures Were Found
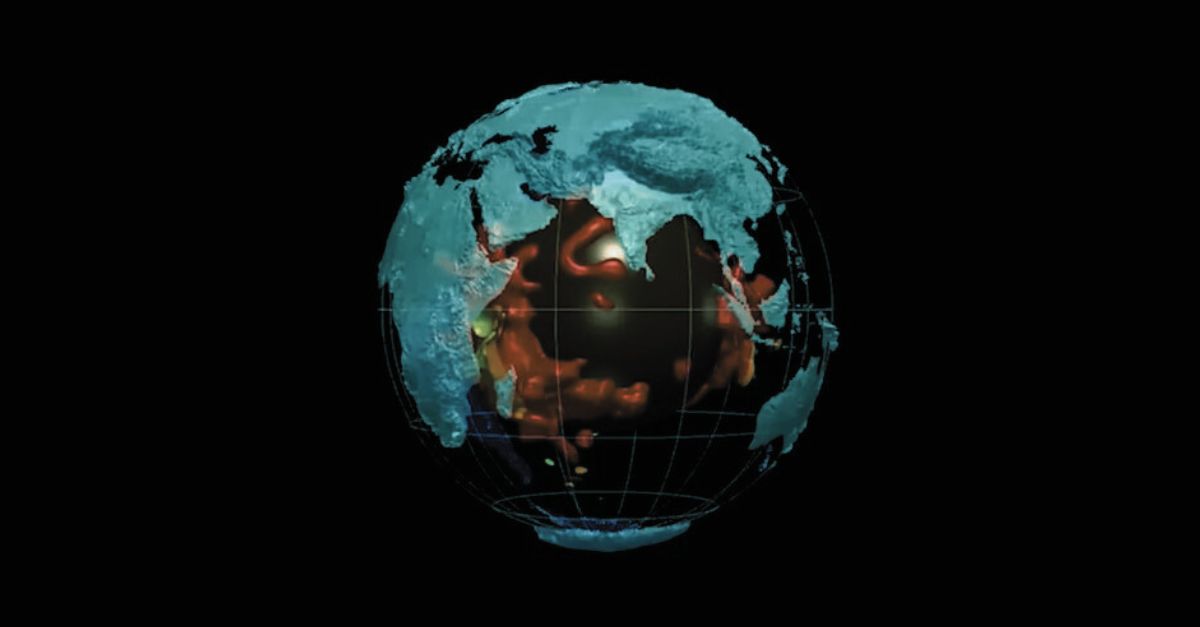
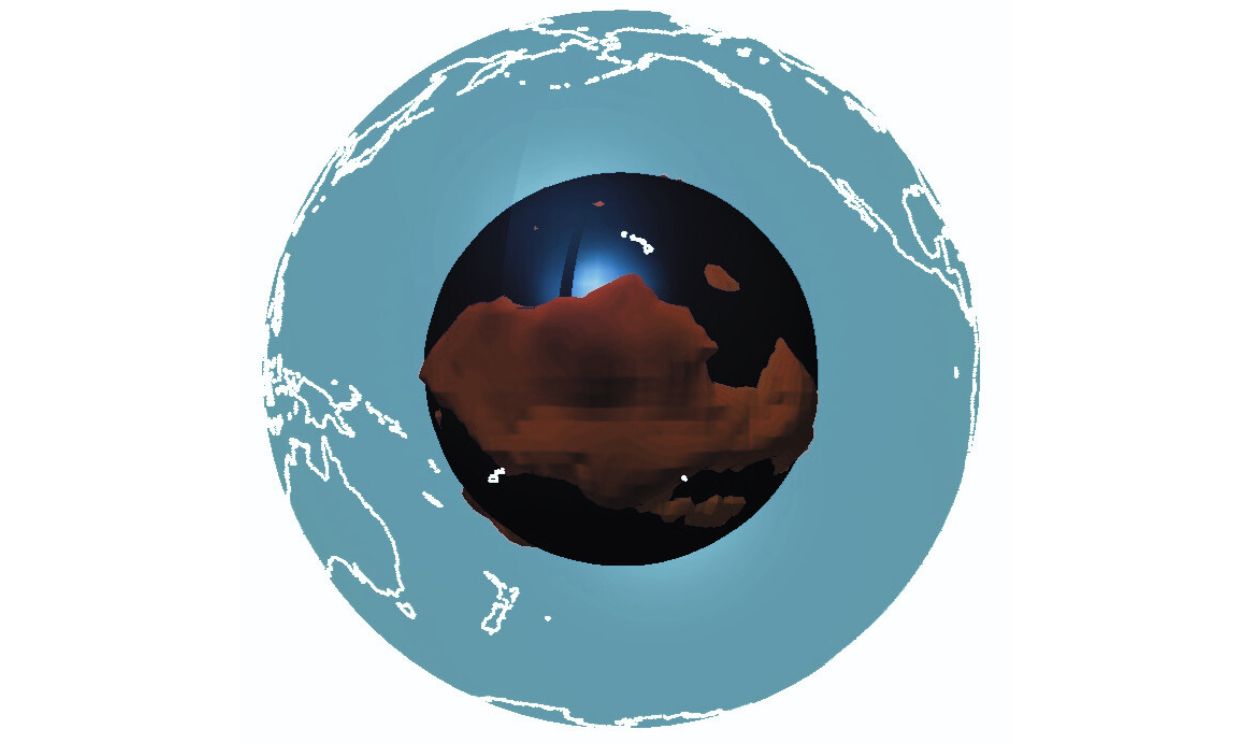
Deep within Earth's mantle lie enigmatic formations known as Large Low Shear Velocity Provinces (LLSVPs). These vast, continent-sized regions are characterized by seismic waves traveling at unusually slow speeds through them to indicate differences in composition or temperature compared to the surrounding mantle.
 Sanne.cottaar, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Sanne.cottaar, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
What Could They Be?
Located beneath Africa and the Pacific Ocean, LLSVPs have intrigued geophysicists for years due to their potential influence on mantle convection, plate tectonics, and surface volcanism. Understanding these structures is essential, as they may hold clues to Earth's formation and its dynamic geological processes.
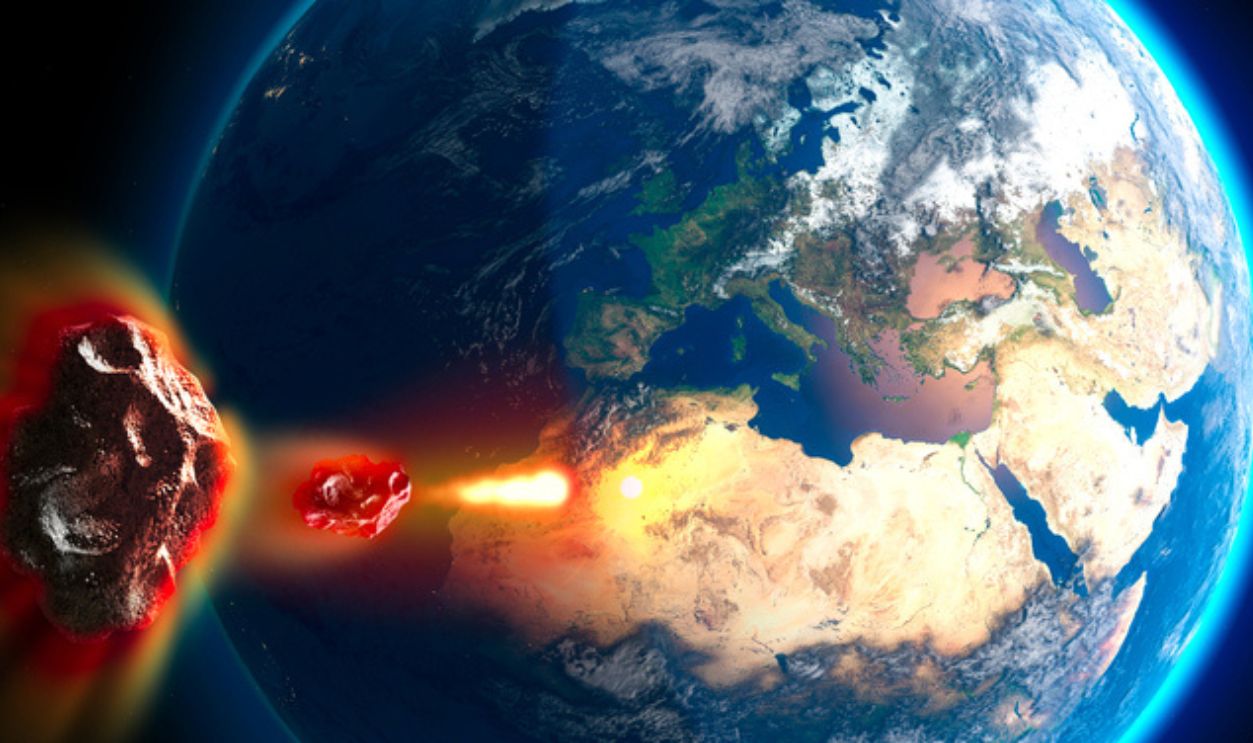
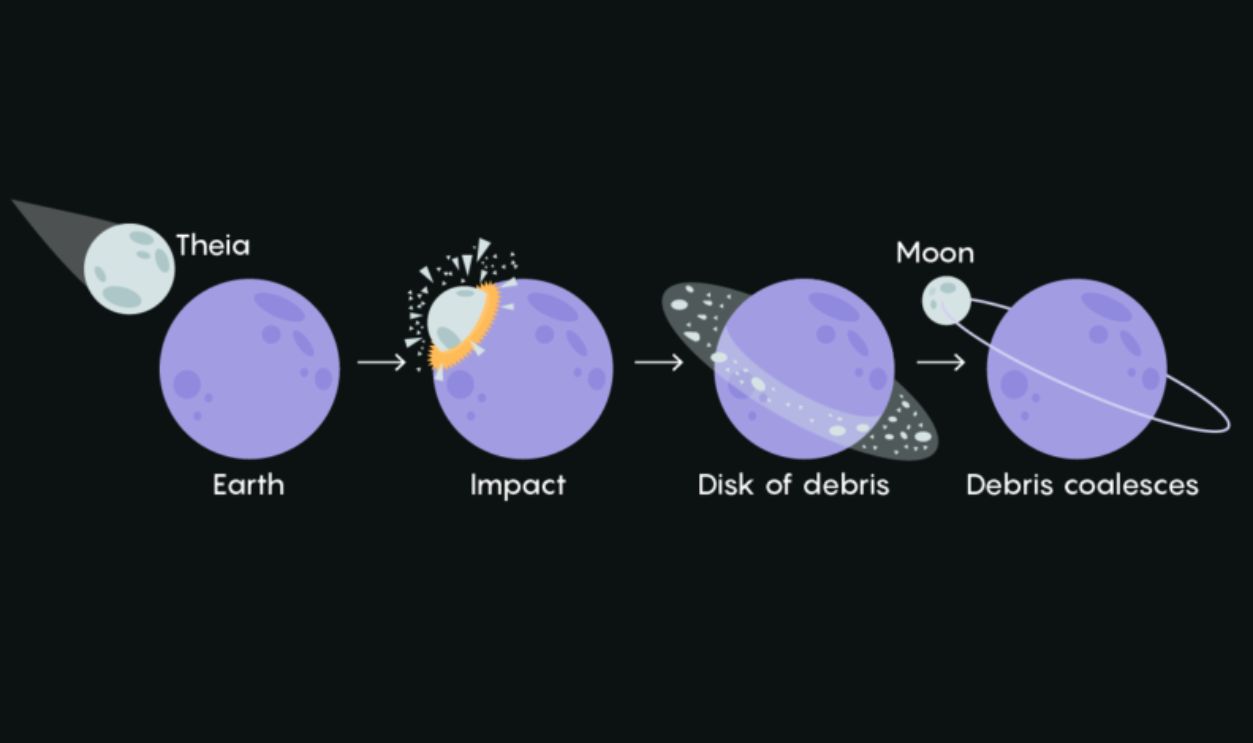
The Giant Impact Hypothesis
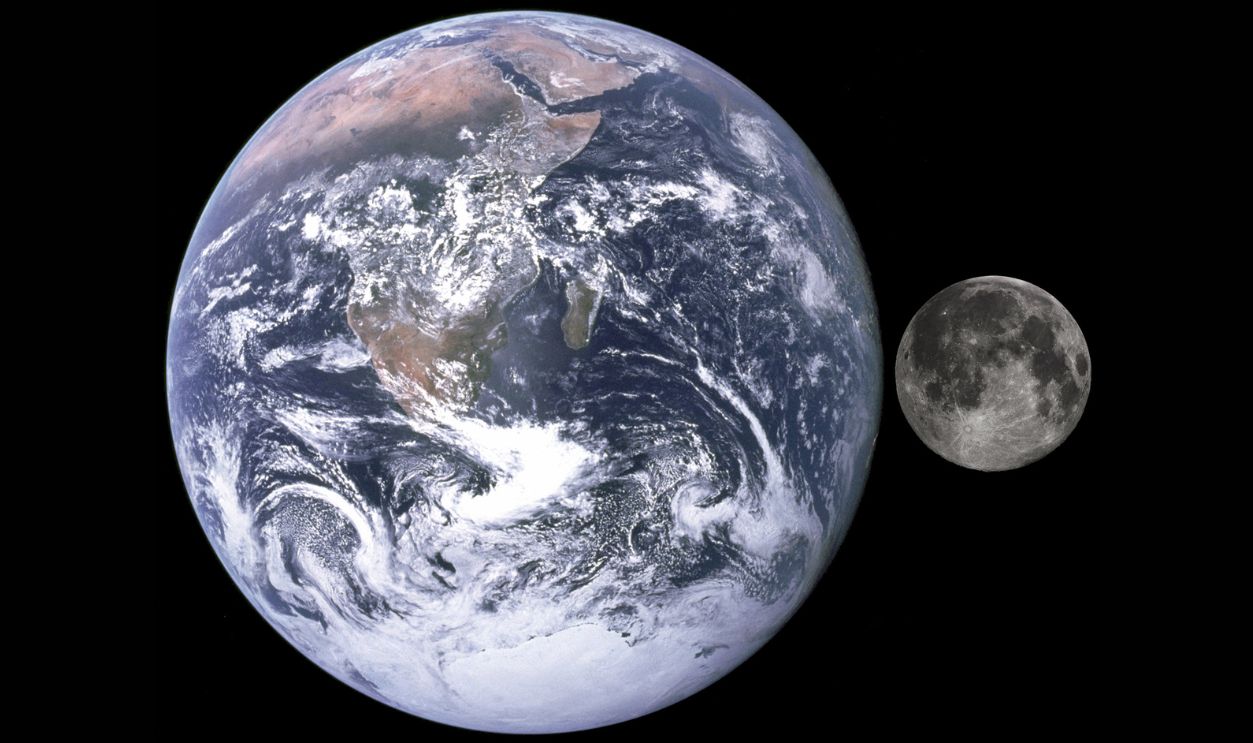
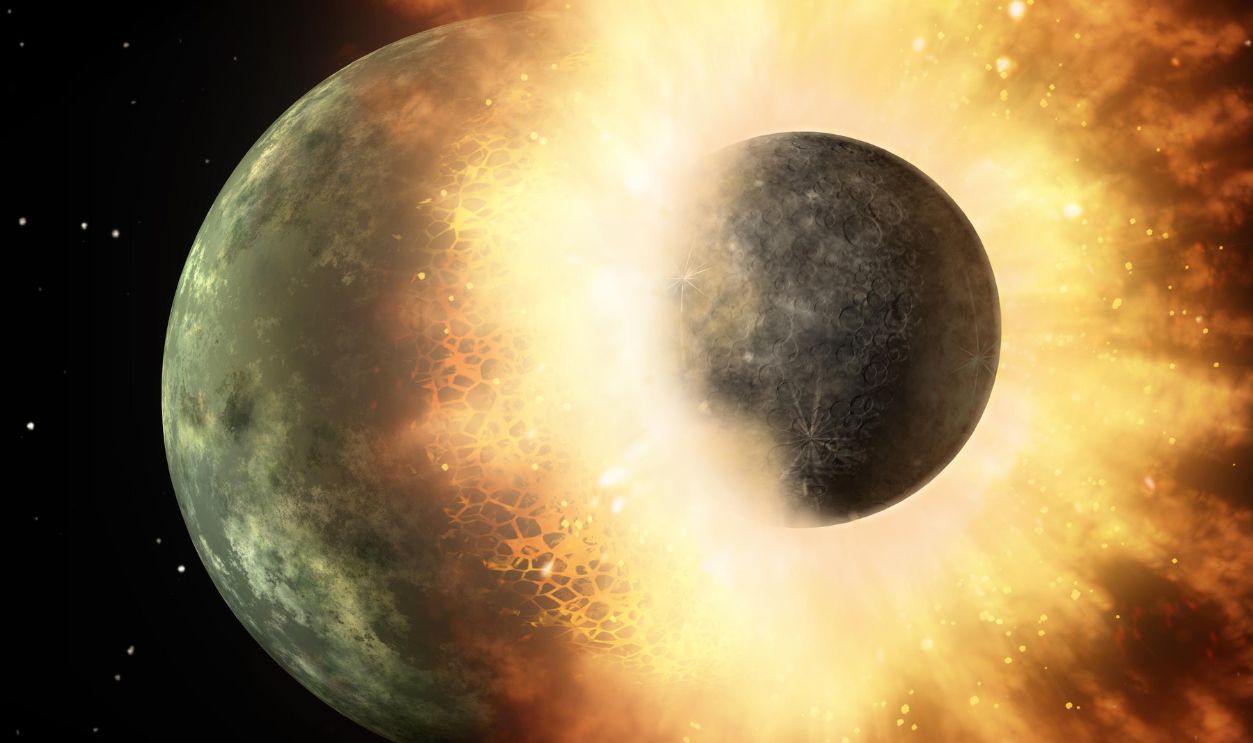
Scientists believe that approximately 4.4 or 4.45 billion years ago, a Mars-sized protoplanet named Theia collided with the early Earth in a monumental event known as the Giant Impact Hypothesis. This colossal collision is believed to have resulted in the formation of the Moon from the ejected debris.
 NASA/JPL-Caltech, Wikimedia Commons
NASA/JPL-Caltech, Wikimedia Commons
Theia's Remnants
The debris expelled into orbit around Earth following the Theia collision gradually coalesced to form the Moon. Traditional theories propose that this process took months or years. However, recent simulations indicate that the Moon may have formed in a shorter period.
It Was Probably So Sudden
Unlike older theories, the Giant Impact Hypothesis suggests that material from Earth and Theia rapidly merged in orbit. Further studies were needed to confirm if it mirrors that of Earth's mantle and shed light on the early dynamics of our planet and its satellite—aka the Moon.
 Citronade, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Citronade, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
But It Wasn’t Just That
Our natural satellite wasn’t the only outcome. This collision has probably significantly influenced Earth's geological and rotational characteristics. Recent studies suggest that remnants of Theia might still reside deep within Earth's mantle, potentially explaining the existence of LLSVPs.
Missing Post-Collision Material
While the Giant Impact Hypothesis accounts for the Moon's origin, it raises questions about the fate of Theia's remaining material. If only a fraction of the debris formed the Moon, where did the rest go? This question has puzzled seismologists and geophysicists for decades.
Time For A Breakthrough
Recent research proposes that substantial portions of Theia's mantle were assimilated into Earth's mantle that sank to great depths due to their higher density. This theory posits that the dense, iron-rich LLSVPs are, in fact, remnants of Theia and offers a compelling explanation for these deep mantle anomalies.
A Closer Look On The LLVPs
Superplumes, also called Large Low Shear Velocity Provinces or LLVPs, exist near the core-mantle boundary. They are among the most prominent features in Earth's lower mantle, which made them appear like giant mysterious blobs that no one understood.
 We Found the Remains of Another Planet Inside Earth by GeologyHub
We Found the Remains of Another Planet Inside Earth by GeologyHub
And How They Affect Our Planet
These structures are thought to influence mantle convection, plate tectonics, and surface volcanism. Their presence affects the dynamics of Earth's interior, potentially contributing to hotspot volcanism and continental breakup. The distinct characteristics of their size and density have led scientists to investigate their origins.
 Cyrus Read, Alaska Volcano Observatory, Wikimedia Commons
Cyrus Read, Alaska Volcano Observatory, Wikimedia Commons
Dr. Yuan's Research
Dr. Qian Yuan, a geophysicist at Caltech, has been studying the Earth’s core for years. His studies focus on the mantle to understand the origins of our planet and how it became habitable. However, there were other suggestions.
A Fascinating Discovery
Other theories linked LLVPs to Theia, the protoplanet believed to have collided with Earth, which led to the Moon's formation. Dr. Yuan realized that the iron-rich material from Theia could have sunk deep into Earth's mantle to form the dense regions we now identify as LLVPs.
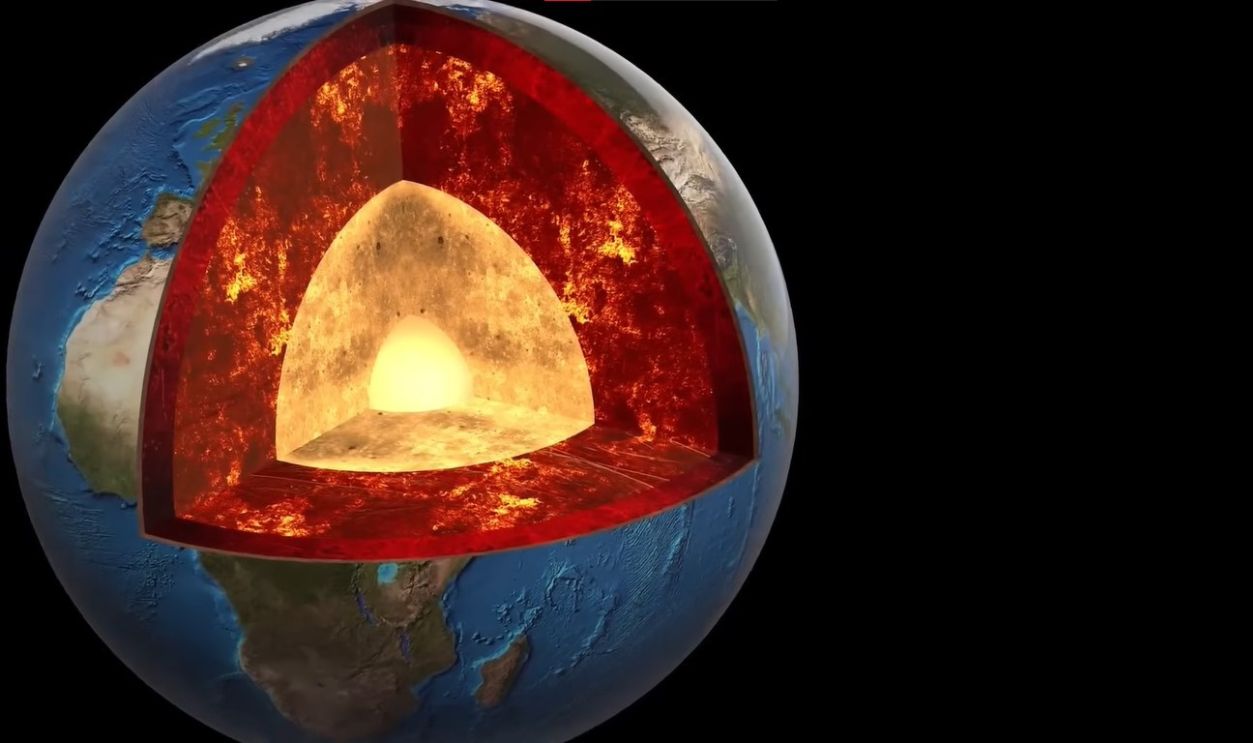
Simulations Supporting Theia's Theory
Recent computational simulations have provided support for the hypothesis that material from Theia was incorporated into Earth's mantle following the giant impact. These models indicate that the collision did not completely melt Earth's lower mantle.
 We Found the Remains of Another Planet Inside Earth by GeologyHub
We Found the Remains of Another Planet Inside Earth by GeologyHub
Due To Its Unique Composition
The composition of the mantle and Theia allowed the dense, iron-rich fragments from the doomed planet to sink and remain largely intact. Over billions of years, these remnants could have accumulated to form the LLVPs observed today.
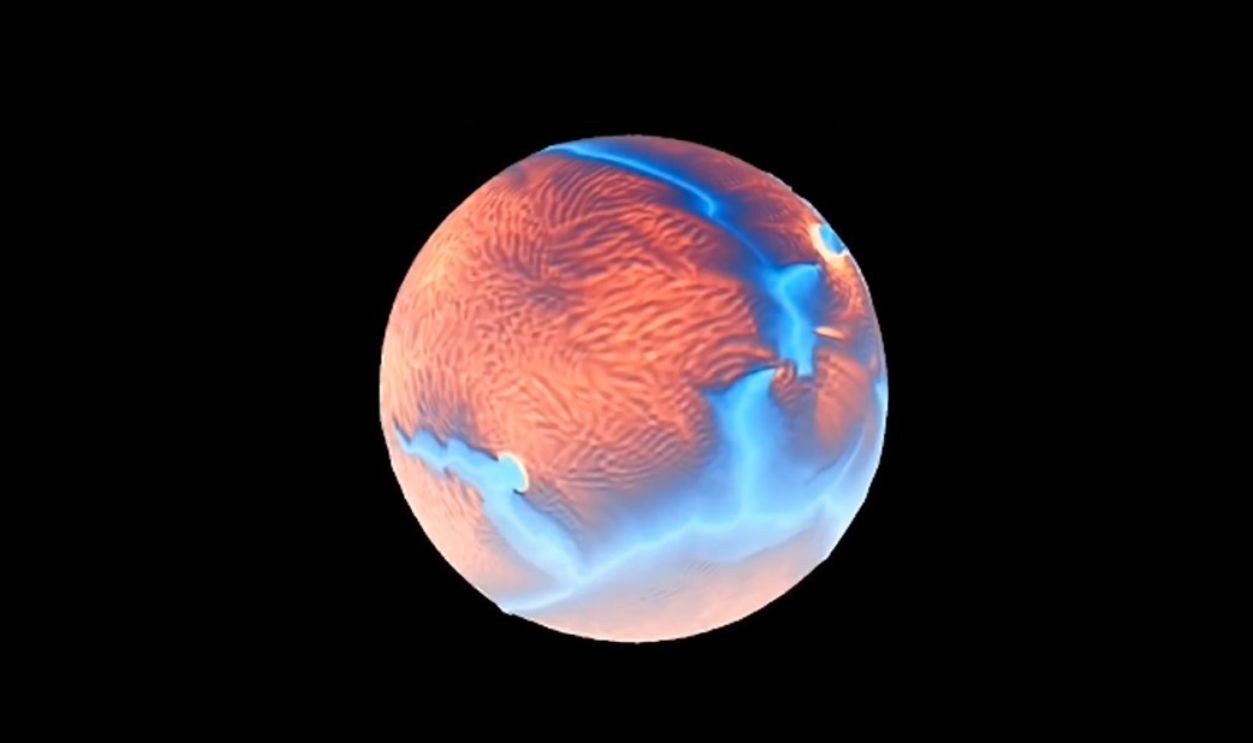 Terrifying Discovery! Lost Planet Theia is Hidden Inside the Earth by Global Update
Terrifying Discovery! Lost Planet Theia is Hidden Inside the Earth by Global Update
The Theory Became Popular
Among different suggestions, this theory offers a plausible explanation for the unique composition and density of these deep mantle structures. It links them directly to the ancient planetary collision that also resulted in the Moon's creation and explains the existence of these masses.
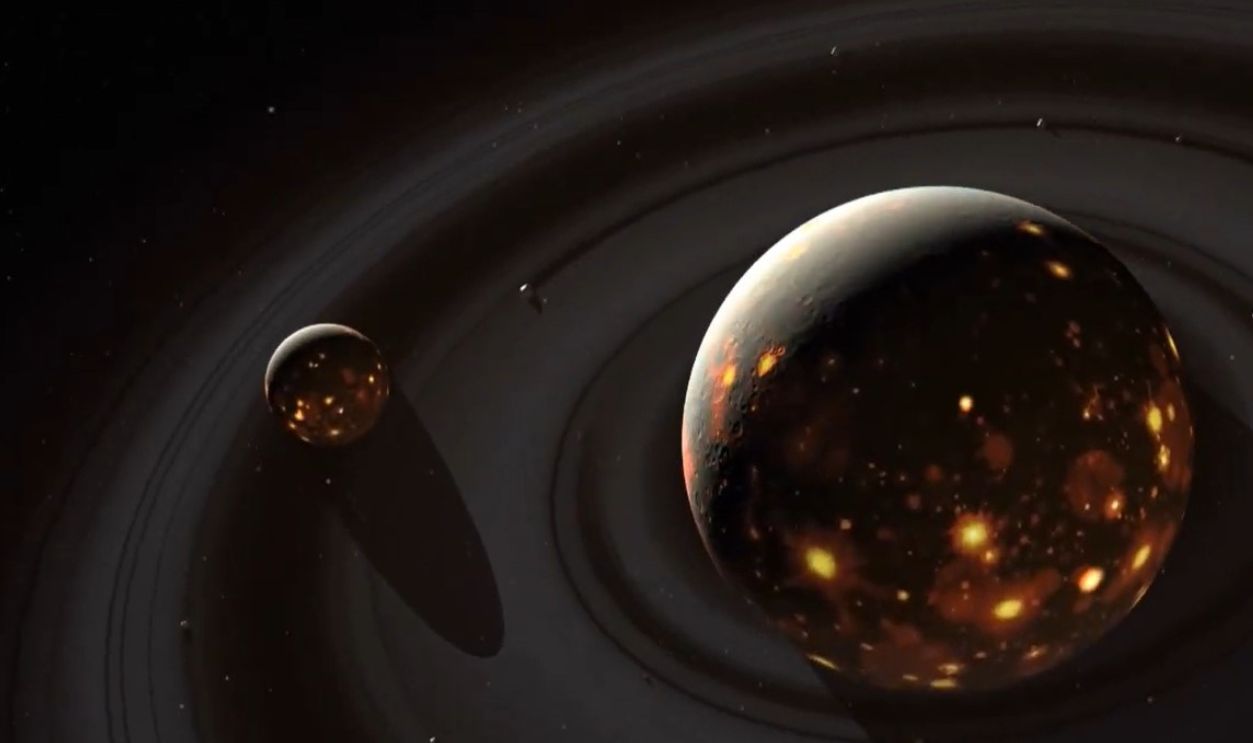 Moon Formation by Mark A. Garlick
Moon Formation by Mark A. Garlick
Because Of Evidence
Lunar samples collected during the Apollo missions revealed that the Moon is unusually rich in heavy elements. This could support the giant-impact hypothesis, as it could suggest that Theia’s core, rich in metallic elements, was ejected during the collision and later re-coalesced with Earth and the Moon.
 James Lovell, John Swigert, Fred Haise, Wikimedia Commons
James Lovell, John Swigert, Fred Haise, Wikimedia Commons
With Unexplained Similarities
Such similarity between Earth’s mantle and the Moon’s surface in isotopic compositions further strengthens the idea that the Moon originated from this ancient impact. Scientists believe that it provides an indirect link to the LLVPs, which are believed to contain remnants of Theia’s material.
 Bryan Derksen, Wikimedia Commons
Bryan Derksen, Wikimedia Commons
Maybe A Common Source?
By comparing the composition of the mantle and the Moon, scientists suggest these two might share a common origin from the same impact event. This connection could show that much of the ejected material during the collision originated from Theia’s core.
 Ram samudrala, CC BY 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Ram samudrala, CC BY 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
But Why So Deep?
Simulations suggest that after the collision, much of Theia's denser, iron-rich core was absorbed into Earth's mantle. Over time, gravitational forces caused this material to sink deeper, eventually settling in the lower mantle. These regions preserved the remnants of Theia over billions of years.
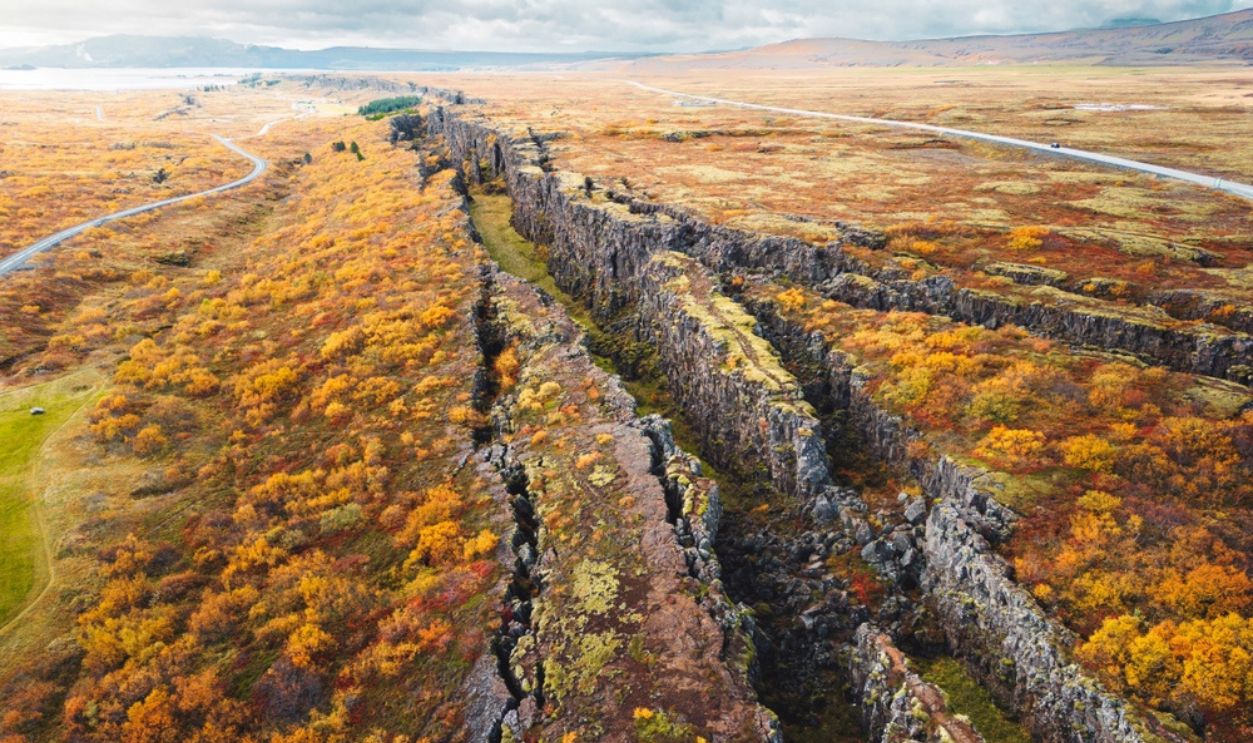
Geologically Unique
LLVPs are not just anomalies. They stretch thousands of kilometers and are very thick. They exhibit lower seismic velocities, which show differences in composition and temperature compared to the surrounding mantle. LLVPs are also chemically distinct and enriched in iron and other heavy elements.
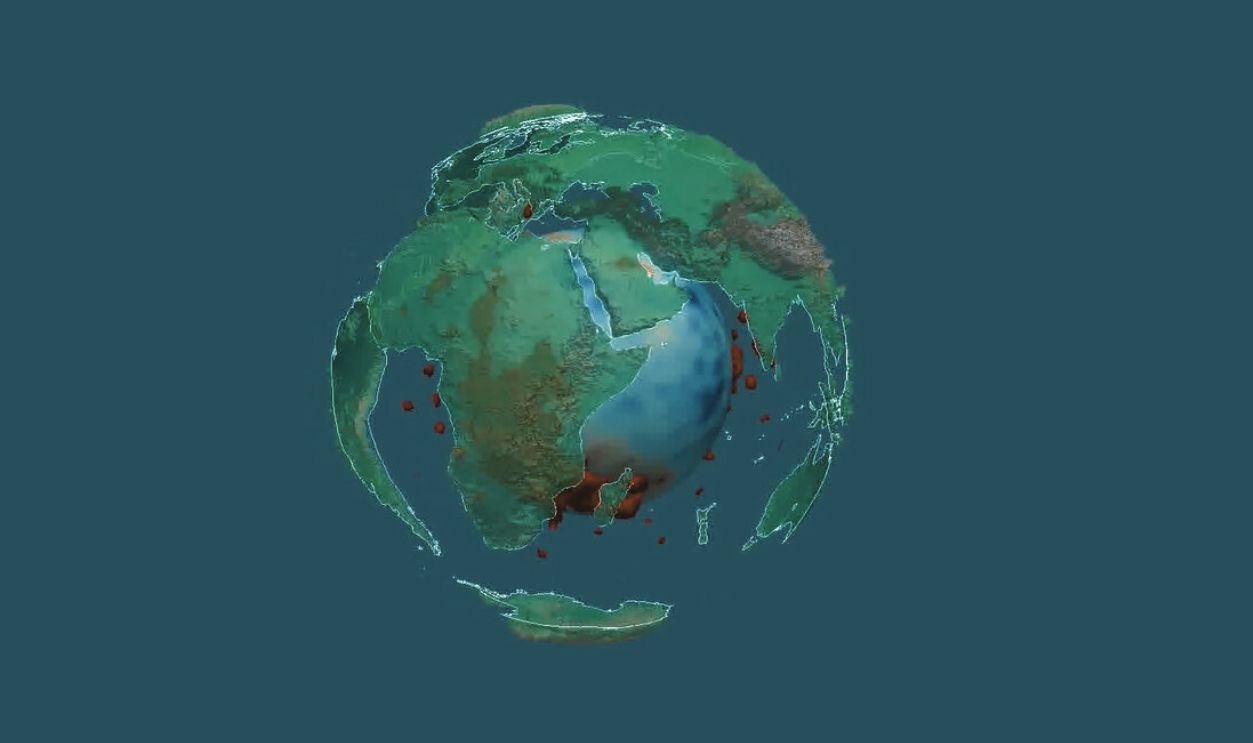 Seismic Tomography of Mantle Structure, Featuring LLSVP by Rick
Seismic Tomography of Mantle Structure, Featuring LLSVP by Rick
That Further Prove The Theory
These features align with the hypothesis that they are remnants of Theia. Their stability over geological timescales and their potential role in influencing mantle dynamics make them a fascinating area of study for understanding Earth’s interior and its evolutionary history.
And Their Role
Such formations have played an active role in shaping Earth’s geological evolution. Their presence affects mantle convection, which drives plate tectonics and influences volcanic activity. These structures may also have contributed to the formation of Earth’s early continents by creating localized thermal and chemical anomalies.
 VisualProduction, Shutterstock
VisualProduction, Shutterstock
Still Studied
Additionally, they could have played a role in the onset of subduction processes, essential for the development of modern plate tectonics. By studying LLVPs, scientists can gain insights into the dynamic processes that have shaped Earth’s surface and interior over billions of years.
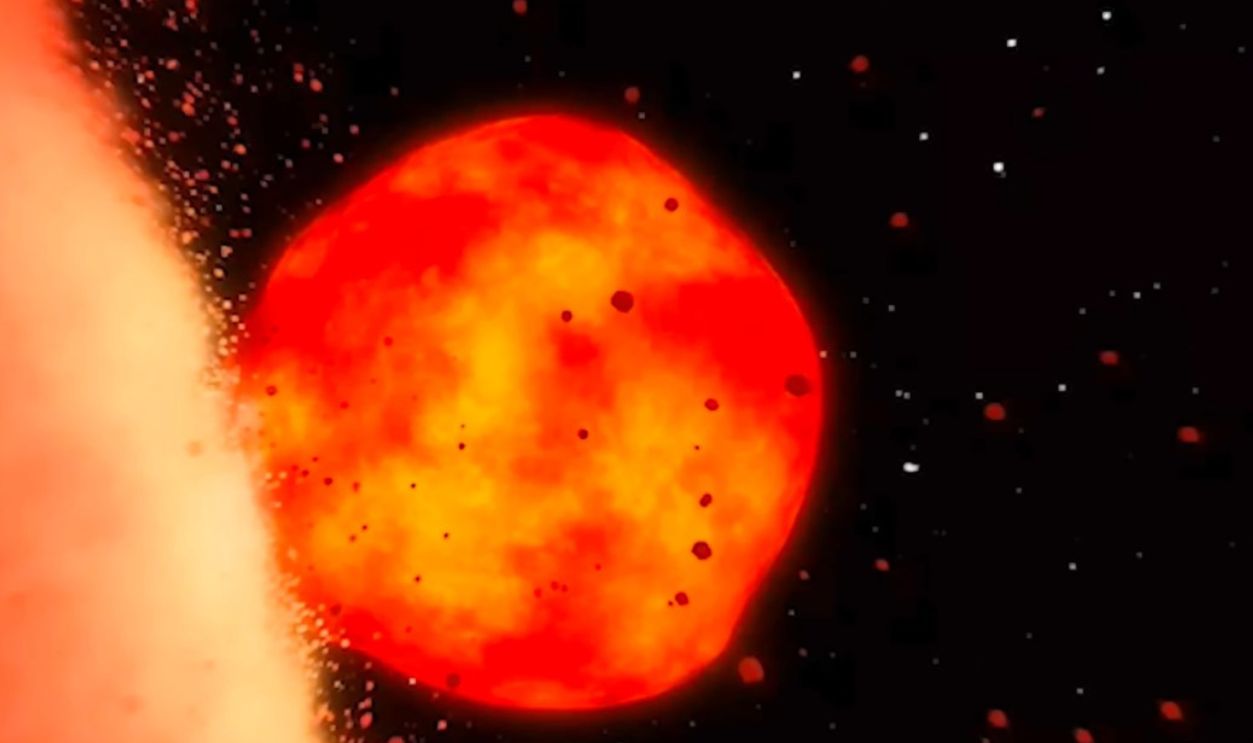
An Additional Insight
Dr. Paul Asimow, a leading geologist at Caltech, highlights the profound implications of linking LLVPs to Theia’s remnants. He explains that if LLVPs are indeed Theia’s legacy, they represent some of the oldest structures within Earth’s mantle that are yet to be discovered.
 Terrifying Discovery! Lost Planet Theia is Hidden Inside the Earth by Global Update
Terrifying Discovery! Lost Planet Theia is Hidden Inside the Earth by Global Update
With Further Room For Exploration
This connection opens avenues for exploring how Theia’s material influenced Earth’s earliest geological features, such as the formation of the first continents and the development of early tectonic processes. Asimow also emphasizes that studying these remnants can help us understand the timeline of our planet.
Early Subduction Processes
LLVPs may have played a critical role in the initiation of subduction processes during Earth’s early history. These dense mantle regions, composed of iron-rich material from Theia, could have created significant gravitational forces that destabilized the overlying crust.
 We Found the Remains of Another Planet Inside Earth by GeologyHub
We Found the Remains of Another Planet Inside Earth by GeologyHub
That Shaped Our Planet
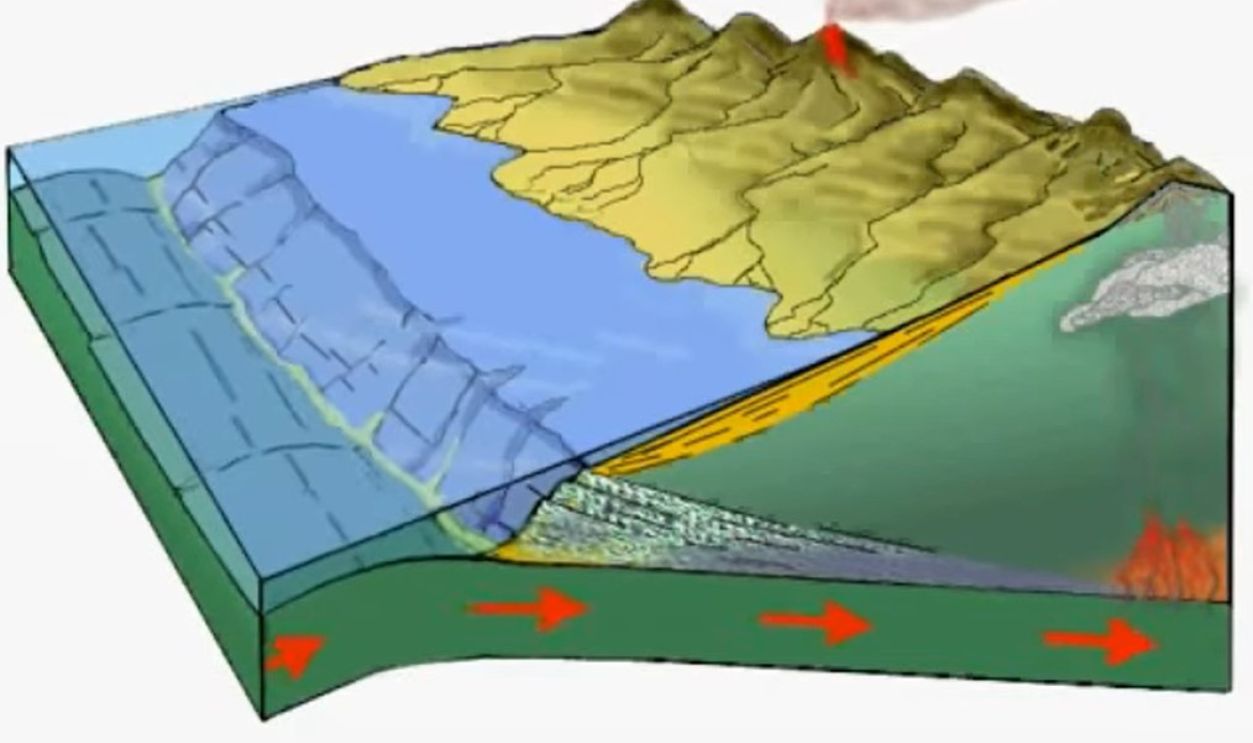
This destabilization may have caused portions of the crust to sink back into the mantle to mark the beginnings of subduction. Subduction is a key component of plate tectonics as it recycles Earth’s crust and drives processes like volcanism and mountain building.
 CHAND ALIi, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
CHAND ALIi, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
And Formed Earth's First Continents
Earth’s first continents were probably also a result of LLVPs. Their high density and unique chemical composition likely caused localized heating in the mantle and generated magma that eventually rose to the surface. This magma could have solidified into the earliest continental crust.
Provided Them With Stability
Over time, repeated volcanic activity in these areas could have expanded and stabilized the continents while forming oceans and islands. This process would have shaped the foundation for Earth’s landmasses and ecosystems that still support life.
LLVPs Are Also Linked To The Oldest Minerals
Earth’s oldest minerals, such as zircons, may hold traces of the chemical and thermal influences exerted by LLVPs. These ancient remnants from Theia likely created unique conditions deep in the mantle that contributed to the formation of these minerals.
 Ivtorov, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Ivtorov, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Like Zircons
Zircons, in particular, are resilient and can survive intense geological processes. In this way, they can provide a record of the early Earth. By analyzing these minerals, scientists have uncovered evidence of early crust formation, water presence, and even temperature fluctuations.
 Parent Géry, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Parent Géry, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Reevaluating Theories
Traditional models of Earth’s formation and evolution are being reshaped to include the impact of Theia and its integration into the planet’s structure. This paradigm shift suggests that the early Earth was shaped by multiple dramatic events, including planetary collisions, which influenced its composition and dynamics.
Thanks To Theia
By studying Theia’s remnants, scientists gain new insights into processes like core formation and the evolution of plate tectonics. This knowledge not only deepens our understanding of Earth’s past but also provides clues about the formation of other planets in the Solar System.
Questioning The Stability
One of the most intriguing aspects of LLVPs is their long-term stability. Despite billions of years of mantle convection and tectonic activity, these dense regions have remained largely unchanged. Their unique composition and density make them resistant to the dynamic forces that constantly reshape Earth’s interior.
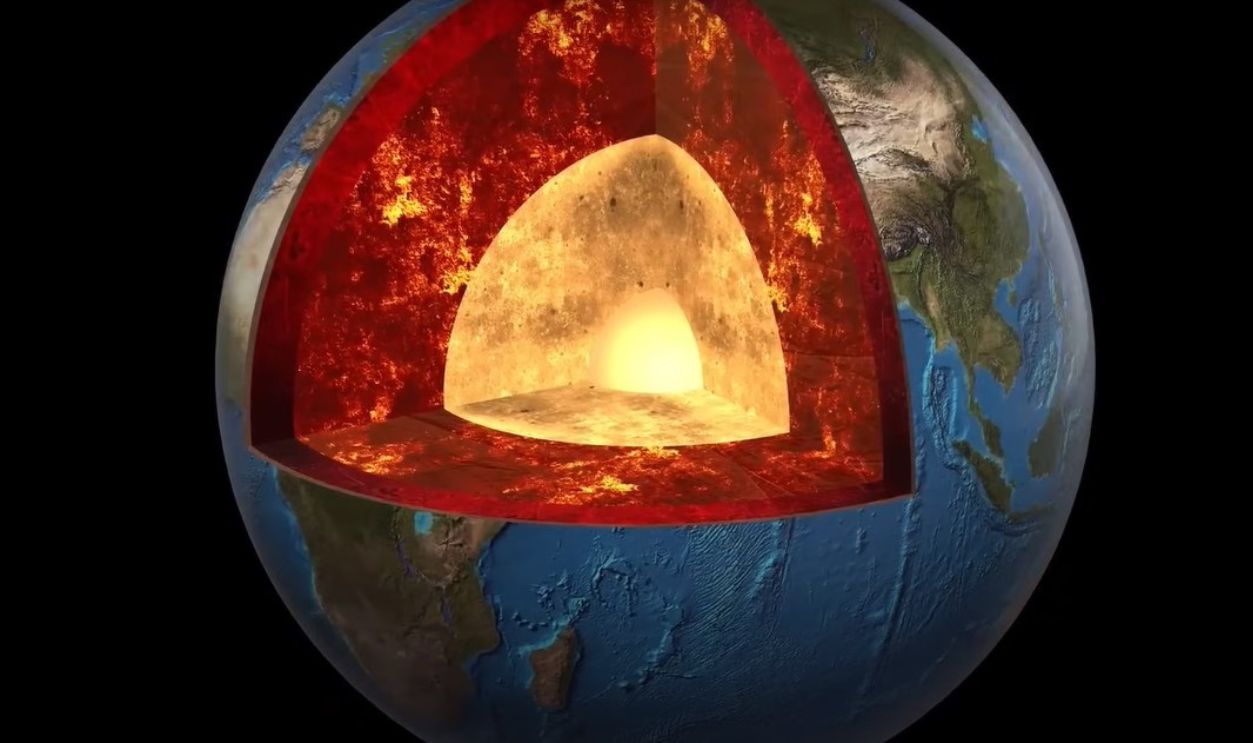 We Found the Remains of Another Planet Inside Earth by GeologyHub
We Found the Remains of Another Planet Inside Earth by GeologyHub
Time Capsules
Scientists believe that LLVPs have persisted since the Theia collision, acting as time capsules preserving ancient material. Their endurance provides a rare opportunity to study the deep history of Earth and gain insights into the early Solar System’s violent past.
LLVPs In Modern Geological Activity
Although LLVPs are relics of an ancient impact, they continue to influence modern geological processes. These regions are linked to hotspots where mantle plumes rise to the surface to drive volcanic activity in areas such as Hawaii and Iceland.
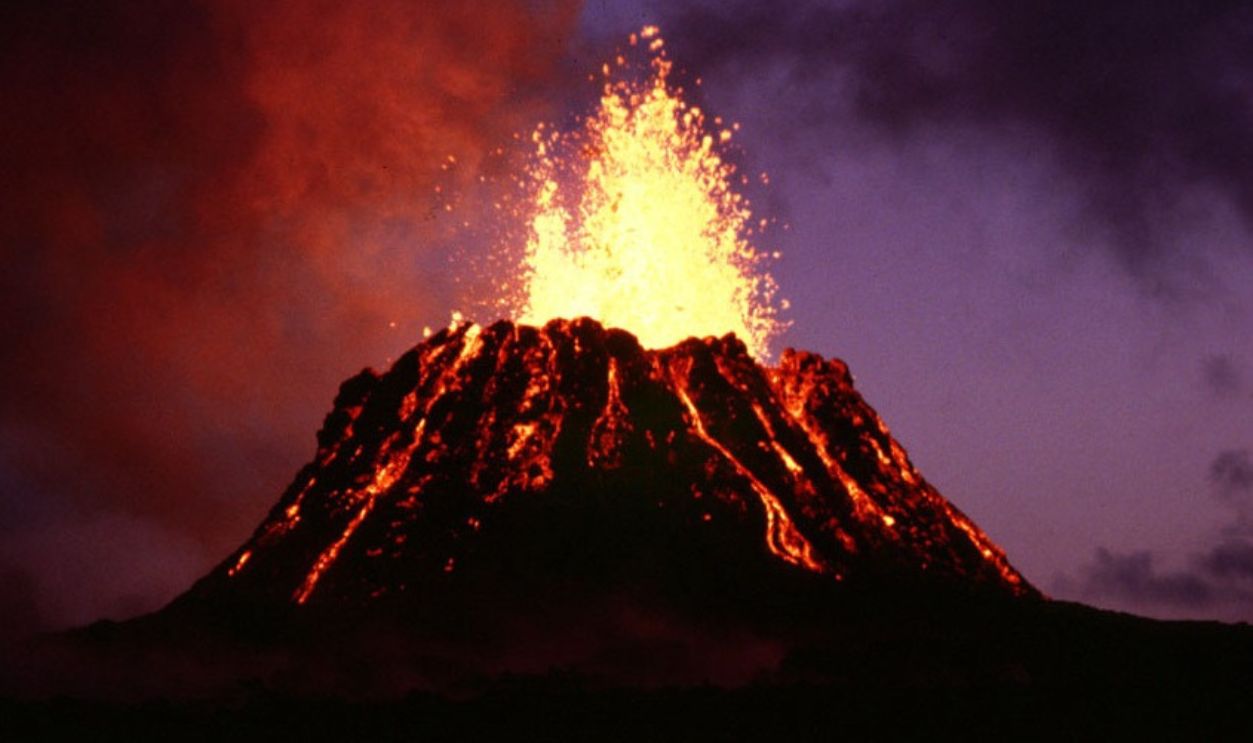 G.E. Ulrich, USGS. Hike395, Wikimedia Commons
G.E. Ulrich, USGS. Hike395, Wikimedia Commons
Specifically, Tectonic Processes
Their density affects the flow of mantle materials and shapes the patterns of plate motion and contributes to tectonic processes. Understanding LLVPs helps scientists predict and interpret phenomena like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions and highlight their ongoing significance in Earth’s geological activity and evolution.
Impact On Earth's Angular Momentum And Rotation
The collision between Theia and Earth also had a profound effect on its angular momentum and rotation. Scientists theorize that the massive impact sped up Earth’s rotation, which eventually led to the 24-hour day we experience today.
To Give Earth Its Planetary Traits
Additionally, the energy transfer during the collision likely tilted Earth’s axis, resulting in the seasons. This rotational acceleration and axial tilt have had lasting effects on Earth’s climate and habitability. Understanding Theia’s role in shaping these fundamental planetary characteristics further explains our planet’s nature.
Clues To Planetary Formation Processes
Today, scientists reflect on LLVPs as windows into the processes that shaped the early Solar System. By studying their composition, scientists can deduce how heavy elements were distributed and how they interacted with Earth’s mantle over time.
 The International Astronomical Union/Martin Kornmesser, CC BY 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
The International Astronomical Union/Martin Kornmesser, CC BY 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Interpreting Data Is An Obstacle
However, data from LLVPs presents significant challenges due to their location deep within Earth’s mantle. Additionally, the extreme conditions of the mantle make recreating LLVP-like environments in laboratories difficult. These hurdles highlight the ingenuity required to uncover Earth’s hidden geological secrets.
Artemis Mission
Some hope lies with the launch of the Artemis Mission. This campaign focuses on collecting samples from the core of the moon. By comparing samples from both mantles, scientists can verify the Giant Impact Theory, and finally prove the significance of Theia.